Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
MBA - Marketing Management
Transféré par
charulakhwan12Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MBA - Marketing Management
Transféré par
charulakhwan12Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ALESSI
Evolution of an Italian
Design Factory
Marketing Management
Team C
EMBA 06
How to control and expand
distribution without
compromising the brand image?
Distribution Structure
Distribution and the Brand Image
Challenges
Next Step
Why Controlling Distribution?
Control Brand Image
Problem of heterogeneity in retailer
strategies over product display
Diversity in distribution channels
Recovering from price and brand
confusion of past ten years
Increase turnover
Distribution Structure
Use distribution as
A channel of distribution
Diversified channels: retail outlets, museum stores, gift shops,
A place to increase brand equity
Luxury retail shops in Italy
Offering: between shopping and specialty
Design-oriented table and kitchen products
Shopping goods (not convenience goods!): about 50% purchases
as gifts, wedding presents, Christmas: overall 25-30% of annual
sales.
Specialty goods: best sellers like M.Suicide, Magic Bunny, etc
Consumer side distribution structure
~1983: Change into streamlined distribution system
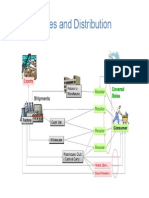
Distribution Structure
Manufacturer
Independent
Distributors
Retailers
Manufacturer
Retailers
orders - deliveries
orders - deliveries orders
Single Country
Independent agents
or subsidiaries
orders
deliveries
1983: streamlined distribution system
Hybrid channel administration
Indirect for orders and direct for deliveries
Agents: independent or company-owned subsidiaries
Benefits: increase of control in distribution, reduction of functional
discrepancies, reduction of delivery costs, economies of scale in order
management, better mapping in assortment of goods and better services
by company-owned subsidiaries
Distribution Structure
Manufacturer
Retailers
orders
Single Country
Agent
orders
deliveries
PUSH strategy
Induce cooperation with retailers,
keep inventory low, display
products, and visibility on shelf
spaces to win voluntary co-
operation.
streamlined distribution system
Shift in market coverage
strategy
From intensive distribution to
selective distribution:
Agents as independent
entities in exclusive
geographical areas
From 9000 retailers in 1989 to
5000 in 2000.
Management of Power in
Distribution Channels
Avoidance Strategy
Differentiation: design oriented and product naming
Focus: Table and kitchen, high-quality
Reduction in costs: Reduction in delivery costs by streamlined
distribution system.
Lately: Resistance and confrontation strategy
Diversification of channels: selected retailers, own stores,
licensing
Controlled distribution system
Management of Power in
Distribution Channels
Power Management increased by streamlined
distribution system
Better control over products and shorter delivery channels
thus reduction of costs of opportunity.
Threat of revocation
Retailer churn=5% in 03
Trainings
Merchandising
Reference value
Identification
Coercive sources
Non-coercive
sources
Power
basic
offering
Services: support in merchandising,
inventory risk, training
service offering
Distribution and the Brand
Distribution on Brand Image
Consistent retail experience to strengthen the brand
Benefits: Customer Loyalty, more inelastic consumer response,
greater trace cooperation and support, possible licensing
opportunity
Shop-in-shop for control over product display, demanding
retailer commitment: ask for minimal surfaces
Mono-brand stores: show rooms and flagship stores
03: 3 moves to expand distribution while increasing
customer-based brand equity value:
Consistent retail experience
Increasing retail penetration in key markets
Licensing the Brand for newer types of products like watches
and cars
Distribution Challenges on
Brand Image
~80s: Too intensive distribution system
Price discrepancy between luxury retailers and
others
confusing brand image
Constant control challenge over product display,
merchandising and pricing
Though selective approach, Licensing still
putting at risk the brand image by partners
controlling manufacturing and distribution.
Luxury Other retailers
Next Step: Multiple Trademarks
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- MBA - Marketing Management - Alessi Case StudyDocument13 pagesMBA - Marketing Management - Alessi Case StudyvenkatdeepakvbPas encore d'évaluation
- Channels of DistributionDocument60 pagesChannels of DistributionRam Manoj Yendru100% (1)
- Channels of Distribution PPT at Bec Doms Bagalkot Mba MarketingDocument60 pagesChannels of Distribution PPT at Bec Doms Bagalkot Mba MarketingBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution ChannelsDocument27 pagesDistribution ChannelsRicha GargPas encore d'évaluation
- LDistri StrategiesDocument24 pagesLDistri StrategiesSuresh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- MarQuity Sales & Distribution CompendiumDocument9 pagesMarQuity Sales & Distribution CompendiumGarvitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Distribution Strategies: Tapan Raval Mohit Motwani Ankit Assudani Sunny ChauhanDocument24 pagesProduct Distribution Strategies: Tapan Raval Mohit Motwani Ankit Assudani Sunny ChauhanChetan GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail ManagementDocument94 pagesRetail ManagementDinesh Bicchewar100% (7)
- Distribution DecisionsDocument40 pagesDistribution Decisionstarang keraiPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing and Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelsDocument42 pagesDesigning and Managing Integrated Marketing ChannelsXaal KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution GroupDocument2 pagesDistribution GroupFady SamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing Channel - Ch-4 - Channel Structure and IntensityDocument25 pagesMarketing Channel - Ch-4 - Channel Structure and IntensityUmair Rasheed100% (2)
- Distribution Strategy PDFDocument42 pagesDistribution Strategy PDFAristide Ahonzo63% (8)
- Selling and Sales Management: Birat Shrestha BBA Emph/Hons, KUSOMDocument31 pagesSelling and Sales Management: Birat Shrestha BBA Emph/Hons, KUSOMAshley WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5-Designing Marketing Programs To Build Brand EquityDocument27 pagesChapter 5-Designing Marketing Programs To Build Brand EquityLuitel_sudhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing and Managing AndIntegrated Marketing Channels - 149-155Document86 pagesDesigning and Managing AndIntegrated Marketing Channels - 149-155Shashiranjan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Merchantising and DistributionDocument25 pagesMerchantising and DistributionShailja Dixit100% (1)
- Trade MarketingDocument73 pagesTrade MarketingLaura Premoli83% (12)
- Part 1 Retailing and Retail ManagementDocument37 pagesPart 1 Retailing and Retail ManagementSarthak Khanna100% (1)
- Distribution LessonDocument20 pagesDistribution LessonHoney amayaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 SummaryDocument5 pagesChapter 12 SummarygeneoeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Prelim 3 Study QuestionsDocument15 pagesPrelim 3 Study QuestionsIla AnandPas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing ChannelsDocument10 pagesMarketing ChannelsPriyum TikmaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Modified StrategyDocument19 pagesModified StrategyloveyournewPas encore d'évaluation
- Product, Services, and Branding StrategiesDocument29 pagesProduct, Services, and Branding StrategiesMd Alamgir HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- Q-1 Explain The Importance of The Retailer Within The ChannelDocument26 pagesQ-1 Explain The Importance of The Retailer Within The Channelyogesh280502Pas encore d'évaluation
- Push Pull Strategy in MarketingDocument25 pagesPush Pull Strategy in MarketingAshok AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- Integration of Sales and Distribution Strategies Final 2003Document24 pagesIntegration of Sales and Distribution Strategies Final 2003Sukesh Kumar50% (2)
- Marketing CommunicationDocument37 pagesMarketing Communicationuzmatabassum1996Pas encore d'évaluation
- 16 RetailmultichannelDocument3 pages16 RetailmultichannelRohan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Retail ManagementDocument6 pagesSummary of Retail ManagementAda Araña DiocenaPas encore d'évaluation
- MarketingDocument3 pagesMarketinghouda boukabbouchaPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing Channels of Distribution: The Marketing Executive's Complete GuideD'EverandManaging Channels of Distribution: The Marketing Executive's Complete GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Marketing ChannelsDocument29 pagesMarketing ChannelsDenis ManolePas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 15 Designing and Managing Integrated Marketing Channels Presented By: Bhumika (13) Nitin (19) Ateet (31) SaurinDocument55 pagesCHAPTER 15 Designing and Managing Integrated Marketing Channels Presented By: Bhumika (13) Nitin (19) Ateet (31) SaurinAshish JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Carrefour DianaDocument20 pagesCarrefour DianaimmacoolcatPas encore d'évaluation
- Retail FinalDocument100 pagesRetail FinalKimi RoutPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 2Document21 pagesModule 2Irfana MubarakPas encore d'évaluation
- PlaceDocument25 pagesPlaceBharat JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 PromotionDocument35 pagesChapter 9 PromotionSandeep RajbharPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution Channel Design Decision MakingDocument18 pagesDistribution Channel Design Decision MakingShek GhPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit3industrial ManagementDocument68 pagesUnit3industrial ManagementpreetsinghalPas encore d'évaluation
- Culinarian CookwareDocument12 pagesCulinarian Cookwaredeepti_bawiskar100% (7)
- Text 13Document1 pageText 13juanevzylPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12 Marketing ChannelsDocument7 pagesChapter 12 Marketing ChannelsTaylor KalinowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sales and DistributionDocument65 pagesSales and DistributionKabo Lucas100% (1)
- Marketing Management - Channel DecisionsDocument4 pagesMarketing Management - Channel DecisionsNandini MukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution ChannelsDocument12 pagesDistribution ChannelsALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Sales Promotion: Forms of Sales Promotions-Consumer Trade & Sales Force-OrientedDocument18 pagesSales Promotion: Forms of Sales Promotions-Consumer Trade & Sales Force-OrientedShruti bansodePas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 8 Distribution ManagementDocument30 pagesChap 8 Distribution ManagementAntonio B ManaoisPas encore d'évaluation
- Retailing Encompasses The Business Activities Involved in Selling Goods andDocument3 pagesRetailing Encompasses The Business Activities Involved in Selling Goods andciriaco janPas encore d'évaluation
- Designing Channels of DistributionDocument2 pagesDesigning Channels of DistributionAkansha SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Mod 1 Introduction To RetailingDocument6 pagesAssignment Mod 1 Introduction To RetailingPrasad TikamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5LexyPas encore d'évaluation
- Hitesh Verma (50614901717) S & DM 3Document27 pagesHitesh Verma (50614901717) S & DM 3anamika vermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sales Promotion: All the tactics you need to turn an outbound prospect into a customerD'EverandSales Promotion: All the tactics you need to turn an outbound prospect into a customerPas encore d'évaluation
- Profitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessD'EverandProfitable Promotions : A Blueprint for Entrepreneurial Advertising SuccessPas encore d'évaluation
- Unlock Multi-Channel Profits: Proven Strategies for Business GrowthD'EverandUnlock Multi-Channel Profits: Proven Strategies for Business GrowthPas encore d'évaluation
- Unlock the Secrets of Profitable Dropshipping: A Comprehensive Guide to Building a Successful Online BusinessD'EverandUnlock the Secrets of Profitable Dropshipping: A Comprehensive Guide to Building a Successful Online BusinessPas encore d'évaluation