Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Session 7
Transféré par
Haifa-mohdCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Session 7
Transféré par
Haifa-mohdDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The self-directed Learner
It has beed studied in SLA and educational thinking and there have been many insights on the language learner.
Leaner autonomy is the ability of the learner to take responsibility for their own learning and to plan, organise, and monitor the learning process independently of the teacher. One of these insights is leaning strategies of the good language learner.
Strategies of the good language learner
Types of learner strategies: one important ways of encouraging self-directed or independent learning is to teach leaning strategies. Definition p.77
1st part: cognitive strategies
2nd part: metacognitive how to manage their learnig.
Strategies of the good language learner
1. Cognitive strategies: processes used directly in learning to deal with information. Examples, analogy, memorisation, repetition, inferencing.
SEE examples p.78
2. Metacognitive strategies: planning for learning, thinking about how to make leaning effective, self-monitoring during learning, evaluation.
3. Communication strategies: use gestures, mime, synonyms, to make themselves understood. These keep the learner involved in conversation even if they lack the knowledge.
4. socio-effective strategies: used to practice the language, collaborating on tasks, watching TV, conversation with native speakers.
Learner Training in the classroom
Learner training: is a set of procedures or activities which raises learners' awareness of what's involved in learning a foreign language, encourage learners to be more involved, active, and responsible in their own learning, help them to develop their learning strategies.
Goals:
to prepare learners to work with the system of self-access facilities. To encourage learners to be aware of the ways they can find and use lang learning opportunities outside the classroom To develop learners who can use the learning opportunities o the classroom effectively by applying some strategies to their interaction. Different types of learner training activity:
Learner Training in the classroom
1. Activities that help learners to reflect on learning:
Teachers need to encourage learners to reflect on their learning needs and problems.
First: by providing a list of expectations that learners could have. SEE Example p.87: it allows teachers to raise expectations. 87 2nd: by asking students to make personal recordings about their strengths and weaknesses. This gives ideas about individual guidance in the classroom. 87 Coursebooks make explicit reference to leaning styles. SEE p.88
Learner Training in the classroom
2. Activities that train strategies and equip learners to be active:
Training cognitive strategies: to increase learners knowledge of useful ways to learn and develop the strategies they need. e.g. learning the meaning of a new word; use dic, guess, clues. EXAMPLE p.91 Training metacognitive strategies: it can be productive at the beginning, so learners share their own strategies with their peers. Teachers & materials writers can promote the use of metacognitive strategies by a range of activity types.
The role of Self-access facilities in Language Learning
School or teachers need to provide resources for leaners. Teachers might help then to use these resources. The aim is to eventually learners will be able to use it in their own way, according to their own goals and using their own strategies to monitor their progress.
Individual resources (electronic) should be appreciated and learners encouraged to use them.
When learners are guided, they will know how to improve their self-study programmes, knowing their aims, monitoring their progress.
EXAMPLE p.97
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Session8 8Document13 pagesSession8 8Haifa-mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Foreign Language Annals Fall 2007 40, 3 Proquest CentralDocument8 pagesForeign Language Annals Fall 2007 40, 3 Proquest CentralHaifa-mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Linguistics: The Twentieth CenturyDocument12 pagesApplied Linguistics: The Twentieth CenturyHaifa-mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Applied Linguistics?: - Interdisciplinary Field (HOW?)Document4 pagesWhat Is Applied Linguistics?: - Interdisciplinary Field (HOW?)Haifa-mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 5 5Document15 pagesSession 5 5Haifa-mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Learners and Learning, Classrooms and ContextsDocument12 pagesLearners and Learning, Classrooms and ContextsHaifa-mohdPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Thomas E. Skidmore-The Politics of Military Rule in Brazil, 1964-1985-Oxford University Press, USA (1988) PDFDocument433 pagesThomas E. Skidmore-The Politics of Military Rule in Brazil, 1964-1985-Oxford University Press, USA (1988) PDFMarcelo Ramos100% (2)
- MCN Drill AnswersDocument12 pagesMCN Drill AnswersHerne Balberde100% (1)
- Conrail Case QuestionsDocument1 pageConrail Case QuestionsPiraterija100% (1)
- The Hawthorne Studies RevisitedDocument25 pagesThe Hawthorne Studies Revisitedsuhana satijaPas encore d'évaluation
- ACE Resilience Questionnaires Derek Farrell 2Document6 pagesACE Resilience Questionnaires Derek Farrell 2CATALINA UNDURRAGA UNDURRAGAPas encore d'évaluation
- Reported Speech StatementsDocument1 pageReported Speech StatementsEmilijus Bartasevic100% (1)
- GN No. 444 24 June 2022 The Public Service Regulations, 2022Document87 pagesGN No. 444 24 June 2022 The Public Service Regulations, 2022Miriam B BenniePas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Care NursingDocument46 pagesCritical Care Nursingraquel_racoPas encore d'évaluation
- Grammar Reference With Practice Exercises: Unit 1Document25 pagesGrammar Reference With Practice Exercises: Unit 1violet15367% (3)
- The Preparedness of The Data Center College of The Philippines To The Flexible Learning Amidst Covid-19 PandemicDocument16 pagesThe Preparedness of The Data Center College of The Philippines To The Flexible Learning Amidst Covid-19 PandemicInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide To Effective Project ManagementDocument102 pagesA Guide To Effective Project ManagementThanveerPas encore d'évaluation
- Progressivism Sweeps The NationDocument4 pagesProgressivism Sweeps The NationZach WedelPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Immersion Experience at Formaply Inustry in Brgy. de Ocampo, Trece Martires City, CaviteDocument34 pagesWork Immersion Experience at Formaply Inustry in Brgy. de Ocampo, Trece Martires City, CaviteKen AshleyPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Future Tense & Future Continuous TenseDocument2 pagesSimple Future Tense & Future Continuous TenseFarris Ab RashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Joshua 24 15Document1 pageJoshua 24 15api-313783690Pas encore d'évaluation
- Serological and Molecular DiagnosisDocument9 pagesSerological and Molecular DiagnosisPAIRAT, Ella Joy M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Conversation Between God and LuciferDocument3 pagesConversation Between God and LuciferRiddhi ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- SEx 3Document33 pagesSEx 3Amir Madani100% (4)
- Fansubbers The Case of The Czech Republic and PolandDocument9 pagesFansubbers The Case of The Czech Republic and Polandmusafir24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Jyotish - 2003 Sri Jagannath Center - Narayan Iyer - Divisional Charts - Divining Through DivisionsDocument36 pagesJyotish - 2003 Sri Jagannath Center - Narayan Iyer - Divisional Charts - Divining Through DivisionsDeepa MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- E1979017519 PDFDocument7 pagesE1979017519 PDFAnant HatkamkarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Mahatma Gandhi in The Freedom Movement of IndiaDocument11 pagesThe Role of Mahatma Gandhi in The Freedom Movement of IndiaSwathi Prasad100% (6)
- Digital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSIONDocument2 pagesDigital TransmissionDIGITAL TRANSMISSIONEla DerarajPas encore d'évaluation
- WFRP - White Dwarf 99 - The Ritual (The Enemy Within)Document10 pagesWFRP - White Dwarf 99 - The Ritual (The Enemy Within)Luife Lopez100% (2)
- Win Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsDocument11 pagesWin Tensor-UserGuide Optimization FunctionsadetriyunitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Feline Neonatal IsoerythrolysisDocument18 pagesFeline Neonatal IsoerythrolysisPaunas JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Pumpkin Moon SandDocument3 pagesLesson Plan Pumpkin Moon Sandapi-273177086Pas encore d'évaluation
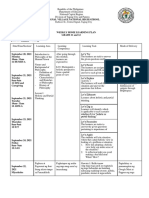
- Quarter: FIRST Week: 2: Ballecer ST., Central Signal, Taguig CityDocument2 pagesQuarter: FIRST Week: 2: Ballecer ST., Central Signal, Taguig CityIRIS JEAN BRIAGASPas encore d'évaluation
- Lista Verbelor Regulate - EnglezaDocument5 pagesLista Verbelor Regulate - Englezaflopalan100% (1)
- Technique Du Micro-Enseignement Une Approche PourDocument11 pagesTechnique Du Micro-Enseignement Une Approche PourMohamed NaciriPas encore d'évaluation