Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Moment of Inertia Defined
Transféré par
Bala SubramanianDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Moment of Inertia Defined
Transféré par
Bala SubramanianDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Moment of Inertia
Moment of Inertia Defined
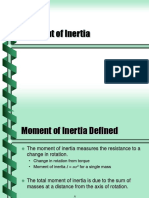
The moment of inertia measures the resistance to a change in rotation.
Change in rotation from torque Moment of inertia I = mr2 for a single mass
The total moment of inertia is due to the sum of masses at a distance from the axis of rotation.
I mi ri 2
i 1
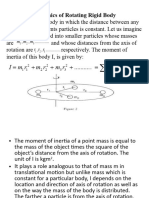
Two Spheres
A spun baton has a moment of inertia due to each separate mass.
I = mr2 + mr2 = 2mr2
If it spins around one end, only the far mass counts.
I = m(2r)2 = 4mr2
Mass at a Radius
Extended objects can be treated as a sum of small masses. A straight rod (M) is a set of identical masses Dm.
distance r to r+Dr
The total moment of inertia is
I (Dm)r
2
Each mass element contributes Dm ( M / L)Dr
I ( M / L) r 2 Dr The sum becomes an integral
length L axis
I ( M / L) r 2 dr
0
I ( M / L)(L3 / 3) (1 / 3) ML2
Rigid Body Rotation
The moments of inertia for many shapes can found by integration.
Ring or hollow cylinder: I = MR2 Solid cylinder: I = (1/2) MR2 Hollow sphere: I = (2/3) MR2 Solid sphere: I = (2/5) MR2
Point and Ring
The point mass, ring and hollow cylinder all have the same moment of inertia.
I = MR2
The rod and rectangular plate also have the same moment of inertia.
I = (1/3) MR2
All the mass is equally far away from the axis.
R M R M
The distribution of mass from the axis is the same.
M
M length R axis length R
Playground Ride
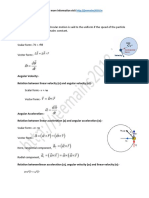
A child of 180 N sits at the edge of a merry-go-round with radius 2.0 m and mass 160 kg. What is the moment of inertia, including the child?
Assume the merry-go-round is a disk.
Id = (1/2)Mr2 = 320 kg m2
Treat the child as a point mass.
W = mg, m = W/g = 18 kg. Ic = mr2 = 72 kg m2
m r M
The total moment of inertia is the sum.
I = Id + Ic = 390 kg m2
Parallel Axis Theorem
Some objects dont rotate about the axis at the center of mass. The moment of inertia depends on the distance between axes.
The moment of inertia for a rod about its center of mass:
h = R/2
M axis
I I CM Mh 2
(1 / 3) MR 2 I CM M ( R / 2) 2 I CM (1 / 3) MR 2 (1 / 4) MR 2 I CM (1 / 12 ) MR 2
Perpendicular Axis Theorem
Iy = (1/12) Ma2
Ix = (1/12) Mb2 M a
For flat objects the rotational moment of inertia of the axes in the plane is related to the moment of inertia perpendicular to the plane.
Iz Ix Iy
Iz = (1/12) M(a2 + b2)
Spinning Coin
What is the moment of inertia of a coin of mass M and radius R spinning on one edge?
The moment of inertia of a spinning disk perpendicular to the plane is known.
Id = (1/2) MR2
R
Id
The disk has two equal axes in the plane. The perpendicular axis theorem links these.
Id = Ie + Ie = (1/2) MR2 Ie = (1/4) MR2
Ie
next
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Moment of InertiaDocument10 pagesMoment of Inertiatr925Pas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia FormulaDocument10 pagesMoment of Inertia Formulasubbu2051Pas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of InertiaDocument10 pagesMoment of InertiaRavikumarPas encore d'évaluation
- SDGDG 07 CDocument10 pagesSDGDG 07 CgowthamAG07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of InertiaDocument10 pagesMoment of InertiaIipo Chennai100% (1)
- Moment of InertiaDocument10 pagesMoment of InertiasenthilcaePas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia-1Document10 pagesMoment of Inertia-1senthilcaePas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia ExplainedDocument10 pagesMoment of Inertia ExplainedsenthilcaePas encore d'évaluation
- Parul Institute of Engineering & Technology: Civil DepartmentDocument11 pagesParul Institute of Engineering & Technology: Civil Departmenttanim sheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - Moment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects (Solved Examples)Document18 pages03 - Moment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects (Solved Examples)upfaupPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 2 Moment of Inertia PDFDocument14 pages08 2 Moment of Inertia PDFReddyvari VenugopalPas encore d'évaluation
- ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PPT-3Document33 pagesROTATIONAL DYNAMICS PPT-3Sangamesh UpsPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia and Friction: September 2014Document25 pagesMoment of Inertia and Friction: September 2014Bee Mah LessPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects (Solved Examples)Document19 pagesMoment of Inertia - Formulas, MOI of Objects (Solved Examples)Manish Kushwaha100% (1)
- Mechanics of Materials - 2Document35 pagesMechanics of Materials - 2awanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational Dynamics (11th P) (Egnlish) - WADocument44 pagesRotational Dynamics (11th P) (Egnlish) - WASwarnlata MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Reminders: and Dynamics) - Questions!)Document24 pagesReminders: and Dynamics) - Questions!)Bosco BeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia Concepts ExplainedDocument6 pagesMoment of Inertia Concepts ExplainedsridharPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational DynamicsDocument17 pagesRotational Dynamicssanits591Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Turning Movement of a Particle About the Axis of Rotation is Called the Angular Momentum of the Particle and is Measured by the Product of the Linear Momentum and the Perpendicular Distance of the Line of Action From the AxDocument24 pagesThe Turning Movement of a Particle About the Axis of Rotation is Called the Angular Momentum of the Particle and is Measured by the Product of the Linear Momentum and the Perpendicular Distance of the Line of Action From the AxSURAJ MAHATOPas encore d'évaluation
- MechanicsDocument1 pageMechanicsz_eguyPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotation and Moment of Inertia ProblemsDocument1 pageRotation and Moment of Inertia ProblemsMinee's KitchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Rotating Rigid BodyDocument187 pagesDynamics of Rotating Rigid BodyIsrael OluwayomiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotatory Motion: Previous Eamcet QuestionsDocument17 pagesRotatory Motion: Previous Eamcet QuestionsAnonymous LTsNUndPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotation - IIT JEE ExamDocument20 pagesRotation - IIT JEE Examfaizan123khanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotatory Motion Concepts Explained in 30 QuestionsDocument4 pagesRotatory Motion Concepts Explained in 30 QuestionsShiva Ram Prasad Pulagam100% (1)
- Physics: System of Particles & Rotational Motion: Dynamics of Rotational MotionDocument4 pagesPhysics: System of Particles & Rotational Motion: Dynamics of Rotational MotionShashi Shekhar TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational MotionDocument34 pagesRotational Motionwissam riyasPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of Inertia Slides-1Document20 pagesMoment of Inertia Slides-1Thato TumeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Rdynamics PDFDocument14 pagesRdynamics PDFGreen KurimawPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculati Moments of Inertia For Rigid Objects of Different Geometries and Parallel Axis TheoremDocument24 pagesCalculati Moments of Inertia For Rigid Objects of Different Geometries and Parallel Axis TheoremSuci Novira AditianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational MotionDocument23 pagesRotational MotionnithiaashreePas encore d'évaluation
- Amateur Physics For The Amateur Pool Player 1Document27 pagesAmateur Physics For The Amateur Pool Player 1Miguel Angel Luque NietoPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion EquationsDocument11 pagesCircular Motion EquationsA AnuragPas encore d'évaluation
- Rigid Body DynamicsDocument55 pagesRigid Body DynamicsKenn ConsueloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 17Document89 pagesChapter 17thulf100% (2)
- Rolling Motion Chapter SummaryDocument23 pagesRolling Motion Chapter SummaryIbrahim AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational MotionDocument28 pagesRotational MotionVansh AwasthiPas encore d'évaluation
- STR 1 Unit 2Document8 pagesSTR 1 Unit 2Milan SuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Moment of InertiaDocument12 pagesMoment of InertiaI M ThamizachiPas encore d'évaluation
- Center of Mass and Moment of InertiaDocument31 pagesCenter of Mass and Moment of InertiaLakshPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics of RotationDocument10 pagesKinematics of RotationWong SunPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10 Rotation of Rigid BodyDocument22 pagesChapter 10 Rotation of Rigid BodylozzzzzPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational ProblemDocument10 pagesRotational Problemursml12Pas encore d'évaluation
- P1Document2 pagesP1Diễm QuỳnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 Rotational DynamicsDocument52 pagesLecture 7 Rotational DynamicsHashir AwanPas encore d'évaluation
- CLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Phy Target-3 Level-1 Chapter-6 PDFDocument31 pagesCLS JEEAD-19-20 XI Phy Target-3 Level-1 Chapter-6 PDFRupak100% (1)
- Amity University Mumbai: Amity School of Applied SciencesDocument7 pagesAmity University Mumbai: Amity School of Applied ScienceshafsaPas encore d'évaluation
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion Part 2 CH7Document19 pagesSystem of Particles and Rotational Motion Part 2 CH7Rishab SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- PH5151 Engineering Physics RegulationsDocument23 pagesPH5151 Engineering Physics RegulationsSWETHA GPas encore d'évaluation
- PH5151 Engineering Physics Class ScheduleDocument23 pagesPH5151 Engineering Physics Class ScheduleSWETHA GPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 1120 SolutionsDocument25 pagesPhysics 1120 SolutionsDhruv singhPas encore d'évaluation
- System of Particles All Derivations NewDocument9 pagesSystem of Particles All Derivations NewManish PattajoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch17 PDFDocument73 pagesCh17 PDFمحمد علي عمرانPas encore d'évaluation
- H3 Physics Summary Notes (GCE A-Level Syllabus 9814) (2019 Edition)Document9 pagesH3 Physics Summary Notes (GCE A-Level Syllabus 9814) (2019 Edition)avinash boodhooPas encore d'évaluation
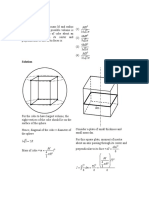
- Moment of Inertia of a Cube Cut from a SphereDocument2 pagesMoment of Inertia of a Cube Cut from a Sphere123iitjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresD'EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- This Contains Some Secret Text Until You Find The Key You Wont Able To ReadDocument1 pageThis Contains Some Secret Text Until You Find The Key You Wont Able To ReadBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- KeysDocument1 pageKeysBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Energy PPT 13Document13 pagesSolar Energy PPT 13Bala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- IC102 Engineering Mechanics-I-year SyllabusDocument1 pageIC102 Engineering Mechanics-I-year SyllabusBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 1 PDFDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 PDFBala Subramanian50% (2)
- Concentration CellsDocument12 pagesConcentration CellsBala Subramanian100% (1)
- Electrical & Electronics Measurements Instrumentation AssignmentDocument3 pagesElectrical & Electronics Measurements Instrumentation AssignmentBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Keys 2Document2 pagesKeys 2Bala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical & Electronics Measurements Instrumentation AssignmentDocument3 pagesElectrical & Electronics Measurements Instrumentation AssignmentBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- AttendanceDocument8 pagesAttendanceBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Hostel Wifi NittDocument9 pagesHostel Wifi Nittlaxman289Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4Document46 pagesGroup 4Bala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes Chapter 2Document43 pagesLecture Notes Chapter 2Bala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of ThermodynamicsDocument35 pagesBasics of ThermodynamicsBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Texts Series Eseries Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Eseries Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Python Tools UtilitiesDocument3 pagesPython Tools UtilitiesXXX100% (1)
- Classic Texts Series Es Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Es Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- A Python BookDocument94 pagesA Python BookGerald GavinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Texts Series Es Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Es Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Texts Series Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TXTXTDocument1 pageTXTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Texts Series Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Higher Algsic Texts Series Highapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TTTTXTXTDocument1 pageTTTTXTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Texts Series Higher Algebrapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Higher Algebrapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TTTTTXTXTXTDocument1 pageTTTTTXTXTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TTXTDocument1 pageTTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Classic Texts Series Higher Algebrapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtDocument1 pageClassic Texts Series Higher Algebrapitmdgt9knxhqjp5gpid 9789350943724&affid NmetxtxtBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TTTTXTXTXTTXTXTDocument1 pageTTTTXTXTXTTXTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TTTXTXTTXTXTDocument1 pageTTTXTXTTXTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- TTXTXTDocument1 pageTTXTXTBala SubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Pap ListDocument11 pagesPap ListMohan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Holiday Homework Class IxDocument3 pagesHoliday Homework Class IxpkPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Theorems - Real AnalysisDocument9 pagesImportant Theorems - Real Analysismmmellyyyy50% (2)
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Document20 pagesCambridge International AS & A Level: Mathematics 9709/13Obert MarongedzaPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Math SurfaceArea&VolumeDocument5 pages10 Math SurfaceArea&VolumeAjay AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Analytical Mechanics: MEEN 617 - Handout 4aDocument20 pagesElements of Analytical Mechanics: MEEN 617 - Handout 4aOliver KrausPas encore d'évaluation
- System of Particles and Rotational Motion Part 1 CH7Document28 pagesSystem of Particles and Rotational Motion Part 1 CH7Rishab SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- C1 Coordinate Geometry - AnswersDocument9 pagesC1 Coordinate Geometry - AnswersNazish UsamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Matthew Hedden - Some Remarks On Cabling, Contact Structures, and Complex CurvesDocument11 pagesMatthew Hedden - Some Remarks On Cabling, Contact Structures, and Complex CurvesDuncan_VimPas encore d'évaluation
- Alexander Horned SphereDocument3 pagesAlexander Horned SphereDARKOVUKICPas encore d'évaluation
- Simulating Weightlessness with Centripetal ForceDocument6 pagesSimulating Weightlessness with Centripetal ForceNrike Duran100% (1)
- Spherical Law of CosinesDocument8 pagesSpherical Law of Cosinesapi-281623170Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Electric FieldDocument7 pages02 Electric FieldFirdous APas encore d'évaluation
- A Student's Manual For A First Course in General Relativity: Robert B. ScottDocument10 pagesA Student's Manual For A First Course in General Relativity: Robert B. Scottmehrdad022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Polygons GBR PDFDocument24 pagesPolygons GBR PDFzxcvuno4307100% (1)
- Today: Homework Due Conservation of Energy Read Chap 13, Sections 6 To 9 Homework: Chap. 13, Problems 57, 61, 67, 76Document12 pagesToday: Homework Due Conservation of Energy Read Chap 13, Sections 6 To 9 Homework: Chap. 13, Problems 57, 61, 67, 76Tony LoogmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry - Vladimir v. KisilDocument38 pagesGeometry - Vladimir v. KisilHagler Araujo RisalvePas encore d'évaluation
- Cables Catenaries PDFDocument47 pagesCables Catenaries PDFsimple-CE-studPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 10-3 Year PlanDocument2 pagesMath 10-3 Year Planapi-250169429100% (1)
- Precalculus ch6 ReviewDocument2 pagesPrecalculus ch6 Reviewapi-213604106Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Graduate Studies in Mathematics) Luis Barreira, Claudia Valls-Ordinary Differential Equations - Qualitative Theory-American Mathematical Society (2012)Document265 pages(Graduate Studies in Mathematics) Luis Barreira, Claudia Valls-Ordinary Differential Equations - Qualitative Theory-American Mathematical Society (2012)BrunoDanielGómezLabra100% (3)
- DiffGeo UCLADocument256 pagesDiffGeo UCLAmaplebrandishPas encore d'évaluation
- Ma6351 Unit IV Fourier TransformsDocument30 pagesMa6351 Unit IV Fourier Transformssatheeshsep24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Moment of InertiaDocument1 pageMass Moment of InertiaJaycee NodadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Landscape RepresentationDocument14 pagesLandscape RepresentationAYOUB AIT–KHALAPas encore d'évaluation
- Latest STPM Phy Project (NewDocument8 pagesLatest STPM Phy Project (NewBong Sheng Feng0% (2)
- Engg Mechanics Ques BankDocument68 pagesEngg Mechanics Ques BankUtkalPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2 - TrigonometryDocument15 pagesModule 2 - TrigonometryJake Canlas100% (1)
- 4024 w03 QP 2Document12 pages4024 w03 QP 2mstudy123456Pas encore d'évaluation
- Time and Background Independence: A ResponseDocument7 pagesTime and Background Independence: A ResponsecalamartPas encore d'évaluation