Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Temperature and Heat.
Transféré par
DerekVladimirSandovalCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Temperature and Heat.
Transféré par
DerekVladimirSandovalDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
What are
temperature
and heat?
Are they the
same?
What causes
heat?
How do we
measure
temperature?
What are we
actually
measuring?
Temperature and Its Measurement
How do we measure temperature?
Thermometer: Device with a physical property
that changes with temperature and can be easily
measured quantitatively.
If two objects are in contact with one another
long enough, the two objects have the same
temperature (thermal equilibrium).
Two or more objects in thermal equilibrium
have the same temperature.
Zeroth law of thermodynamics.
Temperature Scales
The first widely used
temperature scale was devised
by Gabriel Fahrenheit.
Water freezing point: 32F
Water boiling point: 212F
Another widely used scale was
devised by Anders Celsius.
Water freezing point: 0C.
Water boiling point: 100C
Temperature Scales
Conversion between two scales:
E1. An object has a temperature
of 45C. What is its temperature
in degree Fahrenheit?
E2. The temperature of a winter
day is 14F. What is the
temperature in degree Celsius?
T
C
5
9
T
F
32
T
F
9
5
T
C
32
Zero Temperature
The zero point on the
Fahrenheit scale was based on
the temperature of a mixture of
salt and ice in a saturated salt
solution.
The zero point on the Celsius
scale is the freezing point of
water.
Both scales go below zero.
Is there an absolute zero?
What is absolute zero?
If the volume of a gas is kept
constant while the temperature is
different, the pressure will be
different.
The Third Temperature Scale
Absolute Temperature Scale (Kelvin Scale)
Example
Water freezing point: 0C =273.2 K.
Water boiling point: 100C = 373.2 K
T
K
T
C
273 .2
Heat and Temperature
Heat:
Heat is the energy that flows from one object to
another when there is a difference in temperature
between the objects. Heat is the average kinetic
energy of atoms or molecules making up the system.
Temperature:
Temperature is an indication
of whether or not and in which
direction, the heat will flow
(Temperature is an indication
of the average of kinetic energy
of atoms or molecules).
The Flow of Heat
Three basic processes for heat flow:
Conduction
Convection
Radiation
A metal block at room
temperature will feel colder
than a wood block of the exact
same temperature. Why?
The rate of heat flow depends on:
a) the temperature difference between
the objects.
b) the thermal conductivity of the
materials, a measure of how well the
materials conduct heat.
Conduction: heat flow when in contact
Convection: heat is
transferred by the
motion of a fluid
containing thermal
energy.
Radiation, heat energy is
transferred by
electromagnetic waves.
can take place across a
vacuum.
What heat-flow processes are involved in
the greenhouse effect?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Calibrating Pressure Dependent and Independent Multi Yield Surface Soil ModelsDocument49 pagesCalibrating Pressure Dependent and Independent Multi Yield Surface Soil ModelsmohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Analysis (FINALS) PDFDocument45 pagesStructural Analysis (FINALS) PDFJunel Torrejos100% (1)
- ASTM International Constructuring Smooth Hot Mix Asphalt 2003 PDFDocument274 pagesASTM International Constructuring Smooth Hot Mix Asphalt 2003 PDFNur Yanta100% (1)
- The Position of Fermi Level in Intrinsic Semiconductors. (File 3)Document5 pagesThe Position of Fermi Level in Intrinsic Semiconductors. (File 3)Mihai BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concepts: Introduction To Composite DesignDocument10 pagesBasic Concepts: Introduction To Composite DesignraviciviltPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaft Calculation Base PDFDocument27 pagesShaft Calculation Base PDFBarsanu AlexPas encore d'évaluation
- MOL-5906 Elastomers: TUT Plastics and Elastomer Technology (Autumn 2008)Document63 pagesMOL-5906 Elastomers: TUT Plastics and Elastomer Technology (Autumn 2008)arfu~Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5.1 Nonferrous Metals & AlloysDocument28 pages5.1 Nonferrous Metals & Alloysjayvee allineraPas encore d'évaluation
- PHD 2020 Petar KnezevicDocument112 pagesPHD 2020 Petar KnezevicDejan Deki MaticPas encore d'évaluation
- Caustic Embrittlement - Causes and PreventionDocument2 pagesCaustic Embrittlement - Causes and Preventionravi2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sikadur 32, Hi-Mod: High-Modulus, High-Strength, Epoxy Bonding/grouting AdhesiveDocument2 pagesSikadur 32, Hi-Mod: High-Modulus, High-Strength, Epoxy Bonding/grouting AdhesivelobocernaPas encore d'évaluation
- PSC 35m - 4 Girders - 14.5m Width - M50 (As Per Shuttering) (Ch-109+700) PDFDocument315 pagesPSC 35m - 4 Girders - 14.5m Width - M50 (As Per Shuttering) (Ch-109+700) PDFKhirai HelpPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 Fatigue and CreepDocument17 pagesLecture 7 Fatigue and CreepAmmar SafwtPas encore d'évaluation
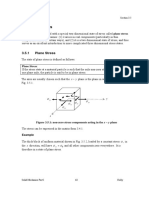
- 03 Stress 05 Plane Stress PDFDocument18 pages03 Stress 05 Plane Stress PDFNasrulPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Optimum Materials for Wind Turbine Tower and BladesDocument17 pagesDesigning Optimum Materials for Wind Turbine Tower and BladesChong Jie MeePas encore d'évaluation
- Dispersion and Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes in Polymer Matrix A ReviewDocument24 pagesDispersion and Alignment of Carbon Nanotubes in Polymer Matrix A ReviewYovaraj Karunakaran0% (1)
- Hexagonal Array Model for Auxetic Microporous PolymersDocument4 pagesHexagonal Array Model for Auxetic Microporous PolymersYc MaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1.2.a Beamdeflection 2Document7 pages2.1.2.a Beamdeflection 2Bailey RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
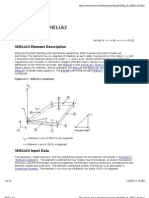
- Ansys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 ElementDocument10 pagesAnsys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 Elementansys Shell 63 ElementvilukPas encore d'évaluation
- Ae1402 Composite Materials and StructuresDocument23 pagesAe1402 Composite Materials and Structuresrakhi_chenPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics Class XIDocument17 pagesThermodynamics Class XIKAMAL KANT KUSHWAHA100% (1)
- Tegangan Normal Teg Ijin Dan Teg TermalDocument12 pagesTegangan Normal Teg Ijin Dan Teg Termalashrin masyhudiPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.002 Mechanics and Materials Ii Spring, 2004Document22 pages2.002 Mechanics and Materials Ii Spring, 2004Indranil BhattacharyyaPas encore d'évaluation
- PEJABAT WILAYAH UTARA SARAWAK TENSILE TEST REPORTDocument3 pagesPEJABAT WILAYAH UTARA SARAWAK TENSILE TEST REPORTSK KG Selanyau SarawakPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials Engineering MIDTERM EXAM 1Document13 pagesMaterials Engineering MIDTERM EXAM 1ahber yenaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Stress Manual CalcDocument62 pagesPipe Stress Manual Calcpipestress100% (7)
- Summary of Changes ASME BPVC - Ii.dDocument16 pagesSummary of Changes ASME BPVC - Ii.dAnonymous xr4GVHPas encore d'évaluation
- Full TextStress-strain Model For Concrete Under Cyclic LoadingDocument14 pagesFull TextStress-strain Model For Concrete Under Cyclic LoadingtoilfulboyPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Structural Components Against Failure Under Static LoadsDocument8 pagesDesigning Structural Components Against Failure Under Static LoadsArpit sharma0% (1)
- Crack Propagation XFEM EnrichmentDocument19 pagesCrack Propagation XFEM EnrichmentBensingh DhasPas encore d'évaluation