Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
External Environment2
Transféré par
Mahesh SatapathyCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
External Environment2
Transféré par
Mahesh SatapathyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
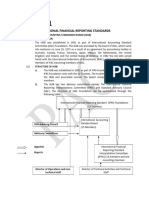
PEST analysis stands for Political, Economic.
Social and Technological Analysis, developed by Johnson and scholes to indicate the external influences. Steps in PEST Analysis - Five Steps Step 1 Understand a categorys relevant trends: Research the important variables of the organizations strategy Step 2 Understand trend intedependencies:
Step 3 Distill likely issues from the identified trends: Validate trends Step 4 Forecast the direction of issues: Fundamental drivers behind a critical trend. Step 5 Derive implications for the organization: Assess effect of critical environmental changes
Political climate Political stability Law and order situation Political attitude towards business Political influence on trade unions Consumer protection laws
State of business cycle Distribution of income within the population Governments monetary and fiscal policies Capacity utilization Unemployment Inflation Interest rates Foreign investments Trends in capital market Foreign exchange rates Government intervention in free market working Growth rate of economy
Scio-cultural and Demographic Environment Technological Environment
Providing education and training, relevant to business either directly through the governments educational institutions or via grants to firms and local councils. Protection of intellectual and physical property by enacting and enforcing appropriate laws Economic planning in key industrial areas Acting as a consumer to the private sector Giving incentives to emerging business Creating entry barriers by restricting the activities of foreign business in the country or by imposing import tariffs. Sustaining research and development Providing new business opportunities through privatization and liberalization.
Environmental regulation requiring costly pollution control devices Health and safety regulation Distortion of markets by the use of indirect taxation and discretionary production licenses Enforcing price controls Defending consumers rights through consumer protection laws Change of policies in response to political pressure leading to uncertain and volatility in financial markets Imposition of restrictions like monopoly controls and equal opportunity legislation Acting solely on behalf of sectional interests.
The threat of new entrants The threat of substitute products or services The bargaining power of customers The bargaining power of suppliers The rivalry amongst current competitors in the industry.
Economies of scale Product differentiation Capital requirements Switching costs Access to distribution channels Government policy.
Those products which are providing a better performance/price standard than the industry standard. Products produced by industries earning high profits. The concentrated purchase of large volumes relative to seller sales. The products it purchases represent a significant fraction of the buyers cost of purchases.
The products it purchases from the industry are standard or undifferentiated It faces few switching costs. It earns low profits. The buyers will pose a credible threat of backward integration. The industrys product is unimportant to the quality of the buyers product. The buyer has full information.
It is dominated by a few companies and is more concentrated than the industry to which it sells It is not obliged to contend with other substitute products for sale to the industry. The industry is not an important customer of the supplier group The suppliers products are differentiated or it has built-up switching costs. The supplier poses a credible threat of forward integration
Numerous or equally balanced competitors Slow industry growth ]High fixed or storage costs Lack of differentiation or switching costs Capacity augmented in large increments Diverse competitors High strategic stakes High exit barriers.
EIC (Economy, Industry, Company) model
Foreign exchange rates of different countries ] Inflation rates, interest rates and wage rates in different countries Economic and trade agreements Double taxation relief agreements Double taxation relief agreements Double taxation relief agreements Entry barriers of different countries Globalization of economy and liberalization of trade Balance of trade and balance of payments of different countries Monetary and economic policies of different countries Personal and corporate tax rates of different countries Freedom of movement of capital, labour and technology Political situation of different countiries.
Efficiency To increase the economic efficiency at the level of individual firm and results in better performance. Decision making To reduce governments interference and increase the speed of decision making Competition To bring private sector culture by introducing competition. Bothe economic and technical efficiencies will be promoted by privatization. Fiscal To raise revenue for government activities. Distribution- To seek political advantage by means of income redistribution. Risk spreading To ensure proper allocation of risk across members of the economy
Public offering of shares Sale of shares to a private buyer or group of buyers Restitution to former owners Buy-outs, buy-ins and other forms of bottome up or insider privatization Lease and management contract Contracting out of services at the local government level with competitive tendering system Franchising whereby ownership would be private but the brand name and technical know-how would be provided by the public sector. Contracting out a government service. Divestiture through equity shares.
Business Intelligence Business Intelligence (BI) refers to skills, technologies, applications and practices used to help a business acquire a better understanding of its commercial text Tactical insight to optimize business processes by identifying trends, anomalies and behaviours that require management action. Strategic insight to align multiple business processes with key business objectives through integrated performance management and analysis.
Most of the organizations have been informally monitoring their competitors about their management, customers, markets, products, services, technologies, finance and other facilities.
Creating profiles of the competitor(s) and on industries. Concentrate on competitors actions Every member of the organization will become a source of intelligence.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 17 Vol 2 No 2Document10 pages17 Vol 2 No 2goyal_khushbu88Pas encore d'évaluation
- Maharishi Giri Surya Swami 10 Miles Chaak Nagon Post-Garvana Via - Sohela BargarhDocument1 pageMaharishi Giri Surya Swami 10 Miles Chaak Nagon Post-Garvana Via - Sohela BargarhMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Insurance Terminology - Gr8AmbitionZDocument10 pagesInsurance Terminology - Gr8AmbitionZBebilson MansinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketingmanagementii Uwsb 130703064628 Phpapp02Document40 pagesMarketingmanagementii Uwsb 130703064628 Phpapp02Mahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- IMIS Bhubaneswar PGDM Revised Time Table Term V 2012-14Document1 pageIMIS Bhubaneswar PGDM Revised Time Table Term V 2012-14Mahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- FiiDocument5 pagesFiiMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- IMIS Bhubaneswar PGDM Revised Time Table Term V 2012-14Document1 pageIMIS Bhubaneswar PGDM Revised Time Table Term V 2012-14Mahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Together, 3rd October, 2013Document3 pagesTogether, 3rd October, 2013Mahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- 8th Science Assignment Lesson - 11 Human Eye and Ch. 15 Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument1 page8th Science Assignment Lesson - 11 Human Eye and Ch. 15 Reaching The Age of AdolescenceMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- CRMDocument37 pagesCRMMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- New Pension System (IFP)Document5 pagesNew Pension System (IFP)Mahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- NCFM BsmeDocument96 pagesNCFM BsmeAstha Shiv100% (1)
- Service RecoveryDocument45 pagesService RecoveryMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- SM 1Document2 pagesSM 1Aishwarya SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Servqual FormsDocument5 pagesServqual FormsChunku PaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaps Model AnalysisDocument20 pagesGaps Model AnalysisMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Gabott, Hogg - Consumer Behaviour and Services, A Review (Cité 21) - 1994Document15 pagesGabott, Hogg - Consumer Behaviour and Services, A Review (Cité 21) - 1994Mireille Vinosu GreceanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer ExpectationDocument20 pagesConsumer ExpectationMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Servqual Form For SbiDocument5 pagesServqual Form For SbiMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer ExpectationDocument20 pagesConsumer ExpectationMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Behavior and Euro Disney's Struggles in FranceDocument32 pagesConsumer Behavior and Euro Disney's Struggles in FranceMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Customer Perceptions 2Document27 pagesCustomer Perceptions 2Mahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- SBI Master Circular on Car Loan SchemeDocument336 pagesSBI Master Circular on Car Loan SchemeMahesh Satapathy67% (3)
- Financial DerivativesDocument29 pagesFinancial DerivativesnandukyPas encore d'évaluation
- F021 Borchure SCLM Seminar PDFDocument2 pagesF021 Borchure SCLM Seminar PDFMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- F002 CVPDocument26 pagesF002 CVPMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Relevant costing and decision makingDocument18 pagesRelevant costing and decision makingMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Sip PresentationDocument16 pagesSip PresentationMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Summer Internship ProjectDocument51 pagesSummer Internship ProjectMahesh SatapathyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Market Structure and Market FailureDocument103 pagesMarket Structure and Market Failureselina fraserPas encore d'évaluation
- DipIFRS Brochure 150205Document4 pagesDipIFRS Brochure 150205kevior2100% (1)
- Mubadala Petroleum Corporate Brochure - 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesMubadala Petroleum Corporate Brochure - 2019 PDFG.A. PermanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Procedures For SugerDocument2 pagesProcedures For SugerUber FoundationPas encore d'évaluation
- Procore ROI Report USDocument31 pagesProcore ROI Report USLe Thi Anh TuyetPas encore d'évaluation
- Point of View: Subsistence NeedsDocument3 pagesPoint of View: Subsistence NeedsJen AdvientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Iridex Group Plastic S.R.L.: B-Dul Eroilor 6 - 8, Cod 077190, Voluntari, Ilfov E-Mail: WebsiteDocument6 pagesIridex Group Plastic S.R.L.: B-Dul Eroilor 6 - 8, Cod 077190, Voluntari, Ilfov E-Mail: WebsiteRoxana IoanaPas encore d'évaluation
- European Innovation Scoreboard 2021Document95 pagesEuropean Innovation Scoreboard 2021Samuel Morales RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- FINS 3616 Lecture Notes-Week 1Document38 pagesFINS 3616 Lecture Notes-Week 1joannamanngoPas encore d'évaluation
- Trắc Nghiệm English Tài Chính Doanh Nghiệp Chương 2Document34 pagesTrắc Nghiệm English Tài Chính Doanh Nghiệp Chương 2Dương Viên NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- Amazon NordstormDocument7 pagesAmazon NordstormyyyPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Management FrameworkDocument32 pagesRisk Management FrameworkC.Ellena100% (1)
- Keynesian Liquidity Preference TheoryDocument12 pagesKeynesian Liquidity Preference TheorySatavisha RayPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Iata Eacp ProgramDocument217 pages5 Iata Eacp Programmiguelsousa_jitPas encore d'évaluation
- Atkinson c08Document27 pagesAtkinson c08mrlyPas encore d'évaluation
- Don Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High School: La Union Schools Division OfficeDocument2 pagesDon Eulogio de Guzman Memorial National High School: La Union Schools Division OfficeMary Joy ColasitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To IFRSDocument4 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To IFRSBahader AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 1 - Pre-Incorporation Subscription Requirement Minimum Subscription Minimum Paid-InDocument5 pagesProblem 1 - Pre-Incorporation Subscription Requirement Minimum Subscription Minimum Paid-InYvonne Duyao100% (1)
- Value Analysis Techniques for Improving ManufacturingDocument1 pageValue Analysis Techniques for Improving ManufacturingSagarPas encore d'évaluation
- Return Expectations From Venture Capital Deals in Europe: A Comparative StudyDocument18 pagesReturn Expectations From Venture Capital Deals in Europe: A Comparative StudySolange GambaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Exam 5Document9 pagesWeekly Exam 5Deyn EstoquePas encore d'évaluation
- Monetary Policy and Central Bank SyllabusDocument5 pagesMonetary Policy and Central Bank Syllabusjose aureo camacamPas encore d'évaluation
- Macroeconomics Lecture Notes SummaryDocument49 pagesMacroeconomics Lecture Notes SummaryMohammed AdemPas encore d'évaluation
- Cebu Technological University: VisionDocument2 pagesCebu Technological University: VisionEuley PunayPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment 2 - Module 2 Quiz - CourseraDocument1 pageAssessment 2 - Module 2 Quiz - CourseraCarla MissionaPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Statement Analysis-SampleDocument39 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis-Samplefchemtai4966Pas encore d'évaluation
- OkcDocument2 pagesOkcpsiyer2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSR DataDocument7 pagesCSR DataNilesh ShobhanePas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review of Financial Analysis of BankingDocument5 pagesLiterature Review of Financial Analysis of Bankingea3c5mfqPas encore d'évaluation
- PM Capstone - Project CharteDocument5 pagesPM Capstone - Project Charteabderazzak zarayakPas encore d'évaluation