Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Metric Conversions
Transféré par
afzabbasiCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Metric Conversions
Transféré par
afzabbasiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
METRIC CONVERSION
How to
convert
within
the
metric
system
Copyright 2003 - 2004. M. J. Krech. All rights reserved.
The Metric System
is based on sets of 10.
1 x 10 = 10
10 X 10 = 100
10 x 100 = 1,000
Is used by
scientists
all over the
world!
The Metric System
Do you remember
King
Henry?
The pneumonic:
King Henry Died Unexpectedly
Drinking Chocolate Milk
Memorize
this!
You must also know
how to convert within the Metric
System. Heres a good device:
On your paper draw a line and add 7
tick marks:
Next:
Above the tick marks write the abbreviations for
the King Henry pneumonic:
k h d u d c m
Write the units in the middle under the U.
m
l
g
Lets add the meter line:
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
L
g
Lets add the liter line:
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
kL hL daL L dL cL mL
g
Deca can also be dk or da
Lets add the gram line:
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
kl hl dal l dl cl ml
kg hg dag g dg cg mg
How to use this device:
1. Look at the problem. Look at the unit
that has a number. On the device put
your pencil on that unit.
2. Move to new unit, counting jumps and
noticing the direction of the jump.
3. Move decimal in original number the same
# of spaces and in the same direction.
Example #1:
(1) Look at the problem. 56 cm = _____ mm
Look at the unit that has a number. 56 cm
On the device put your pencil on that unit.
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
Example #1:
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
2. Move to new unit, counting jumps and
noticing the direction of the jump!
One jump to the right!
Example #1:
3. Move decimal in original number the same
# of spaces and in the same direction.
56 cm = _____ mm
56.0.
Move decimal one jump to the right.
Add a zero as a placeholder.
One jump
to the right!
Example #1:
56 cm = _____ mm
56cm = 560 mm
Example #2:
(1) Look at the problem. 7.25 L = ____ kL
Look at the unit that has a number. 7.25 L
On the device put your pencil on that unit.
k h d u d c m
kl hl dal L dl cl ml
Example #2:
2. Move to new unit, counting jumps and
noticing the direction of the jump!
k h d u d c m
kl hl dal L dl cl ml
Three jumps to the left!
Example #2:
(3) Move decimal in original number
the same # of spaces and in the same
direction.
7.25 L = ____ kL
.007.25
Move decimal to the left three jumps.
Add two zeros as placeholders.
Three jumps
to the left!
Example #2:
7.25 L = ____ kL
7.25 L = .00725 kL
Example #3:
Try this problem on your own:
45,000 g = ____mg
k h d u d c m
kg hg dag g dg cg mg
Example #3:
k h d u d c m
kg hg dag g dg cg mg
Three jumps to the right!
45,000.000.
Example #3:
45,000 g = 45,000,000 mg
Three jumps to the right!
Example #4:
Try this problem on your own:
5 cm = ____ km
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
Example #4:
k h d u d c m
km hm dam m dm cm mm
Five jumps to the left!
.00005.
Example #4:
5 cm = .00005 km
Five jumps to the left!
Examples #5-9:
Solve these five problems on your
own. Show your answers to your
teacher.
You may choose to use the King Henry
Notes.
You may choose the King Henry
Staircase.
You may also choose to make a King
Henry Slider.
Examples #5-9:
(5) 35 mm = ____ cm
(6) 14,443 L = ____ kL
(7) 0.00056 kg = ____ g
(8)35.4 L = ____ mL
(9)16 mm = ____ km
One last caution:
Be careful NOT
to count the
spot you start
from, where you
put your pencil
point.
Only count
the jumps!
The End
You may choose to ask
your teacher for a copy of :
(1) King Henry Notes or
(2) King Henry Staircase or
(3) King Henry Slider.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Exam Questions Involving Bearings and Trigonometry RulesDocument6 pagesExam Questions Involving Bearings and Trigonometry Rulesafzabbasi100% (2)
- Hot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and ShapesDocument8 pagesHot-Rolled and Cold-Finished Age-Hardening Stainless Steel Bars and ShapesradziPas encore d'évaluation
- SEO ReportDocument13 pagesSEO ReportHarish JunejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Year-Dec 2018 Class 7Document16 pagesMid Year-Dec 2018 Class 7afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rise Over Run To Find Gradient With Given Graphs WSDocument2 pagesRise Over Run To Find Gradient With Given Graphs WSafzabbasi100% (1)
- Quartiles For Discrete Data Class 7Document2 pagesQuartiles For Discrete Data Class 7afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Remedial Class Mathematics Grade 7Document1 pageRemedial Class Mathematics Grade 7afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Paper For Mid Term Exam Dec 2019 Class 7 MathematicsDocument11 pagesPractice Paper For Mid Term Exam Dec 2019 Class 7 Mathematicsafzabbasi100% (1)
- 34 A Trig Formula For Area of A TriangleDocument30 pages34 A Trig Formula For Area of A TriangleafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- TransformationsDocument4 pagesTransformationsafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
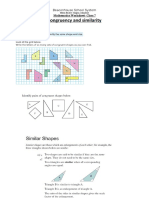
- Congruency and Similarity Congruent Shapes: Mathematics Worksheet-Class 7Document2 pagesCongruency and Similarity Congruent Shapes: Mathematics Worksheet-Class 7afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sine Rule GameDocument3 pagesSine Rule GameafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Algebra ConsolidationDocument5 pagesAlgebra ConsolidationafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 (3rd Term Test 2004 - P2)Document10 pagesGrade 9 (3rd Term Test 2004 - P2)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Trig Eq NsDocument4 pagesSolving Trig Eq NsafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 3-AreaTriangleDocument8 pages7 3-AreaTriangleafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade P8 (Ratio & Proportion)Document2 pagesGrade P8 (Ratio & Proportion)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 AssessmentDocument6 pages11 AssessmentafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 3-AreaTriangleDocument8 pages7 3-AreaTriangleafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Limits (Test)Document1 pageLimits (Test)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Loci (Exercise)Document2 pagesLoci (Exercise)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Percent of ChangeDocument7 pagesPercent of ChangeafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade P8 (Percentages)Document2 pagesGrade P8 (Percentages)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 (Trigonometry)Document2 pagesGrade 9 (Trigonometry)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 (Sets)Document2 pagesGrade 9 (Sets)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th AssessmentDocument6 pages9th AssessmentafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathemtics - Grade 9: Graphs of FunctionsDocument2 pagesMathemtics - Grade 9: Graphs of FunctionsafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 (Limits of Accuracy)Document2 pagesGrade 8 (Limits of Accuracy)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 Maths (Geometry)Document3 pagesGrade 8 Maths (Geometry)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Factorisationa and FormulaeDocument1 pageFactorisationa and FormulaeafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 8 (3rd Term 2003)Document10 pagesGrade 8 (3rd Term 2003)afzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fractions, Aprox EtcDocument2 pagesFractions, Aprox EtcafzabbasiPas encore d'évaluation
- SAIC-H-2032 Rev 4.Document6 pagesSAIC-H-2032 Rev 4.Mohamed Farhan B PositivePas encore d'évaluation
- Centerless-Ground Parts PDFDocument9 pagesCenterless-Ground Parts PDFrrameshsmitPas encore d'évaluation
- Conference Paper TemplateDocument3 pagesConference Paper TemplateDeden MSPas encore d'évaluation
- F40327 Hobart QUANYUM Fkerte PDFDocument8 pagesF40327 Hobart QUANYUM Fkerte PDFAnonymous i2v1e07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adobe Acrobat Reader DC: Help and TutorialsDocument35 pagesAdobe Acrobat Reader DC: Help and TutorialsPras OnezatPas encore d'évaluation
- ServicesDocument10 pagesServicesLukmanKhakimPas encore d'évaluation
- prEN1999 1 4Document58 pagesprEN1999 1 4Pedro BarataPas encore d'évaluation
- Udr 1Document2 pagesUdr 1shazanPas encore d'évaluation
- Caja 8908LL EspDocument2 pagesCaja 8908LL EspDanny M Hurtado TaypePas encore d'évaluation
- Parts Manual: Taurulift T 204 HDocument140 pagesParts Manual: Taurulift T 204 HMiguel ViegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nihon Kohden 9010K Service Manual PDFDocument130 pagesNihon Kohden 9010K Service Manual PDFJumbo JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler FormulasDocument1 pageBoiler FormulasAnvar PaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jere SignatureDocument198 pagesJere SignatureMa. Luisa A. AngsincoPas encore d'évaluation
- SMPR Manual GBDocument64 pagesSMPR Manual GBDang Ngoc VungPas encore d'évaluation
- Nzs 4297 1998 PDFDocument63 pagesNzs 4297 1998 PDFjuan jose100% (1)
- Bowie Dick Testing - Medical Industry - EllabDocument1 pageBowie Dick Testing - Medical Industry - EllabSabinaPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 DDCBF 707 Ada 64327770Document2 pages6 DDCBF 707 Ada 64327770api-465329396Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Crime: What Is Security ?Document49 pagesComputer Crime: What Is Security ?Husein KattabPas encore d'évaluation
- 7900 RangeDocument16 pages7900 RangePhilippine Bus Enthusiasts SocietyPas encore d'évaluation
- User-Manual-3869588 Atoto Sa102 (Eagleplastic)Document33 pagesUser-Manual-3869588 Atoto Sa102 (Eagleplastic)JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- SRS Hostel Management System (HMS)Document19 pagesSRS Hostel Management System (HMS)sona_meet200243% (7)
- Suruhanjaya TenagaDocument43 pagesSuruhanjaya Tenagaavenged sevenfold6989% (9)
- Anexo 05 - Process Planning and Audit v2 1Document33 pagesAnexo 05 - Process Planning and Audit v2 1QMS : Aswin Cold ForgePas encore d'évaluation
- Agile Project Governance PDFDocument19 pagesAgile Project Governance PDFaverav99Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Specifications, Division 16, SECTION 16425 SWITCHGEAR ASSEMBLIES MAIN DISTRIBUTION BOARDDocument21 pagesElectrical Specifications, Division 16, SECTION 16425 SWITCHGEAR ASSEMBLIES MAIN DISTRIBUTION BOARDeng_asayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix H Project Completion Report: SECTION A: Project ProfileDocument3 pagesAppendix H Project Completion Report: SECTION A: Project Profileflee2yasirPas encore d'évaluation
- Water BillDocument11 pagesWater Billrohit88848Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tny 264Document20 pagesTny 264Juri BehariPas encore d'évaluation