Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Regula Falsi
Transféré par
Shan E Zehra LashariTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Regula Falsi
Transféré par
Shan E Zehra LashariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Regula-Falsi Method
Regula-Falsi Method
Type of Algorithm (Equation Solver)
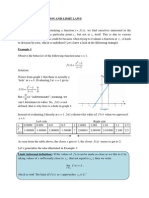
The Regula-Falsi Method (sometimes called the False Position Method) is a
method used to find a numerical estimate of an equation.
This method attempts to solve an equation of the form f(x)=0. (This is very
common in most numerical analysis applications.) Any equation can be written in
this form.
Algorithm Requirements
This algorithm requires a function f(x) and two points a and b for which f(x) is
positive for one of the values and negative for the other. We can write this
condition as f(a)f(b)<0.
If the function f(x) is continuous on the interval [a,b] with f(a)f(b)<0, the algorithm
will eventually converge to a solution.
This algorithm can not be implemented to find a tangential root. That is a root
that is tangent to the x-axis and either positive or negative on both side of the root.
For example f(x)=(x-3)
2
, has a tangential root at x=3.
Regula-Falsi Algorithm
The idea for the Regula-Falsi method is to connect the points (a,f(a)) and (b,f(b))
with a straight line.
Since linear equations are the simplest equations to solve for find the regula-
falsi point (x
rfp
) which is the solution to the linear equation connecting the
endpoints.
Look at the sign of f(x
rfp
):
If sign(f(x
rfp
)) = 0 then end algorithm
else If sign(f(x
rfp
)) = sign(f(a)) then set a = x
rfp
else set b = x
rfp
x-axis
a b
f(b)
f(a)
actual root
f(x)
x
rfp
equation of line:
( ) a x
a b
a f b f
a f y
=
) ( ) (
) (
solving for x
rfp
( )
( )
( )
) ( ) (
) (
) ( ) (
) (
) ( ) (
) ( 0
a f b f
a b a f
a x
a x
a f b f
a b a f
a x
a b
a f b f
a f
rfp
rfp
rfp
=
=
=
Example
Lets look for a solution to the equation x
3
-2x-3=0.
We consider the function f(x)=x
3
-2x-3
On the interval [0,2] the function is negative at 0 and positive at 2. This means
that a=0 and b=2 (i.e. f(0)f(2)=(-3)(1)=-3<0, this means we can apply the
algorithm).
( )
2
3
4
6
3 1
) 2 ( 3
) 0 ( ) 2 (
0 2 ) 0 (
0 =
=
f f
f
x
rfp
8
21
2
3
) (
=
|
.
|
\
|
= f x f
rfp
This is negative and we will make the a =3/2
and b is the same and apply the same thing
to the interval [3/2,2].
( )( )
( )
( )
29
54
58
21
2
3
1 2
3
) 2 (
2
2
3
8
21
2
1
8
21
2
3
2
3
2
3
= + =
f f
f
x
rfp
267785 . 0
29
54
) ( =
|
.
|
\
|
= f x f
rfp
This is negative and we will make the a =54/29
and b is the same and apply the same thing to
the interval [54/29,2].
Stopping Conditions
Aside from lucking out and actually hitting the root, the stopping condition is
usually fixed to be a certain number of iterations or for the Standard Cauchy Error
in computing the Regula-Falsi Point (x
rfp
) to not change more than a prescribed
amount (usually denoted c).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Accuplacer Study GuideDocument84 pagesAccuplacer Study GuideJMC5053100% (1)
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (8)
- Hkcee Mathematics - 13.2 Coordination Geometry - Circles - P.1Document7 pagesHkcee Mathematics - 13.2 Coordination Geometry - Circles - P.1Brian LiPas encore d'évaluation
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"D'EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (2)
- CalculusDocument15 pagesCalculusrpdemaladePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter1 Limits Continuity RevisedDocument12 pagesChapter1 Limits Continuity Reviseddiktatorimhotep8800Pas encore d'évaluation
- Alevel MathDocument10 pagesAlevel Mathjingcong liuPas encore d'évaluation
- Root Finding (Numericals Method)Document14 pagesRoot Finding (Numericals Method)DavePascualPas encore d'évaluation
- Vdocuments - MX - Chapter 7 Resource Masters Math Class NBSPPDF Fileglencoemcgraw Hill PDFDocument88 pagesVdocuments - MX - Chapter 7 Resource Masters Math Class NBSPPDF Fileglencoemcgraw Hill PDFTipitaca MonjePas encore d'évaluation
- School of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandDocument1 pageSchool of Mathematics and Physics, The University of QueenslandVincent LiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Rules of Differentiation of Functions in CalculusDocument7 pagesRules of Differentiation of Functions in CalculusOyedotun TundePas encore d'évaluation
- Simpson's 1/3 Rule of IntegrationDocument12 pagesSimpson's 1/3 Rule of Integrationap021100% (1)
- Osculating Parabola and Numerical ExperimentsDocument16 pagesOsculating Parabola and Numerical ExperimentsKolynPas encore d'évaluation
- Section-2 Roots of Equations: Bracketing MethodsDocument12 pagesSection-2 Roots of Equations: Bracketing MethodsTanilay özdemirPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Quotient ExamplesDocument5 pagesDifference Quotient Examplesapi-126876773Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rational Functions: Rational Functions Are Quotients of Polynomial Functions. This Means ThatDocument16 pagesRational Functions: Rational Functions Are Quotients of Polynomial Functions. This Means ThatSalih AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsDocument11 pagesCalculus Review and Formulas: 1 FunctionsRaymond BalladPas encore d'évaluation
- 151 Exam 1 Review AU10Document3 pages151 Exam 1 Review AU10Nathan W. SerafiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8Document17 pagesLecture 8amjadtawfeq2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 2Document30 pagesChap 2Sharif M Mizanur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Math T 2Document13 pagesMath T 2Sarman TamilselvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Analysis All Lab ReportsDocument23 pagesNumerical Analysis All Lab ReportsZia JanPas encore d'évaluation
- An Inequality of Araki-Lieb-Thirring: (Von Neumann Algebra Case)Document5 pagesAn Inequality of Araki-Lieb-Thirring: (Von Neumann Algebra Case)bibbiblosPas encore d'évaluation
- Matlab For Maph 3071 Lab 6: Numerical IntegrationDocument3 pagesMatlab For Maph 3071 Lab 6: Numerical IntegrationDay AlshojaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inverse Laplace Transform Lecture-3Document22 pagesInverse Laplace Transform Lecture-3SingappuliPas encore d'évaluation
- L03 NMCP Lecture03-1588102457Document30 pagesL03 NMCP Lecture03-1588102457jorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Das 44 9Document5 pagesDas 44 9noob free fire player plz helpPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Computational Methods: Numerical IntegrationDocument59 pagesAdvanced Computational Methods: Numerical IntegrationMohammed HamdyPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Analysis: WwlchenDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Analysis: WwlchenGanesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- MAT10f Midterm PDFDocument19 pagesMAT10f Midterm PDFJulius BoitizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuous Optimization TechiniqueDocument32 pagesContinuous Optimization TechiniqueMuhammad Ali Khan AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions and Their Graphs: Section SummariesDocument14 pagesFunctions and Their Graphs: Section SummariesPattrawut RukkachartPas encore d'évaluation
- Improper Integrals Involving Rational and Exponential Functions PDFDocument10 pagesImproper Integrals Involving Rational and Exponential Functions PDFhammoudeh13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maths 44Document2 pagesMaths 44anasfinkilePas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Analysis: WwlchenDocument16 pagesFundamentals of Analysis: WwlchenHenry Yul De AriesPas encore d'évaluation
- FX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsDocument4 pagesFX X X X Orx X X X FX X X: Test 1 SolutionsexamkillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Y MX B: Linearization and Newton's MethodDocument7 pagesY MX B: Linearization and Newton's MethodTony CaoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Rational Function Is One That Can Be Written As A PolynomialDocument20 pagesA Rational Function Is One That Can Be Written As A PolynomialJhope Jung100% (1)
- Solving Polynomial SystemsDocument164 pagesSolving Polynomial SystemsChristophe LauwerysPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 53 LE 3 Reviewer ProblemsDocument14 pagesMath 53 LE 3 Reviewer ProblemsJc QuintosPas encore d'évaluation
- Relations and Functions PDFDocument4 pagesRelations and Functions PDFRabiya FaheemPas encore d'évaluation
- CrapDocument8 pagesCrapvincentliu11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus I Notes On Limits and Continuity.: Limits of Piece Wise FunctionsDocument8 pagesCalculus I Notes On Limits and Continuity.: Limits of Piece Wise Functionsajaysharma19686191Pas encore d'évaluation
- Very Important Q3Document24 pagesVery Important Q3Fatima Ainmardiah SalamiPas encore d'évaluation
- AssigmentsDocument12 pagesAssigmentsShakuntala Khamesra100% (1)
- Fsolve: Using To Solve A Single Equation: Because Fsolve Uses Numerical TechniquesDocument5 pagesFsolve: Using To Solve A Single Equation: Because Fsolve Uses Numerical Techniquesfajar_dPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics TDocument97 pagesMathematics TPh'ng Jiun YanPas encore d'évaluation
- Limits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityDocument41 pagesLimits and Continuity: - Definition - Evaluation of Limits - Continuity - Limits Involving InfinityAan SajaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAT Subject Math Level 2 FactsDocument11 pagesSAT Subject Math Level 2 FactsSalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Tangent Lines and Rates of Changes 1.1 Average Rate of ChangeDocument16 pagesTangent Lines and Rates of Changes 1.1 Average Rate of Changediktatorimhotep8800Pas encore d'évaluation
- FortranDocument38 pagesFortranwph97nxgymPas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.4 - D-1Document7 pagesThe Fundamental Theorem of Calculus 4.4 - D-1alexlhhcasPas encore d'évaluation
- PortfolioDocument18 pagesPortfoliocharlotawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Shrodinger EqDocument22 pagesShrodinger Eqawais33306Pas encore d'évaluation
- MC TY Explogfns 2009 1Document11 pagesMC TY Explogfns 2009 1lifes.fallenangelPas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical Differentiation: X X X H X H X HDocument19 pagesNumerical Differentiation: X X X H X H X HDini AryantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Mm34casDocument16 pagesChapter 12 Mm34casEric MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- FalseRegDocument11 pagesFalseRegAgoesPas encore d'évaluation
- June 29Document22 pagesJune 29charlotawalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Euler-Heun Method PDFDocument3 pagesEuler-Heun Method PDFCaroline FelixPas encore d'évaluation
- B SC Mathematics 2017 PDFDocument166 pagesB SC Mathematics 2017 PDFKtK -HelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet of Linear Equation With One VariableDocument5 pagesWorksheet of Linear Equation With One VariablekristianasillyPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Euler ProblemsDocument214 pagesProject Euler Problemspeter100% (1)
- Accumulative Difference Image ADI PDFDocument29 pagesAccumulative Difference Image ADI PDFMonique PadovanPas encore d'évaluation
- Omplex Nalysis: C 2014 Ron BuckmireDocument4 pagesOmplex Nalysis: C 2014 Ron BuckmireSasikalaPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSIGNMENT PHYSICS Electrostatics 1 10 QuestionsDocument9 pagesASSIGNMENT PHYSICS Electrostatics 1 10 Questionsiqbalsingh sahaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Logic Gates Boolean Algebra: Instructor: Afroza SultanaDocument44 pagesLogic Gates Boolean Algebra: Instructor: Afroza SultanaSamina Tohfa100% (1)
- Parabola Exercise 2 - ADocument19 pagesParabola Exercise 2 - AAtharva Sheersh PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1815 13 PDFDocument24 pages1815 13 PDFsiamak001Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Binomial Expansion The Binomial and Normal Distribution: ObjectivesDocument38 pagesThe Binomial Expansion The Binomial and Normal Distribution: ObjectivesRafJanuaBercasioPas encore d'évaluation
- Brownian Motion and Geometric Brownian Motion: Graphical RepresentationsDocument54 pagesBrownian Motion and Geometric Brownian Motion: Graphical RepresentationsAssan AchibatPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Differential Calculus PDFDocument45 pagesIntroduction To Differential Calculus PDFMelissa Fullas BriosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Steady-State Temperature in A CylinderDocument8 pagesSteady-State Temperature in A CylinderShally RahmawatyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2011 (Engg-Mat) emDocument9 pages2011 (Engg-Mat) emGandla Ravi ThejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Art Unit Plan Exploring Shapes in ArtDocument13 pagesArt Unit Plan Exploring Shapes in Artapi-265643246Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modelling The Dynamics of A Renewable Resource Under Harvesting With Taxation As A Control VariableDocument30 pagesModelling The Dynamics of A Renewable Resource Under Harvesting With Taxation As A Control Variableopiq nurahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- GE - Math Module 3Document15 pagesGE - Math Module 3Calso Cristel MayPas encore d'évaluation
- Goppa McelieceDocument41 pagesGoppa McelieceleoverobrPas encore d'évaluation
- ENAT (School) Report KS1Document25 pagesENAT (School) Report KS1rodah fajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Paulina Final Case StudyDocument27 pagesPaulina Final Case Studyapi-279970784Pas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist Subject 2019 2020Document31 pagesChecklist Subject 2019 2020batchayPas encore d'évaluation
- Not CNNDocument8 pagesNot CNN장민종Pas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Fractals Art in Ceiling DecorationDocument3 pagesImplementation of Fractals Art in Ceiling DecorationInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementPas encore d'évaluation
- ADA173823Document138 pagesADA173823vuilehaidPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF DocumentDocument149 pagesPDF DocumentfofofPas encore d'évaluation