Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Weather and Atmosphere Test Review
Transféré par
api-169639475Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Weather and Atmosphere Test Review
Transféré par
api-169639475Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Review Atmosphere & Weather
6-4.1 Atmospheric Layers
6-4.2 Water Cycle
6-4.3 Clouds
1. Name the atmospheric layers from Earths surface outward & name an object for each layer. troposphere(weather/planes) stratosphere(ozone) mesosphere(meteors) thermosphere( 18000C ionosphere(electrcally charged particle-ions) exosphere(space shuttles/satellites) 2. What are the two most common gases found throughout all the layers? nitrogen & oxygen 3. Name the form of oxygen found in the stratosphere. ozone 4. What are the important gases for weather conditions that are found in the troposphere? water vapor & carbon dioxide 5. What do we call all of the gases like carbon dioxide, argon and other gases that make up 1% of the atmospheric gases? trace gases
6. What separates the atmospheric layers?
differences in temperatures
7. As altitude __________, temperature ____________ in the troposphere. increases decreases
8. The ______________ is cold except in the upper region where the ozone is located. stratosphere 9. The ______________ is the coldest layer.
mesophere
10. The air is very this in the _____________________ and it is very ______. thin hot
11. The cold regions of outer space extend from the ____________. exosphere 12. ____ ______ is the force exerted by the gases pushing on an object. air pressure
13. Air pressure is greatest in the _________________.
troposphere
14. Air pressure ______________ through the layers farther out from the surface as Earths pull of ______________ decreases. decreases gravity
15. Pressure __________________ as you move from the troposphere to the exosphere.
decreases 16. ________ is always moving between the troposphere and the surface of Earth.
water
17. Condensation is forming ________. Clouds 18. The forms of precipitation are __________,______,______,____,&_______. rain, snow, freezing rain, sleet, & hail 19. Temperature variations within _______ and Earth allows for forms of precipitation. clouds
20. The two ways water enters the atmosphere are _______&_______.
evaporation
transpiration
21. ____________ is plants releasing water vapor. transpiration 22. Water vapor changing to water droplets is called __________________. condensation 23. _________ is formed when water vapor condenses directly onto surfaces. dew
24. ________ is formed when water vapor changes from gas to ice crystals.
frost 25. _____________ is when precipitation that falls on land surfacesattempts to move back toward sea level as surface-water flow or groundwater flow.
run-off
26. Water will remain on the surface when the surface is not _______ or the precipitation is falling too fast to sink into the ground. porous
27. Water will sink into the ground when the ground surface is porous and there is lots of ________ in the soil to hold the water. space 28. Clouds are classified into ________ major groups. three 29. _____________ clouds form at medium or low elevations and are puffy with flat bottoms. cumulus 30. When cumulus clouds are white they signal_______ weather, but when they are darker, they may signal _______ or _________. fair rain thunderstorms
31. ___________ clouds form at medium or low elevations and are spread out layer upon layer. stratus 32. As stratus clouds ________, __________ usually occurs over that area.
thicken
precipitation
33. _________ means rain. nimbus
34. Name two cloud with the prefix nimbus
cumulonimbus
nimbostratus
35. A _________ cloud is also called a thunderhead, is oftne part of thunderstorm conditions that may accompany a _____ ______. cumulonimbus cold front
36. Alto means _______ level.
medium 37. Name two clouds with the prefix alto. altocumulus altostratus
38. Clouds that form when condensation occurs near the ground are called _____. fog 39. ________ ________ are huge bodies of air that form over water or land in tropical or polar regions air masses 40. _______ and _______ within the air masses are important in air masses. temperature humidity
6-4.4 Air Masses,pressure sys&fronts
6-4.5 Tools
6-4.5 Weather data
41. As air masses move and collide with each other, ________ form at the boundaries between them. fronts 42.Name the four types of fronts. warm cold stationary occluded 43.When a warm air mass rides over a cold air mass, long periods of _____ and warmer temperatures may occur. precipitation 44. When a cold air mass slides under a warm air mass, _________and sometimes __________ and cooler temperatures may occur. thunderstorms tornadoes 45. When neither a cold air mass nor a warm air mass moves at a frontal boundary, the result is a __________ _______ and may produce long periods of ____________ stationary front precipitation 46. When a cold air mass pushes into a warm air mass that is behind a cool air mass the warm air mass is pushed up above the cooler air mass. An_________ _________ occurs and a long period of _______ are produced. occluded front precipitation 47. Warm air _____ and cold air _______ combined with the spinning of Earth causes the air to spin forming high & low _____ regions. rising sinking pressure
48. _______ pressure systems usually signal fair weather with winds moving clockwise. high 49. ______ pressure systems usually signal stormy weather with winds moving counter clockwise.
low
50. When pressure differences occur, severe weather conditions called ______. storms 51. ___________ can form in cumulonimbus clouds; usually along a cold front but can form within an air mass. thunderstorm 52. ______ is a rapidly moving funnel-shaped cloud that extends down from a storm cloud.
tornado
53. _______ is a low pressure tropical storm that forms over warm ocean water.The lower the pressure in the center of this storm, the faster the winds blow towards the center of the storm.
hurricane
54. ________ is a condition of Earths atmosphere at any time.
weather
55. Fair weather, showers, light rain, humid conditions, clear skies with cold conditions, days of precipitation, or others that involve storms are all weather _____________ conditions 56. ________ A tool used to measure wind speed.
anemometer 57. ___________ or _____________a tool used to measure wind direction.
wind vane
wind sock
58. Wind direction is described by the direction from which the wind is _______. blowing 59. _________ is a tool used to measure air temperature. thermometer 60. __________ A two- thermometer instrument also referred to as a wet-dry bulb used to measure relative humidity. sling psychrometer
61. Temperature readings on a sling psychrometer are converted using a ________ ________ table. relative humidity 62. __________ is a tool used to measure air pressure. barometer 63. ________ is a tool used to measure the amount of precipitation. rain gauge
64. ________ ________ and patterns can be predicted based on weather data collected from various sources.
weather conditions 65. ________________ observe and measure basic weather conditions at national weather data collection sites. meteorologists 66. In order to make weather predictions, the __________ should be collected on a regular basis over a period of time.
data
67. Patterns in weather conditions can be developed from the __________ of data. analysis
68. Meteorologists can predict the path of a hurricane by using data plotted over time on a ______________ tracking map. hurricane 69. __________ are used on weather maps to indicate high and low pressure systems. isobars 70. _________ are used on a weather map to indicate temperature ranges. isotherms 71. ________ ________ from specific locations provide information that can be used to predict weather patterns. station models 72. The information on a station model can include_________,________,______ and______, _______or _________.
cloud cover temperature barometric pressure
wind direction
speed precipitation,
73. Satellite images are used to see _____ ________ and _______. cloud patterns movements
74. Radar images can be used to detect _____ _______,________, ________ _________, ____________ and _________as well as the potential for ___________ weather. cloud cover 6-4.7 rainfall storm location intensity movement severe
Sun heating Land & Water 6-4.8 Convection
6-4.9 Global winds
75. The source for heating the Earth and circulating Earths atmosphere comes from the ______________. Sun 76. Some of the Suns energy coming through Earths atmosphere is ___________ or ____________ by gases and/or clouds. reflected or absorbed 77. The _____ heats up and releases its heat fairly quickly, but the ______ needs to absorb lots of solar energy to warm up. land water 78. The ________ on Earth helps to regulate the temperature range of Earths atmosphere. water
79. ____________________ is the process of heat from the Sun moving back into the troposphere where it cannot get through the atmosphere and is trapped. greenhouse effect 80. Warm air near the Earths surface rises and then cools and drops, this creats a _________ ________ in the atmosphere. convection current 81. The three atmospheric convection areas are_________ , _______, & ________. tropical temperature polar
82. Convection happens on a global scale in the atmosphere and causes ______ _________. global winds 83. Global winds move _______ ______ and surface _______ _______ in particular direction.
weather systems
ocean currents
84. Due to the spinning of Earth, weather systems move in certain directions because of ___________ ______ __________. global wind belts
85. Convection currents near bodies of water can cause local winds known as __________ ____________ and _______ ___________.
land breezes sea breezes
86. The ______ ________ of Earths oceans circulate warm and cold ocean waters in convection patterns and influence the weather and climate of the land masses nearby.
surface currents
87. The _______ Gulf Stream current influences the eastern Atlantic shoreline of the US. warm
88. The _______ California current influences the Pacific shoreline.
cold 89. The unequal heating of Earth causes ______ _______(tropical,temperature, polar)
climate zones
90. Climate is related to_______regions at various latitudes. convection
91. Climate is related to ________ differences between the equator and the poles. temperature 92. Climate is related to ________ and ______ surface ocean currents. warm cold
93. _______ _______ are found in each convection region.
global winds 94. Because convection cells are in place in the atmosphere and earth is spinning on its axis, the global winds appear to curve. This is known as the __________ ________. Coriolis effect 95. The global wind belt regions, the prevailing direction of the winds and how air moves affect ______ _________.
weather conditions
96. _______ _________ blow from east to west in the tropical region moving warm tropical air in that climate zone. trade winds
97. The prevailing _______ ___________ blow from west to east in the temperature region. westerly winds 98. The temperate zone temperatures are affected most by _____ __________. changing seasons
99. The US is in the ______ wind belt.
westerly 100. The weather sytems move across the country from _____ to ________. west east
101.Tropical weather systems, like hurricanes are moved by prevailing ____ _____. trade winds 102.The______ ______ blow northeast to west in the polar region.
polar winds
103. ___ ______ A fast moving ribbon of air that moves from west to east in the Northern Hemisphere around Earth. jet stream
104.The _______ _______ _______ can bring down cold polar conditions from the north. polar jet stream 105. The _______ _____ ______ can bring warm tropical conditions from the south(in the northern hemisphere). subtropical jet stream
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Tides-2015 LectureDocument17 pagesTides-2015 Lectureapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- World of Plants WebquestDocument4 pagesWorld of Plants Webquestapi-169639475100% (1)
- Nasa Moon Survival ExerciseDocument4 pagesNasa Moon Survival Exerciseapi-169639475100% (1)
- Phases of Matter WebquestDocument6 pagesPhases of Matter Webquestapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- 95 Worlds and Counting Video HandoutDocument2 pages95 Worlds and Counting Video Handoutapi-1696394750% (1)
- Creating A Travel Brochure GuidelinesDocument6 pagesCreating A Travel Brochure Guidelinesapi-169639475100% (1)
- Totally Tourist Tour of Solar System 2Document3 pagesTotally Tourist Tour of Solar System 2api-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Questions For Angiosperms BookletDocument1 pageQuestions For Angiosperms Bookletapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Literacy Article Soil Composting WKSTDocument2 pagesLiteracy Article Soil Composting WKSTapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Composting Fact SheetDocument2 pagesComposting Fact Sheetapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2-Atoms Family Student WsDocument2 pages2-Atoms Family Student Wsapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Creating A Travel Brochure GuidelinesDocument6 pagesCreating A Travel Brochure Guidelinesapi-169639475100% (1)
- 030 Plants Text Book ChapterDocument34 pages030 Plants Text Book Chapterapi-169639475100% (2)
- Photosynthesis and Respiration and Plant ResponsesDocument2 pagesPhotosynthesis and Respiration and Plant Responsesapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rock Identification Lab Study GuideDocument28 pagesRock Identification Lab Study Guideapi-169639475100% (1)
- Atoms Family PowerpointDocument17 pagesAtoms Family Powerpointapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic BasicsDocument4 pagesAtomic Basicsapi-169639475Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Wan Nur Shabira BT Wan Mohd Naser - A12kp0127 - Production LoggingDocument15 pagesWan Nur Shabira BT Wan Mohd Naser - A12kp0127 - Production LoggingmisszombyPas encore d'évaluation
- r050210801 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical EngineeringDocument7 pagesr050210801 Fluid Mechanics For Chemical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- Filtro ISODocument13 pagesFiltro ISORafael LimaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023-Prise List Pan India All ProductDocument12 pages2023-Prise List Pan India All ProductHiren PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Technical Summary Kryvyi Rih Industrial Gases Complex, Kryvyi Rih, UkraineDocument8 pagesNon-Technical Summary Kryvyi Rih Industrial Gases Complex, Kryvyi Rih, UkraineAufklarungPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM Methode D 1066 Vapeur EchantillonnageDocument7 pagesASTM Methode D 1066 Vapeur Echantillonnageaaro_oraalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Reference MANNDocument115 pagesCross Reference MANNElias FernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- Refrigeration CapoteDocument51 pagesRefrigeration CapoteMichelle Angela Cabrera GabisPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Plumbing CourseDocument168 pagesBasic Plumbing CourseAlex Dulay100% (1)
- Discharge Permit Application Form Sample Filled UpDocument2 pagesDischarge Permit Application Form Sample Filled UpRob Closas100% (6)
- Engineering Calculation of Pump CapacityDocument36 pagesEngineering Calculation of Pump CapacityHairil HerliansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Técnico - Pump Haskel - MS 21Document14 pagesManual Técnico - Pump Haskel - MS 21Bruno Pacheco100% (1)
- 1 Natural Solutions ProjectsDocument67 pages1 Natural Solutions ProjectsAjit GokhalePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report Permeability MeasurementDocument9 pagesLab Report Permeability Measurementsher afganPas encore d'évaluation
- KAFCODocument1 pageKAFCOসাইদুর রহমানPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise GasesDocument4 pagesExercise GasesAri AdiantariPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank ME14 303 Fluid MechanicsDocument6 pagesQuestion Bank ME14 303 Fluid MechanicsSudeesh SudevanPas encore d'évaluation
- SafetyDocument58 pagesSafetyAshutosh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Artificial Light SourcesDocument15 pagesTypes of Artificial Light SourcesDonita Villabriga100% (1)
- 119 04 E PDFDocument12 pages119 04 E PDFFelipe Miguel Sánchez Clements100% (1)
- Argon Specification - AIR LIQUIDEDocument2 pagesArgon Specification - AIR LIQUIDElewgne08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Properties of FluidsDocument3 pagesMechanical Properties of FluidsSanal BusherPas encore d'évaluation
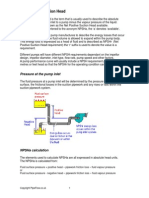
- Net Positive Suction Head or NPSHDocument4 pagesNet Positive Suction Head or NPSHSathish LingamPas encore d'évaluation
- 1231 - USP - Water For Pharmaceutical PurposesDocument51 pages1231 - USP - Water For Pharmaceutical Purposespires35Pas encore d'évaluation
- SULZER Water MixerDocument12 pagesSULZER Water MixerAlfonso José García LagunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Osmosis BasicsDocument5 pagesReverse Osmosis BasicsTalal Ashraf100% (1)
- Aa) Kinetic Theory and DiffusionDocument3 pagesAa) Kinetic Theory and DiffusionMahasweta RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Document6 pagesLab Manual: RGPV University (Bhopal)Pushpendra KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4-Taller 4Document56 pagesChapter 4-Taller 4Héctor F BonillaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Fertigation System Design by Using Venturemeters: Rancang Bangun Sistem Fertigasi Dengan Menggunakan VenturimeterDocument9 pagesThe Fertigation System Design by Using Venturemeters: Rancang Bangun Sistem Fertigasi Dengan Menggunakan VenturimeterAhmad Faqih HidayahPas encore d'évaluation