Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
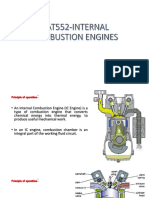
Internal Combustion Engines
Transféré par
Pradeep Kumar MehtaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Internal Combustion Engines
Transféré par
Pradeep Kumar MehtaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Internal Combustion Engines
Internal Combustion Engines
types of heat engines steam engines external combustion turbines Stirling engine
Otto engine internal combustion Diesel engine Vankel engine
Internal Combustion Engines
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of fuel-oxidizer mixture occurs in a confined space
applied in: automotive rail transportation power generation ships aviation garden appliances
Internal Combustion Engines
Internal Combustion Engines
Internal Combustion Engines Carnot cycle -
Internal Combustion Engines two stroke 1. Power / Exhaust
a. b.
2. Intake / Compression
a. b. c. inlet port opens compressed fuel-air mixture rushes into the cylinder piston upward movement provides further compression
c.
ignition piston moves downward compressing fuel-air mixture in the crankcase exhaust port opens
Internal Combustion Engines two stroke Advantages: lack of valves, which simplifies construction and lowers weight fire once every revolution, which gives a significant power boost can work in any orientation good power to weight ratio Drawbacks: lack of a dedicated lubrication system makes the engine to wear faster. necessity of oil addition into the fuel low efficiency produce a lot of pollution
Internal Combustion Engines four stroke -
starting position
1. intake
a. piston starts moving down b. intake valve opens c. air-fuel mixture gets in
2. compression
a. piston moves up b. both valves closed c. air-fuel mixture gets compressed
Internal Combustion Engines four stroke -
ignition
3. power
a. air-fuel mixture explodes driving the piston down
4. exhaust
a. piston moves up b. exhaust valve opens c. exhaust leaves the cylinder
Internal Combustion Engines four stroke Advantages: dedicated lubrication system makes to engine more wear resistant better efficiency that 2-stroke engine no oil in the fuel less pollution
Drawbacks: complicated constriction should work in horizontal position due to lubrication
Internal Combustion Engines Diesel -
air intake
exhaust /intake compression
fuel injection exhaust combustion
Internal Combustion Engines Diesel Advantages: self ignition (without electrical spark plug) better efficiency reliability higher durability supplied with worse fuels Drawbacks: more NOx production more expensive production more weight louder lower revolutions
Internal Combustion Engines Diesel fuel injector
Internal Combustion Engines multi-cylinder -
Internal Combustion Engines multi-cylinder Cylinder layouts
Internal Combustion Engines multi-cylinder Cylinder layouts
flat
inline
Internal Combustion Engines multi-cylinder inline flat boxer
Internal Combustion Engines multi-cylinder 14 cylinder Diesel engine (80 MW)
Internal Combustion Engines multi-cylinder Cylinder layouts radial
Internal Combustion Engines
Valve operation
Internal Combustion Engines
Engine characteristic
Diesel
Petrol
Internal Combustion Engines
Engine cooling
Internal Combustion Engines
Turbocharged engine
Internal Combustion Engines
Wankel rotary engine
Advantages: higher power output no reciprocating mass simpler and lighter construction
Drawbacks: increased wear of rubbing parts higher fuel consumption requirement for better materials
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Introdu To IC EnginesDocument21 pagesIntrodu To IC EnginesSameerAhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion Engine BasicsDocument27 pagesInternal Combustion Engine BasicsSri RPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion Engines GuideDocument27 pagesInternal Combustion Engines GuideSRINIVAS TPas encore d'évaluation
- IcenginesDocument27 pagesIcenginessaravanan l mechPas encore d'évaluation
- Ic EngineDocument27 pagesIc EngineAnil MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Engine & IC EnginesDocument26 pagesHeat Engine & IC EnginesVeeresh Kumar G BPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson One: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument45 pagesLesson One: Understanding Principles of Operation of Internal Combustion Engineswaleed yehiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Combustion Ass 1Document6 pagesCombustion Ass 1Shane Michael BacalsoPas encore d'évaluation
- MARPOWERDocument4 pagesMARPOWERREY SELWYN MANALANGPas encore d'évaluation
- Fuel Properties and Use of Hydrogen I.C.enginesDocument95 pagesFuel Properties and Use of Hydrogen I.C.enginesSiemensPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1Document30 pagesUnit 1RakeshkumarcegPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoDocument33 pagesDiesel Engine: Aguinaldo, Cellan, Gregorio, MedranoHannah AguinaldoPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages of 4 Stroke Engine:-: DifferencesDocument3 pagesAdvantages of 4 Stroke Engine:-: DifferencescidracPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between 4 Stroke & 2 Stroke - EngineDocument6 pagesDifference Between 4 Stroke & 2 Stroke - EngineMOAZPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion Engines - Four vs Two Stroke (39Document73 pagesInternal Combustion Engines - Four vs Two Stroke (39amarparimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion EngineDocument542 pagesInternal Combustion EngineArihant ShijuPas encore d'évaluation
- IC Engine Classification and ComponentsDocument53 pagesIC Engine Classification and ComponentsAshitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Everything You Need to Know About Two Stroke EnginesDocument13 pagesEverything You Need to Know About Two Stroke Enginessherifkazem2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Two Stroke Internal Combustion Engines: How A Two Stroke Engine Works Advantages/DisadvantagesDocument13 pagesTwo Stroke Internal Combustion Engines: How A Two Stroke Engine Works Advantages/DisadvantagesrajfacebookPas encore d'évaluation
- AGR 318 Lec 3 - Engine Cons & CompDocument42 pagesAGR 318 Lec 3 - Engine Cons & CompHaikal SapurataPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo charger: A brief history and overviewDocument22 pagesTurbo charger: A brief history and overviewPragyan Kumar0% (1)
- Team Nozzle Present .: Four Stroke Petrol EngineDocument33 pagesTeam Nozzle Present .: Four Stroke Petrol EngineChamfreit AxereasPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and disadvantages of different engine designsDocument6 pagesAdvantages and disadvantages of different engine designsJILLIEN KAITH ARELLANOPas encore d'évaluation
- EnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 - 3 APC Mobile Sources Aug 2015 v2Document117 pagesEnE 250 Air Quality Management and Pollution Control Lecture 02 - 3 APC Mobile Sources Aug 2015 v2Alexis Bryan RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Document27 pagesEngine and Motor (4 Stroke Engine and 2 Stroke Engine)Bias PanduPas encore d'évaluation
- CSI Tech IC Engine FundamentalsDocument32 pagesCSI Tech IC Engine Fundamentalssamuelben87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion Engine ClassificationDocument43 pagesInternal Combustion Engine ClassificationAhmer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- TurbochargerDocument10 pagesTurbochargernavle krushnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Otto CyclePowePointDocument27 pagesOtto CyclePowePointVamsi KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantDocument60 pagesLecture 1 - Diesel Engine Power PlantbarryPas encore d'évaluation
- Engine and TransmissionDocument26 pagesEngine and TransmissionWFilmy STARPas encore d'évaluation
- 2003 ExhaustDocument47 pages2003 ExhaustThip ZazaPas encore d'évaluation
- LEC# 14. I.C EngineDocument43 pagesLEC# 14. I.C EngineAli Murad JokhioPas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Fuel EngineDocument14 pagesDual Fuel EngineGUJJARI PREM KUMAR 19981A0344Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Fuel Engine & TechnologyDocument10 pagesDual Fuel Engine & Technologyjameela chandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Principles of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument31 pagesUnderstanding Principles of Internal Combustion EnginesNaveen KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- ET Answer KeyDocument9 pagesET Answer KeyGodwinPas encore d'évaluation
- SI vs CI Engines Key DifferencesDocument4 pagesSI vs CI Engines Key DifferencesRicci ObiasPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Principle of Diesel and Petrol EnginesDocument8 pagesOperating Principle of Diesel and Petrol EnginesJonathan MalamulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Combustion Engine ProcessesDocument80 pagesInternal Combustion Engine Processeschoongwenkang100% (1)
- Engine Classification, Parts Identification: To .. Head:yousef Alkhattam V.H: Ahmed Ashraf By:saad Yasser SaadDocument49 pagesEngine Classification, Parts Identification: To .. Head:yousef Alkhattam V.H: Ahmed Ashraf By:saad Yasser SaadSaad YasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Engineering SummaryDocument9 pagesPower Engineering SummarypriagolavinchentPas encore d'évaluation
- Aircraft Engines: Reciprocating EngineDocument46 pagesAircraft Engines: Reciprocating EngineBadal Machchhar100% (1)
- ClasificationDocument30 pagesClasificationSanjay SwainPas encore d'évaluation
- Diesel PPDocument58 pagesDiesel PPManvendra Pratap Singh Bisht100% (1)
- Different Types of IC Engine: - Rated by Their Maximum Horsepower - Three TypesDocument14 pagesDifferent Types of IC Engine: - Rated by Their Maximum Horsepower - Three TypesmharitmsPas encore d'évaluation
- HCCI Engines: A Promising New Combustion TechnologyDocument43 pagesHCCI Engines: A Promising New Combustion TechnologyArpit ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document29 pagesChapter 3Hasif EnazPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Institute of Technology: Dual Fuel Engine OverviewDocument13 pagesModern Institute of Technology: Dual Fuel Engine OverviewVIKASPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition and Classification of EnginesDocument27 pagesDefinition and Classification of EnginesSurjit Kumar GandhiPas encore d'évaluation
- PT 1 - AutoDocument10 pagesPT 1 - Autoselvaganapathy.me20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal 1unit3Document178 pagesThermal 1unit3NAGU2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 3 ThermoDocument11 pagesExperiment 3 ThermoMuneeb NaveedPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Power ProducingDocument17 pages2 Power ProducingShashank AgrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Types of ENGINEDocument31 pagesDifferent Types of ENGINEKarnal 0388Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesD'EverandComparison of Diesel and Petrol EnginesÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Vroom! How Does A Car Engine Work for KidsD'EverandVroom! How Does A Car Engine Work for KidsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Donny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume I: the Twin CamD'EverandDonny’S Unauthorized Technical Guide to Harley-Davidson, 1936 to Present: Volume I: the Twin CamPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercedes E Class Petrol Workshop Manual W210 & W211 SeriesD'EverandMercedes E Class Petrol Workshop Manual W210 & W211 SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Supercharging On The Performance of C.I Engine Using Blends of Pre-Heated Cotton Seed Oil and Diesel As Alternate FuelDocument4 pagesThe Effects of Supercharging On The Performance of C.I Engine Using Blends of Pre-Heated Cotton Seed Oil and Diesel As Alternate FuelPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsDocument8 pagesThe Effects of Supercharging On The Performance and Exhaust Gas Emissions of A Dual-Fuel Engine Fueled With Producer Gas-Diesel and Palm Oil BlendsPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- CricketDocument3 pagesCricketPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Download MATLAB R2015aDocument6 pagesDownload MATLAB R2015aPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Engineering Graphics Xii PDF For WebDocument180 pagesFinal Engineering Graphics Xii PDF For WebRicha Sahni100% (1)
- Lecture 22-23-24 Time Domain Analysis of 2nd Order SystemsDocument73 pagesLecture 22-23-24 Time Domain Analysis of 2nd Order SystemsPradeep Kumar Mehta100% (1)
- Residual Signal Techniques Used For Gear Fault DetectionDocument7 pagesResidual Signal Techniques Used For Gear Fault DetectionPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- MMM Lab Manual 10mel47bDocument108 pagesMMM Lab Manual 10mel47bsimalaraviPas encore d'évaluation
- TM16 Experimental Vibration Using The Universal Vibration ApparatusDocument1 pageTM16 Experimental Vibration Using The Universal Vibration ApparatusPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Universal Vibration (A)Document34 pagesUniversal Vibration (A)shajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Dof Fig.Document10 pagesGear Dof Fig.Pradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010-A Novel Method For The Optimal Band Selection For Vibration Signal Demodulation and Comparison With The Kurtogram-Tomasz BarszczDocument21 pages2010-A Novel Method For The Optimal Band Selection For Vibration Signal Demodulation and Comparison With The Kurtogram-Tomasz BarszczPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Dynamic Modelling of A One Stage Spur Gear System and Vibration Based Tooth Crack Detection Analysis MohammedDocument13 pages2015 Dynamic Modelling of A One Stage Spur Gear System and Vibration Based Tooth Crack Detection Analysis MohammedPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Create Object For Recording - MATLAB AudiorecorderDocument2 pagesCreate Object For Recording - MATLAB AudiorecorderPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- MP Forest PaperDocument21 pagesMP Forest PaperPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- MatlabDocument93 pagesMatlabPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2014 Effect of Backup Ratio and Cutter Tip Radius On Uniform Bending Strength Design of Spur Gears SekarDocument10 pages2014 Effect of Backup Ratio and Cutter Tip Radius On Uniform Bending Strength Design of Spur Gears SekarPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rate of Interest On Single Domestic Term DepositsDocument2 pagesRate of Interest On Single Domestic Term DepositsPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010-Advantages and Drawbacks of Applying Periodic Time-Variant Modal Analysis To Spur Gear Dynamics-Rune PedersenDocument14 pages2010-Advantages and Drawbacks of Applying Periodic Time-Variant Modal Analysis To Spur Gear Dynamics-Rune PedersenPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009-Vibration-Based Fault Diagnosis of Spur Bevel Gear Box Using Fuzzy Technique-N. SaravananDocument17 pages2009-Vibration-Based Fault Diagnosis of Spur Bevel Gear Box Using Fuzzy Technique-N. SaravananPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010-Automatic Faults Diagnosis by Application of Neural Network System and Condition-Based Monitoring Using Vibration Signals-Adyles Arato JuniorDocument11 pages2010-Automatic Faults Diagnosis by Application of Neural Network System and Condition-Based Monitoring Using Vibration Signals-Adyles Arato JuniorPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 1 1 469 5945Document21 pages10 1 1 469 5945Pradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- General SocioDocument22 pagesGeneral SocioPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Below Is The Sectional Cutoff For IBPS PO 2014Document3 pagesBelow Is The Sectional Cutoff For IBPS PO 2014Pradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Generate Electricity with HydropowerDocument22 pagesGenerate Electricity with HydropowerPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 100 Hindi Gkq1Document3 pages100 Hindi Gkq1javed alamPas encore d'évaluation
- On The Capacity of A Cellular CDMA System.: - Anshul PopatDocument23 pagesOn The Capacity of A Cellular CDMA System.: - Anshul PopatPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- MPPSC General Studies Question PapersDocument39 pagesMPPSC General Studies Question PapersPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experience CertificatesDocument3 pagesExperience CertificatesPradeep Kumar MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Komatsu PC01-1 (JPN) 14001-Up Shop ManualDocument217 pagesKomatsu PC01-1 (JPN) 14001-Up Shop Manualhaimay118100% (2)
- Praveen Verma Auto CAD IntershipDocument15 pagesPraveen Verma Auto CAD IntershipPraveen vermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nothophytophthora Gen. Nov., A New Sister Genus of Phytophthora From Natural and Semi-Natural Ecosystems in Europe, Chile and VietnamDocument32 pagesNothophytophthora Gen. Nov., A New Sister Genus of Phytophthora From Natural and Semi-Natural Ecosystems in Europe, Chile and VietnamChi Nguyen MinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Martina: Available Colors For This VersionDocument2 pagesMartina: Available Colors For This VersionUmeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 (Teacher)Document19 pagesChapter 2 (Teacher)ajakazPas encore d'évaluation
- Tax Invoice: New No 30, Old No 24 Bhagirathi Ammal ST, T Nagar, Chennai 600017 CIN: U74900TN2011PTC083121 State Code: 33Document1 pageTax Invoice: New No 30, Old No 24 Bhagirathi Ammal ST, T Nagar, Chennai 600017 CIN: U74900TN2011PTC083121 State Code: 33golu84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Railway noise source modeling and measurement methodsDocument78 pagesRailway noise source modeling and measurement methodsftyoneyamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ashok LeylandDocument4 pagesAshok Leylandsodhiseema100% (1)
- Ratio, Proportion, and Percent: Presented By: John Darryl M. Genio Bocobo #3Document18 pagesRatio, Proportion, and Percent: Presented By: John Darryl M. Genio Bocobo #3John Darryl GenioPas encore d'évaluation
- Ec010 505 Applied Electromagnetic TheoryDocument2 pagesEc010 505 Applied Electromagnetic Theorywalternampimadom100% (1)
- Bildiri Sunum - 02Document12 pagesBildiri Sunum - 02Orhan Veli KazancıPas encore d'évaluation
- Easa Ad 2023-0133 1Document6 pagesEasa Ad 2023-0133 1Pedro LucasPas encore d'évaluation
- RA ELECTRONICSENGR DAVAO Apr2019 PDFDocument6 pagesRA ELECTRONICSENGR DAVAO Apr2019 PDFPhilBoardResultsPas encore d'évaluation
- Derivatives and Foreign Currency: Concepts and Common TransactionsDocument28 pagesDerivatives and Foreign Currency: Concepts and Common TransactionsElle PaizPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Relay PDFDocument3 pagesAutomotive Relay PDFSimon MclennanPas encore d'évaluation
- Build A Tunnel: What You NeedDocument2 pagesBuild A Tunnel: What You NeedManila Business ShopsPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 ( CONSTRUCTION OF THE FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT )Document19 pagesUnit 6 ( CONSTRUCTION OF THE FLEXIBLE PAVEMENT )Zara Nabilah87% (15)
- Computer Assisted Language LearningDocument9 pagesComputer Assisted Language Learningapi-342801766Pas encore d'évaluation
- ChE 4110 Process Control HW 1Document6 pagesChE 4110 Process Control HW 1MalloryPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Com II Year Economics Previous Year QuestionsDocument11 pagesB. Com II Year Economics Previous Year QuestionsShashiMohanKotnalaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Light Sculling Training Boat PDFDocument8 pagesA Light Sculling Training Boat PDFLuis BraulinoPas encore d'évaluation
- CeramicsDocument39 pagesCeramicsD4-dc1 Kelas100% (1)
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2018: Internal Auditing: Theory & PrinciplesDocument39 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2018: Internal Auditing: Theory & PrinciplesSAMANTHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Lembar Kerja Lap Keu - Tahap 1Document4 pagesLembar Kerja Lap Keu - Tahap 1Safana AuraPas encore d'évaluation
- European Management Journal: Pawel Korzynski, Grzegorz Mazurek, Michael HaenleinDocument9 pagesEuropean Management Journal: Pawel Korzynski, Grzegorz Mazurek, Michael HaenleinkharismaPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO 22301 Mandatory DocumentDocument2 pagesISO 22301 Mandatory Documenttrackuse100% (1)
- Architecture Vernacular TermsDocument3 pagesArchitecture Vernacular TermsJustine Marie RoperoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmed (2018)Document9 pagesAhmed (2018)zrancourttremblayPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Leadership Literature ReviewDocument36 pagesE-Leadership Literature ReviewYasser BahaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adverse Drug Reactions in A ComplementaryDocument8 pagesAdverse Drug Reactions in A Complementaryrr48843Pas encore d'évaluation