Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS
Transféré par
Karina FerrerTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS
Transféré par
Karina FerrerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MATH10
ALGEBRA
RELATIONS FUNCTIONS AND GRAPHS
Functions and Their Graphs(Algebra and Trigonometry, Young 2
nd
Edition, page 225-322)
GENERAL OBJECTIVE
At the end of the chapter the students are expected to:
Week 8 Day 1
Determine whether a relation is a function.
Use function notation.
Find the domain and range of a function.
Perform operations on functions.
Sketch the graphs of common functions.
Classify function as odd even, or neither.
Determine whether functions are one-to-one.
Find the inverse of a function.
FUNCTIONS
TODAYS OBJECTIVE
Determine whether a relation is a function.
Determine whether an equation represents a function.
Use function notation.
Find the value of a function.
Determine the domain and range of a function.
Evaluate the difference quotient for a function.
At the end of the lesson the students are expected to:
Week 8 Day 1
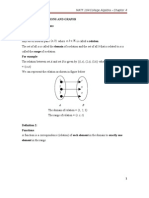
DEFINITION
RELATION
A relation is a correspondence between two sets where each
element in the first set called the domain, corresponds to at least
one element in the second set, called the range.
It is a set of ordered pairs.
The domain is the set of the first components of the ordered
pairs and the range is the set of all the second component of the
ordered pairs.
A relation in which each element of the domain corresponds to
exactly one element in the range is a function.
Week 8 Day 1
DEFINITION
FUNCTION
A function is a correspondence between two sets where each
element in the first set , called the domain, corresponds to exactly
one element in the second set, called the range.
It is a set of ordered pairs with no two pairs having the same first
element.
Week 8 Day 1
Week 8 Day 1
Set A is the domain
1
2
3
4
5
Set B is the range
2
10
8
6
4
Example 1:
one - to-one
{(1,6), (2,2), (3,4), (4,8), (5,10)}
Set A is the domain
1
2
3
4
5
Set B is the range
2
10
8
6
4
Example 2:
many-to-one
{(1,4), (2,4), (3,4), (4,4), (5,4)}
Week 8 Day 1
A good example that you can relate to is that students in our
algebra class this term are set A. The grade youll earn out of this
class is set B. Each student must be assigned a grade and can only
be assigned ONE grade, but more than one student can get the
same grade (we hope so---we want lots of 1s). The example shown
on the previous screen had each student getting the same grade.
1
2
3
4
5
2
10
8
6
4
2 was assigned both 4 and 10, therefore one-to-many or the element in the domain
corresponds to more than one element in the range
NOT a function . It is, however a relation.
{(1,2), (2,4), (2,10), (3,8), (4,6),(5,4)}
Example 3:
x y sin =
1
3
+ = x y
One-to-one and many-to-one functions
Each value of x maps to only one
value of y . . .
Consider the following graphs
Each value of x maps to only one
value of y . . .
BUT many other x values map to
that y.
and each y is mapped from only
one x.
and
One-to-one and many-to-one functions
is an example of
a one-to-one function
1
3
+ = x y
is an example of
a many-to-one function
x y sin =
x y sin =
1
3
+ = x y
Consider the following graphs
and
One-to-many is NOT a function. It is however a relation.
Example 5:
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) { }
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) { }
( ) ( ) ( ) { }
227 page Turn Your
F 00PM,85 : 6 , F 00PM,89 : 2 , F 00AM,83 : 11 . c
7,8 , 5,6 , 1,3 , 1,2 . b
7,6 , 5,6 , 3,2 , 1,2 a.
: functions are relations following the whether Determine
o o 0
Week 8 Day 1
Below is a sample of 2008 cars listed from less expensive to more
expensive, with corresponding gas consumption in miles per
gallon MPG
Kia Rio
Ford Focus
Toyota Corolla
Honda Civic
Toyota Prius
Nissan Altima (H)
Ford Mustang
Dodge Viper
Hummer H2
Aston Martin DB9
DOMAIN
MODEL
25
24
27
21
48
35
17
13
11
11
Is this relation a function?
RANGE
MPG (CITY)
A) YES B) NO
Example 6:
Below is a sample of 2008 cars listed from less expensive to more expensive,
with corresponding gas consumption in miles per gallon MPG
DOMAIN
MPG (city)
Kia Rio
Ford Focus
Toyota Corolla
Honda Civic
Toyota Prius
Nissan Altima (H)
Ford Mustang
Dodge Viper
Hummer H2
Is this relation a function?
RANGE
model & make
A) YES B) NO
25
24
27
21
48
35
17
13
11
Aston Martin DB9
Example 7:
All of the examples discussed are discrete sets in that they
represent countable set of distinct pairs (x,y). A function can
also be defined algebraically by equations.
Week 8 Day 1
An equation assigns to each x-value exactly one corresponding y-value.
FUNCTIONS DEFINED BY EQUATIONS
x 3 x y equation the Given : Example
2
=
x y Ordered Pair
1 -2 (1,-2)
5 10 (5,10)
-2/3 22/9 (-2/3,22/9)
1.2 -2.16 (1.2,-2.16)
x is the independent variable ,first element in the ordered pair
(domain)
y is the dependent variable, second element in the ordered pair
(range)
Week 8 Day 1
Any equation which describes how the elements of the domain and
range of any relation are paired is called the rule of correspondence of
that relation.
It should be made clear that the equation is not the relation.
The relation is the set of ordered pairs which consists of all possible
parings of the elements of the domain and range according to the rule
or the equation which describes the relation.
Week 8 Day 1
Example 1:
229 228 page Example
x y . f
x y . e
x y . d
y x . c
1 y x . b
y x a.
function. a define equations following the whether Determine
3
2
2 2
2
=
=
=
=
= +
=
Week 8 Day 1
VERTICAL LINE TEST
Week 8 Day 1
Given the graph of an equation, if any vertical line that can
be drawn intersects the graph at no more than one point,
the equation defines a function of x. This test is called the
vertical line test.
Use the vertical line test to determine whether the
graphs of equations define functions of x
Week 8 Day 1
x x
y y
# 19 page 239
# 22 page 239
In summary , a function can be expressed in one of
the four ways:
Week 8 Day 1
1. Verbally
2. Numerically
3. Algebraically
4. Graphically
This is sometimes called the Rule of 4.
Verbally Numerically Algebraically Graphically
Example: Expressing a Function
( ) ( ) ( ) { } 1 , 1 , 0 , 0 , 1 , 1 x y =
x
y
Every real
number has a
corresponding
absolute value
FUNCTION NOTATION
Week 8 Day 1
Functions are denoted by letters, the most common of which are
f,g,h, F,G ,H, etc.
Given the equation y=2x+5 which is a function because its graph is
a non vertical line and thus passes the vertical line test.
If we give the said function a name, say, f, then we can use
function notation : f(x)=2x+5
The symbol f(x) is read : f evaluated at x or f of x and represents
the y-value that corresponds to a particular x-value. In other words,
y=f(x).
Week 8 Day 1
Input Function Output Equation
x f f(x) f(x)=2x+5
Independent
variable
(or the
argument)
Mapping Dependent
variable
Mathematical
rule
x
x=0
x=1
x=2
f(x)=2x+5
f(0)=5
f(1)=7
f(2)=9
Domain
Range
Function
f
f
f
The function f maps some value of x in the domain to some value f(x)
in the range.
Week 8 Day 1
EXAMPLE
( )
( ) ( )
232 page 3 . 1 . 3 . Ex Classroom
1 2f - b. 1 - f a. : Compute
1 x x x f Let 1.
4
=
( )
( )
( )
232 page 4 . 1 . 3 . Ex Classroom
0 x f that such x c.Find
2 f Find b.
3 - f Find a. 2.
=
1
2
3
4
-1
-2
-3
-4 -8 -10 4 8 x
(2,-1)
(4,1)
y
Week 8 Day 1
( )
( )
233 page YourTurn
1 x g Evaluate
3 x 2 x x g Let 3.
2
+ =
( )
( )
( ) ( )
233 page 6 . 1 . 3 . x ClassroomE
1 f x f b.
1 x f a. : Compute
. x 2 x f Let 4.
2
+
+
=
( )
( )
233 page 7 . 1 . 3 . Ex lassroom C
x - f - : Compute
. x 2 x 3 x f Let 5.
2
=
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
234 page YourTurn
3
1
G d.
G(3)
G(1)
c.
2 G t G b. 2 - t G a. : Evalaute
, 4 t 3 t G function the Given 6.
|
.
|
\
|
=
( )
235 page YourTurn
1 x x f for
quotient difference the Evaluate 7.
2
=
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) x f g b. x g f a. : Find
5 x 3 2x x g and 2 - x x f If 8.
2
= =
DIFFERENCE QUOTIENT
( ) ( )
quotient. difference the called is
, 0 h where ,
h
x f h x f
expression The =
+
Week 8 Day 1
DOMAIN AND RANGE OF A FUNCTION
All the possible values of x is called the domain and all the possible
values of y is called the range. In a set of ordered pairs, the set of
first elements and second elements of ordered pairs is the domain
and range, respectively.
EXAMPLE: Write the answers in set notation and
interval notation.
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
237 page 10 . 1 . 3 . Ex Classroom
1 x
x
x f . d
x
1 - x
x f . c
x 3 9 x f . b
32 x 2
1 x
x f a.
functions. the of range and domain the Find 1.
2
3
3
3
2
+
= =
=
=
Week 8 Day 1
( ) ( )
237 Page YourTurn
4 x
1
x f . b 3 x x f a.
functions. the of range and domain the Find 2.
2
= =
( )
( )
( ) ( ) ( )
( )
x y e.
241 page 88,70 91, 97, s #
x 25
x
x P . c
3 t
t 2
t Q d. 16 x x f b.
0 x g to s correspond that
x of values the find and 5 x 2 x x f . a
functions. the of range and domain the Find 3.
2
2
2
2
1
2
2
=
=
+
= =
=
=
TODAYS OBJECTIVE
Recognize and graph common functions.
Classify functions as even, odd, or neither.
Graph piecewise-defined function.
Graph greatest integer function.
Add, subtract, multiply and divide functions.
Evaluate composition of functions.
Determine the domain of functions resulting from operations on
and composition of functions.
Find the inverse of a function
At the end of the lesson the students are expected to:
Week 8 Day 2
Week 8 Day 2
KINDS OF FUNCTIONS AND ITS GRAPHS
DEFINITION
If f(x) is a function, then its graph is the set of all points (x,y) in the
two-dimensional plane for which (x,y) is an ordered pair in f(x).
One way to graph a function is by point plotting.
We can also find the domain and range from the graph of a function.
GRAPHS OF FUNCTIONS
Week 8 Day 2
Week 8 Day 2
EXAMPLE: Sketch the graph of the following functions and state
the domain and range in interval notation.
NAME FUNCTION
1. Linear
2.Constant
3. Identity
4.Square
5.Cube
6.Square root
7.Cube root
8.Absolute value
9.Reciprocal
( ) 5 x 3 x f + =
( ) 6 x f =
( ) x x f =
( ) 5 x x f
2
=
( )
3
x 2 x f =
( )
2
x 16 x f =
( )
3
x x f =
( ) 5 x 2 x f =
( )
25 x
1
x f
2
=
The term even is used to describe functions that are symmetric with
respect to the y-axis or vertical axis.
The term odd is used to describe functions that are symmetric with
respect to the origin.
EVEN AND ODD FUNCTIONS
Function Symmetric wrt On replacing x with -x
Even y-axis or vertical axis f(-x)= f(x)
Odd origin f(-x)=-f(x)
Week 8 Day 2
( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
3.2.1 Ex. Classroom
x x 3 x f . e
1 x x 3 x f d. x x 3 x f b.
x x 3 x f c. x x 3 x f . a
neither. or odd even, are functions these if Determine
2
5 3
5 3 5 3
5 3 5 3
=
+ + = =
+ = + =
EXAMPLE
Week 8 Day 2
PIECEWISE DEFINED FUNCTIONS
A piecewise defined function is defined by different formulas on
different parts of its domain.
EXAMPLE: Graph the piecewise-defined function, and state the
domain and range in interval notation.
( ) ( )
256 page Turn Your 254 page #5 Example
1 x x
1 x 1 - 2
-1 x x
x f 2.
1 x x
1 x 1 - 1
1 x x
x G 1.
2
>
< <
s
=
>
s s
<
=
Week 8 Day 2
( )
256 page Example
0 t 1
0 t 0
t H 3.
>
<
=
Week 8 Day 2
GREATEST INTEGER FUNCTION
(
x to equal or than less integer greatest x
by defined is function integer greatest The
=
Example:
(
= 0
(
= 1 . 0
(
= 3 . 0
(
= 9 . 0
(
= 1
(
= 1 . 1
(
= 2 . 1
(
= 9 . 1
(
= 2
(
= 1 . 2
(
= 4 . 3
(
= 4 . 3
(
= 9 . 0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
2
2
3
-4
-1
Week 8 Day 2
LEAST INTEGER FUNCTION
EXAMPLE:
= 0
= 1 . 1
= 2 . 1
= 9 . 1
= 2
= 1 . 2
= 4 . 3
= 4 . 3
= 9 . 0
0
1
1
1
1
2
2
2
2
3
4
-3
0
x to equal or than greater integer least x
by defined is function integer least The
=
= 1 . 0
= 3 . 0
= 9 . 0
= 1
EXAMPLE: Graph the greatest integer function . ( )
(
x x f =
Week 8 Day 2
Week 8 Day 2
OPERATIONS ON FUNCTIONS
AND
COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS
Week 8 Day 2
FUNCTION NOTATION DOMAIN
Sum
Difference
Product
Quotient
( )( ) ( ) ( ) x g x f x g f + = +
( )( ) ( ) ( ) x g x f x g f =
( )( ) ( ) ( ) x g x f x g f =
( )
( )
( ) x g
x f
x
g
f
= |
.
|
\
|
g f
D D
g f
D D
g f
D D
( ) { } 0 x g D D
g f
=
OPERATIONS ON FUNCTIONS
EXAMPLE
( ) ( )
280 page 3.4.1 Ex. Classroom
domains. the State
.
g
f
and , g f , g - f , g f : Compute
x -4 x g and x 2 1 x f Let 1.
3 3
+
= + =
( ) ( )
281 page 3.4.2 Ex. Classroom
domains. the state and
g
f
: Compute
6 - x 3 x g and x 3 x f Let 2. = =
Week 8 Day 2
Week 8 Day 2
NOTATION WORDS DEFINITION
DOMAIN
COMPOSITION OF FUNCTIONS
g f
f g
f composed
with g
g composed
with f
( ) ( ) x g f
( ) ( ) x f g
The set of all real numbers x
in the domain of g such that g(x)
is also in the domain of f.
The set of all real numbers x
in the domain of f such that f(x)
is also in the domain of g.
EXAMPLE
( ) ( )
282 page 3.4.3 Ex. Classroom
domain. the state and , f g and g f : Compute
4 -x x g and x 2 x f Let 1.
2
+ = =
( ) ( )
283 page #4 Example
domain. its state and g f determine
x
1
x g and
1 x
1
x f Let 2.
=
( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
( ) ( ) ( ) ( )
284 page #6 Example
4 - f g d. 3 f g c.
2 - g f b. 1 g f a. evaluate
x 5 x g and 7 - x x f Let 3.
2 2
= =
Week 8 Day 2
INVERSE OF A FUNCTION
If f is a one-to-one function determined by the set of ordered pairs
(x,y), then there is a function f
1
, called the inverse function of f, such
that its set consists of the ordered pairs (y,x) defined by
x = f
1
(y) if and only if y = f (x)
The domain of f
1
is the range of f and the range of f
1
is the domain
of f.
EXAMPLE
( )
( )
293 page 3.5.4 Ex. Classroom
1 2 x x f of inverse the is
2 1 x f that Verify 1.
3
3 1 -
+ =
+ =
( ) ( )
297 page 3.5.7 Example Classroom
1 x 2 x g b. 3x - 1 x f a.
range and domain the state and functions
following the of inverse the Determine 2.
+ + = =
Week 8 Day 2
EXAMPLE
Week 8 Day 2
( )
( )
297 page Turn Your
inverse its Find
function. one - to - one a is
1 x ,
1 x
4
x g function The b.
298 page #8 Example
exists. it if x x f
function the of inverse the Find a. 3.
=
=
=
Find the inverse of
x
x
x f
5 1
1 5
) (
+
=
function. one - to - one a Not D)
C)
B)
A)
5
1
) (
) 1 ( 5
1
) (
) 1 ( 5
1
) (
1
1
1
=
+
=
+
x f
x
x
x f
x
x
x f
4 2 0 2 4
4
2
0
2
4
x
y
f x
1
) ( x f
SUMMARY
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Topic:: Understanding Function and RelationDocument28 pagesTopic:: Understanding Function and RelationCarlos Enriquez IVPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen - Math LAS 1Document5 pagesGen - Math LAS 1Michael hamorPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Transcript 1 Introduction To Functions and Piecewise Functions7Document14 pagesLecture Transcript 1 Introduction To Functions and Piecewise Functions7eve lopezPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 and 2 - General MathematicsDocument6 pagesModule 1 and 2 - General MathematicsMillet PañoPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 General MathematicsDocument10 pagesWeek 1 General MathematicsMarcel Baring ImperialPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 5Document23 pagesTopic 5NUR FADHLINA BINTI IZZUNIDDINPas encore d'évaluation
- Met 1 Q1 PDFDocument8 pagesMet 1 Q1 PDFShannen MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 - General MathematicsDocument40 pagesWeek 1 - General MathematicsSirr AustriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionDocument11 pagesRevisiting Functions: Lesson DescriptionPrincess Joie RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics Module Number 1: Review On Functions ObjectivesDocument53 pagesGeneral Mathematics Module Number 1: Review On Functions ObjectivesGolda Crizelle NoquiaoPas encore d'évaluation
- NJC Functions Lecture Notes Teachers Edition With Tutorial and AnswersDocument43 pagesNJC Functions Lecture Notes Teachers Edition With Tutorial and AnswersbhimabiPas encore d'évaluation
- General Math SHS Module 1Document12 pagesGeneral Math SHS Module 1Kristian IanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen MathDocument8 pagesGen MathHershell ContaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Document95 pagesChapter 3 (Lessons 1-4)Retchelle Palmero SangcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gned03 - Relation and FunctionDocument8 pagesGned03 - Relation and FunctionLeslie mae GioPas encore d'évaluation
- LP-GenMath - Week1Document10 pagesLP-GenMath - Week1Cry BeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions As ModelsDocument88 pagesFunctions As ModelsMii Chel50% (2)
- Ch. 5 Functions GraphsDocument41 pagesCh. 5 Functions GraphsTeo Pui KuanPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics: Grade 11 Quarter 1 Module 1 - Week 1Document18 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Grade 11 Quarter 1 Module 1 - Week 1Joanna Marie RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 111: Functions and RelationsDocument27 pagesMath 111: Functions and Relationsalvin bautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Week 1 - Gen.-Math-2-FINALDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Week 1 - Gen.-Math-2-FINALKenneth IbarraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Rudest Book EverDocument14 pagesThe Rudest Book EverIrene B. LuisPas encore d'évaluation
- FunctionsDocument33 pagesFunctionsIrene Mae BeldaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4: Functions and Graphs 4.1) Basics of Functions Definition 1: RelationsDocument32 pagesChapter 4: Functions and Graphs 4.1) Basics of Functions Definition 1: Relationssf1dPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Week 1 - Quarter 1 - Gen MathDocument12 pagesModule 1 - Week 1 - Quarter 1 - Gen MathKaru GreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen Math Q1 Mod 1Document21 pagesGen Math Q1 Mod 1Joselito UbaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions As Models (General Mathematics)Document8 pagesFunctions As Models (General Mathematics)Myrhelle Grecia100% (1)
- Chapter 3 2 - Intro To FunctionsDocument32 pagesChapter 3 2 - Intro To Functionsapi-263209117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week1 Gen - Math ModuleDocument26 pagesWeek1 Gen - Math ModuleAshrel Rasonable NuynayPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics Week 1 PDFDocument17 pagesGeneral Mathematics Week 1 PDFRussiel DagohoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One: Functions and GraphsDocument16 pagesChapter One: Functions and GraphsSalma DodinPas encore d'évaluation
- Language 0f MathDocument57 pagesLanguage 0f MathChristian Dave Balasa100% (1)
- Unit 8 Functions & Graphs GuideDocument32 pagesUnit 8 Functions & Graphs Guideحفيظو عبداللهPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Functions, Function Notation, Domain & RangeDocument27 pages01 Functions, Function Notation, Domain & RangeThe RantsPas encore d'évaluation
- Function and Its Basic PropertiesDocument5 pagesFunction and Its Basic PropertiesMhaica L. GalagataPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CDocument10 pagesA. Definition of A Function: Video Tutorial For Parts A, B, CmomathtchrPas encore d'évaluation
- LP1 Math1 Unit1 Edited-082321Document15 pagesLP1 Math1 Unit1 Edited-082321hajiPas encore d'évaluation
- CalculusDocument128 pagesCalculusJohn Paul ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide # 2024 - 1Document2 pagesStudy Guide # 2024 - 1ingridgiselavPas encore d'évaluation
- Function. (X Values Cannot Repeat)Document3 pagesFunction. (X Values Cannot Repeat)api-168512039Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operation and Composition of FunctionsDocument42 pagesOperation and Composition of FunctionsRex FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Slideshow PresentationDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Slideshow PresentationJohn Ralph GenabePas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics: Module 1: Introduction To FunctionsDocument17 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Module 1: Introduction To FunctionsPinky PardilladaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsDocument16 pages1.2 The Algebra of FunctionsYukiC123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 GMDocument41 pagesWeek 1 GMJhanjhan BoniPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument28 pagesUntitledRainiel GanarealPas encore d'évaluation
- NP - General Mathematics Q1W1Document8 pagesNP - General Mathematics Q1W1charles stone panuncilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Gen MathDocument7 pagesGen MathLaiza baldado TagacPas encore d'évaluation
- Graph Functions & Analyze Mathematical ModelsDocument28 pagesGraph Functions & Analyze Mathematical ModelsTOP 5 GAMES ANDROIDPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus with Transcendental FunctionsDocument32 pagesCalculus with Transcendental FunctionsHarrdeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching FunctionsDocument7 pagesTeaching FunctionsCatherine MitchellPas encore d'évaluation
- Genmath 11 q1 Week 1Document18 pagesGenmath 11 q1 Week 1Joanna Marie RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1. Functions and Their GraphsDocument7 pagesModule 1. Functions and Their GraphsMori OugaiPas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics - Q1 - Week 1-3Document20 pagesGeneral Mathematics - Q1 - Week 1-3Rayezeus Jaiden Del RosarioPas encore d'évaluation
- FUNCTIONS pptx1Document57 pagesFUNCTIONS pptx1Manuela Kassandra TribianaPas encore d'évaluation
- Functions and Their Graphs: Section SummariesDocument14 pagesFunctions and Their Graphs: Section SummariesPattrawut RukkachartPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Exercises With SolutionsDocument135 pagesCalculus Exercises With Solutionssheena mariePas encore d'évaluation
- 8 4 Function NotationDocument16 pages8 4 Function Notationapi-233527181Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Mathematics: Content: FUNCTIONDocument9 pagesGeneral Mathematics: Content: FUNCTIONLeopoldo MalicdemPas encore d'évaluation
- Material properties and geometry of cross-sectional areasDocument141 pagesMaterial properties and geometry of cross-sectional areasKarina Ferrer100% (2)
- Managing General Overhead Cost: Reporter: Ferrer, Karina D.PDocument9 pagesManaging General Overhead Cost: Reporter: Ferrer, Karina D.PKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Modal ChoiceDocument41 pagesModal ChoiceKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- YFCDocument11 pagesYFCKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Thermal ExpansionDocument9 pages01 Thermal ExpansionKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines for 2 Case Studies on Environmental Pollution Problems and SolutionsDocument1 pageGuidelines for 2 Case Studies on Environmental Pollution Problems and SolutionsKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Newtons Law of Cooling SolutionsDocument7 pagesNewtons Law of Cooling SolutionsGGPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of FluidsDocument29 pagesProperties of FluidsKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- 2012 Management and Leadership QuestionnaireDocument18 pages2012 Management and Leadership QuestionnaireKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Liabilities and EquitiesDocument2 pagesLiabilities and EquitiesKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- FINMAN (Depreciation) UploadDocument4 pagesFINMAN (Depreciation) UploadKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Baloon FramingDocument2 pagesBaloon FramingKarina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 2Document6 pagesHomework 2Karina FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cereals and Pulses - Specs & Test Methods Part-1 RiceDocument43 pagesCereals and Pulses - Specs & Test Methods Part-1 RiceGhulam MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials MarksDocument28 pagesStrength of Materials Markslogeshboy007Pas encore d'évaluation
- English Task For 11th GradeDocument8 pagesEnglish Task For 11th GradeDevi NurulhudaPas encore d'évaluation
- "False Position Method": Engr. Julian A. Carbonel, JRDocument12 pages"False Position Method": Engr. Julian A. Carbonel, JRJulian Carbonel Jr0% (1)
- Noorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester IDocument26 pagesNoorul Islam Centre For Higher Education Noorul Islam University, Kumaracoil M.E. Biomedical Instrumentation Curriculum & Syllabus Semester Iisaac RPas encore d'évaluation
- No SystemDocument15 pagesNo SystemAjeet Singh RachhoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit OpencoursewareDocument14 pages2.161 Signal Processing: Continuous and Discrete: Mit Opencoursewarelovelyosmile253Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Vibration NotesDocument56 pagesMechanical Vibration NotesYadanaPas encore d'évaluation
- USL - Problem StatementDocument3 pagesUSL - Problem StatementMarket CharchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Urriculum Itae Et TudiorumDocument21 pagesUrriculum Itae Et TudiorumEnricoPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo Dynamics Question BankDocument3 pagesThermo Dynamics Question Banknisar_ulPas encore d'évaluation
- Astrophysics and Mathematics With The Constant V 9.209.Document16 pagesAstrophysics and Mathematics With The Constant V 9.209.Mars PartyPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 9Document8 pagesMath 9Erich GallardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Robot Autonomy I: Robotic Sensors and Introduction To Computer VisionDocument38 pagesPrinciples of Robot Autonomy I: Robotic Sensors and Introduction To Computer VisionratjerryPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Predictive Magic Cards.Document26 pagesDesign of Predictive Magic Cards.aries25th3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Average Internal Rate of Return and Investment Decisions: A New PerspectiveDocument40 pagesAverage Internal Rate of Return and Investment Decisions: A New PerspectiveBharat MaraiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Nurses Leadership Skills Mentoring and Motivating Staff Nurses On Rendering High-Quality Nursing CareDocument23 pagesHead Nurses Leadership Skills Mentoring and Motivating Staff Nurses On Rendering High-Quality Nursing CareDaniel RyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan on Subtracting 2-3 Digit NumbersDocument7 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan on Subtracting 2-3 Digit NumbersNhor Jehan SaydinPas encore d'évaluation
- Xtxtset PDFDocument13 pagesXtxtset PDFhoneygggggPas encore d'évaluation
- 06 CSL38 Manual LDDocument9 pages06 CSL38 Manual LDJoshua Daniel RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Solved For Each of The Following Examples Draw A Representative IsoquantDocument1 pageSolved For Each of The Following Examples Draw A Representative IsoquantM Bilal SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Ex NM&RSDocument63 pagesEx NM&RSMuslim HedayetPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy1 11 - 12 Q1 0603 PF FDDocument68 pagesPhy1 11 - 12 Q1 0603 PF FDhiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Gpelab A Matlab Toolbox For Computing Stationary Solutions and Dynamics of Gross-Pitaevskii Equations (Gpe)Document122 pagesGpelab A Matlab Toolbox For Computing Stationary Solutions and Dynamics of Gross-Pitaevskii Equations (Gpe)Pol MestresPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementDocument7 pagesAssignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementKetz NKPas encore d'évaluation
- CV Dr Mohammad ShahzadDocument5 pagesCV Dr Mohammad ShahzadTarique WaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 DeadlocksDocument14 pagesUnit 4 DeadlocksMairos Kunze BongaPas encore d'évaluation
- MPhil PhD Research MethodsDocument2 pagesMPhil PhD Research MethodsSaifullah KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- 590 3D Geometry::i+3+ 2k) + Sei+2j+ KDocument16 pages590 3D Geometry::i+3+ 2k) + Sei+2j+ KnaboryclesatomPas encore d'évaluation
- Automata and Quantum ComputingDocument34 pagesAutomata and Quantum ComputingJorge LeandroPas encore d'évaluation