Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Fiscal Policy Explained
Transféré par
JadedGothTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Fiscal Policy Explained
Transféré par
JadedGothDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
FISCAL POLICY
Submitted by:
Huma Khan
Wajiha Khan
Sehrish Shaukat
Ziyad Bin Mehtab
Jawad Mughal
What is Fiscal Policy?
It is the use of government expenditure and
revenue collection to influence the economy.
Fiscal policy refers to the overall effect of the
budget outcome on economic activity.
Fiscal policy can be contrasted with the other main
type of economic policy, monetary policy, which
attempts to stabilize the economy by controlling
interest rates and the supply of money.
Objectives of Fiscal Policy
Economic Growth
Promotion of Employment.
Economic Stability
Economic Justice or Equity
Price Stability
Fiscal Policy And Macroeconomic Goals
Goal Description
Economic Growth
By creating conditions for increase in
savings & investment.
Employment
By encouraging the use of labor-absorbing
technology.
Stabilization
Fight with depressionary trends and booming
(overheating) indications in the economy.
Economic Equality
By reducing the income and wealth gaps
between the rich and poor.
Price stability
Employed to contain inflationary and
deflationary tendencies in the economy.
How Fiscal Policy Works
Fiscal policy is based on the theories of
British economist John Maynard Keynes. Also
known as Keynesian economics, this theory
basically states that governments can
influence macroeconomic productivity levels
by increasing or decreasing tax levels and
public spending.
This influence, in turn, curbs inflation (generally
considered to be healthy when at a level between
2-3%), increases employment and maintains a
healthy value of money.
Use of Fiscal Policy
Adjustment of income tax allowances rather than rates
of income tax
Extending or amending range of goods covered by VAT
Changing the rules under which tax has to be paid
married persons allowances, inheritance taxes, stamp
duties, etc.
Abolishment of certain tax allowances MIRAS (Mortgage
Income Relief At Source)
Accusations of stealth taxes much of it is a tinkering
with the tax system to achieve certain aims mostly non-
economic (governments these days, for example, rarely
increase taxes to dampen down the economy)
Economic Effects of Fiscal Policy
Governments use fiscal policy to
influence the level of aggregate demand
in the economy, in an effort to achieve
economic objectives of price stability,
full employment, and economic growth.
Instruments of Fiscal Policy
Government Expenditure
Taxation
Direct
Indirect
Public Debt
Impact of Instruments
Changes in the level and composition of
taxation and government spending can
impact on the following variables in the
economy:
Aggregate demand and the level of
economic activity;
The pattern of resource allocation;
The distribution of income.
Government Expenditure
It includes :
Government spending on the purchase
of goods & services.
Payment of wages and salaries of
government servants
Public investment
Transfer payments
Taxation
Non quid pro quo transfer of private
income to public coffers by means of
taxes.
Classified into:
Direct Taxes- Corporate Tax, Div. Distribution
Tax, Personal Income Tax, Fringe Benefit Taxes,
Banking Cash Transaction Tax
Indirect Taxes- Central Sales Tax, Customs,
Service Tax, Exercise Duty
Public Debt
Internal Borrowings
1. Borrowings from the public by means of treasury
bills and govt. bonds
2. Borrowings from the central bank (Monetized
Deficit Financing)
External Borrowings
1. Foreign investments
2. International organizations like World Bank & IMF
3. Market borrowings
Fiscal Policy In Inflation
Control over public expenditure
Increase in taxes
Increase in public borrowing
Delay in the payment of old debts
Fiscal Policy In Deflation
Increase in public expenditure.
Decrease in taxes.
Increase in social welfare expenditure.
Prices support policy.
Budget
A budget is a
detailed plan of
operations for some
specific future
period.
It is an estimate
prepared in advance
of the period to
which it applies.
Where The Rupee Comes From
state's share of
taxes & duties
18%
non plan assistance
to states
5%
planned state
assistance
7%
central plan
20%
interest
20%
defence
12%
subsidies
7%
other non plan exp.
11%
Where Does The Rupee Go To
state's share of
taxes & duties
18%
non plan assistance
to states
5%
planned state
assistance
7%
central plan
20%
interest
20%
defence
12%
subsidies
7%
other non plan exp.
11%
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Currency BasicsDocument18 pagesCurrency BasicsChandan AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Statement Template 19Document4 pagesBank Statement Template 19Thai Chu DinhPas encore d'évaluation
- Apple - Income StatementDocument5 pagesApple - Income StatementhappycolourPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiscal PolicyDocument14 pagesFiscal Policykzakiya17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Macro Economics PerformanceDocument118 pagesUnderstanding Macro Economics PerformanceViral SavlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometrics 1 Topic 1Document38 pagesEconometrics 1 Topic 1Iskandar ZulkarnaenPas encore d'évaluation
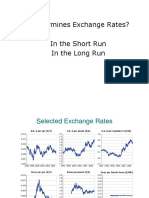
- Exchange Rate Determination and PolicyDocument33 pagesExchange Rate Determination and PolicyJunius Markov OlivierPas encore d'évaluation
- Fixed Rates Macro PolicyDocument10 pagesFixed Rates Macro PolicyJelenaJovanovicPas encore d'évaluation
- Money and Banking 2009 SpringDocument117 pagesMoney and Banking 2009 SpringborchaliPas encore d'évaluation
- EMEA Group2 EgyptDocument11 pagesEMEA Group2 EgyptRAJARSHI ROY CHOUDHURYPas encore d'évaluation
- By: Domodar N. Gujarati: Prof. M. El-SakkaDocument19 pagesBy: Domodar N. Gujarati: Prof. M. El-SakkarohanpjadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- Econometric Methods: Theory Mathematics StatisticsDocument22 pagesEconometric Methods: Theory Mathematics StatisticsGiri PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Financial EconometricsDocument38 pagesIntroduction To Financial EconometricsMohd ZahidPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiscal Policy and Monetary Policy.Document19 pagesFiscal Policy and Monetary Policy.wayandragon247100% (1)
- IMF Promotes Global Economic StabilityDocument19 pagesIMF Promotes Global Economic StabilitySunni ZaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding InflationDocument70 pagesUnderstanding Inflationkiler2424Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1.4 Market FailureDocument42 pages1.4 Market FailureRuban PaulPas encore d'évaluation
- International Parity ConditionsDocument62 pagesInternational Parity ConditionsHaimanot tessemaPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA 3 Sem Finance Notes (Bangalore University)Document331 pagesMBA 3 Sem Finance Notes (Bangalore University)Pramod AiyappaPas encore d'évaluation
- ME Cycle 8 Session 7Document96 pagesME Cycle 8 Session 7OttiliePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 12Document38 pagesChapter 12Shiela MaeaPas encore d'évaluation
- L2 Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument25 pagesL2 Exchange Rate DeterminationKent ChinPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit - Iii: Foreign Exchange Determination Systems &international InstitutionsDocument97 pagesUnit - Iii: Foreign Exchange Determination Systems &international InstitutionsShaziyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document26 pagesChapter 1Hamid UllahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture03 Parity StudentDocument23 pagesLecture03 Parity StudentMit DavePas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange Rates and Balance of Payments LectureDocument18 pagesExchange Rates and Balance of Payments LectureReza AfrisalPas encore d'évaluation
- G Lecture01Document21 pagesG Lecture01Pramudya Arwana HermawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange RatesDocument34 pagesExchange RatesthebfilesPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Markets: Lectures 3 - 4Document48 pagesFinancial Markets: Lectures 3 - 4Lê Mai Huyền LinhPas encore d'évaluation
- INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL SYLLABUSDocument90 pagesINTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL SYLLABUSTarini MohantyPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 FinancialInstrumentsandTheirRelevanceDocument39 pages12 FinancialInstrumentsandTheirRelevanceRizki Fazlur RachmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Overview of The FX MarketDocument24 pagesQuick Overview of The FX MarketpatrocompsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 6 Currency Derivatives (1) : - The End of This Session Students Should Be Able ToDocument24 pagesLecture 6 Currency Derivatives (1) : - The End of This Session Students Should Be Able ToSaurabh MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflation Persistence and The Taylor Rule: Christian Murray, David Papell, and Oleksandr RzhevskyyDocument18 pagesInflation Persistence and The Taylor Rule: Christian Murray, David Papell, and Oleksandr RzhevskyybilalalishahPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Management and Basel II: Bank Alfalah LimitedDocument72 pagesRisk Management and Basel II: Bank Alfalah LimitedMuhammad ArslanPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Markets ExplainedDocument232 pagesFinancial Markets ExplainedThảo Nhi LêPas encore d'évaluation
- "Introduction To International Financial System": "International Finance and Payments"Document425 pages"Introduction To International Financial System": "International Finance and Payments"Ioan 23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Treasury Overview Sesssion 1Document30 pagesTreasury Overview Sesssion 1ravitmadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Exchange RatesDocument35 pagesDetermining Exchange Ratesayush_singhal27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Crisis in Emerging Economies: Case of China 2015Document26 pagesFinancial Crisis in Emerging Economies: Case of China 2015amritaPas encore d'évaluation
- Egypt's Free Floating Exchange RegimeDocument13 pagesEgypt's Free Floating Exchange RegimeWalaa MahrousPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Transaction ExposureDocument53 pagesManagement of Transaction ExposureParminder SalujaPas encore d'évaluation
- MATHEMATICAL ECONOMICSDocument54 pagesMATHEMATICAL ECONOMICSCities Normah0% (1)
- Financial Risk ManagementDocument31 pagesFinancial Risk ManagementDaanPas encore d'évaluation
- chp1 EconometricDocument52 pageschp1 EconometricCabdilaahi CabdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4: Macroeconomic Objectives: EconomicsDocument19 pagesTopic 4: Macroeconomic Objectives: EconomicsAlvin Chai Win LockPas encore d'évaluation
- DerivativesDocument21 pagesDerivativesMandar Priya PhatakPas encore d'évaluation
- DBA 5035 - Financial Derivatives ManagementDocument277 pagesDBA 5035 - Financial Derivatives ManagementShrividhyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Forward and Futures PricingDocument13 pagesForward and Futures PricingMandar Priya PhatakPas encore d'évaluation
- Feenstra Taylor Chapter 1Document10 pagesFeenstra Taylor Chapter 1sankalpakashPas encore d'évaluation
- EconomicsDocument32 pagesEconomicsSahil BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- International Parity Relationships & Forecasting Exchange RatesDocument33 pagesInternational Parity Relationships & Forecasting Exchange RatesKARISHMAATA2Pas encore d'évaluation
- MMS Derivatives Lec 4Document64 pagesMMS Derivatives Lec 4AzharPas encore d'évaluation
- LCH Clearnet SwapClear OTC derivatives clearingDocument9 pagesLCH Clearnet SwapClear OTC derivatives clearingAleis RiquelmePas encore d'évaluation
- FRM Lecture 4 2020 2021 HandoutDocument41 pagesFRM Lecture 4 2020 2021 HandoutDaanPas encore d'évaluation
- ch03 ptg01Document9 pagesch03 ptg01Tran Kim NganPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange RateDocument32 pagesExchange RateCharlene Ann EbitePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Risk Management with Binomial Option TreesDocument39 pagesFinancial Risk Management with Binomial Option TreesDaanPas encore d'évaluation
- From Convergence to Crisis: Labor Markets and the Instability of the EuroD'EverandFrom Convergence to Crisis: Labor Markets and the Instability of the EuroPas encore d'évaluation
- Fiscal PolicyDocument16 pagesFiscal Policyvivek.birla100% (2)
- INDIAN FISCAL POLICY CURRENT SCENARIODocument7 pagesINDIAN FISCAL POLICY CURRENT SCENARIOChaiyaChaithanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- SoftwareDocument20 pagesSoftwareJadedGothPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networks: Presented byDocument34 pagesComputer Networks: Presented byJadedGoth100% (2)
- InternetDocument46 pagesInternetJadedGothPas encore d'évaluation
- Adidas Report - FinalDocument81 pagesAdidas Report - FinalJadedGoth100% (1)
- HardwareDocument29 pagesHardwareJadedGothPas encore d'évaluation
- Meaning Scope of Tax ManagementDocument5 pagesMeaning Scope of Tax ManagementAnish yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Amir Hamza Sikandar. 01-112171-002. Advanced Taxation AssignmentDocument6 pagesAmir Hamza Sikandar. 01-112171-002. Advanced Taxation AssignmentMehreen KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Theoritical Framework &literature ReviewDocument27 pagesTheoritical Framework &literature ReviewGelani PradipPas encore d'évaluation
- Abhibus Ticket Sri Tulasi Travels: Ticket For Chennai-GunturDocument2 pagesAbhibus Ticket Sri Tulasi Travels: Ticket For Chennai-GunturBhavan Sai VakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine VAT and Percentage Tax RatesDocument41 pagesPhilippine VAT and Percentage Tax RatesKim AranasPas encore d'évaluation
- Alumni Fee Voucher UpdatedDocument1 pageAlumni Fee Voucher UpdatedHassan KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Genal ListDocument4 pagesGenal ListErik FarrPas encore d'évaluation
- What is Letter of Credit? Bank Payment Tool for ExportersDocument2 pagesWhat is Letter of Credit? Bank Payment Tool for ExportersCarlos KarmunPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 MondayDocument6 pages1 MondayCeline Marie Libatique AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- Form - 1040 - Schedule BDocument2 pagesForm - 1040 - Schedule BEl-Sayed FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mbeya University of Science and Technology: Students Who Are Not Eligible To Sit For Semester I Examinations in 2021/2022Document12 pagesMbeya University of Science and Technology: Students Who Are Not Eligible To Sit For Semester I Examinations in 2021/2022william siyamePas encore d'évaluation
- SRPL 2300255Document2 pagesSRPL 2300255radhe panelPas encore d'évaluation
- Official Receipt: Global Indian International SchoolDocument1 pageOfficial Receipt: Global Indian International SchoolBadal BhattacharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Composition Scheme Under GST 1.0Document28 pagesComposition Scheme Under GST 1.0Saqib AnsariPas encore d'évaluation
- Tax, Budget, InterstDocument10 pagesTax, Budget, InterstNegese MinaluPas encore d'évaluation
- BQs Tax 2011 2012Document44 pagesBQs Tax 2011 2012Dem SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- EBTax UAT Test Script ARDocument2 pagesEBTax UAT Test Script ARchirag0% (1)
- (Please Write The Name That Appears On Your Card) : PNB Credit Card Rewards Redemption FormDocument1 page(Please Write The Name That Appears On Your Card) : PNB Credit Card Rewards Redemption FormSsa ZabalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fees and Commissions Guide For IndividualsDocument29 pagesFees and Commissions Guide For IndividualsDPas encore d'évaluation
- GST Implementation and Its Impact On Indian EconomyDocument4 pagesGST Implementation and Its Impact On Indian EconomyarcherselevatorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Us 2022 Tax UpdateDocument19 pagesUs 2022 Tax Updateapi-263318846Pas encore d'évaluation
- Biologicla Assets PDFDocument2 pagesBiologicla Assets PDFMjhayePas encore d'évaluation
- Crypto Payments Industry Research ReportDocument55 pagesCrypto Payments Industry Research ReportRodrix DigitalPas encore d'évaluation
- Proposed Adjusting Journal EntriesDocument8 pagesProposed Adjusting Journal EntriesEli Mae Rose Densing100% (1)
- Form App Clearance OutwardDocument1 pageForm App Clearance OutwardNuwani PreethikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Challan Form For Written Test Fee Payment (POLICE CONSTABLE)Document1 pageChallan Form For Written Test Fee Payment (POLICE CONSTABLE)Rashid Abbas0% (1)
- 64309445932019499Document76 pages64309445932019499Prabhat SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Phelps IndustriesDocument3 pagesPhelps IndustriesDilip ReddyPas encore d'évaluation