Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ch9 AC To AC Converters: Classification AC Voltage Controllers AC Power Controllers
Transféré par
herokaboss1987Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ch9 AC To AC Converters: Classification AC Voltage Controllers AC Power Controllers
Transféré par
herokaboss1987Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
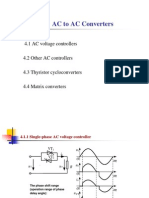
Ch9 AC to AC Converters
Classification
AC voltage controllers
AC power controllers
2
Classification of AC to AC Converters
3
Classification of AC Converters
4
Classification of Frequency Converters
Frequency converter (Cycloconverter):
1) Phase control: thyristor cycloconverter
(Delay angle control)
2) PWM control: matrix converter
(Chopping control)
5
AC voltage controllers
Single-phase AC voltage controller
Three-phase AC voltage controller
Applications:
Lighting control
Soft-start of asynchronous motors
Adjustable speed drive of asynchronous motors
Reactive power control
6
Single-phase AC voltage controller
1) Resistive load
Circuit configuration
7
R
O
u
1
u
o
i
o
VT
1
VT
2
u
1
u
o
i
o
u
VT
et
O et
O et
O et
R
O
u
1
u
o
i
o
VT
1
VT
2
u
1
u
o
i
o
u
VT
et
O et
O et
O et
0 , 0 ,
conducts
2 1 1 0
1
= = =
=
VT VT
u u u u
VT t As o e
blocks naturally VT i t As
VT
0
1 1
= =t e
1 2 1 1 0
2 1
, , 0
u u u u u
block all VT and VT t As
VT VT
= = =
+ < < o t e t
0 , 0 ,
2 1 1 0
2
= = =
+ =
VT VT
u u u u
conducts VT t As o t e
blocks naturally VT i t As
VT
0 2
2 2
= = t e
1 2 1 1 0
2 1
, , 0
2 2
u u u u u
block all VT and VT t As
VT VT
= = =
+ < < o t e t
fundamental analysis:
8
The phase shift range
(operation range of phase delay angle):
t o s s 0
9
Quantitative analysis:
2
1 1
1 1
( 2 sin ) ( ) sin 2
2
o
U U t d t U
t
o
t o
e e o
t t t
= = +
}
RMS value of output voltage
RMS value of output current
o
o
U
I
R
=
RMS value of thyristor current
2
1 1
2 sin 1 1 sin 2
( ) ( ) ( )
2 2 2
T
U t U
I d t
R R
t
o
e t o o
e
t t t
= = +
}
Power factor of the circuit
1 1 1
1
sin2
2
o o o
U I U P
S U I U
t o
o
t t
= = = = +
10
2) Inductive load
VT
1
arctan( / ) L R e =
state. stable in wave sine a is current
load the circuit, short in is thristor If
11
o t s s
sin( ) sin( )
tg
e
u
o u o
+ =
analysis
The phase shift range:
o >
12
t
et
et
et
et
4-5
o
o+t
o
u O
O
O
O
u
1
i
G1
i
G2
i
o
i
T1
i
T2
13
a) the star type joins b) triangle junction of the line control
c) triangle junction of leg control d) triangle junction of center point control
Three phase AC voltage controller:
14
For a time instant, there are 2 possible conduction states:
----Each phase has a thyristor conducting. Load voltage are the
same as the source voltages.
----There are only 2 thyristors conducting, each from a phase. The
load voltages of the two conducting phases are half of the
corresponding line to line voltage, while the load voltage of the other
phase is 0.
Star type joint electric circuit:
three-phase three-line
three-phase four-line
15
1). Use double pulse or the wide pulse.
2). trigger pulses of VT1~ VT6 is in turn 60
3). The range of a :0~150
16
3-phase 3-wire Y connection AC voltage controller
Resistive Load,
17
18
19
3-phase 3-wire branch-controlled triangle
connection AC voltage controller
The operation principle is the same as 3 independent
single-phase AC voltage controllers.
Application----Thyristor-controlled reactor (TCR)
To control the effective current flowing through the
reactor by controlling delay angle, therefore control the
reactive power absorbed by the reactor.
20
three-phase four-line:
Three-phase staggers 120 mutually. The
fundamental wave and harmonics which is
more than 3 times flow in three-phase circuit.
Basic Principles:
The zero curve has large 3 times harmonics.
When a=90,electric current of the zero
curve even approaches effective value of
phase currents.
Shortcoming:
n
n '
a
b
c
u
a
u
b
u
c
i
a
U
ao
VT1
VT3
T
VT4
T
VT5
T
VT6
T
VT2
T
21
AC power controllers
Circuit topologies are the same as AC voltage controllers.
Only the control method is different.
Load voltage and current are both sinusoidal when
thyristors are conducting.
22
Thyristor cycloconverter
23
Single-phase thyristor-cycloconverter:
24
Working process:
1).When P group works, id is a positive value.
2).When N group works , id is a negative value.
3).Two groups work according to the certain frequency, the load can
obtain AC current of this frequency.
changing frequencies of two groups in order to change the output frequency.
changing triggering angle a in order to change peak-to-peak value of
the output voltage.
4) To carry on the sine rule to modulate the angle for enabling ud profile
to approach the sine wave.
25
simulation model
26
single-phase cycloconverter
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 pagesChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: Outlinet1m0thyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document41 pagesChapter 4Anil ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Edusat Programme Lecture Notes ON Power Electronics BY Prof. M. Madhusudhan RaoDocument213 pagesEdusat Programme Lecture Notes ON Power Electronics BY Prof. M. Madhusudhan RaoSana BanuPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Voltage Controller CircuitsDocument211 pagesAC Voltage Controller CircuitsTran Binh DuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 pagesChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlinesambitPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics: AC To DC Converters (Rectifiers)Document79 pagesPower Electronics: AC To DC Converters (Rectifiers)Frew FrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineDocument25 pagesChapter 4 AC To AC Converters: OutlineprofmnsPas encore d'évaluation
- LECTURE 27 (Ch. 11) Ac Voltage Controllers: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsDocument15 pagesLECTURE 27 (Ch. 11) Ac Voltage Controllers: ECE 452 Power ElectronicsSumukha KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Voltage Controller Circuits (Rms Voltage Controllers) : V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument22 pagesAc Voltage Controller Circuits (Rms Voltage Controllers) : V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDasari SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 AC ConverterDocument27 pagesChapter 5 AC ConverterArjun KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Punith 2Document50 pagesPunith 2Punith Kumar YanagandulaPas encore d'évaluation
- EE 435 SCR Notes3Document32 pagesEE 435 SCR Notes3Dado GaudiPas encore d'évaluation
- Voltage Control With Using ThyristorDocument8 pagesVoltage Control With Using ThyristorAnucha YiePas encore d'évaluation
- AC Voltage Controller (AC-AC Converter)Document9 pagesAC Voltage Controller (AC-AC Converter)Nurindah Atika100% (4)
- Ac Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument6 pagesAc Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FRoss ShawPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Voltage ControllerDocument6 pagesAC Voltage ControllerTuhin ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument211 pages02 Power Electronicsకృష్ణ మురళి100% (2)
- L3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersDocument68 pagesL3. Single Phase Ac Voltage ControllersSourabh KhandelwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-PhaseDocument6 pagesPower Electronics Lab Experiment-No. 6 Single-Phase Full and Half Wave Controlled SCR Rectifier Aim: To Study and Analyze The Properties and The Characteristics of A Single-Phaseحسن علي جاسمPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Voltage Controller Circuits: Unit-8Document49 pagesAc Voltage Controller Circuits: Unit-8Naeemo IraqiPas encore d'évaluation
- Controlled RectifiersDocument16 pagesControlled RectifiersVishal Parekh100% (2)
- Power Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Document69 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual-withoutreadingsandprepostlab-EE0314Sankaran Nampoothiri KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Controlled Rectifier Single Phase Full WaveDocument7 pagesControlled Rectifier Single Phase Full WaveJesus BecerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Circuit For TransformerDocument8 pagesShort Circuit For TransformerNoli OtebaPas encore d'évaluation
- ACVC Material PDFDocument75 pagesACVC Material PDFramakrishnaprasad908Pas encore d'évaluation
- DR PeDocument211 pagesDR PeNaeemo IraqiPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument213 pages02 Power Electronicsapi-19608934Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Eee Pe PDFDocument107 pages3 Eee Pe PDFjose19313922Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Voltage Controller PDFDocument36 pagesAc Voltage Controller PDFsolo4000100% (3)
- Single Phase ControlledDocument39 pagesSingle Phase Controlledchandan Goswami50% (2)
- PEI Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument68 pagesPEI Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inINDIAN LEGENDSPas encore d'évaluation
- On AC Voltage ControllersDocument25 pagesOn AC Voltage ControllersSahil ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 2 Intro To DC Motor DrivesDocument52 pagesSection 2 Intro To DC Motor DrivesMak YabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Module-3 (B) - AC Controllers - VII-POWER ELECTRONICS - 2015-17 SchemeDocument48 pagesModule-3 (B) - AC Controllers - VII-POWER ELECTRONICS - 2015-17 SchemeK N DEEPSHIPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Power ElectronicsDocument212 pages02 Power Electronicsmarkschurer223453Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Three System Driver 3.1 MOSFET Control CircuitDocument11 pagesChapter Three System Driver 3.1 MOSFET Control CircuitAlhussain EmbarkPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is An Inverter?: Classification of InvertersDocument11 pagesWhat Is An Inverter?: Classification of Invertersayash mohantyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mukthish B. 2019UEE5136 EE - 3 Semester 5Document11 pagesMukthish B. 2019UEE5136 EE - 3 Semester 5Rahul MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Phase Ac Voltage ControllerDocument3 pagesThree Phase Ac Voltage ControllerShubham DixitPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformer StudiesDocument52 pagesTransformer StudiesSyed JaveedPas encore d'évaluation
- AC Voltage Controller/ RegulatorDocument9 pagesAC Voltage Controller/ RegulatorসৌরভPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 - Ac To Ac ConverterDocument43 pagesChapter 5 - Ac To Ac Converterapolloroka100% (1)
- CHAPTER 8 - Synchronous Machine Transient AnalysisDocument64 pagesCHAPTER 8 - Synchronous Machine Transient AnalysisMohd A IshakPas encore d'évaluation
- Inverter Mode of OperationDocument31 pagesInverter Mode of OperationMichael Adu-boahenPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages of Matrix Over CycloconvertersDocument46 pagesAdvantages of Matrix Over CycloconvertersnazaahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ac Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V FDocument6 pagesAc Voltage Controllers: V Variable AC RMS O/P Voltage AC Input Voltage F V Fcr_neethishPas encore d'évaluation
- Thyristor Converters or Controlled Converters: (1) Power CircuitDocument55 pagesThyristor Converters or Controlled Converters: (1) Power CircuitAbdullrahman Al-ShammaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 4 InvertersDocument86 pagesUnit 4 InvertersHaritha RkPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulse-Width-Modulated (PWM) Inverter : Chapter 10 (Or 6) PDocument35 pagesPulse-Width-Modulated (PWM) Inverter : Chapter 10 (Or 6) PM.h. SawonPas encore d'évaluation
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1D'EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (3)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetD'EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetPas encore d'évaluation
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorD'Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1D'EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Évaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (3)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsD'EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsPas encore d'évaluation
- FDP at NBADocument2 pagesFDP at NBAherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of ExperimentsDocument1 pageList of Experimentsherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Research Promotion Scheme (RPS)Document6 pagesResearch Promotion Scheme (RPS)herokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Attendance DilyDocument17 pagesAttendance Dilyherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- OutlineDocument18 pagesOutlineherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- 19th Exam ProspectusDocument28 pages19th Exam Prospectusherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revised PG PH.D Curriculam PDFDocument239 pagesRevised PG PH.D Curriculam PDFherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- T-29 A FormDocument14 pagesT-29 A Formherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Orthogonal Space-Time Block Coding Over Time-Selective Fading Channels: A PIC Detector For The SystemsDocument5 pagesOrthogonal Space-Time Block Coding Over Time-Selective Fading Channels: A PIC Detector For The Systemsherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Green Energy: The Energy of Universe: 1. AbstractDocument1 pageGreen Energy: The Energy of Universe: 1. Abstractherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- $ 1ryho 8solqn 5hfhlyhu Iru 60 (' (6/Vwhpv ZLWK 2uwkrjrqdo 6xe &kdqqho) HdwxuhDocument5 pages$ 1ryho 8solqn 5hfhlyhu Iru 60 (' (6/Vwhpv ZLWK 2uwkrjrqdo 6xe &kdqqho) Hdwxuhherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ncpeic Conference 5 RevDocument2 pagesNcpeic Conference 5 Revherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Particle Swarm Optimization-Based RBF Neural Network Load Forecasting ModelDocument4 pagesParticle Swarm Optimization-Based RBF Neural Network Load Forecasting Modelherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bhel ReportDocument25 pagesBhel Reportherokaboss1987Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9702 w09 QP 11Document24 pages9702 w09 QP 11YaseenTamerPas encore d'évaluation
- GIS RC Voltage DividerDocument6 pagesGIS RC Voltage DividerEldin EnggPas encore d'évaluation
- Helicopter Flying AND Ground Handling Qualities General Requirements FORDocument14 pagesHelicopter Flying AND Ground Handling Qualities General Requirements FORrashidtajarPas encore d'évaluation
- UE Vs E CablesDocument2 pagesUE Vs E CablesKrishnan KrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipho 1989-1994Document190 pagesIpho 1989-1994ais3000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Design of AbutmentDocument47 pagesDesign of AbutmentRaju Ranjan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CRKT 2 Module 1 Complex and AC CiruitDocument62 pagesCRKT 2 Module 1 Complex and AC CiruitArlie Laica BascoPas encore d'évaluation
- High Voltage Experimenters HandbookDocument219 pagesHigh Voltage Experimenters HandbookreconxPas encore d'évaluation
- Friction - Engineering Mechanics Questions and AnswersDocument7 pagesFriction - Engineering Mechanics Questions and AnswersAmit Kumar Sharma100% (1)
- 04504772-Standardization of Benchmarks For Protective Device Time-Current CurvesDocument11 pages04504772-Standardization of Benchmarks For Protective Device Time-Current CurvesDar Win100% (1)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/COMP March 2021Document13 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Physics 9702/COMP March 2021Osama Mehmood TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 7482,597 B2Document22 pagesUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 7482,597 B2JustaUser2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering PhysicsDocument33 pagesEngineering PhysicsLeony PanjaitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Mechanism of EDM ProcessDocument9 pagesProcess Mechanism of EDM ProcessdongreganeshPas encore d'évaluation
- June 2021 QP - Paper 2 (F) Edexcel Physics GCSEDocument36 pagesJune 2021 QP - Paper 2 (F) Edexcel Physics GCSErayanahmed00123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Formula SheetDocument4 pagesPhysics Formula SheetJeriekoNoznomPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Equipment Presentation CVT AND VFDDocument14 pagesElectrical Equipment Presentation CVT AND VFDKevin Areja CalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Report On WitricityDocument27 pagesSeminar Report On WitricityNITIKA KULVIPas encore d'évaluation
- Mock Test - 1: (Physics)Document29 pagesMock Test - 1: (Physics)kalloliPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrodynamic Couplings and ConvertersDocument16 pagesHydrodynamic Couplings and ConvertersMohan RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Body in Motion Study NotesDocument5 pagesBody in Motion Study NotesAlan VanPas encore d'évaluation
- Catia - FeaDocument240 pagesCatia - FeaFrancescPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficiency of Slopes and Pulleys - TeacherDocument2 pagesEfficiency of Slopes and Pulleys - TeacherAdam ChiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Statics (Exercises Included)Document10 pagesFluid Statics (Exercises Included)Varun RoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Circuit CalculationDocument46 pagesShort Circuit Calculationratnesh_xp1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dual Stator Winding Induction Machine - Problems, Progress, and Future Scope PDFDocument12 pagesDual Stator Winding Induction Machine - Problems, Progress, and Future Scope PDFTaiwoPas encore d'évaluation
- TG 1.1552 Chap 5-7Document2 pagesTG 1.1552 Chap 5-7GIRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Ship Vibration PDFDocument14 pagesShip Vibration PDFdewiPas encore d'évaluation
- DPWM PDFDocument6 pagesDPWM PDFhieuhuech1100% (1)