Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CDMA A
Transféré par
Tejbinder SinghDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CDMA A
Transféré par
Tejbinder SinghDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
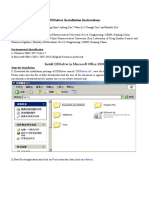
CODE DIVISION MULTIPLE ACCESS
In1993, the first CDMA standard IS-95 was issued. In 1995, CDMA technology was put into commercialization in Hong Kong and America on large scale. In April 2001, China Unicom began to construct CDMA networksthe largest in the world (about 70Million line now). At present, CDMA commercial networks are established in about 40 countries or area, almost 20% of all users in the world.
There are predominantly three types of multiple access methods: 1.FDMA(Frequency Division Multiple Access) 2.TDMA(Time Division Multiple Access) 3.CDMA(Code Division Multiple Access)
Assigns different channels to individual user. No other user can share the same channel. Inefficient if customer does not use the channel. Usually implemented in narrowband systems. No synchronization and framing bits are needed as in TDMA systems. Continuous transmission. AMPS first analog cellular system uses FDMA/FDD.
Divides the spectrum into time slots. Only one user allowed in each time slot to transmit and receive . Cyclic usage of the slots. Multiple slots per user possible. Transmission is non continuous. High synchronization overhead is required. No duplexers are required. Less expensive than FDMA. GSM uses TDMA technique.
All users use the same carrier frequency. Each user has its own pseudorandom codeword. Sender and receiver know the codeword in advance. Other ongoing communication appears as noise. Performance degrades with increase in number of users. cdma2000 uses CDMA technique.
Spread spectrum a transmission technique wherein data occupy a larger bandwidth than necessary There is no restriction on time and frequency in this scheme. All the users can transmit at all times and at all frequencies. Each user has its own pseudorandom codeword which is approximately orthogonal to all other code words.
The receiver needs to know this codeword used by the transmitter and it performs correlation to detect only the specific desired signal. Because users are isolated by code, they can share the same carrier frequency, eliminating the frequency reuse problem encountered in other technologies. This technology is used only when the network interacts with the subscriber or the subscriber interacts with the network.
INTERFERENCE JAMMER
FILTER
INFORMATION SIGNAL i(t)
Data Rate, Ri Bandwidth ,Wi c(t)
BANDWIDTH, W s(t) r(t) d(t)
c(t) SPREADING SEQUENCE Chip Rate, Rc Bandwidth, Wc
SPREADING SEQUENCE Chip Rate ,Rc Bandwidth, Wc
CDMA is a spread spectrum multiple access technique. A spread spectrum technique spreads the bandwidth of the data uniformly for the same transmitted power. In CDMA ,a locally generated code runs at a much higher rate than the data to be transmitted.
The figure shows how a spread spectrum signal is generated. The data signal with pulse duration of Tb is XORed with the code signal with pulse duration of Tc. The bandwidth of the data signal is 1 / Tb and the bandwidth of the spread spectrum signal is 1 / Tc. (Tc is much smaller than Tb ). The ratio Tb / Tc is called the spreading factor or processing gain and determines to a certain extent the upper limit of the total number of users supported.
**REVERSE PROCESS IS FOLLOWED AT RECIEVER SIDE**
No SIM card is required. Improved call quality: CDMA provides better and more consistent sound quality than systems based on other technologies. Enhanced privacy when compared to systems using other technologies. Longer Talk Time, Longer Battery Life and Smaller Phones. Fewer dropped calls due to handoff. Allows the largest number of subscribers to share the same radio frequencies. Dynamic allocation of channels is possible.
Tight synchronization is required to use orthogonal codes.
Since most countries have chosen the GSM standard,
ROAMING on CDMA is limited. Quasi-orthogonal codes cause self-interference, which dominates the performance in most CDMA systems. Near-far problem is a serious hindrance.
Daily Downloads : characters, images, horoscopes. Real time stock quotes Text Communication : chat, instant messaging, SMS, E-mail. Sending photos over the air: MMS messages. Position location services: friend finder, navigation assistance. Games and entertainment: magazine, comic book store.
Technology of choice for 3G generation because of its
Greater total capacity Outstanding voice quality Fewer dropped calls
RF planning and implementation is simplified by its
Capability of re-using single cell frequency Non-contiguous bandwidth requirement
Its use in satellite communication is of great importance
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Microwave CommunicationDocument84 pagesMicrowave CommunicationReymar BelmontePas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Dipole AntennaDocument5 pagesAssignment Dipole AntennaAmir MustakimPas encore d'évaluation
- Vijeo Citect Architecture and Redundancy Study GuideDocument19 pagesVijeo Citect Architecture and Redundancy Study GuideNuwan BandaraPas encore d'évaluation
- PC Version InfoDocument13 pagesPC Version InfoVictor NewmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - Diversity Protection SwitchingDocument20 pages3 - Diversity Protection SwitchingMarkPas encore d'évaluation
- L-6 SatcomDocument80 pagesL-6 SatcomKeshav KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Low-Noise AmplifierDocument115 pagesLow-Noise AmplifierAar Kay Gautam100% (1)
- DEC LAB 06 (Design of A Digital To Analog Converter)Document9 pagesDEC LAB 06 (Design of A Digital To Analog Converter)anon_776365175Pas encore d'évaluation
- 0.18 Um Low Noise AmplifierDocument66 pages0.18 Um Low Noise AmplifierHarish Kumar100% (1)
- Superheterodyne ReceiverDocument10 pagesSuperheterodyne ReceiverAndhika Kumara DjaffriPas encore d'évaluation
- Frenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Document22 pagesFrenzel Exam Sheet (Key To Correction)Patrick James De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication System Unit VDocument8 pagesCommunication System Unit VTangent ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication TheoryDocument156 pagesCommunication TheoryMuumini De Souza NezzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wave Guids PDFDocument32 pagesWave Guids PDFlakshman donepudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission LinesDocument2 pagesTransmission LinesMaria Deborah Vivas BaluranPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Engineering Unit 1 Lecture 1Document22 pagesCommunication Engineering Unit 1 Lecture 1Deepak SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave Communications LectureDocument73 pagesMicrowave Communications LectureKen100% (1)
- Edited 2 MarksDocument24 pagesEdited 2 MarksMohamed RiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Preboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetBDocument15 pagesPreboard EST 2ndbatch April2015 SetBLopez Shian ErvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To The Telephone NetworkDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To The Telephone NetworkPoit X Nincompoops100% (1)
- Angle ModulationDocument8 pagesAngle ModulationEmmanuel MerinPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Scale Fading Discussion-4Document36 pagesSmall Scale Fading Discussion-4Sang Dorjee TamangPas encore d'évaluation
- SSMT Solution ManualDocument12 pagesSSMT Solution ManualPraahas Amin0% (1)
- FSK ResearchDocument42 pagesFSK Researchمهيمن الابراهيميPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction On Telephone TrafficDocument35 pagesIntroduction On Telephone TrafficJanicePeraltaPas encore d'évaluation
- EE342: Microwave Engineering: Week 3: Transmission Line Theory and Equations Instructor: Maira IslamDocument31 pagesEE342: Microwave Engineering: Week 3: Transmission Line Theory and Equations Instructor: Maira IslamDale SteynPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission CalculationDocument8 pagesTransmission Calculationapi-26989621Pas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Document45 pages4 Pulse Code Modulation (PCM)Kunal KatariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Local Multipoint Distribution Service: Presented By: B.Venkatachandu Roll No:-16R01A0414Document14 pagesSeminar Local Multipoint Distribution Service: Presented By: B.Venkatachandu Roll No:-16R01A0414chandu bogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Compilation of Problems by Louis FrenzelDocument5 pagesCompilation of Problems by Louis FrenzelKim Castro AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- BER of OFDM System Using Concatenated Forward Error Correcting Codes (FEC) Over Nakagami-M Fading ChannelDocument5 pagesBER of OFDM System Using Concatenated Forward Error Correcting Codes (FEC) Over Nakagami-M Fading Channelseventhsensegroup100% (1)
- Princom Fundamentals of Frequency ModulationDocument5 pagesPrincom Fundamentals of Frequency Modulationmelwin victoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication ENggDocument11 pagesCommunication ENggSantosh VishnuPas encore d'évaluation
- VSWR LabDocument5 pagesVSWR LabKrishna Prasad PheluPas encore d'évaluation
- QUIZ 1-ADV. COMMS-Definitions TermsDocument2 pagesQUIZ 1-ADV. COMMS-Definitions TermsIan VillarojoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3Document22 pagesUnit 3Shiva ShivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2 Circuit SignallingDocument25 pagesLecture 2 Circuit SignallingMianKashifPas encore d'évaluation
- Microwave Communication Link Basic Design ConsiderationsDocument26 pagesMicrowave Communication Link Basic Design Considerationsgossananicet9915Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exp - No.1-Amplitude Modulation (DSB-LC)Document11 pagesExp - No.1-Amplitude Modulation (DSB-LC)موسى سعد لعيبيPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1: Introduction To Electronic CommunicationsDocument33 pagesChapter 1: Introduction To Electronic CommunicationsMoneth PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Parabolic Antenna Efficiency and Power Gain: Eduardo Punto JRDocument30 pagesParabolic Antenna Efficiency and Power Gain: Eduardo Punto JRXyPas encore d'évaluation
- Noise: Any Unwanted Signal That Interfere With Wanted Signal Impair Communication System Degrade The System PerformanceDocument45 pagesNoise: Any Unwanted Signal That Interfere With Wanted Signal Impair Communication System Degrade The System PerformanceMuhammad Salah ElgaboPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Chapter2Document13 pages07 Chapter2Arslan AliPas encore d'évaluation
- 4EC4-21 ADC Lab AS-16aDocument93 pages4EC4-21 ADC Lab AS-16aSu KoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communication Lecture-1Document175 pagesDigital Communication Lecture-1Ahmed Hassan MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Est Question For Iecep 2012Document4 pagesEst Question For Iecep 2012Ericson Blue Sta MariaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Digital Mod - Part 1Document47 pagesChapter 4 Digital Mod - Part 1posktovaPas encore d'évaluation
- Broadband Isdn ServicesDocument33 pagesBroadband Isdn ServicesElectrotel100% (3)
- Demand Assigned Multiple AccessDocument22 pagesDemand Assigned Multiple Accessanushka shastriPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Telecommunication: Frequency ModulationDocument41 pagesElements of Telecommunication: Frequency ModulationYemuraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line TheoryDocument70 pagesTransmission Line TheorynaingPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. (5) : Frequency Modulation & Demodulation: - ObjectDocument5 pagesExperiment No. (5) : Frequency Modulation & Demodulation: - ObjectFaez FawwazPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiplexing and Multiple Access Techniques Multiplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesDocument89 pagesMultiplexing and Multiple Access Techniques Multiplexing and Multiple Access TechniquesSantosh Thapa0% (1)
- 3GPP LteDocument40 pages3GPP LteMUJIB TAMBOLIPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE4313 Worksheet EndsemDocument5 pagesECE4313 Worksheet EndsemBereketeab ZinabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Telecommunication Switching System Control of Switching System PDFDocument19 pagesTelecommunication Switching System Control of Switching System PDFUdhay Prakash100% (1)
- Electronic Communication System, Chapter 7 AnsDocument16 pagesElectronic Communication System, Chapter 7 AnsRonald ArmstrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Final ExamDocument7 pagesFinal ExamSuleman Jamil0% (1)
- CD MaDocument28 pagesCD MaParminder SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Cdma:: Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Channel Access Method Used byDocument10 pagesCdma:: Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) Is A Channel Access Method Used bySRL MECHPas encore d'évaluation
- Term Paper On CDMADocument5 pagesTerm Paper On CDMATaufeeq Malik100% (1)
- Third Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesD'EverandThird Generation CDMA Systems for Enhanced Data ServicesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- IptvtoolsDocument9 pagesIptvtoolsjhbduhsdPas encore d'évaluation
- Software Testing PPT 1Document24 pagesSoftware Testing PPT 1celinePas encore d'évaluation
- C6 AEEd 01Document50 pagesC6 AEEd 01trance1313Pas encore d'évaluation
- AM-Intro 13.0 WS3 DirectMeshingDocument24 pagesAM-Intro 13.0 WS3 DirectMeshingtakdir115Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 9185 Moesm1 EsmDocument12 pages2010 9185 Moesm1 EsmMuhammad IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Video and Image Processing Suite User Guide: Subscribe Send FeedbackDocument360 pagesVideo and Image Processing Suite User Guide: Subscribe Send FeedbackRiccPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Manager Pro User Manual - EN-V220930RDocument19 pagesE-Manager Pro User Manual - EN-V220930RTuấn Lê QuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Operate A Spreadsheet ApplicationDocument8 pagesOperate A Spreadsheet ApplicationAnonymous PcPkRpAKD5Pas encore d'évaluation
- Online Voting SystemDocument56 pagesOnline Voting Systemajay_anavPas encore d'évaluation
- SP201 - HandoutDocument45 pagesSP201 - Handoutghad shadPas encore d'évaluation
- Itp Akash 2nd Sem2018-05-06 09 - 58 - 27 PDFDocument55 pagesItp Akash 2nd Sem2018-05-06 09 - 58 - 27 PDFSiddharth TyagiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2002-03 The Computer Paper - Ontario EditionDocument113 pages2002-03 The Computer Paper - Ontario EditionthecomputerpaperPas encore d'évaluation
- Compress - Document (1) - 1 - 20230510213530 PDFDocument3 pagesCompress - Document (1) - 1 - 20230510213530 PDFAllen McintoshPas encore d'évaluation
- QRadar High Availability Guide 7.2.2Document58 pagesQRadar High Availability Guide 7.2.2CristianHoracioAresPas encore d'évaluation
- D000PTGC10 Activity Guide FinalDocument360 pagesD000PTGC10 Activity Guide FinalSweater Geek100% (1)
- C++ and Data StructureDocument231 pagesC++ and Data StructureHabtie TesfahunPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect3 - Design MetricsDocument34 pagesLect3 - Design MetricsvarshaksPas encore d'évaluation
- Fact Sheet Mi-Harmony 001-0421ADocument1 pageFact Sheet Mi-Harmony 001-0421ATgNurulhuda Tg Abdul RahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Graphing With Excel Rev 6-10-13Document6 pagesGraphing With Excel Rev 6-10-13Fahad AreebPas encore d'évaluation
- Envirtech TCPIP-DCTU-01 Concentrator and Transceiver For SCADADocument2 pagesEnvirtech TCPIP-DCTU-01 Concentrator and Transceiver For SCADAFurio RuggieroPas encore d'évaluation
- Massive Mimo Ahr (TDD) (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)Document64 pagesMassive Mimo Ahr (TDD) (5g Ran6.1 - Draft A)VVLPas encore d'évaluation
- Create Database EscuelaDocument4 pagesCreate Database EscuelayelsinceroPas encore d'évaluation
- RadmsDocument8 pagesRadmsKiran C NPas encore d'évaluation
- Avamar Gen4T KickstartDocument50 pagesAvamar Gen4T Kickstartdansegui.mir4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Springer10 PDFDocument2 pagesBrochure Springer10 PDFsivapostPas encore d'évaluation
- HTML Notes For Class 10 CbseDocument7 pagesHTML Notes For Class 10 Cbseproodoot50% (6)
- MT6797 Android ScatterDocument20 pagesMT6797 Android ScatterAlfarisy Putri AuliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Epson EcoTank Printer DatasheetDocument2 pagesEpson EcoTank Printer DatasheetArunangshu BiswasPas encore d'évaluation