Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Peripheral Vascular
Transféré par
Kimsha ConcepcionCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Peripheral Vascular
Transféré par
Kimsha ConcepcionDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Prepared by: Angelo P.
Angeles, RN MAN
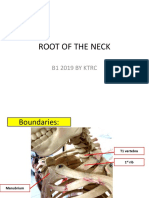
REVIEW OF STRUCTURES AND FUNCTIONS
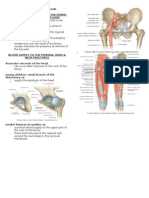
ARTERIES
Carry oxygenated
blood
Receives high
pressure from the LV
of the heart
Brachial Artery
Radial artery
Ulnar artery
Femoral Artery
Popliteal
Anterior branch
Dorsalis Pedis a.
Posterior branch -
Posterior Tibial a.
VEINS
Carry deoxygenated
blood, and wastes
SVC: head, arms,
upper trunk, head
and neck
IVC: lower trunk and
legs
Larger and can
expand in diameter
Deep veins
Femoral vein
Popliteal vein
Superficial veins
Great saphenous
(longest)
Small saphenous
Perforator veins
Mechanisms that propel
blood back to the
heart:
1. Presence of One-way
Valves
2. Muscular contraction
3. Creation of pressure
gradient (though
breathing)
Composed of lymphatic capillaries, lymphatic
vessels, and lymph nodes
Functions:
1. It drains excess fluid and plasma proteins from
body tissues and return them to venous
system
2. Aids in defending the body against MO
3. Absorbs fat from the small intestine into the
bloodstream
Superficial lymph
nodes of the arms and
legs
Epitrochlear lymph
nodes
Inguinal lymph
nodes
Horizontal
Vertical
NURSING HEALTH HISTORY
Change in Skin color, temperature or texture
ARTERIAL INSUFFICIENCY cold, pale, clammy
skin; thin shiny skin with loss of hair
VENOUS INSUFFICIENCY warm skin, brown
pigmentation around the ankles
Leg Pains or Cramps
Intermittent Claudication cramping in the calves,
thighs, or buttocks and weakness upon activity
(ARTERIAL disease)
Heaviness and aching sensation aggravated by
standing or sitting for longer periods (VENOUS
disease)
Leg pain at night (CHRONIC ARTERIAL dse)
Numbness (NEUROPATHY)
Varicose veins
Hereditary
Venous pressure and venous pooling
Leg Ulcers
Arterial painful
Venous painless
Edema (with/without pain)
Obstruction of lymphatic flow, incompetent valves,
osmotic pressure, DVT
Swollen lymph nodes
Infection
Male clients: Change in sexual activity
Leriches syndrome Impotence/Erectile
Dysfunction
PAST HEALTH HISTORY
History of Peripheral Vascular Diseases
History of Cardiovascular surgeries
FAMILY HISTORY
DM, HPN, Coronary Heart Disease,
Hypercholestrolemia
LIFESTYLE AND HEALTH PRACTICES
Cigarette smoking
Exercise
Female clients: Intake of Oral/ transdermal
contraceptives
Stress
Wearing of supportive hose
P H Y S I C A L E X A M I N A T I O N
Preparation
Have client wear examination gown
Upright position
Adjust room temperature
Explain exposure of parts to be assessed
Explain position changes
Equipment
Centimeter tape
Stethoscope
Doppler UTZ device
Conductivity gel
Gauze/tissue
Water proof pen
Blood pressure cuff
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Observe for the arm
size and venous
pattern; look also
for edema
Arms are bilaterally
symmetric; no
edema or
prominent venous
patterning
Lymphedema
(blocked lymphatic
circulation)
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Observe for
coloration of the
hands and arms
Color varies
depending on
clients skin tone
Rapid changes in
color (pallor,
cyanosis, redness)
Raynauds disease
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Palpate for clients
fingers, hands and
arms. Note temp.
Warm bilaterally
from fingertips to
upper arms
Cool extremity/
Cold fingers and
hands
Assess Capillary
Refill
Capillary beds refill
(color returns in 1-2
seconds)
> 2 secs
(vasoconstriction,
CO, shock, arterial
occulsion)
Palpate for the
radial pulse
Equal strength
bilaterally (2+)
Increased
hyperkinetic
Diminished or
absent occlusion
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Palpate for the
ulnar pulses
Equal strength;
may not be
detectable
Lack or resilience
or inelasticity
(arteriosclerosis)
Palpate the brachial
pulse (if suspected
for arterial
insufficiency)
Equal strength
bilaterally
Increased,
diminished, absent
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Palpate for the
epitrochlear lymph
node
Not palpable Enlarged/swollen
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Perform Allen test Pink coloration
return to palms
within 3-5 seconds
Pallor persists
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Observe skin color
while inspecting both
legs from toes to groin
Uniform pigmentation Pallor (elevated) &
rubor (dependent)
A.I.
Brownish V.I
Inspect distribution
of hair
Hair cover the skin
and appears on the
dorsal surface
Loss of hair (A.I)
Inspect for lesions Legs are free of
lesions/ulcers
Ulcers
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Inspect for Edema Identical
size/shape; no
swelling
Bilateral edema
Palpate for Edema No edema Pitting or non
pitting edema
Edema Grading:
1+ = slight pitting
2+ = deeper than 1+
3+ = noticeably deep pit;
looks larger
4+ = very deep pit; gross
edema in extremity
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Palpate bilaterally
for temp of feet and
legs
Equally warm Generalized
coolness (A.I.),
Warmth
(thrombophlebitis)
Palpate superficial
inguinal lymph n.
Nontender, maybe
movable
Swelling >2cm
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Palpate:
Femoral
Popliteal P.
Dorsalis Pedis P.
Posterior Tibial P.
Strong and equal
bilaterally
Weak or absent
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Inspect for
varicosities and
thrombophlebitis
Veins are flat and
barely seen under
the skin
Distended, nodular,
bulging and
tortuous veins
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Check for the
Homans sign
(-) Homanssign
No pain or
tenderness elicited
(+) Homans sign
Calf pain and
tenderness
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Position
change test
Feet: pink to slightly pale in
color (elevation); pinkish
color returns to toes and feet
in 10 secs, 15 secs for
superficial veins on top of
feet. (dangled)
Marked pallor
> 10 secs and > 15
secs (A.I.)
Persistent rubor
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Ankle- brachial
pressure index
(ABPI) ratio of
ankle systolic BP
to brachial systolic
BP.
Ankle pressure is
same or slightly
higher than the
brachial pressure
(ABPI: 1)
ABPI: 0.5 to 0.95
(mild to mod A.I.)
ABPI: 0.25 or lower
(severe stenosis)
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Manual
Compression test
No pulsation is
palpated (competent
valves)
Pulsation with the
upper fingers
(incomptent valves)
Procedure Normal Findings Abnormal Findings
Brodie-
Trendelenburg
test
Saphenous vein fills
from below in 30
seconds; no rapid
filling of veins from
above after removal
of torniquet
Filling from above
with the tourniquet
in place (while
client is standing)
incompetent valves
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- CASE 2 AnatomyDocument14 pagesCASE 2 AnatomyKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5795)
- Find Jobs in PampangaDocument3 pagesFind Jobs in PampangaKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Medicine Ward NCPDocument11 pagesMedicine Ward NCPKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Root of The Neck (Gross)Document21 pagesRoot of The Neck (Gross)Kimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Drug Study DMDocument5 pagesDrug Study DMKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- Deficient Diversional ActivityDocument2 pagesDeficient Diversional ActivityKimsha Concepcion100% (2)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Communicable DiseasesDocument176 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 pagesPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Bigay PusoDocument1 pageBigay PusoKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Imbalance D Nutrition Related To Fatigue As Evidenced by Poor Muscle ToneDocument2 pagesImbalance D Nutrition Related To Fatigue As Evidenced by Poor Muscle ToneKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- What Causes Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeDocument8 pagesWhat Causes Polycystic Ovarian SyndromeKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Ate Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Document2 pagesAte Gara NCP (Activity Intolerance)Kimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Pta 41107 3233666 78096Document11 pagesPta 41107 3233666 78096Casey CoxPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Decision Processes 55:273-297Document1 pageDecision Processes 55:273-297Kimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Neoreviews 2013 Ross E83 8Document8 pagesNeoreviews 2013 Ross E83 8Kimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Generic NameDocument6 pagesGeneric NameKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Alumni Studies in The United Kingdom: John Brennan, Ruth Williams, Alan WoodleyDocument13 pagesAlumni Studies in The United Kingdom: John Brennan, Ruth Williams, Alan WoodleyKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology: Higher Tier Paper 1HDocument28 pagesBiology: Higher Tier Paper 1HkaruneshnPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- LivroDocument44 pagesLivroCebolinha CebolaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Insuficienta Venoasa CronicaDocument15 pagesInsuficienta Venoasa CronicaSimona IonitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Epistaxis: "Bleeding From Inside The Nose"Document12 pagesEpistaxis: "Bleeding From Inside The Nose"Farrukh Mehmood100% (1)
- Key Concepts: Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVMDocument40 pagesKey Concepts: Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVMpukler1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument38 pagesCardiovascular SystemShyn BaldostamonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Edexcel GCE: Biology (Salters-Nuffield)Document20 pagesEdexcel GCE: Biology (Salters-Nuffield)samira_666Pas encore d'évaluation
- @literaturamedica@ CT ThoraxDocument928 pages@literaturamedica@ CT ThoraxPaulHerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- ) To Indicate If Each Class Has The Feature or A Cross (×)Document6 pages) To Indicate If Each Class Has The Feature or A Cross (×)Asif AyazPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Notes of Lower LimbDocument5 pagesClinical Notes of Lower Limbbeia21100% (1)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Anatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood Vessels-1Document10 pagesAnatomy Lecture Notes Unit 7 Circulatory System - The Blood Vessels-1hungerfighterPas encore d'évaluation
- Dams - Last Look - AnatomyDocument9 pagesDams - Last Look - Anatomysk100% (1)
- CH 3 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease,: A. CongestionDocument11 pagesCH 3 Hemodynamic Disorders, Thromboembolic Disease,: A. Congestion賴宥瑄Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chinese AcupunctureDocument945 pagesChinese AcupunctureJudy Tognetti91% (11)
- Lecture 6 Cardiovascular: Vascular System - The HemodynamicsDocument61 pagesLecture 6 Cardiovascular: Vascular System - The HemodynamicsAndreea ŞtefănescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Central Retinal Vein Occlusion Differential DiagnosisDocument12 pagesCentral Retinal Vein Occlusion Differential Diagnosismina2085Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of The Resting ECG Recording: Basic TrainingDocument21 pagesBasics of The Resting ECG Recording: Basic TrainingghoziPas encore d'évaluation
- Alcpt Vocabulary, Meanings and ExamplesDocument12 pagesAlcpt Vocabulary, Meanings and ExamplesRoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapy and WellnessDocument13 pagesTherapy and WellnesskailashchsabatPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomyinnutshel00laug PDFDocument626 pagesAnatomyinnutshel00laug PDFSifu LicePas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Basic First Aid - FuturelearnDocument11 pagesBasic First Aid - FuturelearnSuhaib SghaireenPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy CoronaryDocument6 pagesAnatomy Coronarybri bugelPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Cardiac ShuntsDocument10 pagesUnderstanding Cardiac ShuntsDani GodoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolutionary Trend Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds: Secondary Education Certificate Level 2020 Main Session BiologyDocument32 pagesEvolutionary Trend Fish Amphibians Reptiles Birds: Secondary Education Certificate Level 2020 Main Session BiologyEva KanaevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Original PDF Pathophysiology of Heart Disease A Collaborative 6th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesOriginal PDF Pathophysiology of Heart Disease A Collaborative 6th Edition PDFwilliams.allen717100% (40)
- Portal Hypertension: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasDocument57 pagesPortal Hypertension: Dr. Ravi Gadani MS, FmasRaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Vasodilator Drugs: Therapeutic Use and Rationale Therapeutic Uses of VasodilatorsDocument6 pagesVasodilator Drugs: Therapeutic Use and Rationale Therapeutic Uses of VasodilatorsHuy NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- English Basics and Beyond 4 Yr 2014Document31 pagesEnglish Basics and Beyond 4 Yr 2014Art100% (1)
- Assuit - MCQs (NeDocument84 pagesAssuit - MCQs (NeMax TraderPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory System TurtleDocument32 pagesCirculatory System TurtleVillamorchardPas encore d'évaluation