Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Presentation Ford & Toyota en
Transféré par
kamranp10 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
41 vues40 pagesToyota
Titre original
Presentation Ford & Toyota En
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentToyota
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
41 vues40 pagesPresentation Ford & Toyota en
Transféré par
kamranp1Toyota
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 40
COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS:
FORD MOTOR COMPANY
TOYOTA MOTOR CORP
dr Agata Kocia
based on presentation by:
PAWE ORZECHOWSKI, MACIEJ OWIT &
ANDRZEJ BENCZEK
FORD: the beginning
Henry Ford designed his first moving assembly
line in 1913
Wheels for the world-the motto behind
popularization of cars
Each section of the production process was
divided into component parts
Combination of precision, continuity, and fast-
paced brought the world mass production
In Highland Park, Model T production reached
record levels, every day a car came of the
assembly line every ten seconds
TOYOTA: the beginning
Toyota's history began at the end of XIX century
Sakichi Toyoda invented Japan's first power
loom which revolutionized the countrys textile
industry
Two years later, he founded the company
Toyoda Automatic Loom Works
Toyody Sakichis son, Kiichiro Toyoda invested
100,000 pounds in the creation of Toyota Motor
Corporation in 1937 (TMC)
Sakichi Toyoda received this money for selling
the patent rights to an automatic loom
FORD
The fourth-largest automotive company in the world in terms of sales
Sells cars on 6 continents
Car Brands: Ford, Mercury, Lincoln and Volvo
in March of 2010 confirmation of sale of Geely Automobile Holdings Ltd)
Since the mid-90s Ford continually loses significance in the
American market
Over the same period steadily increases its share in the European
market
Reasons for the gap between the development of the brand in the
U.S. and Europe:
high labor costs in the U.S.
high expenditure on healthcare in the U.S.
strong trade unions in the U.S. (high pension commitments)
strong economic growth in lower combustion cars
TOYOTA
The biggest carmaker in the world in 2009
(more than 7.5 million cars)
Main markets are Japan and North
America, but recently we can see a strong
growth in Asian and South America
markets
Toyota has three brands: Toyota, Lexus
and Scion
FORD: more economic
Dominance of large cars: SUVs, Pick ups
Rapid fluctuations in oil prices and legislators
striving to reduce consumption of materials led
to reorganization
Restructuring of the three production lines for
production of more economic models in Europe
(Mondeo, Focus etc.)
in short-run minimization of costs
Ultimately, Ford intends to make engines in all
their models to be more economical
In 2009 to market were introduced four hybrid
models based on technology leased from Toyota
FORD: hybrid technology
Currently, Ford has four hybrid models
Ford Focus Hybrid is a direct threat to so far the most
popular Prius (hybrid line of Toyota)
In 2010, the company plans to spend an
additional $450 million to develop electric motors
By 2012, Ford wants to produce own hybrid
technology and plug-ins
Ford has invested more than $550 million in
restructuring its manufacturing facility in Michigan
What if the market chooses a different path?
TOYOTA: hybrid technology
Toyota as one of the first ones started a hybrid
cars production line (including leasing its
technology to Ford)
At present, hybrid Toyota - Prius line, represents
approximately 73% of all hybrid vehicles sold in
the U.S.
So far in the U.S. Toyota sold the 1,000,000+
hybrid cars
In addition, Toyota announced its intention to
manufacture electric cars with lithium-ion
batteries Toyota Plug-HV
FORD: ONE FORD
Despite the very large amount
of cars produced, so far Ford
has derives small economies
of scale by applying a
separate, independent
technologies and models for
European, US and developing
markets
One Ford changed
approach
Ford moves the emphasis to
universal models for use in
different regions of the world
(the first "world car"-new Ford
Fiesta)
FORD: wrong sales model
From the 90s Ford has created demand
sales on installments without interest charged
discounts
promotions combined with a loan
Ford exceptionally strong suffered from a crisis on a real
estate market
in recent years, sales in the U.S. were strongly associated with
the property market
it is estimated that in California, 30% of car purchases has been
financed with a mortgage
Feeling the effects of this approach, Ford began to
change strategy
less emphasis on creating demand
emphasis on quality and safety
FORD: developing markets
Ford is mainly engaged in the American market,
which slowly begins to lose its attractiveness
Fords task now is to develop a universal line for
use in every country (European Ford Fiesta in
the U.S., Ford Transit Van in Asia)
Whether european car models will be appealing
to clients in India or Brazil depends the future of
Ford in the long term.
TOTOTA: withdrawal of models
Several serious flaws in the models has significantly hurt
Toyotas image
in 2009, the company had to withdraw from the market 3.8
million vehicles due to the acceleration system flaw
In the short term:
it is estimated that due to defects and withdrawals Toyota
models suffered losses of $ 3 billion in 2010
over the past year, throughout the world over 9 million vehicles
have been withdrawn
for consideration more than 30 lawsuits are waiting
In the long term:
current crisis has significantly hurt the reputation of the company
competition has used well (Chrystler, Ford and Honda
hasorganized the promotions, giving discount on a new car for
customers who got rid of the old Toyota)
TOYOTA: the future
Car Sales in highly developed countries will fall and
remain at low levels
majority of consumers demand is already satisfied
relatively low economic growth
The biggest outlays directed on emerging markets
mainly Brazil, Russia, India, China (BRIC) countries
Toyota earlier than other companies in the sector began to
invest in the development of appropriate infrastructure and brand
awareness in the above countries
in 2009 Toyota announced the beginning of motor vehicle
production in India (the company Toyota Kirloskar)
in 2010 Toyota plans to produce 100,000 cars in the new factory
opened in India
TOYOTA:
trends and expectations (1)
Japan
investing in luxury brands (Lexus)
in 1990 10% of Japan's population was over 65 years, in 2006, the number
suppose to double
older society saves more and raises the demand for more luxury goods
USA
collapse of the real estate market
strength of real estate market has always been related to car market
because consumers often fund the purchase of car with a mortgage owed
stagnation in credit market will reduce demand for new cars
demand for green technologies
oil prices are rising, resulting in increased demand for cars Hybrid (Prius
model)
in December of 2007. U.S. government passed a law requiring the car
manufacturers to reduce the combustion of up to 35 mpg for cars, trucks and
SUVs Toyota,
typically produces small, economical cars and its standards are already
satisfy new requirements
TOYOTA:
trends and expectations (2)
USA
hybrid legislation
USA introduces new law to encourage development of hybrid
technologies
at present, when buying a car you can count on the hybrid
tax relief of up to $ 3,400, depending on the amount of car
sales (the more cars the company sells the smaller the
deduction ) the aim is to support companies desiring to
enter the market with hybrid technology
World Market
demand for cars will depend on the trend in oil, steel
and aluminum prices
FORD/TOYOTA:
general data (in $ mln)
2006 2007 2008
Sales (FORD) 143,249 154,379 129,166
Sales (TOYOTA) 203,874 256,581 2081,262
Income from operations
(FORD)
-7,926
8,031
-4,130
Income from operations
(TOYOTA)
19,058
22,159 -4,674
Net income (FORD) -12,613 -2,723 -14,672
Net income (TOYOTA) 13,996 16,766 -4,430
Employment (FORD) 283 247 213
Employment (TOYOTA) 286 299 316
Total assets (FORD) 279,196 279,264 218,328
Total assets (TOYOTA) 277256 318875 294627
TOYOTA: production (in 1000s)
2006 2007 2008
North America 1201 1205 1268
South America 122 147 150
Europe 623 709 711
Asia, Africa, Australia 1081 1019 1258
Japan 4684 5100 5160
FORD/TOYOTA: sales (in 1000s)
2006 2007 2008
North America (FORD) 3051 2890 2329
(TOYOTA) 2556 2943 2958
South America (FORD) 381 438 435
(TOYOTA) 233 284 320
Europe (FORD) 1846 1918 1820
(TOYOTA) 1023 1224 1284
Asia, Africa, Australia
(FORD)
589 535 464
(TOYOTA) 1384 1361 1559
Japan (TOYOTA) 2364 2273 2188
Risk factors
FORD
Ford is exposed to various kinds of risk not only to the
market risk
currency risk, commodity price changes, interest rate risk,
financing risk, risk of extraordinary events are just some of the
most important kinds of risk present
risk of loss of liquidity: hedge against it by sale of receivables
(securitization), issue of debt and bank loans
insurable risks: the loss (damage) of property, civil liability
companies insure themselves privately
they use derivatives to hedge currency, interest rate or change
in commodity prices risk by forwards, swaps, options
does not use derivative to speculate
TOYOTA
Toyota is exposed to risks arising from:
changes in exchange rates
interest rates
availability of materials
changes in prices of materials
Instruments used to protect:
forward contracts
currency and interest rate options
swaps
Unfortunately, Toyota does not protect itself from price
changes and changes in supply of materials
only protection is to maintain reserves of some materials
TOYOTA: currency risk
Toyota settles its invoices in Japanese yen
which increases its currency risk
Changes in exchange rates reflect very strongly
on company results
change in the dollar-yen exchange rate of 1% will
change revenues by about $42 million
Toyota protect itself from risk with the help of
swaps and futures
Despite this, the company is unable to protect
itself from a falling demand for exports of
Japanese cars due to a change in exchange
rates
Ratio analysis
Liquidity ratios (1)
Current ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 1,00 1,01 1,07
Ford 2,28 2,32 1,33
Liquidity ratios (2)
Quick ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 0,80 0,82 0,87
Ford 2,13 2,19 1,25
Debt ratio
Debt ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 0,62 0,61 0,64
Ford 0,62 0,60 0,71
Turnover ratios (1)
Receivables (A/R) turnover ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 32,14 29,59 26,15
Ford 15,89 17,14 14,95
Turnover ratios (2)
Inventory turnover ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 13,21 14,79 11,80
Ford 13,60 13,20 13,80
Turnover ratios (3)
Asset turvover ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 0,70 0,76 0,66
Ford 0,57 0,62 0,67
Profitability ratios (1)
Net profit margin 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 0,07 0,06 -0,03
Ford -0,08 -0,01 -0,10
Profitability ratios (2)
ROA 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 0.05 0.05 -0.02
Ford -0.05 -0.01 -0.06
Profitability ratios (3)
ROE 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 0.14 0.14 -0.04
Ford 0.00 -2.52 0.00
Market value ratios (1)
Earnings per share 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 4.34 5.40 -1.42
Ford -6.46 -1.38 -6.72
Market value ratios (2)
Price/Earnings ratio 2006 2007 2008
Toyota 29.94 18.68 -44.58
Ford -1.16 -4.86 -0.34
Market value ratios (3)
Dividend yield 2006 2007 2008
Toyota
0,01 0,01 0,02
Ford
0,11 0 0
Cash flow analysis
FORD TOYOTA
Operating Investing Financing Operating Investing Financing
2006
+ - +
+ - -
2007
+ - -
+ - -
2008
- - -
- - -
SWOT analysis
FORD
Strengths
Hybrid technology
Well-known brand in the USA
Weaknesses:
Weak sales results
Inability to accommodate products
to changes on the market
Opportunities:
Promotion of ecology-friendly cars
Appeal of a national brand in crisis
Threaths:
Further evolution of the crisis
TOYOTA
Strengths
Hybrid technology
Ability to cope in crisis
Weaknesses:
Lack of protection against changes
in prices and demand
Opportunities:
Promotion of economical and
ecology-friendly cards
In crisis, lesser importance of
competitors
Threaths:
Rapid increase of material costs or
decrease in supply
Thank you for your attention
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- From the Cradle to the Craze: China's Indigenous Automobile IndustryD'EverandFrom the Cradle to the Craze: China's Indigenous Automobile IndustryPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Ford & ToyotaDocument40 pagesPresentation Ford & ToyotaPhoneix12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comparative Analysis of Ford and ToyotaDocument22 pagesComparative Analysis of Ford and ToyotaSaif RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Ford and ToyotaDocument26 pagesComparing Ford and ToyotaShadman Tauheed100% (3)
- 5 Competitors: Toyota, Ford, and MoreDocument47 pages5 Competitors: Toyota, Ford, and MoreManish SalunkePas encore d'évaluation
- Firm Presentation - ToyotaDocument35 pagesFirm Presentation - ToyotaLavinia GolasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction On Indian AutomobileDocument14 pagesIntroduction On Indian AutomobileZahir ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT AnalysisDocument7 pagesSWOT AnalysislanguagembaPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT Analysis Toyota: StrengthsDocument2 pagesSWOT Analysis Toyota: StrengthsSachin ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota: By, Senthil PrabhuDocument9 pagesToyota: By, Senthil PrabhusenthilmbacaPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT Analysis - Tata Motors LimitedDocument9 pagesSWOT Analysis - Tata Motors Limitednani66215487Pas encore d'évaluation
- AutomobileDocument98 pagesAutomobilesrp188Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota's History and Business OverviewDocument28 pagesToyota's History and Business OverviewLit Yen YeongPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT ToyotaDocument4 pagesSWOT ToyotaMatias DelcontePas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Analysis Automotive IndustryDocument71 pagesIndustrial Analysis Automotive Industrytaghavi1347Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota Revs Up Us SalesDocument3 pagesToyota Revs Up Us Salesseeksudhanshu1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Industry Crisis of 2008-2010: Team MembersDocument8 pagesAutomotive Industry Crisis of 2008-2010: Team MembersMaged M.W.Pas encore d'évaluation
- ToyotaDocument29 pagesToyotagoelankit51Pas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Industry OverviewDocument3 pagesAutomotive Industry OverviewPratik PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- ToyotaDocument22 pagesToyotavidhi_bharatinfraPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Toyota Motors: Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsDocument6 pagesPresentation On Toyota Motors: Bangladesh University of ProfessionalsSadman KabirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ford ProjectDocument29 pagesFord ProjectSunil NaiduPas encore d'évaluation
- New Final ProjectDocument26 pagesNew Final ProjectAsad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Ford Motor Company: 2009Document41 pagesFord Motor Company: 2009Shirley Pearls67% (6)
- Ford MotorsDocument32 pagesFord MotorsTaha MadniPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation 1Document42 pagesPresentation 1JAY BHAVIN SHETH (B14EE014)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota Swot AnalysisDocument3 pagesToyota Swot AnalysisAnkur Anil Nahata100% (4)
- Toyota's Sudden Unintended Acceleration CrisisDocument34 pagesToyota's Sudden Unintended Acceleration CrisisRutuja Kshirsagar HandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analysis On Toyota CompanyDocument2 pagesCase Analysis On Toyota CompanyEng. Tadele DandenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fords Case AnalysisDocument8 pagesFords Case Analysissambalcheese100% (1)
- Toyota's: Globalization StrategiesDocument25 pagesToyota's: Globalization StrategiesitsgouravaroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Ford Motor Company History and SWOT StudyDocument7 pagesFord Motor Company History and SWOT StudyReyte on Publishing A. Johnson60% (5)
- Toyota: Jerry John AcharyaDocument31 pagesToyota: Jerry John AcharyaGinu M Koshy100% (1)
- Tata Buys Jaguar PEST AnalysisDocument3 pagesTata Buys Jaguar PEST AnalysisSanjay Tiwari100% (2)
- Project MRKTDocument20 pagesProject MRKTSafa SehliPas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota FinalDocument39 pagesToyota FinalBhaumik PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Honda Motor Company BackgroundDocument10 pagesHonda Motor Company BackgroundShubham ShimpiPas encore d'évaluation
- ToyotaDocument10 pagesToyotaArun Sanal100% (2)
- ABC of Automotive IndustryDocument81 pagesABC of Automotive Industrysha_ban0% (1)
- Fiat AssignmentDocument17 pagesFiat AssignmentGurpreet Kaur67% (3)
- Toyota SWOTDocument14 pagesToyota SWOTManish GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Management in Auto Mobile IndustryDocument10 pagesStrategic Management in Auto Mobile IndustryVikramaditya ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Global automobile industry: An oligopolistic marketDocument4 pagesGlobal automobile industry: An oligopolistic marketPranav BehkiPas encore d'évaluation
- POSITIONING ANALYSIS Toyota Motor CorporationDocument6 pagesPOSITIONING ANALYSIS Toyota Motor Corporationbonnyjohn50% (2)
- Honda Company BackgroundDocument6 pagesHonda Company BackgroundDilawar Aheer100% (1)
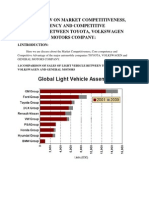
- Overall View On Market Competitiveness, Corecompetency and Competitive Advantage Between Toyota, Volkswagen and General Motors CompanyDocument16 pagesOverall View On Market Competitiveness, Corecompetency and Competitive Advantage Between Toyota, Volkswagen and General Motors CompanySuganthan DuraiswamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Projectonindianautomotiveindustry 121201001808 Phpapp01Document37 pagesProjectonindianautomotiveindustry 121201001808 Phpapp01sid919547Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota Group Project ReportDocument58 pagesToyota Group Project ReportFaiz AlbahrainPas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota's Business Strategies in International MarketsDocument5 pagesToyota's Business Strategies in International MarketsKanishk PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument5 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documentrajmv7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Toyota Motor Corporation Company StudyDocument10 pagesToyota Motor Corporation Company StudyMa. Monica De Los Trinos0% (1)
- Hyundai Motor Company's Operations and Strategies in EthiopiaDocument15 pagesHyundai Motor Company's Operations and Strategies in Ethiopiasamuel debebe100% (1)
- Toyota IncidentDocument6 pagesToyota IncidentPhạm GiaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Toyota: The World's Largest AutomakerDocument11 pagesIntroduction to Toyota: The World's Largest AutomakerAreej JehanPas encore d'évaluation
- Company of ChoiceDocument3 pagesCompany of ChoiceMaisha MahdiatPas encore d'évaluation
- International Management - ToyotaDocument13 pagesInternational Management - ToyotaPriyanka Gulati MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 1: TOYOTA PRIUS: Leading A Wave of HybridsDocument8 pagesCase 1: TOYOTA PRIUS: Leading A Wave of HybridsDon CoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Honda Motor (Review and Analysis of Sakiya's Book)D'EverandHonda Motor (Review and Analysis of Sakiya's Book)Évaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (1)
- The Mediating Effect of Customer Intimacy Perceptions On The Trust - Commitment RelationshipDocument1 pageThe Mediating Effect of Customer Intimacy Perceptions On The Trust - Commitment RelationshipSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Groups S Pss Infer Ential StatisticsDocument42 pagesComparing Groups S Pss Infer Ential StatisticsKatarina VitomirovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Univariate StatisticsDocument17 pagesUnivariate StatisticsSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to PhysiotherapyDocument25 pagesIntroduction to PhysiotherapySana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Read MeDocument1 pageRead MemslightningPas encore d'évaluation
- Example of Interpreting and Applying A Multiple Regression ModelDocument5 pagesExample of Interpreting and Applying A Multiple Regression ModelhgjgjqPas encore d'évaluation
- Correlation: ObjectivesDocument9 pagesCorrelation: ObjectivesJust MahasiswaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented To Sir Yasir: Presented by Sana JavaidDocument18 pagesPresented To Sir Yasir: Presented by Sana JavaidSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- SPSSChapter 8Document8 pagesSPSSChapter 8Syeda Sehrish KiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Example of Interpreting and Applying A Multiple Regression ModelDocument5 pagesExample of Interpreting and Applying A Multiple Regression ModelhgjgjqPas encore d'évaluation
- Moderation Meditation PDFDocument11 pagesModeration Meditation PDFMostafa Salah ElmokademPas encore d'évaluation
- The CommitmentDocument8 pagesThe CommitmentSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Moderation and Mediation by SPSSDocument3 pagesModeration and Mediation by SPSSmehrinfatimaPas encore d'évaluation
- Regression analysis of occupational prestigeDocument20 pagesRegression analysis of occupational prestigeSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Bivariate Correlation in SPSSDocument2 pagesBivariate Correlation in SPSSSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Groups S Pss Infer Ential StatisticsDocument42 pagesComparing Groups S Pss Infer Ential StatisticsKatarina VitomirovicPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview of Government's Poverty Alleviation Policies and ProgrammesDocument21 pagesAn Overview of Government's Poverty Alleviation Policies and ProgrammesSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparing Groups S Pss Infer Ential StatisticsDocument42 pagesComparing Groups S Pss Infer Ential StatisticsKatarina VitomirovicPas encore d'évaluation
- In Term of The Basic Communication Model The Word Interactive Mean Communication Between PeoplesDocument2 pagesIn Term of The Basic Communication Model The Word Interactive Mean Communication Between PeoplesSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- LCDP How To Strategic Plan PDFDocument11 pagesLCDP How To Strategic Plan PDFSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Knowledge Management Strategies: 1. T B P K MDocument8 pagesKnowledge Management Strategies: 1. T B P K MSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Reliability Validity ScalingDocument7 pagesReliability Validity ScalingSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Shahid PDFDocument16 pagesShahid PDFSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Customer Benefits and Company Consequences of Customer-Salesperson Relationships in RetailingDocument22 pagesCustomer Benefits and Company Consequences of Customer-Salesperson Relationships in RetailingSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Bendapudi1997 PDFDocument23 pagesBendapudi1997 PDFSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Harrison2012 PDFDocument17 pagesHarrison2012 PDFSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Ballantyne2006 PDFDocument9 pagesBallantyne2006 PDFSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Cost Accounting Presented To: Sir Sufyan Javaid Presented By: Sana Javaid 12052054-045 Section (BL)Document1 pageSubject: Cost Accounting Presented To: Sir Sufyan Javaid Presented By: Sana Javaid 12052054-045 Section (BL)Sana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication, Commitment & Trust: Exploring The Triad: Published by Canadian Center of Science and EducationDocument11 pagesCommunication, Commitment & Trust: Exploring The Triad: Published by Canadian Center of Science and EducationDanuSusantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Project of MCB (1) HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRDocument29 pagesProject of MCB (1) HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRSana JavaidPas encore d'évaluation