Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Shahzad H. Sh. Taimur Mir Sana Asif Huma Saeed
Transféré par
Taimur MirDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Shahzad H. Sh. Taimur Mir Sana Asif Huma Saeed
Transféré par
Taimur MirDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Shahzad H. Sh.
Taimur Mir Sana Asif Huma Saeed
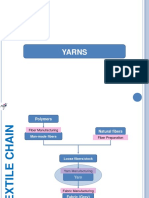
Acrylic fibres are synthetic fibres which are made entirely from chemicals. The other most widely used kinds of synthetic fibers are nylon (polyamide), polyester and olefin. Acrylic fibres contains up to 85 % polymers from polyacrylonitrile also referred to as PAN. PANs are a softer type of plastic, more fibrous and rubbery than a hard plastic.
The acrylonitrile monomers is usually combined with small amounts of other chemicals to improve the ability of the resulting fiber to absorb dyes. These days fabrics are made from acrylics fibres because they are cheap and produce in large quantity. The first acrylic fabric fiber was spun in the 1940s by Dupont and was called Orlon. Orlon was rough and stiff. The process of creating acrylic fabrics has developed since the forties to produce a range of fabrics that are much softer.
The polymer of acrylic fibers are formed by polymerization method. The fiber is then produced by dissolving the polymers in a solvent by mixing N,N-dimethylformamide or aqueous sodium thiocyanate. Later it passes through a multi-hole spinnerette and coagulating the resultant filaments in an aqueous solution of the same solvent. Washing, stretching, drying technique are used and in the end crimping process complete the processing.
Production occurs in two ways of Acrylic fibers. Either by wet spinning or by dry spinning method. Using solvents to dissolve the poylmers, each process then extrudes the polymers and spins them to solidify them. In the dry spinning process, the polymers are dissolved in a suitable solvent, which is forcefully pushed into warm air for solidification by the evaporation of the solvent. After the spinning part is over, it is stretched hot from 3 to 10 times of its original length and then crimped. Example filament fibers it produces.
In the wet spinning process, the polymer is dissolved in solvent and extruded into a coagulating wet substance. It is then dried, crimped and collected as the resulting fabric. For example staple fiber it produces. The fiber is stretched and pulled during its creation creating a tensile strength in the resulting fiber. Fibers are then altered according to the needs of the purchaser. Color, specific stain resistance and tighter weaves can all be modifications to an acrylic fabric.
Main properties of acrylic fibers are: It is ideal for blends with wool . Feels like wool, with high bulk. Very good heat retention and fastness to light. Very good shape retention It is very durable material. It can be easily care and have quick dry qualities. For sport wear training acrylic fibers have low water absorption, quicker water transport, light and weather resistance.
It is lightweight, soft, and warm. It absorbs and releases moisture quickly, thus allowing the fabric to "breathe". It is resilient, retains its shape, and resists shrinkage and wrinkles.
Main properties of acrylic fibres are: It has flexible aesthetics for wool-like, cottonlike or blended appearance. It has excellent pleat retention quality. It is static. It suffers from piling and abrasion problems. Acrylic has recently been used in clothing as a cheaper alternative to cashmere, due to the similar feeling of the materials.
Not only, the acrylic fabrics are high in performance but also they have a luxurious feel and they also drape very well. They are lightweight but have more bulk. This is due to their quality of lower specific gravity. They are odor and mildew resistant too. In cold weather acrylics provide excellent insulation and warmth without any extra weight.
Acrylic has recently been used in clothing as a less expensive alternative to cashmere, due to the similar feeling of the materials. The disadvantages of acrylic are that it tends to fuzz or pill easily and that it does not insulate the wearer as well as wool or cashmere. Many products, like fake pashmina or cashmina, use this fiber to create the illusion of cashmere.
Acrylic has a bad reputation amongst many knitters - however cheap the yarn is, its performance does not come near natural fibers. Also, some knitters complain that the fiber "squeaks" when knitted. Acrylic fabrics is a kind of the synthetic fibre that is artificially manufactured. Acrylic fabrics can also be referred as the imitation of wool. Acrylic fabrics are known for their stiffness and ability of wear and tear resistance. Acrylic also does not losses the glaze for a longer period of time.
Acrylic has a warm and dry hand like wool. Its density is 1.17 g/cc as compared to 1.32 g/cc of wool. It is about 30% bulkier than wool. It has about 20% greater insulating power than wool. It has a tenacity of 5 gpd in dry state and 4-8 gpd in wet state. Breaking elongation is 15% ( both states). It has a elastic recovery of 85% after 4% extension when the load is released immediately.
Acrylic
fabric tends toward fast drying, natural stain resistance, durability and color fastness. Acrylic fabric holds a bright steady color and ultraviolet ray resistance and is great for rugged outdoor wear. It removes dampness, moving it away from the skin and toward the outer portion of the weave thereby allowing the moisture to evaporate more quickly than a natural fabric.
Its
stretchy quality keeps the shape of the garment far longer than natural fabrics. Acrylic fabrics do not shrink and are moth proof. There are those who find acrylic fabrics to be itchy and uncomfortable and some who claim they are allergic to acrylic. Static electricity is a hazard when wearing acrylic because it builds up between the skin and the fabric as a person moves.
Acrylic
is resistant to moths, oils, chemicals, and is very resistant to deterioration from sunlight exposure. However, static and pilling can be a problem. Acrylic can irritate the skin of people with eczema. They are comfortable to wear due to high moisture management. Dyes can be easily applied to them and they are colorfast.
It dyes to bright colors with excellent fastness. It is resistant to moths, oil and chemicals, and sunlight degradation. It has an outstanding stability towards commonly bleaching agents. It has a good resistance to mineral acids. The resistance to weak alkalies is fairly good, while hot strong alkalies rapidly attack acrylic.
It has a good thermal stability. When exposed to temperatures above 175 deg C for prolonged periods some discolouration takes place. Acrylic has a moisture regain of 1.5-2% at 65% RH and 70 deg F.
Major Acrylic Fiber Uses Apparel: Sweaters, socks, fleece wear, circular knit apparel, sportswear and childrens wear Home Furnishings: Blankets, area rugs, upholstery, pile; luggage, awnings,curtains, outdoor furniture , Carpets and rugs. Other Uses: Craft yarns, sail cover cloth, wipe cloths . Industrial Uses: Concrete and stucco reinforcement , technical products, carbon fibres.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Acrylic FiberDocument9 pagesAcrylic FiberNeeraj JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthetic FibreDocument6 pagesSynthetic FibreswaroophoppyPas encore d'évaluation
- SpinningDocument8 pagesSpinningAishee BhowmickPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramie PDFDocument6 pagesRamie PDFkabir_ce06038Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Report On Green Material - Jute FibresDocument7 pagesA Report On Green Material - Jute FibresvaibhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Textiles - DiplomaDocument9 pagesTextiles - DiplomamansiagrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bi ComponentDocument13 pagesBi ComponentA.K.M. Rashedul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Compact SpinningDocument17 pagesCompact SpinningRana Kashif TahirPas encore d'évaluation
- FibreDocument82 pagesFibreShahedul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Man Made Fiber Textile ProcessDocument39 pagesMan Made Fiber Textile ProcessGarmentLearnerPas encore d'évaluation
- Draw FrameDocument50 pagesDraw FrameDev Narayan KushwahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dry Finishing of Wool Fabrics - Pailthorpe M.Document14 pagesDry Finishing of Wool Fabrics - Pailthorpe M.Hugo Eduardo Ipiales MesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yarn Short Questions PDFDocument16 pagesYarn Short Questions PDFNasir Sarwar100% (2)
- Friction SpinningDocument8 pagesFriction SpinningJoshi ParthPas encore d'évaluation
- Wet II Presentation Group 3 Antimicrobial FinishDocument29 pagesWet II Presentation Group 3 Antimicrobial FinishZillur Rahman SaykatPas encore d'évaluation
- Manufacturing of Needle Punched NonwovenDocument14 pagesManufacturing of Needle Punched NonwovenKareena Kalla100% (1)
- Siro Spinning: Presented By: Y.Nikhil ROLL NO:17110079Document7 pagesSiro Spinning: Presented By: Y.Nikhil ROLL NO:17110079Nikhil Nani100% (2)
- Gujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Document2 pagesGujarat Technological University: W.E.F. AY 2018-19Rushi TannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Compact SpinningDocument15 pagesCompact SpinningCẩm TúPas encore d'évaluation
- Solubility of FibresDocument3 pagesSolubility of FibresNasir Sarwar0% (1)
- Ring Spinning Vs All Technologies Part 2Document29 pagesRing Spinning Vs All Technologies Part 2SOhaib KazmePas encore d'évaluation
- MD Mazbah Uddin Bangladesh University of Textiles Yarn Engineering Department Batch 08Document48 pagesMD Mazbah Uddin Bangladesh University of Textiles Yarn Engineering Department Batch 08AliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rings & Ring Travellers DetDocument12 pagesRings & Ring Travellers DetArchana ParidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Weft & Warp TensionDocument8 pagesWeft & Warp Tensionnemat2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Melange YarnDocument11 pagesMelange YarnMd Ariful IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningDocument5 pagesPractical Observation of Material Flow On Ring-Fame, Auto Cone Rotor SpinningTalha saeedPas encore d'évaluation
- Textilelearner - Blogspot.ca-Rayon Fiber Characteristics of Rayon Fiber Manufacturing Process of Viscose Rayon End Uses of RayoDocument4 pagesTextilelearner - Blogspot.ca-Rayon Fiber Characteristics of Rayon Fiber Manufacturing Process of Viscose Rayon End Uses of Rayolyouf100% (1)
- Degumming of SilkDocument7 pagesDegumming of Silkavdhoot7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gross & Fine Structure of Cotton Fiber - Textile Learner 1Document3 pagesGross & Fine Structure of Cotton Fiber - Textile Learner 1RAFIAHAMMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4-Cotton PDFDocument25 pagesUnit 4-Cotton PDFFuad HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Woven FabricDocument9 pages3D Woven FabricCrystal NewmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Objects of Carding in Spinning MillDocument1 pageObjects of Carding in Spinning MillDaksh PuraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Flax FiberDocument29 pagesLecture Flax FiberFahad jutt100% (1)
- Project WorkDocument12 pagesProject WorkSarabjot AzrotPas encore d'évaluation
- Textile Dyeing and Printing: AssignmentDocument8 pagesTextile Dyeing and Printing: AssignmentshailajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Serviceability of FabricDocument64 pagesServiceability of FabricVasant Kothari100% (1)
- Unconventional Fibre PlantsDocument18 pagesUnconventional Fibre PlantsRajendra Singh MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bobtex Spinning ProcessDocument8 pagesBobtex Spinning Processvermadeen0% (1)
- Cardingmachine 140324082245 Phpapp01Document33 pagesCardingmachine 140324082245 Phpapp01SantoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Vortex FDocument2 pagesVortex FNipu SenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 - Secondary Motions of Weaving PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 3 - Secondary Motions of Weaving PDFHugo Eduardo Ipiales MesaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Project Effect On Yarn Quality Due To Different Type of Spacer Are Used and Balancing of Machines in Spinning DepartmentDocument6 pagesA Project Effect On Yarn Quality Due To Different Type of Spacer Are Used and Balancing of Machines in Spinning DepartmentLucky meena100% (1)
- Patterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafDocument33 pagesPatterning in Weft Knitting: Waqas AshrafHifza khalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical FinishingDocument23 pagesMechanical Finishingmahes_texPas encore d'évaluation
- Textile Science - Session 3Document35 pagesTextile Science - Session 3ALOK KUMARPas encore d'évaluation
- Course: Yarn Manufacturing 2Document24 pagesCourse: Yarn Manufacturing 2fekadePas encore d'évaluation
- Ring Spinning MachineDocument11 pagesRing Spinning MachinePradip Gupta100% (1)
- LycraDocument7 pagesLycraFiaz juttPas encore d'évaluation
- The Card: "The Heart of Spinning"Document101 pagesThe Card: "The Heart of Spinning"Umår F ÃfriDiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wrap SpinningDocument12 pagesWrap SpinningvermadeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Textile ScienceDocument22 pagesTextile ScienceAbhinav VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mélange YarnDocument11 pagesMélange YarnshahinPas encore d'évaluation
- Innovation in YarnDocument6 pagesInnovation in YarnDevendra VashisthPas encore d'évaluation
- By: Hemant Ghanghor & Patanjal KumarDocument15 pagesBy: Hemant Ghanghor & Patanjal KumarpatanjaliictPas encore d'évaluation
- Ballistic Protective TextileDocument18 pagesBallistic Protective TextileRahman EfazPas encore d'évaluation
- Yarn StudentsDocument32 pagesYarn Studentskartika ranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Special YarnDocument4 pagesSpecial Yarnshadath072Pas encore d'évaluation
- Staple Cotton Spinning SystemsDocument24 pagesStaple Cotton Spinning Systemsagga1111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fashion CommunicationDocument5 pagesFashion CommunicationTaimur MirPas encore d'évaluation
- Tom FordDocument5 pagesTom FordTaimur MirPas encore d'évaluation
- Fashion Communication (Promotional Campaign) : Presented To: Sir Hammad Khawaja Presented By: Karam MasudDocument21 pagesFashion Communication (Promotional Campaign) : Presented To: Sir Hammad Khawaja Presented By: Karam MasudTaimur MirPas encore d'évaluation
- Barriers Against Agricultural Exports From Pakistan The Role of WTO Sanitary and Phytosanitary AgreementDocument28 pagesBarriers Against Agricultural Exports From Pakistan The Role of WTO Sanitary and Phytosanitary AgreementsalllllPas encore d'évaluation
- EntrepreneurDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurHamid NajmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1 1 27Document36 pages10 1 1 27Taimur MirPas encore d'évaluation
- EntrepreneurDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurHamid NajmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Islamic ArchitectureDocument11 pagesIslamic ArchitectureTaimur MirPas encore d'évaluation
- CommunicationDocument33 pagesCommunicationvikash_thakur23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sweater Manufacturing ProcessDocument23 pagesSweater Manufacturing ProcessManik Karmakar0% (1)
- Monte Carlo ProjectDocument20 pagesMonte Carlo ProjectRajpal Gill100% (1)
- Fabric Identification Burn TestDocument1 pageFabric Identification Burn TestShantnu MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 Clothing Performance Requirements - March 22Document60 pages3.1 Clothing Performance Requirements - March 22Rohan KabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Spandex Fiber: Dorlastan.) Invista, Radicispandex CorporationDocument20 pagesSpandex Fiber: Dorlastan.) Invista, Radicispandex CorporationShantnu MittalPas encore d'évaluation
- Acrylic FibersDocument53 pagesAcrylic FibersImran Anwar80% (5)
- Company Directory America Technical TextileDocument50 pagesCompany Directory America Technical TextileSk SalimuzzamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Company InformationDocument30 pagesCompany InformationVicPas encore d'évaluation
- Apic2014 Yang QinDocument27 pagesApic2014 Yang QinDani CRPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon FibersDocument1 130 pagesCarbon Fibersaagun1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revista Crochet AccesoriosDocument148 pagesRevista Crochet Accesoriosfemorale100% (24)
- Non Asbestos GasketDocument11 pagesNon Asbestos GasketloqPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsDocument50 pagesSynthetic Fibres and PlasticsDhyani PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- GRS Combined List PDFDocument30 pagesGRS Combined List PDFPankhil DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Textile Research Journal: Static Electricity in TextilesDocument11 pagesTextile Research Journal: Static Electricity in TextilesRasibPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsDocument3 pages03 Synthetic Fibres and PlasticsRohan MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Identifying Fibres by Burning TestDocument5 pagesIdentifying Fibres by Burning TestARIFUL ISLAMPas encore d'évaluation
- Ekoten Textile Test Report - Lululemon - E00730Document4 pagesEkoten Textile Test Report - Lululemon - E00730eacik7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Textile Basics NotesDocument33 pagesTextile Basics Notesparthraj89100% (3)
- China Product Safety: For China: Three Dimensional Embellishments Are Not Permitted Anywhere On Decorative CordsDocument12 pagesChina Product Safety: For China: Three Dimensional Embellishments Are Not Permitted Anywhere On Decorative Cordsvrinda soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment On Different Types Synthetic Fibers: AcrylicDocument8 pagesAssignment On Different Types Synthetic Fibers: AcrylicZAyedPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecturer in Textile Technology: Module I: General Knowledge and Current AffairsDocument17 pagesLecturer in Textile Technology: Module I: General Knowledge and Current AffairsRitikk patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Mary Lisa Gavenas - The Fairchild Encyclopedia of Menswear-Fairchild Publications, Inc. (2008)Document448 pagesMary Lisa Gavenas - The Fairchild Encyclopedia of Menswear-Fairchild Publications, Inc. (2008)irayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Factory Profile of Ekram Sweater..Document62 pagesFactory Profile of Ekram Sweater..Muhammad Nayim HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- QUIZ - FiberDocument3 pagesQUIZ - FiberRebecca DumlaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Smart Investment 10-16 Dec 2023Document82 pagesSmart Investment 10-16 Dec 2023vijibaskPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Static FinishDocument6 pagesAnti Static FinishManjeet PradhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fabrics and Soft Furnishings: TapestryDocument7 pagesFabrics and Soft Furnishings: TapestrySamikBanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- TLE G6 Q2 Module 3Document16 pagesTLE G6 Q2 Module 3Leo CerenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pilling 1Document16 pagesPilling 1Indhu IndhhuuPas encore d'évaluation