Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Switch & Hub
Transféré par
gaurav_juneja_4Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Switch & Hub
Transféré par
gaurav_juneja_4Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
ARP Address Resolution Protocol ARP works by broadcasting packets to all hosts attached to the LAN ARP packet contains IP address in which sender is interested in communicating with hosts keep a list of
ARP responses in an ARP table
ARP is propagated through Bridges/Switches but not through Routers
2
1.1 wants to send the data to 1.3
192.168.1.4 00-20-18-C0-07-74
ource MAC Source IP -18-C0-07-71 192.168.1.1 Segment
ination MAC Destination IP -18-C0-07-73192.168.2.1
192.168.1.1 00-20-18-C0-07-71
192.168.1.3 00-20-18-C0-07-73
192.168.1.2 00-20-18-C0-07-72
Data Encapsulation & De-capsulation
192.168.1.1 00-20-18-C0-07-71
Application Presentation
Data
Data
Session
Transport Network
Data
TH Data Segment
Packet Segment NH Packet DHFrame DT Bits
Data Link
Physical
Data Encapsulation & De-capsulation
192.168.1.1 00-20-18-C0-07-71
Application Presentation
Data
Data
Session
Transport Network
Data
TH Data Segment
Data Link
Physical
Hub It is a Physical layer device (Layer 1) It is Dummy Device It works with 0s and 1s (Bits)
It works with broadcasting
It works with shared bandwidth It is has 1 Broadcast Domain and 1 Collision Domain Collisions are identified using Access Methods called CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA
Broadcast Domain & Collision Domain
Broadcast Domain Set of all devices that receive broadcast frames originating from any device within the set. Collision domain
In Ethernet, the network area within which frames that
have collided are propagated is called a collision domain. Repeaters and hubs propagate collisions, LAN switches, bridges, and routers do not.
7
Types of Hubs Active Hubs uses power supply and regenerates the data (i.e.) strengthens the signals in case of disturbances. Passive Hubs doesnt use power supply and it will not not regenerates the data (i.e.) strengthens the signals in case of disturbances. It is used only to share the physical media Intelligent Hubs are sometimes called as smart hubs. These devices basically function as active hubs, but also include a microprocessor chip and diagnostic capabilities
and are useful in troubleshooting situations.
8
Switch It is Datalink layer device (Layer 2) Its is An Intelligent device It works with Physical addresses (i.e. MAC addresses)
It works with fixed bandwidth
It works with Flooding and Unicast It has 1 Broadcast domain and Number of Collision domains depends upon the number of ports. It maintains a MAC address table
Types of Switches
Manageable switches On a Manageable switch an IP address can be assigned and configurations can be made. It has a console port .
Unmanageable switches On an Unmanageable switch configurations cannot be made, an IP address cannot be assigned as there is no console port.
10
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Ethernet ManualDocument44 pagesEthernet ManualstridertheviperPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Semester 1: Layer 3 ProtocolsDocument65 pagesCCNA Semester 1: Layer 3 ProtocolsTung HoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Hardware Essentials Chapter: Repeaters, Hubs, Switches, Wireless APs & NICsDocument12 pagesNetwork Hardware Essentials Chapter: Repeaters, Hubs, Switches, Wireless APs & NICsTrynaBeGreatPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Hardware Essentials Chapter: Repeaters, Hubs, Switches, Wireless APs & NICsDocument12 pagesNetwork Hardware Essentials Chapter: Repeaters, Hubs, Switches, Wireless APs & NICsTrynaBeGreatPas encore d'évaluation
- Mobile Technologies SummaryDocument55 pagesMobile Technologies SummarynsbirariPas encore d'évaluation
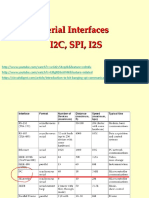
- Serial Communication Protocols part 2: I2C and SPI Protocols ExplainedDocument26 pagesSerial Communication Protocols part 2: I2C and SPI Protocols ExplainednobodyPas encore d'évaluation
- CN LAB EXPT 4 TO 9 (2)Document22 pagesCN LAB EXPT 4 TO 9 (2)Tanusha handePas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT III Network Layer DeviceDocument20 pagesUNIT III Network Layer DeviceHOD-DIT PSG-PTCPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication DevicesDocument22 pagesCommunication Deviceshadirehman488Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networking 2Document25 pagesComputer Networking 2Jermyn G EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computernetworking 130909043556Document117 pagesComputernetworking 130909043556Jermyn G EvangelistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication InterfaceDocument45 pagesCommunication Interfaceprabhabathi devi100% (1)
- Lec 15networking DevicesDocument33 pagesLec 15networking DevicesJyoti SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Serial Interfaces I2C, Spi, I2SDocument37 pagesSerial Interfaces I2C, Spi, I2Seugen lupu100% (2)
- Options With Highlight Colours Are Correct Answer: - Destination Network AddressDocument4 pagesOptions With Highlight Colours Are Correct Answer: - Destination Network Addressmerengues9000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practical - 1: Aim: - Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorDocument7 pagesPractical - 1: Aim: - Introduction To 8085 MicroprocessorMandy745Pas encore d'évaluation
- 07 NetworkingConceptsDocument53 pages07 NetworkingConceptsPrasad GantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch.9 Static and Dynamic RoutingDocument27 pagesCh.9 Static and Dynamic Routingvictorbittar29Pas encore d'évaluation
- STM32F3 UsartDocument67 pagesSTM32F3 UsartZarija Aleksoski100% (1)
- COIT11238-Week03-V23S3 - JH T3 2023Document39 pagesCOIT11238-Week03-V23S3 - JH T3 2023Rahul DasPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Ethernet Switching BasicsDocument38 pages07 Ethernet Switching BasicsAdeyemiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sybex CCNA 640-802 Chapter 02Document21 pagesSybex CCNA 640-802 Chapter 02xkerberosxPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Multitasking Real-Time ComputingDocument3 pagesComputer Multitasking Real-Time ComputingAlazar DInberuPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet MODM7AE70 100 200IRDocument13 pagesDatasheet MODM7AE70 100 200IRBenny LangstonPas encore d'évaluation
- LAN Et VLAN TutorialDocument50 pagesLAN Et VLAN TutorialChristian HahnPas encore d'évaluation
- Program: - 1 Aim: To Study Various Networking Components. Major Computer Network ComponentsDocument11 pagesProgram: - 1 Aim: To Study Various Networking Components. Major Computer Network ComponentsSandip MouryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction The Serial Communications: Parallel Data TransferDocument20 pagesIntroduction The Serial Communications: Parallel Data Transferisrat jahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Subnet Mask That Should Be Assigned To Routes That Are Learned From Neighboring Classless Routers?Document16 pagesSubnet Mask That Should Be Assigned To Routes That Are Learned From Neighboring Classless Routers?Kinga JanasińskaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter-1-LAN BasicsDocument19 pagesChapter-1-LAN BasicsFaizan JavedPas encore d'évaluation
- Ccna Class 3Document135 pagesCcna Class 3ntimamaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pin Diagram and Functions of 8085 MicroprocessorDocument87 pagesPin Diagram and Functions of 8085 MicroprocessorRohan VaidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networks: Topics To Be CoveredDocument65 pagesComputer Networks: Topics To Be CoveredSaravanan NallusamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Devices and Communication Buses For Devices NetworkDocument211 pagesDevices and Communication Buses For Devices NetworkDhrumeet PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Devices ExplainedDocument20 pagesNetwork Devices Explainedsanamsuri369Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exercise 01 LABDocument7 pagesLab Exercise 01 LABFareen BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- IP Networks: Nasir Majeed Manager (Certification) Cisco Academy Support Centre (ASC) PTCL AcademyDocument41 pagesIP Networks: Nasir Majeed Manager (Certification) Cisco Academy Support Centre (ASC) PTCL AcademyMuhammad AsifPas encore d'évaluation
- ModemDocument24 pagesModemHrithik ReignsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sybex CCNA 640-802: Chapter 1: Connectivity DeviceDocument29 pagesSybex CCNA 640-802: Chapter 1: Connectivity DeviceIsrael KiflePas encore d'évaluation
- IOT UNIT 2 Part 2Document34 pagesIOT UNIT 2 Part 2Hdurjriro3k DirrkrjriPas encore d'évaluation
- LESSON 1 Understanding Network DevicesDocument24 pagesLESSON 1 Understanding Network DevicesLeo Walican AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 - Redundancia Con HSRP-VRRP-GLBPDocument48 pages7 - Redundancia Con HSRP-VRRP-GLBPMiltonXavierOrdoñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Interfacing MCDocument57 pagesInterfacing MCMaha DevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Internetworking Devices: Izaz A KhanDocument28 pagesInternetworking Devices: Izaz A KhanWaqas GhaffariPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To Networking Essentials, 6 Edition: Chapter 2: Network Hardware EssentialsDocument44 pagesGuide To Networking Essentials, 6 Edition: Chapter 2: Network Hardware EssentialsDcs JohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Motorola MC68000Document33 pagesMotorola MC68000havocPas encore d'évaluation
- SDA - Serial Data, SCL - Serial ClockDocument10 pagesSDA - Serial Data, SCL - Serial ClockPavan Kulkarni100% (3)
- IoT-Lecture-11 - Networking and Communication - IVDocument19 pagesIoT-Lecture-11 - Networking and Communication - IVARNAV JAINPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Serial Data CommunicationDocument32 pagesIntroduction To Serial Data CommunicationVickyPas encore d'évaluation
- l3 - Part 2 - Computer Buses - v22Document35 pagesl3 - Part 2 - Computer Buses - v22Pham Xuan ThuyPas encore d'évaluation
- Serial Interfaces, Part Deux C and SPI: December 4, 2002 Presented by Eugene HoDocument18 pagesSerial Interfaces, Part Deux C and SPI: December 4, 2002 Presented by Eugene HoPronadeep BoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networks Lab ManualDocument61 pagesComputer Networks Lab Manualjenisha100% (2)
- Tutorial 3 2 2022-2023 AnswerDocument5 pagesTutorial 3 2 2022-2023 AnswerZam SkemaPas encore d'évaluation
- iiot notesDocument14 pagesiiot noteswagoyey799Pas encore d'évaluation
- Need For Communication Interfaces: Why Are Communication Interfaces Required in Embedded SystemsDocument76 pagesNeed For Communication Interfaces: Why Are Communication Interfaces Required in Embedded SystemsAcharya SuyogPas encore d'évaluation
- Arm I2cDocument25 pagesArm I2cNarendra SvPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Rev Road RaggingDocument22 pages1st Rev Road RaggingElamaruthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Network ComponentsDocument18 pagesComputer Network ComponentsLittle bit SpicyPas encore d'évaluation
- I2C/SPI Host Adapter.Document63 pagesI2C/SPI Host Adapter.sruiz7100% (2)
- ICND1 Cisco Study NotesDocument52 pagesICND1 Cisco Study NotesmasaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Data Acquisition for Instrumentation and Control SystemsD'EverandPractical Data Acquisition for Instrumentation and Control SystemsPas encore d'évaluation
- 16100lectre39 CJDocument3 pages16100lectre39 CJefe_011Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 ICAO EUROCONTROL RTCA BiggsDocument12 pages2.1 ICAO EUROCONTROL RTCA BiggsvinaysulePas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Start Guide 2015Document1 pageQuick Start Guide 2015aishwaryaPas encore d'évaluation
- How Bits and Bytes WorkDocument7 pagesHow Bits and Bytes Workapi-19737301Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Jet Propulsion: Strong and Reliable Muscles For The AircraftDocument22 pagesIntroduction To Jet Propulsion: Strong and Reliable Muscles For The Aircraftgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Communication Signals & Systems OverviewDocument221 pagesDigital Communication Signals & Systems Overviewgaurav_juneja_4100% (1)
- Assignment Problem: Ans:e (3cos 3t - 5sin3t)Document3 pagesAssignment Problem: Ans:e (3cos 3t - 5sin3t)gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Literacy Project: PMJDY, Loans, Savings & Banking ServicesDocument7 pagesFinancial Literacy Project: PMJDY, Loans, Savings & Banking Servicesgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Freq Mod - 8Document127 pagesFreq Mod - 8gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Modulation TechDocument63 pagesDigital Modulation Techgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Signal Representation & Analysis IntroductionDocument21 pagesSignal Representation & Analysis Introductiongaurav_juneja_40% (1)
- History of Optical Storage MediaDocument56 pagesHistory of Optical Storage Mediagaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier Transform Definition and Key FunctionsDocument8 pagesFourier Transform Definition and Key Functionsgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier Transform PropertieZsDocument13 pagesFourier Transform PropertieZsgaurav_juneja_4100% (1)
- Filter 2Document18 pagesFilter 2gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Look-Up Table: Solving Differential EquationsDocument10 pagesLook-Up Table: Solving Differential Equationsgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fourier Theory Made Easy (?)Document30 pagesFourier Theory Made Easy (?)gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 2Document13 pagesPresentation 2gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Part 1Document12 pagesChapter 10 Part 1gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- MicrowavesDocument26 pagesMicrowavesgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Power Divider, Combiner and CouplerDocument60 pagesPower Divider, Combiner and Couplergaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analogy BW Vector ND SignalsDocument7 pagesAnalogy BW Vector ND Signalsgaurav_juneja_450% (2)
- Sampling TheoremDocument34 pagesSampling Theoremgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Communication Systems by Taub & SchillingDocument119 pagesPrinciples of Communication Systems by Taub & SchillingInsane Clown Prince40% (5)
- Catalyst Switch OperationsDocument61 pagesCatalyst Switch Operationsgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- B P Lathi - Modern Digital and Analog Communication SystemsDocument400 pagesB P Lathi - Modern Digital and Analog Communication Systemsnnn100% (1)
- Catalyst Switch OperationsDocument61 pagesCatalyst Switch Operationsgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day07 3Document8 pagesDay07 3gaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- SwitchDocument21 pagesSwitchgaurav_juneja_4Pas encore d'évaluation
- CPT105 Final Exam Revision Term1 2013 With AnswersDocument6 pagesCPT105 Final Exam Revision Term1 2013 With Answersmnx4everPas encore d'évaluation
- Macbook Pro 15-Inch Repair GuideDocument22 pagesMacbook Pro 15-Inch Repair GuideLance100% (1)
- R44 Maintenance Manual Chapter 1 IntroductionDocument60 pagesR44 Maintenance Manual Chapter 1 IntroductionLoki WartoothPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Partition ManagerDocument58 pagesVirtual Partition ManagerAdam Ben AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Fall 2019/20 - Lecture Notes # 5: - Flag Registers and Bit FieldsDocument10 pagesFall 2019/20 - Lecture Notes # 5: - Flag Registers and Bit FieldsHifsah NasirPas encore d'évaluation
- 5717-Datasheet-8Zone - LAN - Expander 2Document2 pages5717-Datasheet-8Zone - LAN - Expander 2Iain PerriePas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Switch Configuration Guide With ExamplesDocument11 pagesBasic Switch Configuration Guide With ExamplesasalihovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Avocent Vertiv 18.5 Rack Console - BrosuraDocument4 pagesAvocent Vertiv 18.5 Rack Console - BrosuraMarius SimonPas encore d'évaluation
- HP ProLiant ML110 G7 DatasheetDocument4 pagesHP ProLiant ML110 G7 DatasheetDeepak Gupta (DG)Pas encore d'évaluation
- RobotStudio 2023-1 Release NotesDocument34 pagesRobotStudio 2023-1 Release Notesduy.nguyen.2501Pas encore d'évaluation
- PSP Game ListDocument4 pagesPSP Game ListFaisal KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- VATS Bypass ModuleDocument3 pagesVATS Bypass ModuleSHOOTEEPas encore d'évaluation
- Security Considerations For Ipv6 NetworksDocument50 pagesSecurity Considerations For Ipv6 NetworkserratixPas encore d'évaluation
- DS2431 PDFDocument27 pagesDS2431 PDFscribd2827Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thin Clients DOCU V13 enDocument76 pagesThin Clients DOCU V13 ennew2trackPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual Panasonic Ny MDDocument3 pagesManual Panasonic Ny MDPopescu IonutPas encore d'évaluation
- Monica AN24 Vs BrochureDocument4 pagesMonica AN24 Vs Brochurehablando0% (1)
- Technical Seminar: Electrocardiograph (ECG) Ecg-K Ecg- K・ECG- KDocument60 pagesTechnical Seminar: Electrocardiograph (ECG) Ecg-K Ecg- K・ECG- Kchanlal0% (1)
- IoulistDocument4 pagesIoulisthaji85Pas encore d'évaluation
- Leaflet WL10Document2 pagesLeaflet WL10Bogdan MohoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pds PB Function 2013Document49 pagesPds PB Function 2013Virendra SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Frame Relay TutorialDocument9 pagesFrame Relay TutorialplanifikuesiPas encore d'évaluation
- Installation Manual - OPGW Tension SetDocument3 pagesInstallation Manual - OPGW Tension Sethcindustry100% (2)
- Components of A Computer - Information Technology and CommunicationDocument7 pagesComponents of A Computer - Information Technology and CommunicationDarryl John PasambaPas encore d'évaluation
- HP DesignJet T830Document2 pagesHP DesignJet T830wort85Pas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Modul 11Document8 pagesCCNA Modul 11Hery Tjah KakoiPas encore d'évaluation
- IoT Based Smart Currency Counter Using NodeMCUDocument47 pagesIoT Based Smart Currency Counter Using NodeMCUprabhu rachuti100% (1)
- Dgca Module 07 Part 08Document19 pagesDgca Module 07 Part 08iftiPas encore d'évaluation
- Workshop Manual Ibiza SC TrophyDocument29 pagesWorkshop Manual Ibiza SC Trophysalekojic53320% (1)