Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1 Operations Madnagement
Transféré par
Tajmeer KhanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Chapter 1 Operations Madnagement
Transféré par
Tajmeer KhanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHAPTER 1
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
The business function responsible for planning, coordinating, and controlling the resources needed to produce products and services for a company.
A management function
An organizations core function
In every organization whether Service or
Manufacturing, profit or Not for profit
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN 2
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
Companies often do not understand the differences between operational efficiency and strategy Operational efficiency is performing tasks well, even better than competitors Strategy is a plan for competing in the marketplace Operations strategy is to ensure all tasks performed are the right tasks
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN 5
A business strategy is developed after taking into many factors and following some strategic decisions such as; What business is the company in (mission) Analyzing and understanding the market (environmental scanning) Identifying the companies strengths (core competencies)
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
Operations Strategy is a plan for the design and management of operations functions Operation Strategy developed after the business strategy Operations Strategy focuses on specific capabilities which give it a competitive edge competitive priorities
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
Four Important Operations Questions: Will you compete on Cost? Quality? Time? Flexibility? All of the above? Some? Tradeoffs?
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
10
Offering product at a low price relative to competition
Typically high volume products
Often limit product range & offer little customization May invest in automation to reduce unit costs Can use lower skill labor Probably use product focused layouts
Low cost does not mean low quality
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
11
Quality is often subjective Quality is defined differently depending on who is defining it Two major quality dimensions include
High performance design:
Superior features, high durability, & excellent customer service
Product & service consistency:
Meets design specifications Close tolerances Error free delivery
Quality needs to address
Product design quality product/service meets requirements Process quality error free products
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
12
Time/speed one of most important competition
priorities
First that can deliver often wins the race Time related issues involve
Rapid delivery:
Focused on shorter time between order placement and delivery
On-time delivery:
Deliver product exactly when needed every time
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
13
Company environment changes rapidly Company must accommodate change by being flexible
Product flexibility:
Easily switch production from one item to another
Easily customize product/service to meet specific requirements of a customer
Volume flexibility:
Ability to ramp production up and down to match market demands
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
14
Decisions must emphasis priorities that support business strategy Decisions often required trade offs Decisions must focus on order qualifiers and order winners
Which priorities are Order Qualifiers? e.g. Must have excellent quality since everyone expects it
Which priorities are Order Winners? e.g. PIA, SHAHEEN & AIR BLUE VS EMIRATES competes on cost McDonalds competes on consistency FedEx TCS DHL competes on speed Custom tailors compete on flexibility
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
15
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
16
To add value Increase product value at each stage Value added is the net increase between output product value and input material value Provide an efficient transformation Efficiency means performing activities well for least possible cost
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
17
Manufacturing
Tangible product Product can be inventoried Low customer contact Longer response time Capital intensive
Services
Intangible product Product cannot be inventoried High customer contact Short response time Labor intensive
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
18
Both use technology Both have quality, productivity, & response issues Both must forecast demand Both will have capacity, layout, and location issues Both have customers, suppliers, scheduling and staffing issues Manufacturing often provides services Services often provides tangible goods
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
19
Some organizations are a blend of service/manufacturing/quasimanufacturing Quasi-Manufacturing (QM) organizations QM characteristics include
Low customer contact & Capital Intensive
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
20
All organizations make decisions and follow a similar path
First decisions very broad Strategic decisions
Strategic Decisions set the direction for the entire company;
they are broad in scope and long-term in nature.
Following decisions focus on specifics - Tactical decision
Tactical decisions: focus on specific day-to-day issues like resource needs, schedules, & quantities to produce are frequent
Strategic decisions less frequent Tactical and Strategic decisions must align
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN 21
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
22
Customers demand better quality, greater speed, and lower costs Companies implementing lean system concepts a total systems approach to efficient operations Increased cross-functional decision making
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
23
OM has the most diverse organizational function Manages the transformation process OM has many faces and names such as;
V. P. operations, Director of supply chains, Manufacturing manager Plant manger, Quality specialists, etc.
All business functions need information from OM in order to perform their tasks Most businesses are supported by the functions of operations, marketing, and finance The major functional areas must interact to achieve the organization goals
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN 24
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT CHAPTER 1 SARDAR ROHAIL KHAN
25
Technology has positive and negative potentials
Positive
Improve processes Maintain up-to-date standards Obtain competitive advantage
Negative
Costly Promotes dependency Risks such as overstating benefits
Wiley 2010
26
Technology should
Support competitive priorities Can require change to strategic plans Can require change to operations strategy
Technology is an important strategic decision
Wiley 2010
27
Productivity is a measure of how efficiently inputs are converted to outputs
Productivity = output/input
Total Productivity Measure:
Total Productivity = (total output)/(total of all inputs)
Partial Productivity Measure:
Partial Productivity = (total output)/(single input)
Multi-factor Productivity = (total output)/(several inputs)
Multifactor Productivity Measure:
Wiley 2010
28
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Laptop Power SequenceDocument16 pagesLaptop Power SequenceDelwar Hossain90% (10)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Stress Relief PrescriptionDocument8 pagesThe Stress Relief PrescriptionRajesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Directory of Importers Associations Worldwide 2009Document57 pagesDirectory of Importers Associations Worldwide 2009Thanh Tam75% (12)
- Fact SheetDocument27 pagesFact SheetTajmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Monsanto Case Study For InternetDocument8 pagesMonsanto Case Study For InternetTajmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Lecture Rationales For Initiation of Projects FddsafsdpDocument55 pages2 Lecture Rationales For Initiation of Projects FddsafsdpTajmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Economy of Pakistan Is The 26th Largest in The World in Terms of Purchasing Power ParityDocument5 pagesThe Economy of Pakistan Is The 26th Largest in The World in Terms of Purchasing Power ParityTajmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Operations ManagmentDocument2 pagesCase Study Operations ManagmentTajmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Decentralize Power Sector to End LoadsheddingDocument3 pagesDecentralize Power Sector to End LoadsheddingTajmeer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- NTS Book For GAT General Free Download PDFDocument142 pagesNTS Book For GAT General Free Download PDFMuhammad Ramzan100% (3)
- Financial Accounting PDFDocument43 pagesFinancial Accounting PDFJaya SudhakarPas encore d'évaluation
- FormatCARS KAAUH Alqahtani 106Document8 pagesFormatCARS KAAUH Alqahtani 106ZEYNOPas encore d'évaluation
- BBK SMP123HDT2 SMP124HDT2 Service ManualDocument25 pagesBBK SMP123HDT2 SMP124HDT2 Service ManualdanielPas encore d'évaluation
- RAN KPI MonitorDocument8 pagesRAN KPI MonitorOmer WaqarPas encore d'évaluation
- KTO12 Curriculum ExplainedDocument24 pagesKTO12 Curriculum ExplainedErnesto ViilavertPas encore d'évaluation
- Bid ProcessDocument85 pagesBid ProcessRobiatol Adawiah Mohammad ShamsidiPas encore d'évaluation
- AS 2 Communication in Health, Social Care and Early Years Settings EguideDocument25 pagesAS 2 Communication in Health, Social Care and Early Years Settings EguideAmy liliet BajahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trade ReportDocument6 pagesTrade ReportIKEOKOLIE HOMEPCPas encore d'évaluation
- MMA Electrode ClassificationDocument3 pagesMMA Electrode ClassificationRathnakrajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: AI Is A Fundamental Risk To The Existence of Human CivilizationDocument19 pagesElon Musk: AI Is A Fundamental Risk To The Existence of Human CivilizationBDApp StarPas encore d'évaluation
- Spatial data analysis with GIS (DEMDocument11 pagesSpatial data analysis with GIS (DEMAleem MuhammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 2Document2 pagesAssignment 2shivam souravPas encore d'évaluation
- Air CasterDocument25 pagesAir CasterPrabir Kumar Pati100% (1)
- Beamware 2: Users ManualDocument14 pagesBeamware 2: Users ManualAdi FaizinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chlorine (Free or Total) Manual For Test Kits CN-70, CN-70F, CN-70TDocument6 pagesChlorine (Free or Total) Manual For Test Kits CN-70, CN-70F, CN-70TDemétrius Ivo FernandesPas encore d'évaluation
- GIYA Classroom VisitationDocument4 pagesGIYA Classroom VisitationRussell Moralla100% (2)
- Comparisonofweldingeconomy Kehlnaht 12551752Document10 pagesComparisonofweldingeconomy Kehlnaht 12551752Asebaho BadrPas encore d'évaluation
- Materi HAZOP Dan Relevansi Terhadap ASME Dan APIDocument9 pagesMateri HAZOP Dan Relevansi Terhadap ASME Dan APIAhmad KharisPas encore d'évaluation
- Kamran Afzal ResumeDocument2 pagesKamran Afzal ResumeChelsea ElizabethPas encore d'évaluation
- This Study Resource Was: Practice Questions and Answers Inventory Management: EOQ ModelDocument7 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Practice Questions and Answers Inventory Management: EOQ Modelwasif ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
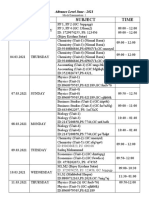
- Mock Examination Routine A 2021 NewDocument2 pagesMock Examination Routine A 2021 Newmufrad muhtasibPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 4 The DC Compound Generator: Muhammad Al-Ariff Bin Selamat (112215), Muhammad Azfar Amin Bin Ahmad MokhtarDocument5 pagesExperiment 4 The DC Compound Generator: Muhammad Al-Ariff Bin Selamat (112215), Muhammad Azfar Amin Bin Ahmad MokhtarOne Love Jah LovePas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of The Molecular Weight of Polymers From Viscosity MeasurementsDocument10 pagesDetermination of The Molecular Weight of Polymers From Viscosity MeasurementsAbdullah MunawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Drilling RisersDocument13 pagesDrilling Risersadvantage025Pas encore d'évaluation
- ĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP HỌC KÌ 1-LỚP 12Document15 pagesĐỀ CƯƠNG ÔN TẬP HỌC KÌ 1-LỚP 12Anh Duc VuPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Project Planning and Tracking Using Microsoft Project v2.7Document47 pagesPractical Project Planning and Tracking Using Microsoft Project v2.7Nelson Aguirre BravoPas encore d'évaluation
- ECU Designing and Testing Using NI ProductsDocument6 pagesECU Designing and Testing Using NI ProductsOmar Eladel MahmoudPas encore d'évaluation
- BHCC Peri 5c Jyps - MK Classroom Toilet (Pending To Sign by Moe) - Removed - RemovedDocument8 pagesBHCC Peri 5c Jyps - MK Classroom Toilet (Pending To Sign by Moe) - Removed - RemovedrajavelPas encore d'évaluation