Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
GSM System Overview: Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
Transféré par
andhu4u22Description originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
GSM System Overview: Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
Transféré par
andhu4u22Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1
GSM System Overview
Wireless and Mobile Network Architecture
2
Contents
Introduction
GSMArchitecture
LocationTrackingandCallSetup
Security
Dataservices
UnstructuredSupplementaryServiceData
3
Introduction
GSM(GlobalSystemforMobileCommunications)isdigital
wirelessnetworkstandard
MajorEuropeantelecommunicationsoperatorsand
manufacturers
ThebasicrequirementsofGSM
Service
Qualityofservicesandsecurity
Radiofrequencyutilization
Network
Cost
4
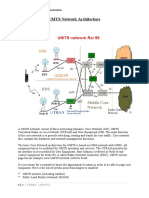
GSMarchitecture
MS:MobileStation
BSS:BaseStationSystem
NSS:NetworkandSwitchingSystem
MSC:MobileSwitchingCenter
5
Mobilestation
Composition
SIM(SubscriberIdentityModule)
Asmartcard,usuallythesizeofacreditcard
Asmaller-sizedplug-inSIM
ProtectedbyaPIN(PersonalIdentityNumber)
Modifiedbysubscriber
UpdatedovertheairthoughSIMToolkit
ME(Mobileequipment)
Containsthenoncustomer-relatedhardwareandsoftwarespecifictothe
radiointerface
Propertyofthesubscriber
TE(TerminalEquipment)
MEandSIMarecalledtheMT(MobileTerminal)
6
BSS
Composition
BTS(BaseTransceiverStation)
Containstransmitter,receiver,signalingequipment
TRAU(Transcoder/RateAdapterUnit)
Speechencoding/decodingandrateadaptionindatatrasmission
BSC(BaseStationController)
ResponsiblefortheswitchingfunctionintheBSS
Supportsradiochannelallocation/releaseandhandoffmanagement
CommunicateswiththeBTSsusingISDNprotocolviatheA-bisinterface
7
NSS
Supportstheswitchingfunctions,subscriberprofiles,and
mobilemanagement
Interface
Signalingprotocolusedinthetelephonenetwork
CurrentlocationofaMS
MaintainedbyHLRandVLR
AuC(AuthenticationCenter)
securitydatamanagementfortheauthenticationofsubscriber
MSC
GMSC(GatewayMSC)
8
Radiointerface
Radiolink
FDMAandTDMAtechnologies
Frequencyband
Downlinksignal:935~960MHz
Uplinksignal:890~915MHz
200KHzcarrierfrequency:124pairsoffrequencyduplexchannel
Theframeisdividedintoeightbursts(timeslots)
GSMburststructure
Tailing Data Flag Training Guard
3 57 bits 1 26 bits 1 57 bits 3 8.25 bits
Burst (148 bits or 0.546 msec)
Time Slot (156.25 bits or 0.577 msec)
Flag Data Tailing
9
Logicalchannel(1/2)
Twotypes
TCHs(TrafficChannels)
CCHs(ControlChannels)
TCH
TCH/F(Full-rateTCH)
Forspeech:13Kbps
Fordata:9.6,4.8,or2.4Kbps
TCH/H(Half-rateTCH)
Forspeech:6.5Kbps
Fordata:4.8or2.4Kbps
CCH
Carrysignalinginformation
Threetype
CCCHs(Commoncontrolchannels)
DCCHs(Dedicatedcontrolchannels)
BCHs(Broadcastchannels)
10
Logicalchannel(2/2)
CCCH
PCH(pagingchannel)
AGCH(Accessgrantchannel)
RACH(Randomaccesschannel)
DCCH
SDCCH(Standarddedicatedcontrolchannel)
SACCH(Slowassociatedcontrolchannel)
FACCH(Fastassociatedcontrolchannel)
CBCH(Cellbroadcastchannel)
BCH
FCCH(Frequencycorrectionchannel)
BCCH(Broadcastcontrolchannel)
11
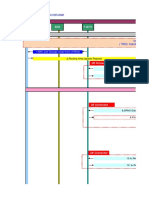
Originationandtermination
PCH (page MS)
RACH (request signaling channel)
AGCH (assign signaling channel)
SDCCH (respond to paging)
MS BSS
Call setup procedure
GSM call termination
SDCCH message exchanges for call setup
RACH (request signaling channel)
AGCH (assign signaling channel)
SDCCH (request call setup)
SDCCH (assign TCH)
FACCH (complete assignment)
GSM call origination
MS BSS
12
Locationtrackingandcallsetup(1/2)
Registration
13
Locationtrackingandcallsetup(2/2)
Termination
14
Security
Twoaspects
Authentication
Encryption
Ki
A8 A3 A8 A3
Ki
SRES
RAND
SRES Equal
?
Kc
Kc
Kc
ciphering
deciphering
deciphering
ciphering
Frame number
MS
Home system
Authentication
Encryption
Visited system
Chiphered
information
A5 A5
data
data data
data
reject
no
yes
accept
15
Dataservices
GSMphase2supportstwodataservicegroups
Shortmessageservices
Bearerservices
Shortmessageservices
Partofthebasicsubscriptionpackage
Bearerservices
SimilartotheISDNservices
Datarate:9.6Kbps
Circuit-switchedconnection
Channelresourcesarereserved:callsetuptimeistoolong
GSMphase2+standard
HSCSD(HighspeedCircuit-SwitchedData)
GPRS(GeneralPacketRadioService)
16
HSCSD(1/2)
HSCSDarchitecture
TE(TerminalEquipment)
IWF(InterworkingFunction)
TAF(TerminalAdaptionFunction)
PSDN(PublicSwitchedDataNetwork)
PSTN(PublicSwitchedTelephoneNetwork)
17
HSCSD(2/2)
Circuit-switchedprotocolforlargefiletransferand
multimediaapplications
UsingmultipleTDMAtimeslotanddatacompression
techniques
Radiointerface
Multiple,independenttimeslot
RLP(RadioLinkProtocol)
Disadvantageofmultipletime-slot
Blockingrateofthesystemwillbeincreased
Solution
Flexibleresourceassignment
18
GPRS(1/2)
GPRSarchitecture
SGSN(ServingGPRSSupportNode)
GGSN(GatewayGPRSSupportNode)
19
GPRS(2/2)
Packet-switchedprotocol
Requiresitsowntransportnetwork
Twonewentities
SGSN:receivesandtransmitspacketsbetweentheMSandPSDN
GGSN:interworkswiththePSDN
Cache
Containinglocationinformationtospeeduptheroutingprocedure
Radiolink
MAC(MediaAccessControl)forpacketswitching
GPRSsupports
Upto100userswithonetoeightchannels
Broadcastandmultisessions
20
USSD(UnstructuredSupplementaryServiceData)
SupportsnewservicesinoldMS
GSM02.90,03.90,04.90
UsedasaGSMtransparentbearerforoldMS
Flexiblemessagelength
Plustheasterisk(*)andpound(#)keys
Forexample
Commandcode159forcallforwarding
*159*5288128#
USSDarchitecture
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- GSM Handover, Localisation and Call HandlingDocument17 pagesGSM Handover, Localisation and Call HandlingHrishikesh UglePas encore d'évaluation
- GprsDocument24 pagesGprsSalahuddin HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM: System Architecture: Prepared by Mehrin MeherDocument28 pagesGSM: System Architecture: Prepared by Mehrin MeherRajib MistryPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On GSM Network and TechnologyDocument40 pagesPresentation On GSM Network and TechnologybhavyamitsPas encore d'évaluation
- Future Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsDocument12 pagesFuture Developments in Non-Repudiation in GSM WAP ApplicationsJournal of Mobile, Embedded and Distributed Systems (JMEDS)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By:-Karan Kumar Goyal, 7080710244, Eee-Ii Guided By: - Vineet SharmaDocument25 pagesPresented By:-Karan Kumar Goyal, 7080710244, Eee-Ii Guided By: - Vineet SharmaAbhishiekh SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation - On - GSM - Network Day2 Comb of All Slides FINALDocument36 pagesPresentation - On - GSM - Network Day2 Comb of All Slides FINALSaurabh SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Global System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Document65 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communication (GSM)Svv KarthikPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 4Document17 pagesLecture 4Salahuddin HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Case+StudyDocument34 pagesGSM Case+StudySakshi Jain100% (1)
- Sniffing GSM Traffic Using RTL-SDR and Kali Linux OSDocument6 pagesSniffing GSM Traffic Using RTL-SDR and Kali Linux OSAnonymous CUPykm6DZPas encore d'évaluation
- Global System For Mobile (GSM) Is A Second Generation Cellular Standard Developed To Cater Voice Services and Data Delivery Using Digital ModulationDocument17 pagesGlobal System For Mobile (GSM) Is A Second Generation Cellular Standard Developed To Cater Voice Services and Data Delivery Using Digital ModulationnitishkhebbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On GSM NetworkDocument39 pagesPresentation On GSM NetworkSonu TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On GSM NetworkDocument40 pagesPresentation On GSM NetworkNgoy SaroPas encore d'évaluation
- Security & Encryption in GSM, GPRS & CDMADocument77 pagesSecurity & Encryption in GSM, GPRS & CDMAbinsalah100% (5)
- Expt: GSMDocument8 pagesExpt: GSMSachin RuikarPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM & Umts - SecurityDocument21 pagesGSM & Umts - SecurityVikas1984301Pas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On GSM NetworkDocument42 pagesPresentation On GSM NetworkTaingren HutPas encore d'évaluation
- 2G Communication 1. GSM:: 2. StandardsDocument15 pages2G Communication 1. GSM:: 2. StandardsRajendra TalelePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1Document4 pagesExperiment 1Neev_GhodasaraPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM System OverviewDocument12 pagesGSM System Overviewvemala vandanaPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Technology: Architecture, Security and Future ChallengesDocument6 pagesGSM Technology: Architecture, Security and Future ChallengesamgreengPas encore d'évaluation
- Digit AnalysisDocument50 pagesDigit Analysisesther_kakani2029100% (1)
- Finalised GSM OverviewDocument33 pagesFinalised GSM OverviewishanrajdorPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Technology Architecture Security and Future ChallengesDocument6 pagesGSM Technology Architecture Security and Future ChallengesJihed Athimni100% (1)
- Mobile Communication: ECED, SVNIT, SuratDocument97 pagesMobile Communication: ECED, SVNIT, SuratSHUBHAM RANKAWAT SVNITPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Global Systems For Mobile CommunicationsDocument42 pagesOverview of GSM, GPRS, and UMTS Global Systems For Mobile Communicationsميسرة شوشانيPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM and GPRS SecurityDocument12 pagesGSM and GPRS Securityphandaka100% (5)
- Presented By:-Priyanka Mutha B.C.A.VI SemDocument24 pagesPresented By:-Priyanka Mutha B.C.A.VI Semmutha123Pas encore d'évaluation
- GSM and GprsDocument25 pagesGSM and Gprseng_diaa_alharsPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Network ArchitectureDocument5 pagesGSM Network Architecturenarayanan07Pas encore d'évaluation
- GSM: The European Standard For Mobile TelephonyDocument23 pagesGSM: The European Standard For Mobile Telephonydriade3092Pas encore d'évaluation
- Telecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Document7 pagesTelecommunication: GSM (Global System For Mobile Communication)Simum100% (1)
- GSM Presentation-Asim IhsanDocument21 pagesGSM Presentation-Asim IhsanEngr Asim IhsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3 v1 DFP6033Document40 pagesChapter 3 v1 DFP6033Vimalan RamanathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-4 (Wireless Communication)Document15 pagesUnit-4 (Wireless Communication)Anonymous EjQbY1CPas encore d'évaluation
- UMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationDocument11 pagesUMTS Network Architecture: Wireless Principles and CommunicationNuces LahorePas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioDocument5 pagesGSM Control Channels With RTL-SDR and GNU RadioImen DjebliPas encore d'évaluation
- The GSM Technology: Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument31 pagesThe GSM Technology: Global System For Mobile Communicationdips04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Global System For Mobile (GSM)Document17 pagesGlobal System For Mobile (GSM)Barhav SarbastPas encore d'évaluation
- BSNL Certification in Mobile Communication: Regional Telecom Training Centre, TrivandrumDocument25 pagesBSNL Certification in Mobile Communication: Regional Telecom Training Centre, TrivandrumWIMAX NOCEKMPas encore d'évaluation
- International Telecommunication Union European Telecommunications Standards Institute Third Generation Partnership ProjectDocument28 pagesInternational Telecommunication Union European Telecommunications Standards Institute Third Generation Partnership ProjectprashantdpatkePas encore d'évaluation
- Global System For MobileDocument14 pagesGlobal System For MobileKabir RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Engineering: (Gsm+Cdma+Gprs)Document34 pagesCommunication Engineering: (Gsm+Cdma+Gprs)Tazmil DityPas encore d'évaluation
- Overcoming Channel Bandwidth Constraints in Secure Sim ApplicationsDocument11 pagesOvercoming Channel Bandwidth Constraints in Secure Sim ApplicationsKhusnulloh AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Fundamental Principle: Radio Network Planning & Optimization Dept Mobile DivisionDocument80 pagesGSM Fundamental Principle: Radio Network Planning & Optimization Dept Mobile Divisiondiar_asPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Security and EncryptionDocument2 pagesGSM Security and EncryptionAbraham Rohith RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsDocument25 pagesOverview of The Global System For Mobile CommunicationsLiyang ChangPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Report On GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) Presented By: Sunil Kumar DCRUST MurthalDocument21 pagesProject Report On GSM (Global System For Mobile Communications) Presented By: Sunil Kumar DCRUST MurthalRakesh SaberwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Authentication and Ciphering in 3G and Simulation: Presentation OnDocument54 pagesAuthentication and Ciphering in 3G and Simulation: Presentation OnshailendrabagriPas encore d'évaluation
- Global System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Document30 pagesGlobal System For Mobile Communications (GSM)Prakash PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On GSM Network: Ravi Kumar Khandelwal Vii Sem Ec-BDocument35 pagesPresentation On GSM Network: Ravi Kumar Khandelwal Vii Sem Ec-Bprerak kumar joshiPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Security and Encryption: Seminar Conducted by Mrs. SHILPA.K.R (Asst. Professor) Ms. BHARATI (Asst. Professor)Document15 pagesGSM Security and Encryption: Seminar Conducted by Mrs. SHILPA.K.R (Asst. Professor) Ms. BHARATI (Asst. Professor)M Sachin KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gayathri GSM 2 (1) FinalDocument66 pagesGayathri GSM 2 (1) FinalumasreePas encore d'évaluation
- Threats and Challenges To Global Systems For Mobiles Security PosterDocument5 pagesThreats and Challenges To Global Systems For Mobiles Security Postermodafar_atiPas encore d'évaluation
- mULTIPLEXING and GSMDocument34 pagesmULTIPLEXING and GSMDoncollins MunenePas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Global System For Mobile Communications: Telecommunication EngineeringDocument23 pagesGSM Global System For Mobile Communications: Telecommunication EngineeringAbid SagorPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Operations & Maintenance: BSNL, LucknowDocument19 pagesGSM Operations & Maintenance: BSNL, Lucknowpallavi_srivastav_22Pas encore d'évaluation
- MTC Flow: Chirag JoshiDocument24 pagesMTC Flow: Chirag JoshiKannan SelvamPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Call FlowsDocument40 pagesGSM Call FlowsAtanu MondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Camel - Cap2 Cap3 Call FlowsDocument20 pagesCamel - Cap2 Cap3 Call Flowssanjay.pathak100% (3)
- Message AllDetailDocument24 pagesMessage AllDetailstephen_lePas encore d'évaluation
- CAP Operations OverviewDocument5 pagesCAP Operations OverviewO'Tobiloba AjibawoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G Call FlowDocument5 pages3G Call FlowSarath ChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Call From PSTN To MSDocument4 pagesCall From PSTN To MSnagendra_badamPas encore d'évaluation
- GSMDocument33 pagesGSMHemangi Priya Devi DasiPas encore d'évaluation
- 3G Technology PresentationDocument27 pages3G Technology PresentationSancha SaringcarinkulPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter01.Cellular Concept GSM ArchitectureDocument62 pagesChapter01.Cellular Concept GSM ArchitectureBsnl Bareilly100% (1)
- GSM BSS OverviewDocument20 pagesGSM BSS OverviewchadidiabPas encore d'évaluation
- 2G SMS FlowDocument37 pages2G SMS FlowShaharyar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nokia: ConfidentialDocument11 pagesNokia: ConfidentialLeonard GržetićPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Inter MSC Handover Call FlowDocument3 pagesGSM Inter MSC Handover Call Flowhanhdung08Pas encore d'évaluation
- BCCH BCH Sys Info Type 11Document19 pagesBCCH BCH Sys Info Type 11ABHILASHPas encore d'évaluation
- ... A Global Mobile Communication SystemDocument18 pages... A Global Mobile Communication SystemmerinekcPas encore d'évaluation
- Parameter Management in EIR, HLR, and VLRDocument33 pagesParameter Management in EIR, HLR, and VLRtamnguyen29842764Pas encore d'évaluation
- Egprs On BCCH TRX Trial Report TaoDocument44 pagesEgprs On BCCH TRX Trial Report TaoPhuong LePas encore d'évaluation
- 3gPP Specs GPRS Error Causes Before CC14Document3 pages3gPP Specs GPRS Error Causes Before CC14Iftikhar Safavi SyedPas encore d'évaluation
- BSSPAR1: Chapter 3 Idle Mode Operation: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksDocument21 pagesBSSPAR1: Chapter 3 Idle Mode Operation: 1 © Nokia Siemens NetworksJunaidPas encore d'évaluation
- BSS S-RNC UE: L3 Messages - Inter-RAT Handover ProcedureDocument23 pagesBSS S-RNC UE: L3 Messages - Inter-RAT Handover ProcedureQuan DaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Serving RS RP DBM 0Document1 484 pagesServing RS RP DBM 0mehran_4xPas encore d'évaluation
- Call Fail CauseDocument7 pagesCall Fail CauseHendraLiyusman100% (1)
- BSNL GSM 145M Lines 20091231024000 SSIN2012041001SENP2GUS Haryana Mr. Subhash ChanderDocument2 pagesBSNL GSM 145M Lines 20091231024000 SSIN2012041001SENP2GUS Haryana Mr. Subhash ChanderMohammad AslamPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM - Architecture - TutorialspointDocument2 pagesGSM - Architecture - TutorialspointChristopher AiyapiPas encore d'évaluation
- GSM Call RoutingDocument22 pagesGSM Call Routingriadelectro100% (1)
- Nokia BSC MML CommandsDocument11 pagesNokia BSC MML CommandsAndik ManchesterUnitedPas encore d'évaluation
- USSD Call FlowsDocument2 pagesUSSD Call FlowsMurly Rajendran100% (2)
- 2G ScriptDocument13 pages2G ScriptHeriPas encore d'évaluation