Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
OFM Presentation 00
Transféré par
Jose NaviaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
OFM Presentation 00
Transféré par
Jose NaviaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
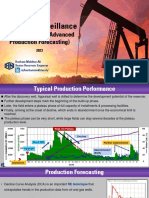
Oil Field Manager ~ Presentation
11 April 2013
OFM helps engineers manage more wells effectively in less time
2
Data Organisation in OFM
All data stored in relational database.
Since OFM 2000, OFM uses Microsoft
Access for data storage.
Links to other databases possible via
ODBC:
Permanent download to Access.
Live link to external database (no data
duplication).
Access
DB
External Database
OFM
3
Data Input Levels in OFM
Master Table is used to set the project key.
Corresponds to the lowest level at which data is
available (usually either Completion or Wellbore).
Other well information may be included (well co-
ordinates etc).
Completion
Completion
Field
Wellbore
4
Base Map
5
Base Map
6
Filtering Capabilities In OFM
7
Sample Production Plots
8
Sample Production Plots
9
Sample Production Plots
10
Basic Production Plot
1976 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
0
100
200
300
400
500
160001177110038801S01
Oil Rate (Cal. Day) ( bbl/d )
Water Rate (Cal. Day) ( bbl/d )
Liquid Rate (Cal. Day) ( bbl/d )
Unocal - Basic Production Plot #1
CumGas = 2.992 ( Bcf )
CumOil = 604.621 ( Mbbl )
CumWater = 115.114 ( Mbbl ) 160001177110038801S01 Flowunit = BU1 6 RD E006
1976 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
0
15
30
45
60
75
0
40
80
120
160
200
Axis 1
Water Cut ( % ) 160001177110038801S01
Axis 2
Gas Oil Ratio ( Mcf /bbl ) 160001177110038801S01
Unocal - Basic Production Plot #1
CumGas = 2.992 ( Bcf )
CumOil = 604.621 ( Mbbl )
CumWater = 115.114 ( Mbbl ) 160001177110038801S01 Flowunit = BU1 6 RD E006
1976 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90
0
600
1200
1800
2400
3000
160001177110038801S01
Cumulative Oil Production ( Mbbl )
Cumulative Gas Production ( MMcf )
Cumulative Water Production ( Mbbl )
Unocal - Basic Production Plot #1
CumGas = 2.992 ( Bcf )
CumOil = 604.621 ( Mbbl )
CumWater = 115.114 ( Mbbl ) 160001177110038801S01 Flowunit = BU1 6 RD E006
Productivity decrease drastically
as soon as the water hit the well:
AL?, Emulsion problems? Scale?
Fines migration?
11
DCA in OFM
12
Bubble Maps In OFM ~ Monthly Production
13
Sample Bubble Maps
14
Sample Bubble Maps
15
Sample Bubble Maps
16
Lesson 3.4
Sample Bubble Maps
17
Sample Bubble Maps
Sample Bubble Maps
18
Sample Bubble Maps
19
Sample Bubble Maps
20
OOIP and grid map in OFM
OFM can calculate the original-oil/gas-in-place for reservoirs. This
technique uses the volumetric equation and grid arithmetic.
Boi
gridmap Swi gridmap
gridmap
h A
N
) )( 1 ( * ) ( * ) ( *
=
|
21
OOIP and grid map in OFM
22
OOIP and grid map in OFM
Boi
* *
=
23
Normalized Mapping (OOIP-Np) Map
Area of low recovery
efficiency workover
potential exist?
Area of over recovery
efficiency Potential
additional pay presents ?
24
Basic Production Maps
Best gas well
Zones with very low recovery of gas
-Undrained zones?
-Potential for new wells?
-Stimulation opportunities?
25
Production Heterogeneity Index
Heterogeneity indexing is -
Comparing individual wells to the average of a well group
A fast way to identify over- and underperforming wells, best
completion practices etc.
1 =
wells of average
well
value
value
HI
26
Desired results and interpretation
27
Re - perforation Analysis
Due to different perforation
techniques, some wells experienced
problems
Underbalanced perforating (through
tubing) may not have achieved full
penetration
Cumulative liquid produced per perf
foot is a technique to evaluate
perforation productivity
Grid map/bubble map results
28
Damage Indicator
Formation damage analysis
Simple damage analysis
Formation Damage Index (FDI)
Grid map
Pressure transient is preferred for
calculating skin
Treatment = acidize well to remove
damage
|
|
.
|
\
|
+
A
= =
s
r
r
B
p
kh
q
FDI
w
e
o o
ln
007078 . 0
29
Decline Curve Analyses Equations
Exponential Decline Conversions (where b = 0)
Hyperbolic Decline Conversions (where 0 < b < 1)
Harmonic Decline Conversions (where b = 1)
( )
( )
b
i
i
t bD
q
t q
1
1+
=
( )
t D
i
i
e
q
t q =
( )
( ) t D
q
t q
i
i
+
=
1
30
DCA in OFM
Potential zones with high Reserves
31
Volumetric Drainage Radius Estimation
Visual representation of the drainage area per well in the reservoir.
Areas not being drained by wells are quickly identified visually with bubble
mapping
32
Technical Discussion
Volumetric Drainage radius (r
ev
) calculation
Literally, the volume occupied by the produced fluid at reservoir conditions
Assume uniform pressure reservoir
Volumetric method
Drainage radius for Np and EUR
Additional variable can be displayed with drainage radius to provide insight of
reservoir performance
| | f t
S S h
B N
r
or w
oi p
ev
) 1 (
615 . 5
=
| t
33
Volumetric Drainage Radius Example
Drainage Radius at Np
Undeveloped spots
Drainage Radius at EUR
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- TGL Reservoir Engineering EngDocument15 pagesTGL Reservoir Engineering Engbabak_dearPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisD'EverandHydraulic Fracturing in Unconventional Reservoirs: Theories, Operations, and Economic AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- Streamline Numerical Well Test Interpretation: Theory and MethodD'EverandStreamline Numerical Well Test Interpretation: Theory and MethodPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout OFM Fund-Int Trisakti-FIN2Document292 pagesHandout OFM Fund-Int Trisakti-FIN2FikriMuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Getting Started With The OFM APIDocument30 pagesGetting Started With The OFM APIOmar Santamaría CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Waterflooding Using EclipseDocument18 pagesWaterflooding Using EclipseAakriti BhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Well Test Analysis PDFDocument23 pagesWell Test Analysis PDFJaime Alberto Aranibar CabreraPas encore d'évaluation
- ECLIPSE SimulationDocument34 pagesECLIPSE SimulationKaoru AmanePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 History MatchingDocument42 pages11 History Matchingali100% (1)
- PetrelRE Complete WorkflownewsourceDocument38 pagesPetrelRE Complete WorkflownewsourceLija BinuPas encore d'évaluation
- Pvtsim Technical Overview 2016 Download v3Document16 pagesPvtsim Technical Overview 2016 Download v3Jorge Vásquez CarreñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigate A Gas Well Performance Using Nodal AnalysisDocument15 pagesInvestigate A Gas Well Performance Using Nodal Analysisrafiullah353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Parameters in Reservoir Simulation For Good Performance MatchingDocument18 pagesBasic Parameters in Reservoir Simulation For Good Performance MatchingkrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Simulation History Matching and ForecastingDocument60 pagesReservoir Simulation History Matching and ForecastingnoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Requirement For Eclipse Input File PDFDocument9 pagesData Requirement For Eclipse Input File PDFnajmudeen100% (1)
- OFM 2007.1 Forecast Analysis FundamentalsDocument100 pagesOFM 2007.1 Forecast Analysis FundamentalsJustin Perez0% (1)
- History Matching/PredictionDocument17 pagesHistory Matching/PredictionNguyễn Hữu DanhPas encore d'évaluation
- History MatchingDocument114 pagesHistory MatchingAlexander AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Saturation Modelling: From Petrophysics To Volumes and SimulationDocument54 pagesWater Saturation Modelling: From Petrophysics To Volumes and Simulationarjun2014Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Reservoir ManagementDocument17 pagesReview of Reservoir ManagementJessica KingPas encore d'évaluation
- OFM 2005 1 FundamentalsDocument252 pagesOFM 2005 1 FundamentalsAdamec Pacheco100% (3)
- Relative PermeabilityDocument116 pagesRelative PermeabilityYinzhang100% (2)
- HPT-SNL Technology - Redefining Production LoggingDocument6 pagesHPT-SNL Technology - Redefining Production Loggingmhuf89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4 - Decline Curve AnalysisDocument41 pagesLecture 4 - Decline Curve Analysisgeber39Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir SurveillanceDocument28 pagesReservoir Surveillanceابوالحروف العربي ابوالحروفPas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Simulation: Alwyn FieldDocument49 pagesReservoir Simulation: Alwyn Fieldiskander100% (1)
- Matching of PressureDocument53 pagesMatching of Pressureb3114880Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir SimulationDocument487 pagesReservoir SimulationAbhinav Shahi100% (2)
- Well Test AnalysisDocument23 pagesWell Test Analysisleong_guoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prosper CompleteDocument552 pagesProsper CompleteYusuf Oktoviyanto100% (1)
- Reservoir Simulation Texas A&MDocument205 pagesReservoir Simulation Texas A&MArjun Guglani100% (1)
- Waterflooding Surveillance PaperDocument10 pagesWaterflooding Surveillance Paperginozky0% (1)
- Integrated Field Modeling and OptimizationDocument158 pagesIntegrated Field Modeling and OptimizationMossad Khôi NguyênPas encore d'évaluation
- History Matching ReportDocument28 pagesHistory Matching ReportsergeyPas encore d'évaluation
- TM4112 - 1 Reservoir Simulation OverviewDocument40 pagesTM4112 - 1 Reservoir Simulation OverviewRay YudaPas encore d'évaluation
- UserGuides Tutorials Examples OFM 2014 PDFDocument262 pagesUserGuides Tutorials Examples OFM 2014 PDFRavi Garchar100% (4)
- OFM 2007.2 FundamentalsDocument308 pagesOFM 2007.2 Fundamentalsmkwende100% (1)
- Reservoir-Simulation Lect 3Document41 pagesReservoir-Simulation Lect 3كهلان البريهيPas encore d'évaluation
- Devex 2018 Introduction To Reservoir SimulationDocument52 pagesDevex 2018 Introduction To Reservoir SimulationKonul AlizadehPas encore d'évaluation
- Examples - Heavy Oil Reservoirs Field Development PlanDocument4 pagesExamples - Heavy Oil Reservoirs Field Development PlanChukwunoso NwonyePas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Transient Formation and Well Testing: Convolution, Deconvolution and Nonlinear EstimationD'EverandPressure Transient Formation and Well Testing: Convolution, Deconvolution and Nonlinear EstimationÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- PvtiDocument16 pagesPvtiDhiaa LaMiPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Reservoir Asset Management: Principles and Best PracticesD'EverandIntegrated Reservoir Asset Management: Principles and Best PracticesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- (3) Reservoir Management Jawad - د جواد راضي العسلDocument153 pages(3) Reservoir Management Jawad - د جواد راضي العسلAbdou BoukhalfaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 - WaterfloodingDocument68 pages3 - Waterfloodingpermanahend100% (1)
- Introduction To Well Testing and Interpretation: WCP1 CourseDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Well Testing and Interpretation: WCP1 Courserabahnali75% (12)
- Eclipse Office Simulation Workflow LectureDocument586 pagesEclipse Office Simulation Workflow Lectureyou seefPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Reservoir Simulation Training Course PDFDocument33 pagesApplied Reservoir Simulation Training Course PDFnguyenmainam100% (1)
- Tutorial Prosper Nodal Analysis: Ir. Andry Halim, MMDocument23 pagesTutorial Prosper Nodal Analysis: Ir. Andry Halim, MMStiv WowilingPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 PROSPER IntroductionDocument7 pages1 PROSPER IntroductionGustavo ChacónPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Condensate PVTDocument28 pagesGas Condensate PVTapi-3718100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reservoir Engineering AnalysisDocument282 pagesReservoir Engineering AnalysisOlaoluwa Olatona100% (2)
- Reservoir Management For WaterfloodsDocument5 pagesReservoir Management For WaterfloodsAnonymous Xy309m9Sm9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Sand Management For Effective Hydrocarbon Flow AssuranceD'EverandIntegrated Sand Management For Effective Hydrocarbon Flow AssurancePas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationD'EverandPractical Reservoir Engineering and CharacterizationÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Quantifying Uncertainty in Subsurface SystemsD'EverandQuantifying Uncertainty in Subsurface SystemsCéline ScheidtPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding TightOil FINALDocument27 pagesUnderstanding TightOil FINALJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- SW Versus Phie UsesDocument10 pagesSW Versus Phie UsesJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding TightOil FINALDocument27 pagesUnderstanding TightOil FINALJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Tight OilDocument20 pagesUnderstanding Tight OilLiz HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- PEmerability and Skin Factor LogsDocument8 pagesPEmerability and Skin Factor LogsJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Petroleum Society Monograph 1 - Determination of Oil and Gas ReservesDocument394 pagesPetroleum Society Monograph 1 - Determination of Oil and Gas Reservesshamshadakhtar100% (6)
- 101 Investment Tools For Buying Low and Selling HighDocument292 pages101 Investment Tools For Buying Low and Selling HighJose Navia100% (2)
- 40 - Estimation of Oil and Gas ReservesDocument38 pages40 - Estimation of Oil and Gas Reservesrizal tri susilo50% (2)
- Impact of AggregationDocument13 pagesImpact of AggregationJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- 101 Dynamite Answers To Interview QuestionsDocument189 pages101 Dynamite Answers To Interview QuestionsSivaT97% (31)
- Front End Oil and GasDocument4 pagesFront End Oil and GasJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Zolotukhin Reservoir Engineering 002Document217 pagesZolotukhin Reservoir Engineering 002Anttonio Gómez86% (14)
- Front End Oil and GasDocument4 pagesFront End Oil and GasJose NaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Porosity, Permeability & Skin FactorDocument27 pagesPorosity, Permeability & Skin FactorPratick Tibrewala100% (1)
- Unit 10-Maintain Knowledge of Improvements To Influence Health and Safety Practice ARDocument9 pagesUnit 10-Maintain Knowledge of Improvements To Influence Health and Safety Practice ARAshraf EL WardajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Vocabulary Practice Unit 8Document4 pagesVocabulary Practice Unit 8José PizarroPas encore d'évaluation
- h6811 Datadomain DsDocument5 pagesh6811 Datadomain DsChristian EstebanPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Vision and Action Recognition A Guide For Image Processing and Computer Vision Community For Action UnderstandingDocument228 pagesComputer Vision and Action Recognition A Guide For Image Processing and Computer Vision Community For Action UnderstandingWilfredo MolinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stainless Steel 1.4404 316lDocument3 pagesStainless Steel 1.4404 316lDilipSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Analysis of Mutual Fund SchemesDocument29 pagesComparative Analysis of Mutual Fund SchemesAvinash JamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityBhavesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Bharat Heavy Electricals LimitedDocument483 pagesBharat Heavy Electricals LimitedRahul NagarPas encore d'évaluation
- It14 Belotti PDFDocument37 pagesIt14 Belotti PDFHolis AdePas encore d'évaluation
- Cinnamon Peelers in Sri Lanka: Shifting Labour Process and Reformation of Identity Post-1977Document8 pagesCinnamon Peelers in Sri Lanka: Shifting Labour Process and Reformation of Identity Post-1977Social Scientists' AssociationPas encore d'évaluation
- Community-Based Monitoring System (CBMS) : An Overview: Celia M. ReyesDocument28 pagesCommunity-Based Monitoring System (CBMS) : An Overview: Celia M. ReyesDiane Rose LacenaPas encore d'évaluation
- AdvertisingDocument2 pagesAdvertisingJelena ŽužaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sika Saudi Arabia: Safety Data SheetDocument4 pagesSika Saudi Arabia: Safety Data Sheetusman khalid100% (1)
- Installation Manual EnUS 2691840011Document4 pagesInstallation Manual EnUS 2691840011Patts MarcPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Management - Pgpmi - Class 12Document44 pagesMarketing Management - Pgpmi - Class 12Sivapriya KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- EP2120 Internetworking/Internetteknik IK2218 Internets Protokoll Och Principer Homework Assignment 4Document5 pagesEP2120 Internetworking/Internetteknik IK2218 Internets Protokoll Och Principer Homework Assignment 4doyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Statable 1Document350 pagesStatable 1Shelly SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Planas V Comelec - FinalDocument2 pagesPlanas V Comelec - FinalEdwino Nudo Barbosa Jr.100% (1)
- Technical Manual: 110 125US 110M 135US 120 135UR 130 130LCNDocument31 pagesTechnical Manual: 110 125US 110M 135US 120 135UR 130 130LCNKevin QuerubinPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer System Sevicing NC Ii: SectorDocument44 pagesComputer System Sevicing NC Ii: SectorJess QuizzaganPas encore d'évaluation
- CENT - Company Presentation Q1 2020 PDFDocument22 pagesCENT - Company Presentation Q1 2020 PDFsabrina rahmawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- VB 850Document333 pagesVB 850Laura ValentinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 7373 16038 1 PBDocument11 pages7373 16038 1 PBkedairekarl UNHASPas encore d'évaluation
- Modal Case Data Form: GeneralDocument4 pagesModal Case Data Form: GeneralsovannchhoemPas encore d'évaluation
- Spa ClaimsDocument1 pageSpa ClaimsJosephine Berces100% (1)
- E OfficeDocument3 pagesE Officeஊக்கமது கைவிடேல்Pas encore d'évaluation
- Catalogue of The Herbert Allen Collection of English PorcelainDocument298 pagesCatalogue of The Herbert Allen Collection of English PorcelainPuiu Vasile ChiojdoiuPas encore d'évaluation
- DevelopersDocument88 pagesDevelopersdiegoesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hoja Tecnica Item 2 DRC-9-04X12-D-H-D UV BK LSZH - F904804Q6B PDFDocument2 pagesHoja Tecnica Item 2 DRC-9-04X12-D-H-D UV BK LSZH - F904804Q6B PDFMarco Antonio Gutierrez PulchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aisc Research On Structural Steel To Resist Blast and Progressive CollapseDocument20 pagesAisc Research On Structural Steel To Resist Blast and Progressive CollapseFourHorsemenPas encore d'évaluation