Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture National Airspace System (USA)
Transféré par
kennedyjuliusTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lecture National Airspace System (USA)
Transféré par
kennedyjuliusDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
National Airspace System (USA)
By 1930s, a network of ground station had been completed. A-N ranges were mainly for en route navigation and homing beacons. DC-3 was the most modern aircraft equipped with:
-Direction finding receiver for homing beacons.
- A low frequency receiver for A-N range and communication.
A-N range and homing beacons have several problems:
Frequencies used are affected by variety of atmospheric conditions; electrical noise from lightning strokes and precipitation static (Pstatic) course by ice crystal. Low frequency signals are degraded by atmospheric propagation
The wave not only travel in straight lines along the surface of the earth but bounce off the ionosphere. The reflected signal (sky wave) interfere with ground wave.
ADF Antenna
Beginning WW2, enhance network of radio beacons for air navigation were use but lacking the precision and versatility for military operation. Radar was developed to detect targets. Secondary radar for determining target identity. IFF (Identification friend or foe) scheme is still in use.
In civil use, Secondary radar is used to display aircraft altitude, enabling radar to depict an aircraft position in 3D. The civil system is known as the Air Traffic Control Radar Beacon System. During WW2, lacking in landing navigation aid has led to VHF system capable of providing a large number of services.
VOR: To provide range
Localizer: landing horizontal guidance.
UHF frequency range was used to develop system for providing glide slope during landing. Localizer, Glide Slope and ancillary equipment are called the ILS (Instrument Landing System). 1947, International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) was formed and adopted ILS and VOR as en route, approach and landing system for world.
Communication evolved during WW2, from HF to VHF system. Long Range Navigation (LORAN) was develop during WW2, but early system was slow and cumbersome and intended for ship. A later version, LORAN-C, is used extensively on aircraft.
1950 1970 was a time of technology development in both aircraft and electronics
1950s to the late 80s saw tremendous advances in electronics, beginning with the transistor, followed by the integrated circuit.
Key to miniaturization and development of microprocessor.
Regulatory and Advisory Agencies (USA)
International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO)
Under the administration of UN Headquartered in Montreal, Canada Most worlds countries are member of ICAO
Agree to implement recommendations put forth by the organization.
Malaysia is a member country. Non member country will find it difficult convincing airline to service their country.
ICAO covers all phase of aviation.
e.g. ICAO Annex 14 describes airport characteristic, specifying the size and shape of runways
It is no coincidence that every runway looks much the same.
ICAO annex 10 regulates radio navigation aids and communication, insuring that signals from ground stations or satellites are compatible in every part of the world
ICAO can only make recommendation, known as Standards and Recommended Practices SARPS.
FAA: Federal Aviation Administration
Agency responsible for regulating aviation safety in the US. In Malaysia we have Department of Civil Aviation (DCA) under the administration of The Ministry of Transport.
FAA / DCA write and enforces regulations for many phase of private and commercial aviation.
All written regulations in the US are contained in Title 14 of the Code of Federal Regulation (CFR). Cover:
The design and manufacturing of aircraft Testing and licensing of Pilots Mechanics and Air Traffic Controller Testing and Certification of aircraft.
Similar code also exist in Malaysia under the supervision of DCA
FCC: Federal Communication Commission.
Responsible for the orderly operation of communications within the US.
Malaysian Communications & Multimedia Commission (MCMC).
Under the purview of Ministry of Energy, Communications and Multimedia. In Malaysia, the Communications and Multimedia Act (CMA) 1998 is the main legislation that regulate the converging communications and multimedia industries
The Commission is given the power to regulates the communication and multimedia industries through the CMA.
ITU: International Telecommunication Union is the international advisory organization for communication. Based in Geneva, Switzerland MCMC is responsible for the orderly operation of communication in Malaysia
RTCA: Requirement and Technical Concepts in Aviation.
An organization started in 1935 as Radio Technical Commission for Aviation. An advisory committee to FAA. A non-profit making organization, supported by dues of members, which include avionics manufacturers, airlines, military, universities and interested individuals.
Most RTCA activity occurs in special Committee, often requested by FAA. E.g. in 1992, FAA requested RTCA to form a special committee (designated as SC-177) to conduct an investigation about incidents of interference from portable electronic devices carried aboard aircraft.
Document produce SC-177 : DO-233
RTCA provide important information to FAA in area such as:
Minimum Operation Performance Standards (MOPS) The standards produced were the basis of Technical Standard Order (TSO) issued by FAA
ARINC: Aeronautical Radio Incorporated
A non-profit making organization owned by U.S. air carrier Provide services to airlines, mainly the operation of a private air-ground communications system called the Aeronautical Telecommunications Network (ATN). Company communications not handled by FAA such as departure and arrival times, maintenance information, crew and passenger data, provision, gate assignments and so on.
Second function of ARINC is generating avionics standards and research. ARINC standards cover more than basic operating parameter such as physical dimensions, connector description, pin numbers and signal definitions. These standard known as ARINC Characteristic, describe the form, fit and function for airline avionics.
Sufficient detail is provided in the document so an avionics unit made by one manufacturer can plug in and replace a unit of another brand.
This does not mean the inner circuits of the box are the same. Equipment meeting ARINC Characteristics are primarily line replaceable unit (LRU)
Current technology in cockpit instrumentations
Cessna 172
Boeing B737-800
In US, the National Airspace System, (NAS), consists of navigation aid, air traffic control, surveillance radar, pilot advisories and other services. Components of NAS are provided by FAA. In Malaysia similar set-up exist and provided by DCA
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Base Station Antenna: HXHM4X6B2124032T06Document1 pageBase Station Antenna: HXHM4X6B2124032T06ИгорьPas encore d'évaluation
- ADU451503Document2 pagesADU451503Raluca Roxana SzaszPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulation of Multipath Fading Channels Using Rayleigh Model and Its Behaviour For Different Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument5 pagesSimulation of Multipath Fading Channels Using Rayleigh Model and Its Behaviour For Different Digital Modulation Techniquesnirikshith pPas encore d'évaluation
- Glosario InstrumentosDocument4 pagesGlosario InstrumentosmateoPas encore d'évaluation
- Jma-5212-4/6 Jma-5212-4/6 Jma-5222-7/9 Jma-5222-7/9 Jma-5212-4hs/6hs Jma-5212-4hs/6hsDocument172 pagesJma-5212-4/6 Jma-5212-4/6 Jma-5222-7/9 Jma-5222-7/9 Jma-5212-4hs/6hs Jma-5212-4hs/6hsjaliltaghdarehPas encore d'évaluation
- Prestta P822601 P822602 Standard Cellular Octa Band 20160904Document3 pagesPrestta P822601 P822602 Standard Cellular Octa Band 20160904AjaySoniPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF Manual de Manutenao Tad1344ge DLDocument84 pagesPDF Manual de Manutenao Tad1344ge DLStop RUSH100% (1)
- 18airborne Collision Avoidance SystemDocument22 pages18airborne Collision Avoidance SystemArif HbkPas encore d'évaluation
- 9955 V6.9 RN Ed.03Document96 pages9955 V6.9 RN Ed.03evrammPas encore d'évaluation
- FM DemodulationDocument2 pagesFM DemodulationAlzonne Mark ManansalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimization of Digital Beamforming For Smart AnteDocument119 pagesOptimization of Digital Beamforming For Smart AntedsnPas encore d'évaluation
- Drive Test and Radio Optimization For UMTS - GSM NetworksDocument13 pagesDrive Test and Radio Optimization For UMTS - GSM NetworkssingsanitPas encore d'évaluation
- 1-Port Omni Exposed Dipole Antenna, 150-160 MHZ, 360° HPBW, Fixed Electrical TiltDocument2 pages1-Port Omni Exposed Dipole Antenna, 150-160 MHZ, 360° HPBW, Fixed Electrical TiltMaurizio De MarchisPas encore d'évaluation
- MTR2000 Spec SheetDocument2 pagesMTR2000 Spec SheetwanradPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece153 Handout RF Hardware ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesEce153 Handout RF Hardware ConsiderationsMico Francis de LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ic 84Document5 pagesIc 84Mrinal MitraPas encore d'évaluation
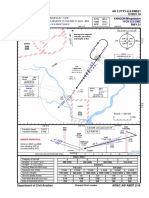
- Vyyy Ilsdme21 Airac 2016 02 PDFDocument1 pageVyyy Ilsdme21 Airac 2016 02 PDFWIN MINPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Barring (RAN15.0 02)Document51 pagesCell Barring (RAN15.0 02)hekriPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Microwave Communi Cation Principles: Security Level:INTERNALDocument113 pagesDigital Microwave Communi Cation Principles: Security Level:INTERNALedwin sama100% (1)
- Wireless Remote Control: Instruction ManualDocument20 pagesWireless Remote Control: Instruction ManualLuis Otavio TrindadePas encore d'évaluation
- Gojan School of Business and Technology Satellite Communication Important Questions Part-A UNIT-1Document3 pagesGojan School of Business and Technology Satellite Communication Important Questions Part-A UNIT-1Dharani KumarPas encore d'évaluation
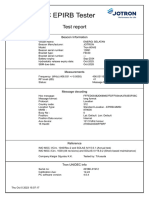
- JOTRON Tron 60AIS 13891Document1 pageJOTRON Tron 60AIS 13891marine f.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Putian Antenna SpecificationDocument109 pagesPutian Antenna SpecificationMukesh Jung Thapa100% (1)
- Satellite Network Designers GuideDocument75 pagesSatellite Network Designers GuideTariq EhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- 60 GHZDocument9 pages60 GHZjackofmanytradesPas encore d'évaluation
- B.Tech III Year I Semester (R15) Supplementary Examinations June 2018Document1 pageB.Tech III Year I Semester (R15) Supplementary Examinations June 2018Crypto ChaserPas encore d'évaluation
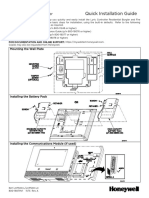
- Lyric Controller Quick Install GuideDocument4 pagesLyric Controller Quick Install GuideAlarm Grid Home Security and Alarm MonitoringPas encore d'évaluation
- WDC Assignment-1Document3 pagesWDC Assignment-1SAI KUMAR N,CSE 16 Vel Tech, ChennaiPas encore d'évaluation
- We Are Going On A Bear HuntDocument4 pagesWe Are Going On A Bear HuntSladjana KomacPas encore d'évaluation
- Baofeng Uv 5rDocument9 pagesBaofeng Uv 5rljnjombangPas encore d'évaluation