Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Data Definition Language (DDL) : - Specification Notation For Defining The Database Schema
Transféré par
Jose AntonyDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Data Definition Language (DDL) : - Specification Notation For Defining The Database Schema
Transféré par
Jose AntonyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Data Definition Language (DDL)
Specification notation for defining the database schema
E.g. create table account ( account-number char(10), balance integer)
DDL compiler generates a set of tables stored in a data dictionary Data dictionary contains metadata (i.e., data about data)
database schema Data storage and definition language
language in which the storage structure and access methods used by the database system are specified Usually an extension of the data definition language
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Data Manipulation Language (DML)
Language for accessing and manipulating the data organized by the appropriate data model
DML also known as query language
Two classes of languages
Procedural user specifies what data is required and how to get those data Nonprocedural user specifies what data is required without specifying how to get those data
SQL is the most widely used query language
SQL
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
SQL: widely used non-procedural language
E.g. find the name of the customer with customer-id 192-83-7465 select customer.customer-name from customer where customer.customer-id = 192-83-7465 E.g. find the balances of all accounts held by the customer with customer-id 192-83-7465 select account.balance from depositor, account where depositor.customer-id = 192-83-7465 and depositor.account-number = account.account-number
Application programs generally access databases through one of
Language extensions to allow embedded SQL Application program interface (e.g. ODBC/JDBC) which allow SQL queries to be sent to a database
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Database Users
Users are differentiated by the way they expect to interact with the system Application programmers interact with system through DML calls Sophisticated users form requests in a database query language Specialized users write specialized database applications that do not fit into the traditional data processing framework.
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Database Administrator
Coordinates all the activities of the database system; the database administrator has a good understanding of the enterprises information resources and needs. Database administrator's duties include:
Schema definition Storage structure and access method definition Schema and physical organization modification Granting user authority to access the database Specifying integrity constraints Acting as liaison with users Monitoring performance and responding to changes in requirements
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Transaction Management
A transaction is a collection of operations that performs a single logical function in a database application Transaction-management component ensures that the database remains in a consistent (correct) state despite system failures (e.g., power failures and operating system crashes) and transaction failures. Concurrency-control manager controls the interaction among the concurrent transactions, to ensure the consistency of the database.
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Storage Management
Storage manager is a program module that provides the interface between the low-level data stored in the database and the application programs and queries submitted to the system. The storage manager is responsible to the following tasks:
interaction with the file manager efficient storing, retrieving and updating of data
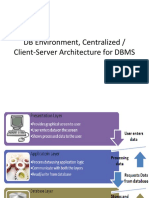
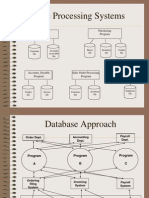
Overall System Structure
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
Amity School of Engineering & Technology
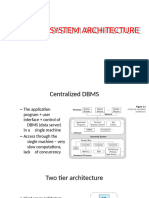
Application Architectures
Two-tier architecture: E.g. client programs using ODBC/JDBC to communicate with a database Three-tier architecture: E.g. web-based applications, and applications built using middleware
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- SQL Server 2008 Replication Technical Case StudyDocument44 pagesSQL Server 2008 Replication Technical Case StudyVidya SagarPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument103 pagesDBMS Lab ManualokokokPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 Lesson 2 Basic Concepts For Construction DatabaseDocument23 pagesModule 1 Lesson 2 Basic Concepts For Construction DatabaseErza LeePas encore d'évaluation
- HRPDocument70 pagesHRPvamsiPas encore d'évaluation
- DB2 9 for z/OS Database Administration: Certification Study GuideD'EverandDB2 9 for z/OS Database Administration: Certification Study GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- TWP Oracle Database in Memory 19cDocument44 pagesTWP Oracle Database in Memory 19cprasemiloPas encore d'évaluation
- PPTDocument36 pagesPPTShahina Shawls Shaa100% (1)
- DbmsDocument34 pagesDbmsAbhinav GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 Database - PPT Compatibility ModeDocument30 pages9 Database - PPT Compatibility ModeBagus FatkhurroziPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management Systems-Chapter 1: Dr. M. Brindha Assistant Professor Department of CSE NIT, Trichy-15Document26 pagesDatabase Management Systems-Chapter 1: Dr. M. Brindha Assistant Professor Department of CSE NIT, Trichy-15Rashika KhannaPas encore d'évaluation
- National Bank of Pakistan offers interest free student loansDocument57 pagesNational Bank of Pakistan offers interest free student loansMaria ChaudhryPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 1Document37 pagesLect 1MitPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Data Base Management System: Compiled By: Er. Dharmendra MishraDocument40 pagesAdvanced Data Base Management System: Compiled By: Er. Dharmendra MishrakamalgaihrePas encore d'évaluation
- Slide 1Document31 pagesSlide 1dejenedagime999Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management SystemsDocument24 pagesDatabase Management SystemsDivya Elangovan100% (2)
- DBMS Lecture 1 Introduction to Database Management SystemsDocument24 pagesDBMS Lecture 1 Introduction to Database Management SystemsHamza BasharatPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - I Introduction To Database ConceptsDocument26 pagesUnit - I Introduction To Database ConceptsBurner AccountPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1Document36 pagesWeek 1Mohammed FoysalPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity School of Engineering & Technology: B. Tech. (CSE/IT), III Semester Database Management Systems Jitendra RajpurohitDocument16 pagesAmity School of Engineering & Technology: B. Tech. (CSE/IT), III Semester Database Management Systems Jitendra RajpurohitKaramjeet KalraPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Database Management System LectureDocument29 pagesAdvanced Database Management System LectureephremPas encore d'évaluation
- Dbms ManualDocument22 pagesDbms ManualJaysheel ElamgodilPas encore d'évaluation
- Databases: Instructor: Engr. Muhammad Umer HaroonDocument42 pagesDatabases: Instructor: Engr. Muhammad Umer Haroonehtisham aliPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Database Management SystemsDocument48 pagesDBMS Database Management Systemssai kiranPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS-History, Architecture and Data AbstractionDocument16 pagesDBMS-History, Architecture and Data AbstractionEedula GaneshreddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity School of Engineering & Technology: B. Tech. (MAE), V Semester Rdbms Sunil VyasDocument13 pagesAmity School of Engineering & Technology: B. Tech. (MAE), V Semester Rdbms Sunil VyasJose AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS ch1Document25 pagesDBMS ch1SonalS NaikPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of DB: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument36 pagesIntroduction of DB: Database System Concepts and ArchitectureMichelle JaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Dbms Unit-IDocument80 pagesDbms Unit-ILaxmi Venki100% (4)
- DB Environment, Centralized / Client-Server Architecture For DBMSDocument19 pagesDB Environment, Centralized / Client-Server Architecture For DBMSVickyPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Database Management Systems (DBMSDocument64 pagesIntroduction to Database Management Systems (DBMSSanthana KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE-223 - Lec-01 IntroductionDocument29 pagesCSE-223 - Lec-01 IntroductionFaisal MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Database Systems & DBMSDocument17 pagesIntro To Database Systems & DBMSgurungePas encore d'évaluation
- Adbms 1.1234Document53 pagesAdbms 1.1234Anoo ShresthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 IntroductionDocument30 pagesCh1 IntroductionTrijeth DatlaPas encore d'évaluation
- W2. Database EnvironmentDocument40 pagesW2. Database EnvironmentSABOOR UR RAHMANPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management Systems: Sibanarayan DashDocument22 pagesDatabase Management Systems: Sibanarayan DashdeepsdashPas encore d'évaluation
- CSCI 4850/8856 Database Management Systems: (Revised From Silberschatz Et Al.) (Chap. 1 of 6 Ed of Textbook)Document42 pagesCSCI 4850/8856 Database Management Systems: (Revised From Silberschatz Et Al.) (Chap. 1 of 6 Ed of Textbook)suryaalla89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Database Architecture Types and SQL OverviewDocument21 pagesDatabase Architecture Types and SQL OverviewDev BabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- CSC103: Database Management SystemsDocument25 pagesCSC103: Database Management Systemsaftab saeediPas encore d'évaluation
- IT244 Week 2Document45 pagesIT244 Week 2WalidOmarPas encore d'évaluation
- CSC 2108 Database ConceptsDocument21 pagesCSC 2108 Database ConceptshudaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Database System ArchitectureDocument10 pagesDatabase System ArchitectureSakkaravarthi SPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Unit 1Document47 pagesDBMS Unit 1Faisal Nazir (ANDY)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anand Kumat Lec-2 DB SystemsDocument37 pagesAnand Kumat Lec-2 DB SystemsSubham MohapatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument31 pagesDatabase Chapter 1 Introductionkeith mushiningaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 Database System Concepts and ArchitectureDocument43 pagesModule 2 Database System Concepts and ArchitectureM MMPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Registration SystemDocument17 pagesOnline Registration SystemSukhmeet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Ism Second ModuleDocument73 pagesIsm Second ModuleABOOBAKKERPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Users and DBMS BenefitsDocument27 pagesDatabase Users and DBMS BenefitsVidhi GovilPas encore d'évaluation
- Database System Architecture L2 2023Document7 pagesDatabase System Architecture L2 2023Pra SanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management SystemsDocument34 pagesDatabase Management SystemsRam Prasad Reddy SadiPas encore d'évaluation
- File Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramDocument35 pagesFile Processing Systems: Billing Program Purchasing ProgramJan Reinhart PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Database SlidesDocument23 pagesDatabase SlidesBilal AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Base System Ch2Document31 pagesData Base System Ch2betiadmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Management SystemsDocument306 pagesDatabase Management SystemsSarvesh BossPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Architecture: Kocbk Database Management SystemDocument23 pagesDBMS Architecture: Kocbk Database Management SystemAbhishek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Basic ConceptsDocument52 pagesDBMS Basic ConceptsPuru RajPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER_1Document50 pagesCHAPTER_1yishaktumoregidePas encore d'évaluation
- The Database Management System DBMSDocument15 pagesThe Database Management System DBMSRichard LumawagPas encore d'évaluation
- Database Systems IntroductionDocument26 pagesDatabase Systems IntroductionHamid RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME DBMS Unit1 FinalDocument139 pagesME DBMS Unit1 FinalSendurusrinivas NadarPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Data Base NoteDocument62 pagesAdvanced Data Base NoteDesyilalPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Relational Database Management System: Sugandha Singh Hooda (Reader, CSE) +91-9717457888Document28 pagesIntroduction To Relational Database Management System: Sugandha Singh Hooda (Reader, CSE) +91-9717457888Radheshyam HolambePas encore d'évaluation
- SS Jain Subodh Management Institute Lab Report on HR SoftwareDocument3 pagesSS Jain Subodh Management Institute Lab Report on HR SoftwareJose AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Velocify and ICMIS Software DetailsDocument10 pagesVelocify and ICMIS Software DetailsJose AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Sem ReportDocument62 pages3rd Sem ReportJose AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- ER Model Conceptual Data Modeling LectureDocument33 pagesER Model Conceptual Data Modeling LectureJose AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Amity School of Engineering & Technology: B. Tech. (MAE), V Semester Rdbms Sunil VyasDocument13 pagesAmity School of Engineering & Technology: B. Tech. (MAE), V Semester Rdbms Sunil VyasJose AntonyPas encore d'évaluation
- DP 2 2 PracticeDocument2 pagesDP 2 2 PracticeGUFakaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP BW DataSourceDocument21 pagesSAP BW DataSourceTsaniNugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hands On Database 2Nd Edition Steve Conger Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument40 pagesHands On Database 2Nd Edition Steve Conger Test Bank Full Chapter PDFharveyadelaqblydh100% (8)
- SQL SERVICE INTEGRATION SERVICES RECAPDocument35 pagesSQL SERVICE INTEGRATION SERVICES RECAPSajan NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Android Content ProvidersDocument31 pagesAndroid Content ProvidersJavier MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Antecedentes de La Planeacion Educativa en MexicoDocument6 pagesPDF Antecedentes de La Planeacion Educativa en MexicoKaren Josceline PLPas encore d'évaluation
- Binary Tree TraversalDocument6 pagesBinary Tree TraversalDrSuresh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- VR Ajp 18Document9 pagesVR Ajp 181213 Vaibhav KotharePas encore d'évaluation
- Structured Query Language3Document78 pagesStructured Query Language3ramtin_khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Extending An LVM VolumeDocument3 pagesExtending An LVM VolumeFahmi Anhar CPas encore d'évaluation
- CSQL Usermanual 1Document51 pagesCSQL Usermanual 1Rahul JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To SQL SQL:: Eg: AlterDocument60 pagesIntroduction To SQL SQL:: Eg: AlterSai HiteshPas encore d'évaluation
- DBA Interview Questions With Answers Part8Document13 pagesDBA Interview Questions With Answers Part8anu224149Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sap NwbiDocument20 pagesSap NwbiFernanda Castillo AlmeidaPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS CS&T2022-23CT1Document2 pagesDBMS CS&T2022-23CT1abcdPas encore d'évaluation
- DBMS Models: Hierarchical Mode Network Model Entity-Relationship Model Relational ModelDocument5 pagesDBMS Models: Hierarchical Mode Network Model Entity-Relationship Model Relational ModelVinay SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Tableau - The Leading Data Visualization ToolDocument17 pagesTableau - The Leading Data Visualization ToolManish ChpuhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 21BCB0241 VL2023240101046 Ast01Document24 pages21BCB0241 VL2023240101046 Ast01Sathvik MuppidiPas encore d'évaluation
- File CarvingDocument39 pagesFile CarvingRin TohsakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sim - Modul 6Document25 pagesSim - Modul 6Sakura PratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Running Head: Database Development 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Database Development 1Jack SikoliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelly Hadoop Hyd May 2018Document14 pagesKelly Hadoop Hyd May 2018dilip kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterprise Geodatabase Size and Name LimitsDocument3 pagesEnterprise Geodatabase Size and Name LimitsHsuain100% (1)
- Excel Pivot Tables April 2016Document36 pagesExcel Pivot Tables April 2016Bernard ToplakPas encore d'évaluation
- Distributed DBMS - CS712 Power Point Slides Lecture 11Document13 pagesDistributed DBMS - CS712 Power Point Slides Lecture 11Hafiz Muhammad KashifPas encore d'évaluation