Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cyclic Strain Control: High Cycle: A e F B
Transféré par
prakush01975225403Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Cyclic Strain Control: High Cycle: A e F B
Transféré par
prakush01975225403Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
For elastic-dominated strains
at high cycles, adapt
Basquins equation:
Intercept on strain axis of extrapolated
elastic line = o
f
/E.
High cycle = elastic strain control:
slope (in elastic regime) = b = -n/(1+5n)
The high cycle fatigue strength, o
f
, scales
with the yield stress high strength good in
high-cycle
o
a
= E
Ac
e
2
= ' o
f
2N ( )
b
Cyclic Strain control: high cycle
Total strain (plastic+elastic) life
Low cycle, high strain = plastic control: slope = c
Add the elastic and plastic strains.
Cross-over between elastic and plastic control is
typically at N
f
= 10
3
cycles.
Ductility useful for low-cycle and high strain
Strength for high cycle and low strain
Examples of Maraging steel for high cycle
endurance, annealed 4340 for low cycle fatigue
strength.
A
2
=
Ac
el
2
+
Ac
pl
2
=
' o
f
E
2N
f
b
+ ' c
f
2N
f
c
c
The fatigue life at which the transition occurs
is
When mean stress is not zero
) /( 1
'
'
2
c b
f
f
t
E
N
|
|
.
|
\
|
=
o
c
( )( )
b
m f a
N 2
'
o o o =
Strain amplitude - cycles
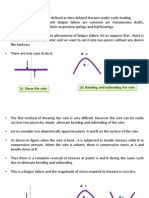
Structural changes during fatigue
Crack initiation: early development of fatigue
damage
Slip-band crack growth: deepening of initial
crack on high shear planes- stage I crack
growth
Crack growth on planes of high tensile stress:
crack growth normal to the max tensile stress-
stage II crack growth
Ultimate ductile failure
Fatigue crack stages
Stage 1
Stage 2
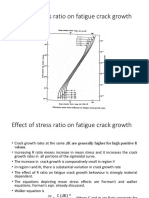
Fatigue Crack Propagation
Crack Length := a.
Number of cycles := N
Crack Growth Rate := da/dN
Amplitude of Stress Intensity := K = oa.
Define three stages of crack growth, I, II and III,
in a plot of da/dN versus K.
Stage II crack growth: application of linear elastic fracture
mechanics.
Can consider the crack growth rate to be related to the applied
stress intensity.
Crack growth rate somewhat insensitive to R (if R<0) in Stage II
Environmental effects can be dramatic, e.g. H in Fe, in increasing
crack growth rates.
Fatigue Crack Propagation
Three stages of crack
growth, I, II and III.
Stage I: transition to a
finite crack growth rate
from no propagation
below a threshold value
of K.
Stage II: power law
dependence of crack
growth rate on K.
Stage III: acceleration of
growth rate with K,
approaching catastrophic
fracture.
da/dN
K
K
th
K
c
I
II
III
Non-propagating
fatigue crack
p
( )
p
K A
dN
da
A =
U
n
s
t
a
b
l
e
c
r
a
c
k
g
r
o
w
t
h
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Determination of The Formula Unit of A CompoundDocument5 pagesDetermination of The Formula Unit of A CompoundSharvina Parsha0% (3)
- Report Lab 109: One Dimensional MotionDocument3 pagesReport Lab 109: One Dimensional MotionBalthazar Torres0% (1)
- Lecture 12 FatigueDocument23 pagesLecture 12 Fatigueantoine demeire100% (2)
- Deflection Due To PrestressDocument85 pagesDeflection Due To PrestresscamillePas encore d'évaluation
- Tanaka - Fatigue Crack Propagation From A Crack Inclined To The Cyclic Tensile Axis PDFDocument16 pagesTanaka - Fatigue Crack Propagation From A Crack Inclined To The Cyclic Tensile Axis PDFDavid C HouserPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue Lecture5Document7 pagesFatigue Lecture5prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fracture MechanicsDocument11 pagesFracture Mechanicsbomeje5457Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue PDFDocument21 pagesFatigue PDFsuzilamatsallehPas encore d'évaluation
- Structures and Materials Section 7 Stress ConcentrationDocument21 pagesStructures and Materials Section 7 Stress ConcentrationAdi Adams AndaroffsaPas encore d'évaluation
- Creep SlidesDocument52 pagesCreep SlidesiJordanScribdPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To Fracture Mechanics, Fatigue and CreepDocument40 pagesIntro To Fracture Mechanics, Fatigue and CreepM.USMAN BIN AHMED100% (1)
- Fatigue Ch12Document87 pagesFatigue Ch12mkumar_234155Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue of MaterialsDocument54 pagesFatigue of Materialsc_gaspard0% (1)
- Me A Chapter 1Document92 pagesMe A Chapter 1arandersPas encore d'évaluation
- FatigueDocument32 pagesFatigueMostaMostafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Strain RelationshipDocument92 pagesStress Strain RelationshipUpulHettiarachchiPas encore d'évaluation
- Me16A: Introduction To Strength of Materials: CourseDocument92 pagesMe16A: Introduction To Strength of Materials: CourseRimti BhowmikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lefm NotesDocument8 pagesLefm NotesSolomon GracioPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue Analysis of Piping System Using Caesar IIDocument9 pagesFatigue Analysis of Piping System Using Caesar IIHmd Mokhtari100% (1)
- Unit 2 Variable Stresses, Design of Shafts, Keys and CouplingsDocument134 pagesUnit 2 Variable Stresses, Design of Shafts, Keys and CouplingsDravid PrabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics For Fatigue Analysis of Piping System Using Caesar IIDocument6 pagesBasics For Fatigue Analysis of Piping System Using Caesar IIPrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Creep - MSE 305Document46 pagesCreep - MSE 305Badmus AbdulmalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Crack Propagation Under Variable Amplitude LoadingDocument8 pagesCrack Propagation Under Variable Amplitude LoadingKelvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 - Fatigue Tests - 1Document36 pagesChapter 6 - Fatigue Tests - 1HebaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 LEFM Edited31Mac2014Document50 pagesCHAPTER 2 LEFM Edited31Mac2014wandee2393100% (1)
- Free SpaningDocument37 pagesFree SpaningAnonymous ZMLlQvBopPas encore d'évaluation
- Aa - Failure of Mat12421Document39 pagesAa - Failure of Mat12421Drw ArcyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 13Document32 pagesLecture 13Gift Thrive ZimbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Failure Theory For Piping MaterialDocument29 pagesFailure Theory For Piping MaterialsaadvikhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 2 - Plate Girders - EC3 - Part 2Document39 pagesLec 2 - Plate Girders - EC3 - Part 2Ace LowPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue of MaterialsDocument40 pagesFatigue of MaterialsnitinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pme Lab 3Document5 pagesPme Lab 3Shakil Rahman AfidPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Strains and Element of The Theory of PlasticityDocument29 pagesThermal Strains and Element of The Theory of Plasticity이희영100% (1)
- Lecture 11 Fatigue 2Document8 pagesLecture 11 Fatigue 2giovanniPas encore d'évaluation
- TENSION MEMBERS Yielding Shear LagDocument28 pagesTENSION MEMBERS Yielding Shear LagEhsan WasimPas encore d'évaluation
- Creep & FatigueDocument20 pagesCreep & Fatiguegaspardo123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 Introduction Fundamentals of Fluid MechanicsDocument45 pagesCh1 Introduction Fundamentals of Fluid MechanicsAsif SunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Creep and FatigueDocument20 pagesCreep and Fatiguecheveresan123100% (2)
- 17.creep & FatigueDocument20 pages17.creep & FatigueaderancPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Design For Strength - Fatigue Strength Variable LoadingDocument37 pagesChapter 2 Design For Strength - Fatigue Strength Variable LoadingHilmyZulkifliPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Stress Concentration StudentDocument5 pages04 Stress Concentration StudentEJ GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture #4 STRDocument26 pagesLecture #4 STRHarry PiyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect 5Document45 pagesLect 5Hüseyin xPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Stress Analysis For PROCESSDocument6 pagesPiping Stress Analysis For PROCESSFredie UnabiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Wind Engineering - Lecture 1 - Bluff Body Aerodynamics1Document25 pagesWind Engineering - Lecture 1 - Bluff Body Aerodynamics1Vishwaka BandaraPas encore d'évaluation
- NEEP 541 - Hardening: Fall 2002 Jake BlanchardDocument41 pagesNEEP 541 - Hardening: Fall 2002 Jake BlanchardezekingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue FailureDocument22 pagesFatigue FailureHimanshu YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.00 Failure AnalysisDocument35 pages3.00 Failure AnalysisMohamad Al-nemrawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fatigue Ch12Document87 pagesFatigue Ch12Bolaji Suberu100% (1)
- Lecture 4 (Material Properties) PDFDocument49 pagesLecture 4 (Material Properties) PDFJunhong BapPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter One 1Document30 pagesChapter One 1Saad Al HelyPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM)Document19 pagesLinear Elastic Fracture Mechanics (LEFM)Chimwemwe KaongaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6Document19 pagesLecture 6Iftekhar ArefinPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.1 Fatigue: Progressive FractureDocument18 pages1.1 Fatigue: Progressive FractureSai KiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Binder CreepDocument29 pagesBinder CreepettypasewangPas encore d'évaluation
- Fracture PresentationDocument9 pagesFracture PresentationGoutham BurraPas encore d'évaluation
- Stresses in TracksDocument23 pagesStresses in Tracksvikalp161Pas encore d'évaluation
- Glanfill Module 1 - Part 2Document57 pagesGlanfill Module 1 - Part 2LeiVasAllanigueVillanueva100% (1)
- Lifting AnalysisDocument14 pagesLifting Analysisruhul72Pas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresD'EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Single-Molecule Tracking of Polymer Surface Di Ffusion: Michael J. Skaug, Joshua N. Mabry, and Daniel K. SchwartzDocument6 pagesSingle-Molecule Tracking of Polymer Surface Di Ffusion: Michael J. Skaug, Joshua N. Mabry, and Daniel K. Schwartzprakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- 076 PDFDocument6 pages076 PDFprakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- List of ChemicalsDocument1 pageList of Chemicalsprakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diat HTT Lect-28Document12 pagesDiat HTT Lect-28prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5.isca RJRS 2012 356Document4 pages5.isca RJRS 2012 356prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Methods and Models of Quantum Dot SynthesisDocument34 pagesChapter 3: Methods and Models of Quantum Dot Synthesisprakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diat HTT Lect 25 To 27Document12 pagesDiat HTT Lect 25 To 27prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment: Dr. Santosh S. HosmaniDocument5 pagesHeat Treatment: Dr. Santosh S. Hosmaniprakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diat HTT Lect 22 To 24Document13 pagesDiat HTT Lect 22 To 24prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment: Dr. Santosh S. HosmaniDocument7 pagesHeat Treatment: Dr. Santosh S. Hosmaniprakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diat HTT Lect 4 5 6Document9 pagesDiat HTT Lect 4 5 6prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diat HTT Lect 7 8 9Document11 pagesDiat HTT Lect 7 8 9prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Diat HTT Lect 1 2 3Document12 pagesDiat HTT Lect 1 2 3prakush01975225403Pas encore d'évaluation
- Description and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure)Document12 pagesDescription and Identification of Soils (Visual-Manual Procedure)Igor BarcelosPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Artificial Sensor Technique For Functional Electrical StimulationDocument11 pagesVirtual Artificial Sensor Technique For Functional Electrical StimulationCarlos Alexandre FerriPas encore d'évaluation
- Head Losses in Pipes: NomenclatureDocument2 pagesHead Losses in Pipes: NomenclatureAudrey Patrick KallaPas encore d'évaluation
- R.D. Nelson Et Al - A Linear Pendulum Experiment: Effects of Operator Intention On Damping RateDocument19 pagesR.D. Nelson Et Al - A Linear Pendulum Experiment: Effects of Operator Intention On Damping RateDominos021Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fulltext VimpDocument117 pagesFulltext VimpmayureshPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Amplifier Application NoteDocument3 pagesPower Amplifier Application NoteSanthos KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Full State Feedback ControlDocument29 pagesFull State Feedback ControlBi Chen100% (1)
- 4 Bar HingeDocument9 pages4 Bar HingelalalamxPas encore d'évaluation
- WRC368Document33 pagesWRC368fahid masoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure2Document2 pagesAtomic Structure2api-350245383100% (5)
- B.SC MathematicsDocument39 pagesB.SC MathematicsSelvamPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 GeoStrucAnal Cylinder Elastic PDFDocument12 pages01 GeoStrucAnal Cylinder Elastic PDFSiddhant KaushikPas encore d'évaluation
- k3 B No. 2 Set 1Document4 pagesk3 B No. 2 Set 1koonweiPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout 4Document26 pagesHandout 4coppernitratePas encore d'évaluation
- M.Tech Geotechnical Engineering Syllabus PDFDocument13 pagesM.Tech Geotechnical Engineering Syllabus PDFernestnsabimana74Pas encore d'évaluation
- Horowitz Singularities in String TheoryDocument46 pagesHorowitz Singularities in String TheoryEvanAdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Forces and Magnetic Fields QuestionsDocument6 pages10 Forces and Magnetic Fields QuestionsAnonymous oQEx3zPas encore d'évaluation
- Spec Sheet Pegasus BT 4DDocument2 pagesSpec Sheet Pegasus BT 4DWempic Aulia FauziPas encore d'évaluation
- IWCF Mark PDFDocument175 pagesIWCF Mark PDFDanish Khan100% (2)
- Rock Class CriepiDocument3 pagesRock Class Criepirizka rahmadani100% (1)
- Assignment-12 and SolutionDocument11 pagesAssignment-12 and SolutionadimeghaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advances in Addition-Cure Phenolic ResinsDocument98 pagesAdvances in Addition-Cure Phenolic Resinsvirk_70Pas encore d'évaluation
- Skew Bridges-N.rajagopalan PDFDocument26 pagesSkew Bridges-N.rajagopalan PDFkrish100% (12)
- Testing of Fiber Reinforced ConcreteDocument254 pagesTesting of Fiber Reinforced ConcreteGurbirPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Houck - Excerpt From Energy Healing and PsychokinesisDocument12 pagesJack Houck - Excerpt From Energy Healing and PsychokinesisTuytm2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering AspectsDocument11 pagesColloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering AspectsFernando HenriquePas encore d'évaluation
- CE 343-Lab-Summer-2012 From DR Khaled GuzlanDocument62 pagesCE 343-Lab-Summer-2012 From DR Khaled GuzlanfarisPas encore d'évaluation