Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Essentials of KM Class Presentation
Transféré par
Sk PrasadDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Essentials of KM Class Presentation
Transféré par
Sk PrasadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
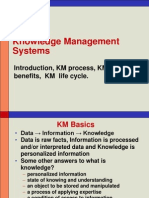
ESSENTIALS OF KM
Knowledge Management is the explicit and systematic management of vital knowledgeand its associated processes of creation, organization, diffusion, use and exploitationin pursuit of business objectives. The levers of KM initiatives: Customer Knowledge- the most vital knowledge for creation, survival and growth of any business activity or organization
ESSENTIALS OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENTanagement
Knowledge of Processes- Applying the best know how in various business processes Product/Service Knowledge- to provide smarter solutions, customized users needs Knowledge of People- Nurturing and harnessing human intellect Organizational Experiences; Learning from past
ESSENTIALS OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENTanagement
Knowledge in relationship- understanding of knowledge that underpins successful collaboration Knowledge assets- measuring and managing intellectual capital
ESSENTIALS OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENTanagement
Information
Static Independent of Individual Explicit Digital Easy to duplicate Easy to broadcast No Intrinsic meaning
Knowledge
Dynamic Dependent on Individuals Implicit/Tacit Analogue Must be re-created Face to Face Meaning has to be personally assigned
ESSENTIALS OF KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENTanagement Landscape
Important Dimensions of Knowledge
Knowledge: Is a firm asset Has different forms Has a location Is situational
The Knowledge Management Landscape
Important Dimensions of Knowledge
Knowledge Wisdom Tacit knowledge
Explicit knowledge
The Knowledge Management Landscape
Organizational Learning and Knowledge Management
Organizational learning: Creation of new standard operating procedures and business processes reflecting experience Knowledge management: Set of processes developed in an organization to create, gather, store, disseminate, and apply knowledge
The Knowledge Management Landscape
The knowledge management value chain
Figure 1-1
The Knowledge Management Landscape
The Knowledge Management Value Chain
Knowledge acquisition Knowledge storage Knowledge dissemination Knowledge application
The Knowledge Management Landscape
The Knowledge Management Value Chain
Chief Knowledge Officer (CKO): Senior executive in charge of the organization's knowledge management program Communities of Practice (COP): Informal groups who may live or work in different locations but share a common profession
Types of Knowledge Management Systems
Types of Knowledge Management Systems
Enterprise Knowledge Management Systems: General purpose, integrated, and firm-wide systems to collect, store and disseminate digital content and knowledge
Knowledge Work Systems (KWS): Information systems that aid knowledge workers in the creation and integration of new knowledge in the organization Intelligent Techniques: Datamining and artificial intelligence technologies used for discovering, codifying, storing, and extending knowledge
Types of Knowledge Management Systems
Major types of knowledge management systems
Figure 1-2
Enterprise-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
Structured Knowledge Systems
Structured knowledge Semistructured knowledge Knowledge repository Knowledge network
Enterprise-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
Enterprise-wide knowledge management systems
Figure 1-3
Enterprise-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
KPMG knowledge system processes
Figure 1-4
Enterprise-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
Knowledge Networks
Key Functions of an Enterprise Knowledge Network
Knowledge exchange services Community of practice support Auto-Profiling Capabilities Knowledge management services
Enterprise-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
Portals, Collaboration Tools, and Learning Management Systems
Teamware: Group collaboration software running on intranets that is customized for teamwork
Enterprise-Wide Knowledge Management Systems
Portals, Collaboration Tools, and Learning Management Systems
Learning Management Systems (LMS): Tools for the management, delivery, tracking, and assessment of various types of employee learning
Knowledge Work Systems
Knowledge Workers and Knowledge Work
Knowledge workers perform 3 key roles:
Keeping the organization current in knowledge as it develops in the external world Serving as integral consultants regarding the areas of their knowledge, the changes taking place, and opportunities Acting as change agents
Knowledge Work Systems
Requirements of knowledge work systems
Figure 1-5
Management Issues for Knowledge Management Systems
Implementation Challenges
Insufficient resources available to structure and update the content in repositories Poor quality and high variability of content quality because of insufficient mechanisms Content in repositories lacks context, making documents difficult to understand
Management Issues for Knowledge Management Systems
Implementation Challenges
Individual employees not rewarded for contributing content, and many fear sharing knowledge with others on the job
Search engines return too much information, reflecting lack of knowledge structure or taxonomy
Obtaining Value from Knowledge Management Systems
Obtaining Value from Knowledge Management Systems
1.
2.
Develop in stages
Choose a high-value business process
3.
4.
Choose the right audience
Measure ROI during initial implementation
5.
Use the preliminary ROI to project enterprisewide values
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- U11 Managing Knowledge 2022 Mar July 23Document56 pagesU11 Managing Knowledge 2022 Mar July 23Noppon SETTASATIENPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management SystemsDocument15 pagesKnowledge Management SystemsManish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mengelola Knowledge Di Dalam Organisasi ModernDocument56 pagesMengelola Knowledge Di Dalam Organisasi ModernHenni OktafiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 11Document38 pagesModule 11Madam asdfghjkPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 11 2020 StudentsDocument45 pagesLect 11 2020 Studentsakash jainPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 5Document19 pagesCH 5Ebsa AdemePas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management SolutionsDocument32 pagesKnowledge Management SolutionsapiconpikkPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-11 - Managing KnowledgeDocument45 pagesCh-11 - Managing KnowledgeAnkit MirajkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Im1 Chapter 6Document8 pagesIm1 Chapter 6Si EfPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management Systems: Introduction, KM Process, KM Benefits, KM Life CycleDocument13 pagesKnowledge Management Systems: Introduction, KM Process, KM Benefits, KM Life CycleTusharSoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge ManagementDocument31 pagesKnowledge Managementbirbal mahatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge ManagementDocument7 pagesKnowledge Managementjandy6734Pas encore d'évaluation
- Information Management & Strategic Decision TakingDocument36 pagesInformation Management & Strategic Decision TakingfoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 Knowledge ManagementDocument35 pagesLecture 7 Knowledge ManagementAmit JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management Systems Among Fastest - Information EconomyDocument54 pagesKnowledge Management Systems Among Fastest - Information EconomyRushikesh DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Knowledge Management ConceptDocument37 pagesUnderstanding Knowledge Management ConceptTheerapan CPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management SystemsDocument9 pagesKnowledge Management Systemskanika aggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Mangement. Batch 1Document48 pagesKnowledge Mangement. Batch 1Jayesh MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mis Presentation FinalDocument29 pagesMis Presentation FinalSourav Kumar ShawPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.1 Knowledge ManagementDocument19 pages4.1 Knowledge ManagementWajid AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three: Key System Applications For The Digital AgeDocument37 pagesChapter Three: Key System Applications For The Digital Ageobsinan dejenePas encore d'évaluation
- Knowladge ManagementDocument22 pagesKnowladge ManagementaminulPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Knowledge at WorkDocument28 pagesManaging Knowledge at WorkADB Knowledge Solutions100% (3)
- Knowledge Management Syste: Presented ByDocument21 pagesKnowledge Management Syste: Presented BySanket MohapatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-KM - FundamentalsDocument31 pagesChapter 1-KM - FundamentalsdemelashPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1ruby_shaPas encore d'évaluation
- Name:-Saniya Kazi Roll No: - 21 Subject: - Knowledge Management Assignment: - No:02 Topic: - Introduction To Knowledge ManagementDocument9 pagesName:-Saniya Kazi Roll No: - 21 Subject: - Knowledge Management Assignment: - No:02 Topic: - Introduction To Knowledge ManagementSaniya KaziPas encore d'évaluation
- SwotDocument109 pagesSwotCarlos VelazquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Decision Support Systems ExplainedDocument33 pagesDecision Support Systems ExplainedSurekha PuriPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management SystemsDocument23 pagesKnowledge Management SystemsSuganya HarishPas encore d'évaluation
- IS Development Business Value of Information Systems and Management KnowledgeDocument45 pagesIS Development Business Value of Information Systems and Management Knowledgeahmadamminudin89Pas encore d'évaluation
- 19KMDocument9 pages19KMPrabhat ChawlaPas encore d'évaluation
- KM KICM PPT FinalDocument27 pagesKM KICM PPT FinalAbhishek IyerPas encore d'évaluation
- KMSPquickreview1 5Document17 pagesKMSPquickreview1 5vkPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Elements of Knowledge ManagementDocument25 pagesChapter 4 Elements of Knowledge Managementuzma buttPas encore d'évaluation
- KM - Building A KM SystemDocument41 pagesKM - Building A KM SystemVishal ChawlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management Process FrameworkDocument46 pagesKnowledge Management Process FrameworkShivendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Knowledge in BusinessDocument7 pagesManaging Knowledge in BusinessHUSSEIN ABED AL KARIMPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledgement Management PPT at BEC DOMS MBADocument30 pagesKnowledgement Management PPT at BEC DOMS MBABabasab Patil (Karrisatte)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge ManagementDocument41 pagesKnowledge ManagementGuest HousePas encore d'évaluation
- 2ka3 CH11Document49 pages2ka3 CH11RyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Knowledge Management and AI SystemsDocument18 pagesPrinciples of Knowledge Management and AI SystemsArooj ArifPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - FlowDocument87 pagesChapter 4 - FlowAartika SardanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment No 1Document11 pagesAssignment No 1TauseefAhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Significance of Knowledge Management in EducationDocument16 pagesSignificance of Knowledge Management in EducationFakhruddin GodhrawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Information Systems OverviewDocument20 pagesBusiness Information Systems OverviewhemajanarthananPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Sharing.: Knowledge Sharing Is A Process Through Which Knowledge IsDocument16 pagesKnowledge Sharing.: Knowledge Sharing Is A Process Through Which Knowledge Issarika_85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Difficulties Approach Techniques IT Support External LinksDocument6 pagesDifficulties Approach Techniques IT Support External LinkssaravkiruPas encore d'évaluation
- Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionDocument44 pagesManagement Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm: Fifteenth EditionCan AvcıPas encore d'évaluation
- Information ArchitectureDocument25 pagesInformation ArchitectureRostum Dullesco Decolongon Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 Decision Support and Knowledge Management ConceptsDocument33 pagesUnit 3 Decision Support and Knowledge Management ConceptsjrvinodPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Smarter With Knowledge ManagementDocument12 pagesWork Smarter With Knowledge ManagementBreaking LawPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - KM Solution, Cycle, Architecture and ProcessesDocument44 pagesChapter 3 - KM Solution, Cycle, Architecture and ProcessesPatcernaPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK - 01 - IntroductionDocument49 pagesWEEK - 01 - IntroductiondarkrainingeveningPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Knowledge Management and Learning Essentials (For Print)Document19 pagesUnderstanding Knowledge Management and Learning Essentials (For Print)ADB Knowledge Solutions100% (9)
- Amity Business School: KM InfrastructureDocument2 pagesAmity Business School: KM InfrastructureDaksh ChadhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management: By: Jenny Enderby and Chris PapinDocument26 pagesKnowledge Management: By: Jenny Enderby and Chris PapinPratibha KainPas encore d'évaluation
- KM Chapter 8Document30 pagesKM Chapter 8fia saqibPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA KM ReportDocument18 pagesMBA KM ReportCA Naveen Kumar ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- StartupsDocument20 pagesStartupsSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 ScreeningDocument60 pagesUnit 5 ScreeningSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Organisational Development Techniques & ApplicationsDocument18 pagesOrganisational Development Techniques & ApplicationsSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Team Building InterventionsclDocument35 pagesTeam Building InterventionsclSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Business CLDocument6 pagesFamily Business CLSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Social Entrepreneurship: Driving Social ChangeDocument18 pagesSocial Entrepreneurship: Driving Social ChangeSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Team Building InterventionsclDocument35 pagesTeam Building InterventionsclSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Through Case MethodDocument14 pagesLearning Through Case MethodSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian Higher Education and Emerging GlobalDocument21 pagesIndian Higher Education and Emerging GlobalSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Information Services in Digital EnvironmentDocument11 pagesManagement of Information Services in Digital EnvironmentSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Od ProcessDocument14 pagesOd ProcessSk PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors That Influence The Change of Human Behavior in Student's Online ActivityDocument5 pagesFactors That Influence The Change of Human Behavior in Student's Online ActivityDenise ClaudiaPas encore d'évaluation
- HR 6055organising and Managing Across Cultures: Titles: Choose Any ONE of The Following TopicsDocument6 pagesHR 6055organising and Managing Across Cultures: Titles: Choose Any ONE of The Following TopicsnaveenPas encore d'évaluation
- CIA-1 Subject: English Topic: The Way Relationships Work TodayDocument4 pagesCIA-1 Subject: English Topic: The Way Relationships Work TodayNikshitha PRPas encore d'évaluation
- Individual Behavior: The Teacher and The Community, School, Culture and Organizational LeadershipDocument20 pagesIndividual Behavior: The Teacher and The Community, School, Culture and Organizational Leadershipshara santosPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Management Case StudyDocument4 pagesStress Management Case Studyapi-712131532Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced English: Skills for Academic SuccessDocument2 pagesAdvanced English: Skills for Academic Successabdellatif elaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- DVOREF College of Law 2 Semester, AY 2017-2018 SyllabusDocument2 pagesDVOREF College of Law 2 Semester, AY 2017-2018 SyllabusPatrickHidalgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Fantasies, Feelings, and Fun in Experiential ConsumptionDocument10 pagesConsumer Fantasies, Feelings, and Fun in Experiential ConsumptionYash Aggarwal BD20073Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 Lesson on the Human Breathing SystemDocument2 pagesGrade 9 Lesson on the Human Breathing SystemLoida Cabus AroPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 18 and 19 - Jonathan CaliriDocument4 pagesLesson 18 and 19 - Jonathan Caliriapi-610129783Pas encore d'évaluation
- Here Are Some Ways To Find An Online Tutor That Can Help Your Child and Keep Him EngagedDocument3 pagesHere Are Some Ways To Find An Online Tutor That Can Help Your Child and Keep Him EngagedAstha MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Orem & Roys Nursing Models: A ComparisonDocument4 pagesOrem & Roys Nursing Models: A ComparisonlisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Schütz - 1951 - Making Music Tohether A Study in Social RelationshipDocument23 pagesSchütz - 1951 - Making Music Tohether A Study in Social RelationshipKily Cortés RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- The Person That I Admire MostDocument4 pagesThe Person That I Admire MostSri Sakthy0% (1)
- Accounting Information SystemDocument55 pagesAccounting Information SystemRodPas encore d'évaluation
- 21st Century Skills and Literacy SkillsDocument10 pages21st Century Skills and Literacy SkillsLeomel De Jesus100% (1)
- Research TemplateDocument8 pagesResearch TemplateCholo CantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Literature (RRLDocument12 pagesReview of Literature (RRLRyan NegadPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of MYP ObjectivesDocument13 pagesOverview of MYP ObjectivesandreaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Infancy and Toddler HoodDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Infancy and Toddler HoodNicz Lanz DejzPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Div Mobile Library HUbDocument12 pagesImplementation of Div Mobile Library HUbJack Key Chan AntigPas encore d'évaluation
- TOK Exhibition Planning Document 1Document3 pagesTOK Exhibition Planning Document 1ilgyu1207100% (1)
- Sa 2 Integrating Simple, Continous and Perfect - Practice - Level Ii - Uces - Iarossi - 2021Document7 pagesSa 2 Integrating Simple, Continous and Perfect - Practice - Level Ii - Uces - Iarossi - 2021Carolina De VincenziPas encore d'évaluation
- Anagement Ystem Esults-Ased Erformance: PortfolioDocument32 pagesAnagement Ystem Esults-Ased Erformance: PortfolioFactura Neil50% (2)
- Part 1. WRICM PDFDocument22 pagesPart 1. WRICM PDFPatrick PascasioPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On The Techniques of Teaching English Vocabulary To Children at Elementary School AL Munawarah Plus Pamekasan PDFDocument11 pagesA Study On The Techniques of Teaching English Vocabulary To Children at Elementary School AL Munawarah Plus Pamekasan PDFannisa boru sasadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Challenges Encountered by The Private School TeachersDocument8 pagesChallenges Encountered by The Private School TeachersKiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Event Processing For Business Organizing The Real Time Enterprise PDFDocument2 pagesEvent Processing For Business Organizing The Real Time Enterprise PDFPamPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE Lesson on Selecting Farm ToolsDocument3 pagesTLE Lesson on Selecting Farm ToolsMarjorie Joy MartirNalupa AninoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan For English Grade V Using Explicit InstructionDocument3 pagesLesson Plan For English Grade V Using Explicit InstructionBea DeLuis de Tomas89% (131)