Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
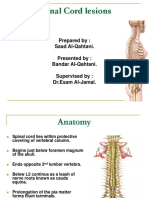
Human Nervous-System
Transféré par
hwzeeeTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Human Nervous-System
Transféré par
hwzeeeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Nervous System
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
1. Central Nervous System (CNS): brain and spinal cord
Central vs. Peripheral Nervous System
2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): cranial nerves, spinal nerves and ganglia
* (Ganglion=group of neuron cell bodies located outside CNS)
Sensory division vs. Motor division
1. Sensory Division: receives information FROM body and transmits it TO the CNS for processing
a) Somatic Sensory component receives sensory information from skin, joints, muscle, special senses b) Visceral Sensory component receives sensory info from blood vessels and viscera
2. Motor Division: transmits info FROM the CNS TO muscles and glands
a. Somatic motor component: innervates skeletal muscle b. Autonomic motor (Autonomic Nervous System): innervates smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and glands of viscera (organs)
NERVOUS TISSUE CELLS
A. Neurons: respond to stimuli and conduct nerve impulses
NERVOUS TISSUE CELLS
B. Glial Cells: support and protect neurons (maintenance)
NEURON COMPOSITION (p 104)
A. Cell Body: B. Nucleus:
C. Dendrites:
D. Axon: E. Synapse:
NEURON CLASSIFICATION
1. Sensory (Afferent) Neuron: brings information TO the CNS
2. Motor (Efferent) Neuron: takes information FROM CNS to other parts of the body, cell body located in CNS
3. Interneuron (Association Neurons): helps coordinate and integrate info between sensory and motor neurons, cell body located in CNS
GLIAL CELLS - PNS
A. Satellite Cells: surround neuron cell bodies in spinal ganglia * (Ganglion=group of neuron cell bodies located outside CNS) B. Schwann cells: myelinate axons in PNS
Glial Cells - CNS
C. Astrocytes: regulate transfer of materials from blood to the brain - help the workings of "blood -brain barrier" D. Oligodendrocytes: myelinate axons in CNS E. Microglia: phagocytize damaged neurons F. Ependymal Cells: line central canal and ventricles help circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
MYELINATION OF AXONS
wrapping an axon with myelin
The Brain
4 Regions
Cerebrum
R & L Hemispheres
Diencephalon Brain Stem Cerebellum
Brain Cerebrum
Largest Region Gyri (twisters) & Sulcus (grooves) Fissures (deep grooves)
Longitudinal (hemispheres) Divide Lobes
Brain Cerebrum (lobes)
Parietal Lobe
Somatic sensory area homunculus
Brain Cerebrum (lobes)
Occipital Lobe
Visual area
Brain Cerebrum (lobes)
Temporal Lobe
Olfactory
Deep inside
Brain Cerebrum (lobes)
Frontal Lobe
Primary Motor Area Speech Language
Cerebrum
Cerebral Gray Matter (Cortex)
superficial
Cerebral White Matter
deeper
connects hemispheres
Corpus Callosum
Diencephalon (interbrain)
Sits atop brain stem Enclosed by cerebrum Structures
Thalamus Hypothalamus Epithalamus
Diencephalon
Thalamus
Relay station from spinal cord Crude impulse
Pleasant vs. Unpleasant
Diencephalon
Hypothalmus (under the thalmus)
ANS (Emotional Visceral Brain) Body Temp, H2O balance, Metabolism Appetites (thirst, hunger) Pleasure & Pain
Diencephalon
Epithalamus
Pineal body (endocrine system) Choroid plexus (cerebrospinal fluid)
Brain Stem
About size of thumb Areas
Midbrain
Convey impulses Controls breathing Heart rate, BP, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc.
Pons
Medulla Oblongata
Cerebellum
Convoluted surface Precise timing of Skeletal muscles Balance Auto-Pilot
Protection of Brain
Meninges
dura mater (tough mother) arachnoid mater pia mater (gentle mother)
Eliminate waste
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Blood-Brain Barrier
Least-permeable membrane in body
Spinal Cord
Aprox. 17 in long Continuation of Brain Stem Ends Below ribs
Spinal Cord
Gray Matter
Posterior Horns (dorsal) Anterior Horns (ventral) Central Canal
Vertebrae Dura mater Arachnoid Pia mater
CSF
Protection
Spinal Cord
Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccygeal
Spinal Cord - Cervical
8 Cervical Nerves C1C8 Diaphragm, Shoulders, Neck Damage may result in:
Respiratory Paralysis
Spinal Cord - Thoracic
T1-T12 Intercostal
Spinal Cord - Lumbar
L1-L5 Lower abdomen, buttocks, anterior & medial thigh, hip muscles, skin of thigh Damage:
Inability to flex hip Loss of cutaneous sensation Inability to adduct thigh
Spinal Cord Sacral & Coccygeal
S1-S5 + Coccygeal Nerve Lateral & posterior leg/foot, gluteus, lower trunk Damage:
Inability to extend hip Inability to flex knee
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Classification and Comparison of Receptor TypesDocument1 pageClassification and Comparison of Receptor TypesRaymart RaymundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 102 Handout Muscular SysDocument3 pagesBio 102 Handout Muscular Sysgjsup100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology ReviewerDocument10 pagesAnatomy and Physiology ReviewerMae Christelle FigueroaPas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument29 pagesEndocrine System Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsAlyssum Marie50% (2)
- Bones of The SkullDocument3 pagesBones of The SkullJethro Floyd QuintoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction in Human Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument35 pagesIntroduction in Human Anatomy and Physiologyraul nino MoranPas encore d'évaluation
- Axial Skeleton PDFDocument48 pagesAxial Skeleton PDFSharadambigai SamarasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Nursing Mnemonics TipsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Nursing Mnemonics TipsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Study GuideDocument4 pagesUnit 1 Study GuideNic Alcala100% (1)
- Major Arteries and Their BranchesDocument6 pagesMajor Arteries and Their BranchesPriya Farooq100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricDocument23 pagesChapter 4 Tissue - The Living FabricMariaPas encore d'évaluation
- AnaPhy Lesson 6 Muscular SYstemDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lesson 6 Muscular SYstemLM KishimotoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy 2 MnemonicsDocument29 pagesAnatomy 2 MnemonicsOmenaalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Document36 pagesMusculoskeletal Anatomy and Physiology 5Dennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMPas encore d'évaluation
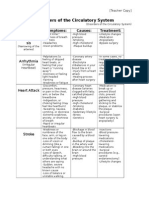
- Disorders of The Circulatory System Table-AnswersDocument2 pagesDisorders of The Circulatory System Table-Answersapi-281108263Pas encore d'évaluation
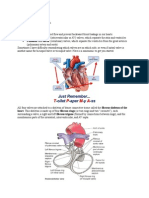
- Cardiovascular Anatomy Physiology PDFDocument22 pagesCardiovascular Anatomy Physiology PDFMahesh ChendakePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Anatomy SCDocument92 pages1 Anatomy SCAmber Ian Bouie Divina-DayaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord and Spinal NervesDocument39 pagesSpinal Cord and Spinal NervesBenner BagsterPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System: More Than Just The HeartDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System: More Than Just The HearteliseudesafatePas encore d'évaluation
- A&P1 Final Exam Study GuideDocument7 pagesA&P1 Final Exam Study GuideRhett ClarkPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Structures and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesBrain Structures and Their FunctionsVasudha RohatgiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesChapter 6 Anatomy and PhysiologyDiah Mariano0% (1)
- Anatomy 2 MnemonicsDocument17 pagesAnatomy 2 MnemonicsRosalie Catalan EslabraPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 1 Study Guide: Exam. These Scantrons Are Sold in The Science & Math Lab On The First FloorDocument3 pagesExam 1 Study Guide: Exam. These Scantrons Are Sold in The Science & Math Lab On The First Floorfishycocoa1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide QuestionsDocument4 pagesStudy Guide QuestionszaidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 2 Memorization Hacks in Nursing & Learning About Meal PlanDocument69 pagesSession 2 Memorization Hacks in Nursing & Learning About Meal Planataraxialli100% (1)
- Exam A-3Document11 pagesExam A-3yapues87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument19 pagesRespiratory System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBDPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvis and Perineum - Anatomy, Vessels, Nerves - KenhubDocument11 pagesPelvis and Perineum - Anatomy, Vessels, Nerves - KenhubDhika100% (1)
- Skeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)Document10 pagesSkeletal System Skeletal Anatomy: (Typical)anon_660872041Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anato Head and Neck MnemonicsDocument10 pagesAnato Head and Neck MnemonicsLaura Lopez RocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Cord Lesions: Jia Yan-Jie M.D PH.DDocument170 pagesSpinal Cord Lesions: Jia Yan-Jie M.D PH.Dapi-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument2 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyKamille Jeane Stice CavalidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muscles ReviewDocument32 pagesMuscles ReviewCorine RepatoPas encore d'évaluation
- U6C6 - Carty Soriano - Heart ValvesDocument6 pagesU6C6 - Carty Soriano - Heart ValvesXio LinaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Document4 pagesSheep Brain Observation LAB 2015Leo MatsuokaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.the Nervous SystemDocument31 pages6.the Nervous SystemElaine Victoria ElizanPas encore d'évaluation
- Integumentary System: Functions of SkinDocument7 pagesIntegumentary System: Functions of SkinSoniyaJI84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Physiology: General Physiology The Cell HomeostasisAnanta Subedi100% (1)
- Chapter 15 Brain and Cranial NervesDocument5 pagesChapter 15 Brain and Cranial NervesSuperjunior8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture - Midterm (Labelling)Document15 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture - Midterm (Labelling)KRISTINE ZAINAB PUENTE100% (1)
- Anatomy ExamDocument9 pagesAnatomy ExamFoo FuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroscience - 4.3 - Examination of Cerebellar Systems and Meninges (KSD)Document4 pagesNeuroscience - 4.3 - Examination of Cerebellar Systems and Meninges (KSD)Kevin C. AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Between The Erythrocytes and PlasmaDocument5 pagesBetween The Erythrocytes and Plasmajonette carataoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Document13 pagesLecture Note Human Anatomy and Fisiologi (Skeletal System)Muhammad FaizPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemAltaf Hussain Khan50% (2)
- Muscles of The ThoraxDocument4 pagesMuscles of The ThoraxKieth Roland PalosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendicular Skeleton: Upper Lower Limbs GirdlesDocument37 pagesAppendicular Skeleton: Upper Lower Limbs GirdlesAprilSensengPas encore d'évaluation
- Nervous System - GeneralDocument84 pagesNervous System - GeneralAman SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Level 2 Stroke Awareness Award: SFC QCF Unit SCM 201Document57 pagesLevel 2 Stroke Awareness Award: SFC QCF Unit SCM 201Marissa Qurniati100% (1)
- 7-Nervous SystemDocument69 pages7-Nervous SystemCarl Vincent VingnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Physiology NOTESDocument3 pagesRespiratory Physiology NOTESJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (1)
- ABC Dictionary of Urinary SystemDocument26 pagesABC Dictionary of Urinary Systemaby_romero9750% (2)
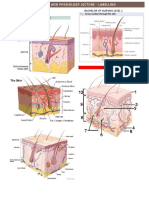
- The Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. RickDocument17 pagesThe Integumentary System - The Dermis: T. Rickapi-464344582Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy MnemonicsDocument51 pagesAnatomy MnemonicsDrKhawarfarooq SundhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Pathobiology and Management of Paget’s Disease of BoneD'EverandAdvances in Pathobiology and Management of Paget’s Disease of BoneSakamuri V. ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Emotional Intelligence, Emotional Labor, and Job Satisfaction Among PhysiciansDocument12 pagesEmotional Intelligence, Emotional Labor, and Job Satisfaction Among PhysicianshwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Emotional Intelligence and Patient-Centred CareDocument7 pagesEmotional Intelligence and Patient-Centred CarehwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Impact of Gender and Parenthood On Physician CareersDocument10 pagesImpact of Gender and Parenthood On Physician CareershwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Doctor's Perception of Doctor-Patient RelationshipsDocument10 pagesDoctor's Perception of Doctor-Patient RelationshipshwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- The Social Gradient in Doctor-PatientDocument14 pagesThe Social Gradient in Doctor-PatienthwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Doctor-Patient Communication in The E-Health EraDocument7 pagesDoctor-Patient Communication in The E-Health ErahwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Emotional Intelligence Skills For Maintaining Social Networks in Healthcare OrganizationsDocument9 pagesEmotional Intelligence Skills For Maintaining Social Networks in Healthcare OrganizationshwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Gender and Emotional IntelligenceDocument7 pagesGender and Emotional IntelligencehwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Values of Family Physicians and Practice OutcomesDocument5 pagesValues of Family Physicians and Practice OutcomeshwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Depressive Disorders Practice ParameterDocument24 pagesDepressive Disorders Practice ParameterjorgePas encore d'évaluation
- Bowen TheoryDocument10 pagesBowen Theorynorociel8132Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anxiety During Public SpeakingDocument11 pagesAnxiety During Public SpeakinghwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Limbic System Structures B2oBDocument25 pagesLimbic System Structures B2oBhwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Academic Self-Regulation Questionnaire (SRQ-A)Document5 pagesAcademic Self-Regulation Questionnaire (SRQ-A)hwzeee100% (1)
- Phineous GageDocument16 pagesPhineous GagehwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- DIY Sculpting ToolsDocument8 pagesDIY Sculpting Toolshwzeee100% (2)
- Lecture03 BrainAnatomyDocument12 pagesLecture03 BrainAnatomynyamka_89893864Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Brain!: An Interactive Presentation By: Jackie Fincher ED 205-Section 15Document15 pagesThe Brain!: An Interactive Presentation By: Jackie Fincher ED 205-Section 15hwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- Intro CBT PDFDocument12 pagesIntro CBT PDFFRosariopsiPas encore d'évaluation
- 0 The Mega BrainDocument388 pages0 The Mega Brainhwzeee100% (14)
- Brain Lesson Parts and FunctionDocument7 pagesBrain Lesson Parts and FunctionhwzeeePas encore d'évaluation
- 1000 Cuvinte EnglezaDocument10 pages1000 Cuvinte EnglezaNotar SorinPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 FootcareDocument23 pagesGroup 4 FootcareAngelo AbiganiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Energetic TherapyDocument19 pagesBio Energetic TherapyVishnu Moorthy Raja Singam100% (2)
- NYSORA Thoracic Paravertebral BlockDocument16 pagesNYSORA Thoracic Paravertebral BlockYee Yeow100% (1)
- Spinal Cord Lesions 1Document43 pagesSpinal Cord Lesions 1Worthless Boys100% (4)
- Workk Safely CompileDocument167 pagesWorkk Safely CompileBarbara AlvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Outline Fall 2007Document30 pagesTorts Outline Fall 2007crlstinaaa100% (18)
- Acute Nerve InjuryDocument28 pagesAcute Nerve InjuryEdgar RobledoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan #1 Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Independent Short TermDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan #1 Cues Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term: Independent: Independent Short TermAlmer OstreaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Wound Is A Break in The Continuity of A Tissue of The BodyDocument6 pagesA Wound Is A Break in The Continuity of A Tissue of The BodyChristine Katherine LibuitPas encore d'évaluation
- Nose Landing Gear OhDocument171 pagesNose Landing Gear OhChristian DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Spinal Mobility Flow Motion FitDocument14 pagesSpinal Mobility Flow Motion Fitpol san gregorioPas encore d'évaluation
- Hip Joint: 5 December 2016 Anatomy Lecture By: DR Anita RaniDocument38 pagesHip Joint: 5 December 2016 Anatomy Lecture By: DR Anita RaniDr'Dinesh MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Spanish SquatDocument7 pagesSpanish Squatapi-551757456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Banana Fish FinalDocument4 pagesBanana Fish Finallsweener123Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 People You Meet in HeavenDocument3 pages5 People You Meet in HeavenNik Razin Azim IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- SCAT3 PocketDocument2 pagesSCAT3 PocketProfPT44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Physiotherapy Assessment Aidaaaaa 2Document15 pagesPediatric Physiotherapy Assessment Aidaaaaa 2Khaled M.A. AlqedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6-Repair & Healing - 382Document33 pagesLecture 6-Repair & Healing - 382MirghaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Safe Lifting of Non-Cargo LoadsDocument52 pagesSafe Lifting of Non-Cargo Loadsaveselov88100% (1)
- Ginn Hale ShyDocument32 pagesGinn Hale Shymnem360Pas encore d'évaluation
- Krok 1 Anatomy 10Document1 pageKrok 1 Anatomy 10Sandeep KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Aviation Ins (Fahamkan Je Tau)Document4 pagesIntro To Aviation Ins (Fahamkan Je Tau)Anisah NiesPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Meniscus InjuryDocument6 pagesKnee Meniscus InjuryHazel Aikulola GriffithPas encore d'évaluation
- TM 9-2350-247-10 M548a1 NSN 2350-01-096-9356 and M548a3 NSN 2350-01-369-6081Document640 pagesTM 9-2350-247-10 M548a1 NSN 2350-01-096-9356 and M548a3 NSN 2350-01-369-6081AdvocatePas encore d'évaluation
- Krok 1 - 2014 (Anatomy)Document20 pagesKrok 1 - 2014 (Anatomy)Shameem UabackerPas encore d'évaluation
- John Bollino v. Baltimore & Ohio Railroad Company, 856 F.2d 186, 4th Cir. (1988)Document5 pagesJohn Bollino v. Baltimore & Ohio Railroad Company, 856 F.2d 186, 4th Cir. (1988)Scribd Government DocsPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Risk For FallsDocument5 pagesNCP - Risk For FallsMae CeaesarPas encore d'évaluation
- Document Title TP Document No. Revision Project Title Contract Number Contractor Doc No. Con. Doc. RevisionDocument15 pagesDocument Title TP Document No. Revision Project Title Contract Number Contractor Doc No. Con. Doc. RevisionComsip400Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biomechanics of PitchingDocument49 pagesBiomechanics of PitchingSamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomechanics of TennisDocument7 pagesBiomechanics of TennisrainbrPas encore d'évaluation