Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Streptococcal Diseases: Streptococcus Pyogenes
Transféré par
Dian FairuzaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Streptococcal Diseases: Streptococcus Pyogenes
Transféré par
Dian FairuzaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
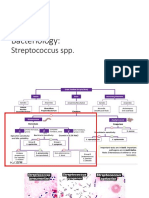
Streptococcal Diseases
Streptococcus pyogenes
Streptococcus pyogenes
Pyogenes means pus producing
One of the most important pathogens
Gram positive cocci in chains
Lancefield Serological Group A
Beta Hemolytic on blood agar
Gram Stain of S. pyogenes
Hemolysis on Blood Agar
Plates
Alpha hemolysis-organism excretes
hemolysins which partially break down rbc
(incomplete hemolysis) thus a greenish zone
appears around colony. S. pneumoniae
Beta hemolysis-organisms excretes potent
hemoysins which completely lyse rbc
(complete hemolysis) thus a clear zone
appears around colony. S. pyogenes
S.pyogenes
S. pneumonia
Beta
hemolysis
Alpha
hemolysis
Diseases caused by S. pyogenes
Strep throat
Impetigo
Erysipelas
Cellulitis
Invasive Strep A infections
Necrotizing fasciitis
Myositis
Toxic shock-like syndrome
Erysipelas
Acute infection and imflammation of the
dermal layer of skin.
Painful red patches which enlarge and
thicken
Treatment -penicillin or erythromycin
Erysipelas
Strep Throat
Most common of all Strep diseases
Spread by saliva or nasal secretions
Incubation period 2-4 days
Sore throat, slight fever (101)
Important to treat immediately to avoid
post strep diseases
Diagnosis and treatment of Strep Throat
Tell tale symptoms are slight fever
associated with sore throat and visual of
pus in back of throat
Quick diagnostic tests (Molecular)
available but must be confirmed by
throat swab and growth on blood agar
(beta hemolysis)
Diagnosis and treatment of Strep Throat
If the strain of S. pyogenes is lysogenic
for a particular phage which expresses
an erythrogenic toxin the result is
Scarlet fever
Rash appears and characteristic is the
strawberry colored tongue
Strawberry Tongue
Treatment of Strep
Penicillin G or Erythromycin are drugs
of choice
Although the disease is self-limiting it is
important to treat immediately to avoid
post strep complications
Poststreptococcal diseases
Rheumatic Fever-autoimmune disease
involving heart valves,joints, nervous
system. Follows a strep throat
Acute glomerulonehritis or Brights
Disease-inflamatory disease of renal
glomeruli and structures involved in
blood filter of kidney. Due to deposition
of Ag/Ab complexes
Rheumatic Fever
Most common cause of permanent
heart valve damage in children
Exact cause not yet known but there
appears to be some antibody cross
reactivity between the cell wall of S.
pyogenes and heart muscle
Rheumatic Fever
Diagnosis is based on symptoms and is
difficult
Occurs most frequently between ages
of 6 and 15
US it is about 0.05% of pop having strep
infections
100x more frequent in tropical countries
Rheumatic Fever
Treatment is via salicylates (aspirin
derivatives) and corticosteroids to
decrease inflammation and fever.
Glomerular Nephritis
Diagnosis based on history of Strep
throat and clinical findings.
Symptoms include fever,
malaise,edema, hypertension and blood
or protein in urine
Occurs in 0.5% of those having strep
throat.
Glomerular Nephritis
Treatment and Recovery
Penicillin or erythromycin to eradicate
and residual strep infection
80-90% of cases recover with bed rest
lasting for months
Kidney damage in the remainder is
often permanent resulting in chronic
glomerular nephritis
Streptococcus Pneumonia
Caused by infection with Streptococcus
pneumoniae
Gram positive, alpha hemolytic, not of
lancefield serotype A
Often part of normal flora of respiratory
track and becomes infective once hosts
resistance is lowered. Classified as an
endogenous infection.
Strep Pneumonia
Strep Pneumonia
S. pneumoniae
Alpha hemolysis
Strep pneumonia
Predisposing factors: upper respiratory
viral infection, diabetes, alcoholism
60-80% of all pneumonias
Strep Pneumonia
Cause of strep pneumonia
Primary virulence factor is the capsular
polysaccharide which protects the
organism against phagocytosis
Pathogenesis is due to rapid growth of
bacteria in alveolar spaces
Symptoms of Strep
Pneumonia
Onset abrupt
Chest pains
Chills
Labored breathing
Diagnosis of Strep pneumonia
Chest Xray
Culture and staining
Biochemical tests of isolated organism
Treatment of Strep
Pneumonia
Typically treated with Penicillin G
cefotaxime, oflaxacin or for those
allergic to penicillins can be treated with
erythromycin or tetracycline
Pneumococcal vaccine (Pneumovax 23
or Pnu-immune 23) is available for the
elderly
Staphylococcal infections
One of the most common of all
infections
Staphylococcus are divided into
pathogens and non pathogens based
on possession of the enzyme coagulase
Coagulase + are usually S. aureus and
pathogenic
Coagulase - are organisms like S.
epidermidis are less invasive
Diseases of Staphylococcus
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Most in women using superabsorbant
tampons
Staphylococcus aureus-Gram positive
cocci
Low blood pressure, fever, diarrhea,
skin rash can be fatal
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Symptoms mainly caused by toxic
shock syndrome toxin 1(TSST1)
Several other enterotoxins also involved
Staph skin infections
Most common cause of acne, boils,
furuncle and cabuncles
Treatment can be difficult because of
antibiotic resistance.Usually can be
treated with methicillin,
cephalosporins,or vancomycin
Methicillin resistant strains=MRSA
Staph skin infections
superficialfolliculitis
Deep folliculitis
Furuncle
(infected hair
follicle
Carbuncle
Multiple abcesses
Around many hair
follicles
Staph impetigo
Scalded skin
syndrome
Scalded Skin Syndrome
Due to strains of S. aureus containing a
special toxin-exfoliatin
Diagnosis
Culture and stain-gram positive in
grape-like clusters
Catalase and coagulase tests
DNA fingerprinting
S. aureus
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- StreptococciDocument43 pagesStreptococciAyeshaPas encore d'évaluation
- MicroPara Lecture 6Document24 pagesMicroPara Lecture 6Pearl NoconPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram +/-Cocci: Thao Nguyen, PHD Thao - Nguyen@Ttu - Edu.VnDocument98 pagesGram +/-Cocci: Thao Nguyen, PHD Thao - Nguyen@Ttu - Edu.VnNguyen Phan TrongPas encore d'évaluation
- Pericardial DX Endocarditis MyocarditisDocument14 pagesPericardial DX Endocarditis MyocarditisJefry SPas encore d'évaluation
- Pemicu 3 (Anak) : William Gilbert SatyanegaraDocument56 pagesPemicu 3 (Anak) : William Gilbert Satyanegarawilliam_SatyanegaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper Respıratory Tract InfectıonsDocument68 pagesUpper Respıratory Tract InfectıonsMekdes ZewdePas encore d'évaluation
- Micro PSGNDocument32 pagesMicro PSGNMahmoud hilmyPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 MumpsDocument18 pages4 MumpsAyu PratiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument35 pagesCervical LymphadenopathyMAHMUDPas encore d'évaluation
- StreptococciDocument46 pagesStreptococcimulatumelesePas encore d'évaluation
- 4 MumpsDocument18 pages4 MumpsNamira Caroline ErchoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pedi Respir... DR - BrukDocument81 pagesPedi Respir... DR - BrukMatusala BafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharyngitis: Dr.M.KarimiDocument60 pagesPharyngitis: Dr.M.KarimiJessa AdenigPas encore d'évaluation
- Nephritic SyndromeDocument19 pagesNephritic SyndromesangheetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Poststreptococcal GNDocument35 pagesAcute Poststreptococcal GNKebede TesfayePas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnostic Microbiology Lecture 5 (2023-2024) ModifiedDocument28 pagesDiagnostic Microbiology Lecture 5 (2023-2024) Modified589zvgww47Pas encore d'évaluation
- PBL Haematology (Bleeding) - B5Document49 pagesPBL Haematology (Bleeding) - B5nishibuchiPas encore d'évaluation
- UPPER Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument14 pagesUPPER Respiratory Tract InfectionsYousif Ahmed DAPas encore d'évaluation
- INFECTIOUS DISEASE MAGNETIC LINES by David HarrisonDocument28 pagesINFECTIOUS DISEASE MAGNETIC LINES by David Harrisonnfaruki83Pas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal SepsisDocument18 pagesNeonatal SepsisMoe KebabPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory and Nosocomial InfectionsDocument70 pagesRespiratory and Nosocomial InfectionsCezar Alexander GuevaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Family StreptococcaceaeDocument4 pagesFamily StreptococcaceaeChynna Izzabelle Alcantara AbellanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs and Symptoms: AdultsDocument12 pagesSigns and Symptoms: AdultsMiralles AnielynPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec No (4) - Viral Respiratory Tract InfectionsDocument60 pagesLec No (4) - Viral Respiratory Tract InfectionsMohammedu IhthishamPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 - Pharyngitis BronchitisDocument31 pages4 - Pharyngitis BronchitisAishwaryaPas encore d'évaluation
- SEPTICEMIA in Neonatal Period in FMCDocument40 pagesSEPTICEMIA in Neonatal Period in FMCIghodaro IsokenPas encore d'évaluation
- Https://ar - scribd.com/document/391648283/OET Future Land Full Book Final Edition July 2018Document52 pagesHttps://ar - scribd.com/document/391648283/OET Future Land Full Book Final Edition July 2018Qutaiba ShdaifatPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Tract: Elijah Quiaño Miguel Quilit 1-NU01Document59 pagesRespiratory Tract: Elijah Quiaño Miguel Quilit 1-NU01im. EliasPas encore d'évaluation
- Family Spirochaetaceae AND LeptospiraceaeDocument33 pagesFamily Spirochaetaceae AND Leptospiraceaeyosef awokePas encore d'évaluation
- Necrotizing Pneumonia and Lung AbscessDocument11 pagesNecrotizing Pneumonia and Lung AbscessIman KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument53 pagesPneumoniaAtif100% (1)
- Reckettsia and ChlamediaDocument37 pagesReckettsia and ChlamediaMuqtadir “The Ruler” KuchikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of PneumoniaDocument13 pagesClassification of PneumoniaRaisa DilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheumatic Fever: Fanny Budiman Bullpoopers & SOCA BOBOK 2019Document16 pagesRheumatic Fever: Fanny Budiman Bullpoopers & SOCA BOBOK 2019Fanny BudimanPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City, Philippines: Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument62 pagesUniversity of Saint Louis Tuguegarao City, Philippines: Maternal and Child Health NursingErica Veluz LuyunPas encore d'évaluation
- PharyngitisDocument27 pagesPharyngitisSubhada GosaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument24 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisNipul MondolPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Positive Cocci: StaphylococciDocument57 pagesGram Positive Cocci: StaphylococciJill PardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Smle Pictorial JunayedDocument86 pagesSmle Pictorial Junayedmonirul islam shohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyogenic Microorganisms: Roy, Nova, Jessie, Szechia, and ShangyoungDocument34 pagesPyogenic Microorganisms: Roy, Nova, Jessie, Szechia, and ShangyoungMitra NofembriPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Aspect of GABHSDocument13 pagesMicrobial Aspect of GABHSAdelia Maharani DPas encore d'évaluation
- Tuberculosis in Infancy and ChildhoodDocument55 pagesTuberculosis in Infancy and ChildhoodIna AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Immunology 13-11-2022: Post-Streptococcal Autoimmune DisordersDocument50 pagesClinical Immunology 13-11-2022: Post-Streptococcal Autoimmune Disordersphoto copyhemnPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Rheumatic Fever: Prof - Univ.Dr. Corina ZorilăDocument40 pagesAcute Rheumatic Fever: Prof - Univ.Dr. Corina ZorilăGermanyPas encore d'évaluation
- S. PyogenesDocument21 pagesS. PyogenesRachanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Meningitis LectureDocument20 pagesMeningitis LectureIDIOVWA PRINCEPas encore d'évaluation
- General Xtics. Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus) : Gram-Negative CocciDocument19 pagesGeneral Xtics. Neisseria Meningitidis (Meningococcus) : Gram-Negative CocciMoses Tamba MomohPas encore d'évaluation
- Lymph Ad en Op A ThyDocument24 pagesLymph Ad en Op A ThyAlyaa El SayedPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia in Plab PDFDocument6 pagesPneumonia in Plab PDFBeaulahPas encore d'évaluation
- BacteriologyDocument39 pagesBacteriologyGrape JuicePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Rheumatic Fever?Document9 pagesWhat Is Rheumatic Fever?Annapoorna SHPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 PharngitisDocument26 pages10 PharngitisCabdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Staph Infection & HIV (GP B1)Document48 pagesStaph Infection & HIV (GP B1)Jared Khoo Er HauPas encore d'évaluation
- Neutropenia and Febrile Neutropenia-1Document42 pagesNeutropenia and Febrile Neutropenia-1safia ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Upper Respiratory AlterationDocument34 pagesUpper Respiratory AlterationJulia ManaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (Apsgn) in ChildrenDocument22 pagesAcute Poststreptococcal Glomerulonephritis (Apsgn) in ChildrenOlivia PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To Common Respiratory DiseaseDocument57 pagesApproach To Common Respiratory DiseaseRajhmuniran KandasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- PowerDocument6 pagesPowerkakardawood50Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group 2, Problem 3: Refky Juliandri 405090149Document24 pagesGroup 2, Problem 3: Refky Juliandri 405090149refkyjuliandriPas encore d'évaluation
- Arbeitsheft 2018Document147 pagesArbeitsheft 2018Pamela MusabelliuPas encore d'évaluation
- Infectious DiseasesDocument37 pagesInfectious Diseasespolaris_027Pas encore d'évaluation
- Typhoid FeverDocument12 pagesTyphoid Feverlaura122334100% (1)
- Identification of Proteus Vulgaris From An Unknown SampleDocument10 pagesIdentification of Proteus Vulgaris From An Unknown SamplePraise Selah DagocPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicable DiseasesDocument8 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKarla Fralala100% (1)
- Pandemic - Contagion (2016)Document27 pagesPandemic - Contagion (2016)DusanPaunovicPas encore d'évaluation
- (Paul Insel, Walton Roth) Connect Core Concepts in Health 13th Brief EditionDocument449 pages(Paul Insel, Walton Roth) Connect Core Concepts in Health 13th Brief EditionRoyletaTrueheartFoster84% (19)
- DOH Food HandlersDocument15 pagesDOH Food HandlersmornePas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 NSTPDocument43 pagesLesson 2 NSTPylrcy imPas encore d'évaluation
- Branches & Clasification of MicrobiologyDocument66 pagesBranches & Clasification of MicrobiologyJareena BegumPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacterial InfectionDocument4 pagesBacterial InfectionKamalakannan ShunmugamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- The Public Health ModelDocument7 pagesThe Public Health ModelJay Thomas Taber100% (1)
- Aso Test For Semester2Document3 pagesAso Test For Semester2Tarun AroraPas encore d'évaluation
- AM - ICD-10-AM GuideDocument26 pagesAM - ICD-10-AM GuidedrrskhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Meningitis PediatricDocument5 pagesMeningitis PediatricLydia Angelia YanitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Microbiology-I SEMESTER-IDocument26 pagesClinical Microbiology-I SEMESTER-IAreeba NazPas encore d'évaluation
- HePatic AbscessDocument67 pagesHePatic AbscessCharlie Mignonette BalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Gender and Development (Gad) Plan and Budget: Mooe PS CODocument16 pagesAnnual Gender and Development (Gad) Plan and Budget: Mooe PS COjennifer vegaPas encore d'évaluation
- ParvovirusDocument8 pagesParvovirusAldila safitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Gatherings Evidence ReviewDocument72 pagesMass Gatherings Evidence ReviewRoguePas encore d'évaluation
- Micp ReviewerDocument30 pagesMicp ReviewerFrancisca NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Christopher B. Hackett - Salmonella - Prevalence, Risk Factors and Treatment Options (2015, Nova Science Publishers Inc)Document213 pagesChristopher B. Hackett - Salmonella - Prevalence, Risk Factors and Treatment Options (2015, Nova Science Publishers Inc)Andi Zul TasyriqPas encore d'évaluation
- Joc 911151Document8 pagesJoc 911151Daniel BorgesPas encore d'évaluation
- MV Lec PDFDocument102 pagesMV Lec PDFJonas Datu100% (1)
- NCP RHDocument3 pagesNCP RHMariquita Buenafe57% (7)
- Week 7-8Document13 pagesWeek 7-8Glaiza Dalayoan FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- 11.TBL Training Participant Manual 2021Document253 pages11.TBL Training Participant Manual 2021Adebabay DessiePas encore d'évaluation
- Stool Exam - Routine, Conc. Method - Students'Document27 pagesStool Exam - Routine, Conc. Method - Students'AnastasiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Medicine Including Infectious Diseases Epidemiology Clinical Pharmacology S Inf. Diseases 4c.Document8 pagesInternal Medicine Including Infectious Diseases Epidemiology Clinical Pharmacology S Inf. Diseases 4c.Noor SeckamPas encore d'évaluation
- COVID-19 Long Term EffectsDocument22 pagesCOVID-19 Long Term EffectsMcKenzie Stauffer100% (10)