Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
New Product Diffusion Model For Class (Bass Model)
Transféré par
sidharth_1984Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
New Product Diffusion Model For Class (Bass Model)
Transféré par
sidharth_1984Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NEW PRODUCT DIFFUSION MODEL: BASS MODEL
Rajdeep Chakraborti
ASSUMPTIONS OF BASS MODEL
The consumer can adopt the new product only once. There are only two types of customers: innovators and imitators Innovators are not influenced by either by the other innovators or imitators
It was also assumed that there are no other categories of customers except innovators and imitators
ASSUMPTIONS OF BASS MODEL
No repeat or replacement purchase has taken place The potential number of buyers remain constant One adopting unit will adopt only once The diffusion process was assumed to be binary in nature
ASSUMPTIONS OF BASS MODEL
Diffusion of innovation is independent of all other innovations Nature of innovation does not change over time WOM communication was assumed to exist within a particular country
BASS MODEL
Let, m= market potential or, market size p, q specify the shape of the curve and also indicate that how fast the adoption of the new product is expected to proceed Bass Model says that:
Likelihood of purchase= p + {q N(t-1)}/m
BASS MODEL
Where, p= probability/rate that an innovator will adopt the new product. It represents the intrinsic tendency of the innovators to adopt the product (coeff. of initial or external influence)
q= imitation coefficient. It represents the interpersonal communication between the innovators and imitators. It is also known as the coeff. of internal influence
BASS MODEL
N(t-1) is the cumulative number of adopters in time t
The numbers of adopters in time t= S(t) = [p + {qN(t-1)}/m]*[m-N(t-1)]
Where, [m-N(t-1)] represents the adopters who left
BASS MODEL
The time when sales will reach its peak: t*= [1/(p+q)]*ln (q/p)
Peak sales is given by: S(t*)= m(p+q)^2/4q
GENERALISED BASS MODEL
Assumptions: a) Price decrease is assumed to affect the number of adoptions in that period only
b)
The action of the firms through its marketing mix affects every one in the same manner, though in Bass model it was assumed that innovators and imitators behave in different manner
GENERALIZED BASS MODEL
S(t) = [p + {qN(t-1)}/m]*[m-N(t-1)]*Z(t) Where, Z(t)= 1+ 1[ P(t)/ P(t)]+ 2[A(t)/A(t)]
1 and 2 represent the coefficients that indicate the percentage increase in the speed of diffusion that results from a 1% decrease in price and advertising respectively
P(t) and A(t) are the price and advertising in time t while P(t) and A(t) are the rate of change of price and advertising in time t respectively
USES OF BASS MODEL
Forecasting the maximum sales in terms of sales and time for the consumer durables. It is assumed that p and q have same value Pricing, advertising and product characteristics have an impact on the diffusion curve. Thus the generalized Bass model can be used to forecast these By predicting the future sales, Bass model helps to plan for the capacity that would be required to meet that demand.
USES OF BASS MODEL
For the international market, Bass model can be used to assess the diffusion curve To plan the timing of the introduction of innovation which is dependent on the diffusion of the primary innovation It can be used to plan the timing of introduction of successive innovations in which the successive innovations can cannibalize the previous innovation
CRITIQUE
The marketing variables which have possible impact on the adoption process have not been considered The model has considered aggregate probability of adoption by the innovators and the imitators and not at the individual level.
Competition has not been considered in Bass model
CRITIQUE
Bass model assumed that diffusion of innovation is independent of any other innovations, but it is not true always. As for example; Blue Ray discs and the Blue Ray software are dependent on each other
Bass assumed that the nature of innovation remains stationary over time. But successive innovation cannibalizes the old innovation. Ex: Microsoft Windows operating system
CRITIQUE
Bass has not considered the fact that the product and market characteristics do influence the diffusion. This limitation of Bass model was later rectified by considering p and q as the functions of product and market characteristics.
CRITIQUE
It was found that WOM does not remain restricted only within a country, it may flow across borders also. There can be other options available to the customers apart from innovators or imitators. These options like knowledge, awareness, action and indifference to the product, were not considered
REFERENCE
Bass Frank M.; A New Product Growth for Model Consumer Durables; Management Science; Vol 50, No-12, Dec 2004, p 1825-1832
New-product diffusion models; edt by- Mahajan Vijay, Muller Eitan and Wind Yoram; Kluwer Academic Publishers, Boston; p 99-122
BOTTOM LINE AND QUOTATION
In Forecasting the Time of Peak It is Helpful to Know that a Peak Exists - Frank Bass
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Blue Ocean Strategy Concept - Overview & Analysis: Achieve success through innovation and make the competition irrelevantD'EverandBlue Ocean Strategy Concept - Overview & Analysis: Achieve success through innovation and make the competition irrelevantÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (9)
- Product Life CycleDocument23 pagesProduct Life CycleDrArjun GawasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Competitive Power of the Product Lifecycle: Revolutionise the way you sell your productsD'EverandThe Competitive Power of the Product Lifecycle: Revolutionise the way you sell your productsPas encore d'évaluation
- Product DevelopmentDocument14 pagesProduct DevelopmentChan LiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pricing Types: Signalling Market Positioning IntentD'EverandPricing Types: Signalling Market Positioning IntentPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuesday, October 30, 2007 Services MarketingDocument9 pagesTuesday, October 30, 2007 Services Marketingssatish909Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Second (Review and Analysis of Markrides and Geroski's Book)D'EverandFast Second (Review and Analysis of Markrides and Geroski's Book)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fourt-Woodlock Equation: ReferencesDocument11 pagesFourt-Woodlock Equation: ReferencesSasho NefovskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Enhancement in Voluntary Carbon Markets: Opening up for MainstreamD'EverandQuality Enhancement in Voluntary Carbon Markets: Opening up for MainstreamPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion Confusion - The Rising Role of The Replacement CycleDocument17 pagesDiffusion Confusion - The Rising Role of The Replacement Cyclepjs15Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Development Prospect of Cleaning Robot in Chinese Market in The Next Ten YearsDocument6 pagesThe Development Prospect of Cleaning Robot in Chinese Market in The Next Ten Yearstoto eloprePas encore d'évaluation
- Design and ForecastingDocument45 pagesDesign and Forecastingamrinder_sohalPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Product Life Cycle? Stages and Examples: Get Coca-Cola Company ReportDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Product Life Cycle? Stages and Examples: Get Coca-Cola Company ReportVishal SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 PsDocument3 pages4 PskillerinstinctajayPas encore d'évaluation
- Bass ModelDocument5 pagesBass ModelManish PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- GRP 8 PPT PresentationDocument21 pagesGRP 8 PPT PresentationTinotenda ChivesePas encore d'évaluation
- Product Life CycleDocument4 pagesProduct Life CyclekqsyedPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Life Cycle Accounting and Target CostingDocument36 pagesProduct Life Cycle Accounting and Target CostingWilrencePas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3: Innovations Within Firms:: Meaning and DefinitionDocument26 pagesUnit 3: Innovations Within Firms:: Meaning and DefinitionkrutibhattPas encore d'évaluation
- ES 010 - Lecture 04Document58 pagesES 010 - Lecture 04Ruel Rick V. RanayPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul BDD 40303Document65 pagesModul BDD 40303ZulkhairiPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Life Cycle:: Group MembersDocument18 pagesProduct Life Cycle:: Group MembersimykoPas encore d'évaluation
- Look Page 11 and 12 - Virtual Factory Concept - PomDocument14 pagesLook Page 11 and 12 - Virtual Factory Concept - PomAbhay GroverPas encore d'évaluation
- TM5120 Case Study - 02Document6 pagesTM5120 Case Study - 02MethmiePas encore d'évaluation
- The BASS ModelDocument3 pagesThe BASS ModelCarla GonçalvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion OF Innovation and Openion Leaderhip Family Decision MakingDocument38 pagesDiffusion OF Innovation and Openion Leaderhip Family Decision MakingDivyansh Singh baghelPas encore d'évaluation
- MB0030 - Marketing ManagementDocument15 pagesMB0030 - Marketing ManagementKanchan WadhwaPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovation Diffusion: How Do Technologies Evolve Over Time?Document4 pagesInnovation Diffusion: How Do Technologies Evolve Over Time?Umberto Curti da PortoPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics of Advertising 2Document19 pagesEconomics of Advertising 2Aksel DahlPas encore d'évaluation
- Economics of AdvertisingDocument14 pagesEconomics of AdvertisingAksel DahlPas encore d'évaluation
- Demand ForecastingDocument13 pagesDemand ForecastingRavneet KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 - Strategor 7th-2Document37 pagesChapter 4 - Strategor 7th-2Luca DesimoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11.Forecasting-AnalysisDocument7 pagesChapter 11.Forecasting-AnalysisMarysol AlcorizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Disruptive Innovation in Need of Better TheoryDocument7 pagesDisruptive Innovation in Need of Better TheoryokuytPas encore d'évaluation
- Illustrating The Competitive Dynamics of An Industry: The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods Industry Case StudyDocument53 pagesIllustrating The Competitive Dynamics of An Industry: The Fast-Moving Consumer Goods Industry Case StudyjjgalvisPas encore d'évaluation
- C. Six Major Types of Business Case: BrainteaserDocument11 pagesC. Six Major Types of Business Case: Brainteaserrahul281081Pas encore d'évaluation
- Innovation NewDocument5 pagesInnovation NewSaad AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- NPDpaper BookChapter JDOwensDocument30 pagesNPDpaper BookChapter JDOwensAshlesha DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategy: Porter 5 Forces + Example UberDocument31 pagesStrategy: Porter 5 Forces + Example Uberratty1971Pas encore d'évaluation
- MktgTool BassDocument4 pagesMktgTool BassAnand SarafPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Two Design of The Operations/production Systems 2.1. Product-Service Design and DevelopmentDocument46 pagesChapter Two Design of The Operations/production Systems 2.1. Product-Service Design and DevelopmentThomasGetyePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1-2: Pyndick Resume: Yunastiti PurwaningsihDocument45 pagesChapter 1-2: Pyndick Resume: Yunastiti PurwaningsihHanif Afif NaufalPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Marketing and DevelopmentDocument7 pagesUnderstanding Marketing and DevelopmentLintangkerty SuryanagariPas encore d'évaluation
- The Product Life Cycle ConceptDocument29 pagesThe Product Life Cycle ConceptAdam StevensonPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Review On Lateral MarketingDocument12 pagesBook Review On Lateral Marketingabub4u100% (2)
- Unit 1 - 2 MarksDocument9 pagesUnit 1 - 2 MarksshruthicivilPas encore d'évaluation
- New Product Development: The ProcessDocument6 pagesNew Product Development: The ProcessFathmath XaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 8 Consumer Behvior NoteDocument17 pagesModule 8 Consumer Behvior NoteAnirban MandalPas encore d'évaluation
- What'S Going On in The New Product Process? The Concept Evaluation SystemDocument3 pagesWhat'S Going On in The New Product Process? The Concept Evaluation SystemHector MalloPas encore d'évaluation
- Predicting The Demand For New Products and Services: Mohsen Hamoudia International Institute of ForecastersDocument27 pagesPredicting The Demand For New Products and Services: Mohsen Hamoudia International Institute of ForecastersrizileePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document8 pagesChapter 8Shenne Minglana50% (4)
- Subject: New Product Development Researc HDocument4 pagesSubject: New Product Development Researc Habhisheksinha9Pas encore d'évaluation
- BUS 5112 - Marketing Management-Written Assignment Unit 4Document10 pagesBUS 5112 - Marketing Management-Written Assignment Unit 4YoYoPas encore d'évaluation
- The New Blue Ocean Strategy CasebookDocument9 pagesThe New Blue Ocean Strategy CasebookDevendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2Document30 pagesLecture 2Daniel MengistuPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Competition: Tell MeDocument17 pagesTypes of Competition: Tell MeSamah MaaroufPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Life Cycle and Other Theories of International BusinessDocument23 pagesProduct Life Cycle and Other Theories of International BusinessSandip Timsina100% (1)
- MB0030 Marketing Management CompleteDocument18 pagesMB0030 Marketing Management Completepranay srivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product ManagementDocument108 pagesProduct ManagementEvan Sen100% (2)
- Private Labels and New Product Development: # Springer Science + Business Media, LLC 2009Document18 pagesPrivate Labels and New Product Development: # Springer Science + Business Media, LLC 2009Srinath AkulaPas encore d'évaluation
- AVEVA World Focus Oil Gas 2015 PDFDocument52 pagesAVEVA World Focus Oil Gas 2015 PDFsidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Sustainability Report Statoil PDFDocument51 pages2015 Sustainability Report Statoil PDFsidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pricing For ClassDocument35 pagesPricing For Classsidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
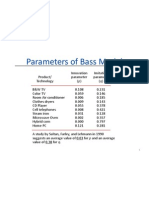
- Parameters of Bass ModelDocument1 pageParameters of Bass Modelsaikiran38Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing MetricsDocument32 pagesMarketing Metricssidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research PaperDocument10 pagesResearch Papersidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- On Air DeccanDocument23 pagesOn Air Deccansidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- McCain AnnounementDocument5 pagesMcCain Announementsidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final SIP Report Sagar ShahDocument126 pagesFinal SIP Report Sagar Shahsidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing MetricsDocument32 pagesMarketing Metricssidharth_1984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jet Vs Kingfisher (With SWOT Analysis)Document14 pagesJet Vs Kingfisher (With SWOT Analysis)debayanrPas encore d'évaluation
- Durum Sorulari PDFDocument18 pagesDurum Sorulari PDFGökçen Aslan AydemirPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 S Implication-InterferenceDocument50 pages11 S Implication-InterferenceLe Minh ThanhPas encore d'évaluation
- PRE572 OgbeideDocument22 pagesPRE572 OgbeideChukwudi DesmondPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Site Selection Criteria and FactorsDocument4 pages2.1 Site Selection Criteria and Factorseric swaPas encore d'évaluation
- LNG Industry March 2012Document100 pagesLNG Industry March 2012erojaszaPas encore d'évaluation
- Feasibility StudyDocument38 pagesFeasibility StudyMerceditas Plameras0% (1)
- Engineering Economy 1stDocument1 pageEngineering Economy 1stMatthew DavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundations of Business 6th Edition Pride Test BankDocument35 pagesFoundations of Business 6th Edition Pride Test Bankdanielwilkinsonkzemqgtxda100% (29)
- Amway MarkettingDocument13 pagesAmway MarkettingRoopesh AggarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Legend ReportsDocument100 pagesList of Legend Reportsapi-137303031Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ethics Lost in False AdvertisingDocument15 pagesEthics Lost in False Advertisingapi-253211089Pas encore d'évaluation
- Examiners' Commentaries 2016: EC1002 Introduction To EconomicsDocument48 pagesExaminers' Commentaries 2016: EC1002 Introduction To EconomicskashmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Argus Mccloskeys Coal Price Index ReportDocument2 pagesArgus Mccloskeys Coal Price Index Reportsahbana krisna ramadanPas encore d'évaluation
- SAPMDocument10 pagesSAPMadisontakke_31792263Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of CapitalDocument63 pagesCost of CapitalTejaswini VashisthaPas encore d'évaluation
- PHT and KooistraDocument4 pagesPHT and KooistraNilesh PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Paper PDFDocument17 pagesOnline Paper PDFManisha TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Adam Smith and The Invisible HandDocument9 pagesAdam Smith and The Invisible Handdream4poojaPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 2 ButanGas Serbia Goran Djurdjevic Serban PopaDocument13 pagesSession 2 ButanGas Serbia Goran Djurdjevic Serban Popatrinhvonga7289Pas encore d'évaluation
- PT. Pertamina Retail: PO Service Purchase Order (PO)Document2 pagesPT. Pertamina Retail: PO Service Purchase Order (PO)Firman PrimahardhikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade Name: - Date: - GradeDocument2 pagesGrade Name: - Date: - GrademasPas encore d'évaluation
- One-Pagers: High YieldDocument212 pagesOne-Pagers: High Yieldapi-161028199Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ceekay Daikin LTDDocument2 pagesCeekay Daikin LTDanon-783264Pas encore d'évaluation
- Operation MGT Indivitual AssignmentDocument10 pagesOperation MGT Indivitual AssignmentEyu Des100% (1)
- Personal Selling Exam 3 Study GuideDocument13 pagesPersonal Selling Exam 3 Study GuideAnonymous a0WvrRAQJVPas encore d'évaluation
- ValuationDocument227 pagesValuationmohammad sadegh movahedifarPas encore d'évaluation
- MOU - Devesh JainDocument4 pagesMOU - Devesh Jainboops007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Warren Buffett 1985Document7 pagesWarren Buffett 1985anil1820Pas encore d'évaluation
- IDX Statistic 2021Q2Document216 pagesIDX Statistic 2021Q2LisaPas encore d'évaluation