Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
A Form of Questions
Transféré par
noratiqahrCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A Form of Questions
Transféré par
noratiqahrDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Yes-no questions
How to form yes-no questions In English, a special word order (Verb Subject Object) is used to form yes-no questions.
Examples: Affirmative ~They are American. ~She is nice
Yes or No Question ~Are they American? ~Is she nice?
The rules 1. If the main verb of the sentence is "to be", simply invert the subject and the verb to be:
Examples: > They are American. Are they American? > They are nice. Are they nice?
2. If
the sentence includes a main verb and another or other helping (auxiliary) verb(s), invert the subject and the (first) helping (auxiliary) verb.
Examples: >They are visiting Paris. Are they visiting Paris?
>She has done the housework. Has she done the housework >Nancy has been working all night long. Has Nancy been working all night long? >He will be reading the book. Will he be reading the book?
3.
If the sentence includes a verb which is not the verb "to be" and doesn't include a helping (auxiliary) verb, the transformation is more complex. a. If the verb is in the present tense, add either do or does and put the main verb in its base form:
do if the subject is the first person singular, second person singular, first person plural, second person plural and third person plural (I, you, we, they) Examples: ~I like apples. Do you like apples? ~They go to a high school. Do the go to a high school? does if the subject is the third person singular (he, she, it). Examples: ~Nancy reads a lot. Does Nancy read a lot? ~He hates basketball. Does he hate basketball? b.If the verb is in the past tense, add did and put the main verb in its base form:
Examples: ~He discovered the truth. Did he discover the truth? ~She write a nice essay. Did she write a nice essay? ~They did the homework. Did they do the homework?
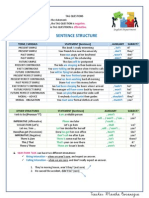
DEFINITION: A "tag" is something small that we add to something larger. For example, the little piece of cloth added to a shirt showing size or washing instructions is a tag. We use tag questions at the end of statements to ask for confirmation. They mean something like: "Am I right?" or "Do you agree?" They are very common in English. The basic structure is: Notice that the question tag repeats the auxiliary verb (or main verb when be) from the statement and changes it to negative or positive.
statement + Positive statement, Snow is white, Negative statement, You don't like me,
question tag negative tag? isn't it? + positive tag? do you?
Positive Statement Tag Questions
Look at these examples with positive statements. You will see that most of the time, the auxiliary verb from the positive statement is repeated in the tag and changed to negative.
positive statement [+] subject auxiliary main verb negative tag [-] auxiliary not personal pronoun (same as subject) you? we? notes:
You We
are have
coming, finished,
are have
n't n't
You
You They I We He
do
like
like
coffee,
coffee,
do
do wo can must
n't
n't n't 't n't n't
you?
you? they? I? we? he? You (do) like...* won't = will not
will can must should
help, come, go, try harder,
should
You
John
are
was
English,
there,
are
was
n't
n't
you?
he?
no auxiliary for main verb beprese nt & past
Negative Statement Tag Questions
Look at these examples with negative statements. Notice that the negative verb in the original statement is changed to positive in the tag.
negative statement [-]
positive tag [+]
subject
auxiliary
main verb
auxiliary
personal pronoun (same as subject)
it? we? you? they? they? I? we? he? you? you? he?
It We You They They I We He You You John
is have do will wo can must should wo
n't never n't not n't never n't n't n't
raining, seen like help, report do tell drive be are was n't not us, it right, her, so fast, late, English, there, that, coffee,
is have do will will can must should will are was
Answer a tag question according to the truth of the situation. Your answer reflects the real facts, not (necessarily) the question. For example, everyone knows that snow is white. Look at these questions, and the correct answers:
tag question Snow is white, isn't it? Snow isn't white, is it? Snow is black, isn't it? Snow isn't black, is it?
correct answer Yes (it is). Yes it is! the answer is the same in both cases because snow IS WHITE! but notice the change of stress when the answerer does not agree with the questioner
No it isn't! No (it isn't).
the answer is the same in both cases because snow IS NOT BLACK!
In some languages, people answer a question like "Snow isn't black, is it?" with "Yes" (meaning "Yes, I agree with you"). This is the wrong answer in English! >Here are some more examples, with correct answers: ~The moon goes round the earth, doesn't it? Yes, it does. ~The earth is bigger than the moon, isn't it? Yes. ~The earth is bigger than the sun, isn't it? No, it isn't! ~Asian people don't like rice, do they? Yes, they do! ~Elephants live in Europe, don't they? No, they don't! ~Men don't have babies, do they? No. ~The English alphabet doesn't have 40 letters, does it? No, it doesn't.
Tag Question Special Cases
Negative Adverbs
The adverbs never, rarely, seldom, hardly, barely and scarcely have a negative sense. Even though they may be in a positive statement, the feeling of the statement is negative. We treat statements with these words like negative statements, so the question tag is normally positive. Look at these examples:
positive statement treated as negative statement
positive tag
He never came again, did he?
She can rarely come these days, can she? You hardly ever came late, did you? I barely know you, do I?
You would scarcely expect her to know would you? that,
Some More Special Cases
I am right, aren't I? You have to go, don't you?
aren't I (not amn't I) you (do) have to go...
I have been answering, haven't use first auxiliary I? Nothing came in the post, did it? treat statements with nothing, nobody etc like negative statements
Let's go, shall we?
He'd better do it, hadn't he?
let's = let us
he had better (no auxiliary)
WH Question Words Definition: A term in generative grammar for a question that is formed with an interrogative word (what, who, whom, whose, which, when, where, why, or how) and that expects an answer other than "yes" or "no." Contrast with yes-no question.
Question Word what
Function asking for information about something asking for repetition or confirmation
Example What is your name? What? I can't hear you. You did what? What did you do that for? When did he leave? Where do they live? Which colour do you want? Who opened the door? Whom did you see? Whose are these keys? Whose turn is it? Why do you say that? Why don't I help you?
what...for when where which who whom whose why why don't
asking for a reason, asking why asking about time asking in or at what place or position asking about choice asking what or which person or people (subject) asking what or which person or people (object) asking about ownership asking for reason, asking what...for making a suggestion
how
asking about manner asking about condition or quality
How does this work? How was your exam?
see examples below How far is Pattaya from Bangkok? How long will it take? How many cars are there? How much money do you have? How old are you? How come I can't see her?
how + adj/adv
asking about extent or degree how far distance how long length (time or space) how many quantity (countable) how much quantity (uncountable) how old age
how come (informal)
asking for reason, asking why
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Puzle MtorDocument1 pagePuzle MtornoratiqahrPas encore d'évaluation
- English Language Academic: Institut Perguruan Sultan Mizan, 22200 Besut, TerengganuDocument12 pagesEnglish Language Academic: Institut Perguruan Sultan Mizan, 22200 Besut, TerengganunoratiqahrPas encore d'évaluation
- Real ReportDocument12 pagesReal ReportnoratiqahrPas encore d'évaluation
- LogDocument5 pagesLognoratiqahrPas encore d'évaluation
- English Language Academic: Institut Perguruan Sultan Mizan, 22200 Besut, TerengganuDocument13 pagesEnglish Language Academic: Institut Perguruan Sultan Mizan, 22200 Besut, TerengganunoratiqahrPas encore d'évaluation
- Verbs and AdverbsDocument9 pagesVerbs and AdverbsZainal Ariffin Ab GhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Speaking in A British Dialect PDFDocument19 pagesSpeaking in A British Dialect PDFEmily ParrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Forensic LinguisticDocument18 pagesForensic LinguisticAzwin HasyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Past Progressive StoryDocument8 pagesPast Progressive StoryMyralba Hernández100% (1)
- Question Tags ExplainedDocument7 pagesQuestion Tags ExplainedtinevimboPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Question TagsDocument4 pagesGrammar Question TagsMarini BudiartiPas encore d'évaluation
- English With Fluency Academy PlansDocument10 pagesEnglish With Fluency Academy PlansnearhirumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Think l2 Grammar Reference PDFDocument6 pagesThink l2 Grammar Reference PDFIsrael SánchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 23Document24 pagesTopic 23Ana Merchán PoncePas encore d'évaluation
- Transformational Rules in TGG LectureDocument5 pagesTransformational Rules in TGG Lecturegeorge bensonPas encore d'évaluation
- English Material Grade 4Document25 pagesEnglish Material Grade 4azizahPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes English 1423-24-25Document37 pagesNotes English 1423-24-25ramzanm100% (3)
- 10th English 1Document35 pages10th English 1PoojaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ingles Grado 9Document8 pagesIngles Grado 9Katerine de la RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Progressive Story 1Document7 pagesFuture Progressive Story 1Eddie Hernandez Santiago100% (1)
- Nowadays, The Time Is Too Short, Isn T It ?Document3 pagesNowadays, The Time Is Too Short, Isn T It ?oscar sossaPas encore d'évaluation
- Question TagsDocument2 pagesQuestion TagsGabriela Cutipa AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Question TagsDocument4 pagesQuestion TagsenagatPas encore d'évaluation
- Here?: Complete These Statements With The Right Question TagsDocument2 pagesHere?: Complete These Statements With The Right Question Tagsileana stoica100% (2)
- Lesson Plan English Grade ViDocument53 pagesLesson Plan English Grade ViVangie Evans Sandoval100% (11)
- Question TagsDocument15 pagesQuestion TagsRita Patricia Patiño100% (1)
- Martha Silva VigoDocument11 pagesMartha Silva VigoNiel Linarez NarroPas encore d'évaluation
- Tag QuestionDocument15 pagesTag QuestionPixma PrintPas encore d'évaluation
- Tag Questions Part 2Document23 pagesTag Questions Part 2Ana Karen Torrez CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Gs Question Tags - ExercisesDocument2 pagesGs Question Tags - ExercisesAbigail Martínez VargasPas encore d'évaluation
- English DWDM 2022 Book 5 Int Sample PagesDocument11 pagesEnglish DWDM 2022 Book 5 Int Sample PagesLuiz Roberto MartinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 84: You Are My Friend, Aren't You?: Tag QuestionsDocument5 pagesLesson 84: You Are My Friend, Aren't You?: Tag Questionsorlandini2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- New English File Upper Intermediate Students Book Oxford University Press 68 74Document7 pagesNew English File Upper Intermediate Students Book Oxford University Press 68 74Fabrizio ArratiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Homework 2 - Tag QuestionsDocument2 pagesHomework 2 - Tag QuestionsSergio Daniel Ramirez Gil100% (1)
- Teaching Plan For B6, L1: A Firefighter's Job Means A Lot To Us, Doesn't It?Document21 pagesTeaching Plan For B6, L1: A Firefighter's Job Means A Lot To Us, Doesn't It?Richmond AmborPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample English Vii Nukuu 0753439834-1Document15 pagesSample English Vii Nukuu 0753439834-1abiliusapolinaryPas encore d'évaluation