Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Metallurgy
Transféré par
Basem Al-HajCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Metallurgy
Transféré par
Basem Al-HajDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Metallurgy
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
2 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
3000F
1650C
900F
480C
400F
205C
3 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Refining Process
Lower Carbon Contents
Refine the quality
4 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Ingot Molds
5 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Cast Iron vs. Steel
Cast Iron = Iron + 2- 4% Carbon
Brittle with little or no ductility
Steel = Iron + 0.02- 2% Carbon
Stronger, harder, tougher and ductile
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
6 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Carbon Levels for Steel
Low Carbon 0.02 - 0.25%
Medium Carbon 0.25 - 0.50%
High Carbon 0.50 - 2.00%
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
7 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Alloy Steel
Alloy Steel = Low, Medium, High Carbon Steel
+ Alloying Agent (Chrome, Nickel, Vanadium,
Tungsten, Molybdenum)
Improved properties such as tensile strength,
toughness and corrosion resistance
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
8 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Metal Structure
Inclusions
Grain
Grain
Boundary
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
9 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Metal Structure
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
10 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Forming Methods
Cast
Wrought
Rolling
Forging
Extrusion
Drawing
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
11 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Cast
Random Grain
structure
Brittle structure
Easily Machined
12 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Rolled
Grain Flow
Metal Structure
13 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Forged
14 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Cast Vs. Forged
Cast
Random
Grain
Structure
Forged
Flow
Lines
15 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Heat Treatment
Increased
Strength
Toughness
Wear Resistance
Tree Steps
Austenitizing
Quenching
Tempering
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
16 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Austenitizing
17 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Austenitizing (heat) Methods
Furnace Heating
Induction Heating
> 6 mm deep
Flame Heating
> 12 mm deep
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
18 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Quenching
19 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Quenching (cooling) Methods
Sprayed Water
Moving Water
Water Bath
Moving Oil
Oil Bath
Moving Air
Still Air
Induction Heating
> 6 mm deep
Flame Heating
> 12 mm deep
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
20 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
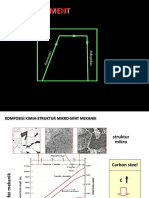
Tempering
Relieve Stresses
Improve Toughness
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
21 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Case Hardening Carburizing
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Carburizing is a method of increasing the
carbon content of the surface of low-
carbon steel through absorption and
diffusion. It is done to prepare the steel
for quench hardening. Steel is heated
above its upper critical temperature 930C
in the presence of carbon to allow it to
absorb into the metal to the desired depth.
Process Characteristics:
Applied to low-carbon steel
Produces a hard surface
Work piece cores largely retain their
toughness and ductility
Produces case hardness depths of up to
6 mm
Need quenching and tempering after
wards. May also need straightening due to
distortion.
22 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Case Hardening Carbonitriding
Carbonitriding is a diffusion-hardening
process for ferrous metals in which
both carbon and nitrogen are
introduced into the part surface by
heating the part while in contact with a
gas or liquid containing carbon and
nitrogen.
Process Characteristics:
The part are heated to 760C in a
carbon and nitrogen atmosphere or a
cyanide bath.
Produces thin, very hard surface layers
of uniform depth.
Little distortion
Has a maximum case depth of 0.3 mm
in.
Produces better surface wear
characteristics than carburizing
23 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Case Hardening Nitriding
Nitriding is a diffusion-hardening
process for ferrous metals in which
nitrogen are introduced into the part
surface by heating the part while in
contact with a gas or liquid containing
nitrogen.
The part are heated to 540C in a
nitrogen atmosphere or a cyanide
bath.
Produces thin, very hard surface
layers of uniform depth.
No distortion
Has a maximum case depth of 0.3 mm
Quenching and tempering before the
nitriding, Part is ready for use after
process
24 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Hardness Test
25 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Subsurface Refining impurities Defects, Inclusions)
Dirt
Slag
Furnace Brick
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
26 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Inclusion Bulls Eye
27 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Forming Defects
Subsurface
Shrinkage
cavities
Gas pockets
Slag Inclusions
Pipe
Flakes
Forging hot
spots
Surface
Coldshuts
Hot tears
Handling
cracks
Seams
laps
Grinder
burns
Cast
Wrought
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
28 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Shrinkage Cavity
30 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Forging Hot Spots
31 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Forging Lap
32 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
Heat Treat Defects
Quench Cracks
Soft Spots
Straightening Cracks
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
33 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Quench Crack
34 Service Training Malaga
AFA I
Lion DVD
CHAPTER: Metallurgy
Straightening Crack
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basic MetallurgyDocument62 pagesBasic MetallurgyMustafa Oğuzhan100% (2)
- Welding MetallurgyDocument37 pagesWelding Metallurgyhemant1886100% (4)
- Engineering MetallurgyDocument540 pagesEngineering Metallurgymadhuriaddepalli100% (1)
- Steel MakingDocument35 pagesSteel MakingBharichalo007Pas encore d'évaluation
- MetallurgyDocument75 pagesMetallurgymmramachandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding MetallurgyDocument69 pagesWelding MetallurgyManish Sharma100% (8)
- MetallurgyDocument252 pagesMetallurgyAsif Hameed100% (1)
- Cast IronDocument21 pagesCast Irondellibabu509Pas encore d'évaluation
- MetallurgyDocument190 pagesMetallurgyJose J. Nuñez100% (2)
- Physical Metallurgy For Engineers by Clark and VarneyDocument656 pagesPhysical Metallurgy For Engineers by Clark and VarneyMohnish100% (3)
- Physical Metallurgy Principles and PracticeDocument245 pagesPhysical Metallurgy Principles and PracticeShashank Shekhar50% (2)
- SM TupkaryDocument666 pagesSM TupkaryElio100% (5)
- Hot Rolled Steel SheetDocument38 pagesHot Rolled Steel Sheetkhwanta-bta100% (4)
- Presentation On Heat TreatmentDocument43 pagesPresentation On Heat Treatmentgosaye desalegnPas encore d'évaluation
- Titanium Alloy GuideDocument48 pagesTitanium Alloy GuidePatrick DominguezPas encore d'évaluation
- 2017-91 Heat Treatment of SteelDocument74 pages2017-91 Heat Treatment of SteelJen Megah Bremanda SembiringPas encore d'évaluation
- Iron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramDocument52 pagesIron Carbon Equilibrium DiagramSohan Lal100% (2)
- Metallurgy: Defined As Art and Science of Procuring and Adopting Metals and Alloys To Satisfy Human WantsDocument130 pagesMetallurgy: Defined As Art and Science of Procuring and Adopting Metals and Alloys To Satisfy Human WantsgregkilatonPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Alloying Elements On SteelsDocument245 pagesEffect of Alloying Elements On SteelsCharlie Chong100% (9)
- MTech Industrial Metallurgy E Learning Executive Summary &FAQsDocument6 pagesMTech Industrial Metallurgy E Learning Executive Summary &FAQsakshukPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding MetallurgyDocument30 pagesWelding MetallurgySamanthaPereraPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic MetallurgyDocument72 pagesBasic MetallurgyMuhammad Haris100% (1)
- Week 5. Quenching and TemperingDocument41 pagesWeek 5. Quenching and TemperingCheeragPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermal Analysis of Cast Iron PDFDocument27 pagesThermal Analysis of Cast Iron PDFRasoul SadeghiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nodular Cast IronDocument20 pagesNodular Cast Ironpoluri manicharanPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics and Applications of Induction FurnacesDocument54 pagesBasics and Applications of Induction Furnacespioneerinvincible100% (4)
- Physical Metallurgy of SteelDocument174 pagesPhysical Metallurgy of SteelMarisa RobertsPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding Metallurgy-2Document9 pagesWelding Metallurgy-2Nur SyahroniPas encore d'évaluation
- Primary Aluminium Casting Alloys 2010 - Rheinfelden Alloys - ENDocument117 pagesPrimary Aluminium Casting Alloys 2010 - Rheinfelden Alloys - ENtahera aqeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Carbon Steel HandbookDocument138 pagesCarbon Steel HandbookRajul SaxenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical MetallurgyDocument670 pagesPhysical MetallurgyprasadPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.the Basics of Ferrous MetallurgyDocument83 pages1.the Basics of Ferrous MetallurgyfenasikerimPas encore d'évaluation
- Affect of Elements On SteelDocument82 pagesAffect of Elements On SteelAditya PratapPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat TreatmentDocument30 pagesHeat Treatmentjhamlal100% (2)
- Heat Treatment Lecture NotesDocument24 pagesHeat Treatment Lecture Notestbmari100% (5)
- Type of CorrosionDocument12 pagesType of CorrosionNur Afiqah100% (2)
- Case HardeningDocument14 pagesCase HardeningmasoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Case HardeningDocument34 pagesCase HardeningSachinPas encore d'évaluation
- Surface TreatmentDocument35 pagesSurface TreatmentAnshul VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- MMEN 120 - Surface HardeningDocument19 pagesMMEN 120 - Surface HardeningnattydreadfathelahPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment Chapter 2Document24 pagesHeat Treatment Chapter 2patel ketan100% (4)
- Case Hardening Heat TreatmentDocument15 pagesCase Hardening Heat Treatmentmohit1990dodwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Deepesh Heat TreatmentDocument26 pagesDeepesh Heat TreatmentVaidPas encore d'évaluation
- MINEX Metallurgical CoDocument41 pagesMINEX Metallurgical CoPriyank SamagraPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture-6: Heat Treatment of Metals and Alloys - Importance Heat Treatment Processes NormalisingDocument47 pagesLecture-6: Heat Treatment of Metals and Alloys - Importance Heat Treatment Processes NormalisingSarojKumarSinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Case HardeningDocument28 pagesCase Hardeningdramilt100% (1)
- Surface HardeningDocument17 pagesSurface HardeningMahesh MakwanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment: Dr. Mohamed Abd Elmonem DahaDocument23 pagesHeat Treatment: Dr. Mohamed Abd Elmonem DahashoroukPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment of Low Carbon SteelDocument39 pagesHeat Treatment of Low Carbon SteelZhang FeiPas encore d'évaluation
- MMS Unit 3 Hardening of SteelsDocument17 pagesMMS Unit 3 Hardening of SteelsPraveen KolukulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Heat TreatmentDocument40 pagesGear Heat TreatmentvishnuPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER - Heat Treatment 3rd Sem ManufacturingDocument11 pagesCHAPTER - Heat Treatment 3rd Sem Manufacturingkaranragav12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Treatment, Case HardeningDocument15 pagesHeat Treatment, Case HardeningM Insan KamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat - Treatment of SteelDocument39 pagesHeat - Treatment of Steel113314Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hardening Is Usually Done To: Heat Treatment of AlloysDocument8 pagesHardening Is Usually Done To: Heat Treatment of AlloysMadhavanIcePas encore d'évaluation
- Aviation Maintenance Technician B1 - Certification Series: Summary MaterialsDocument71 pagesAviation Maintenance Technician B1 - Certification Series: Summary MaterialsSMK Penerbangan SPN Dirgantara BatamPas encore d'évaluation
- Galvanising ProcessDocument13 pagesGalvanising ProcesschepurthiPas encore d'évaluation
- Neral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Springs and GearsDocument31 pagesNeral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Springs and GearsbrotaccristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Shafts and BearingsDocument43 pagesShafts and BearingsMario AndrewPas encore d'évaluation
- Neral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Materials and ProcessesDocument54 pagesNeral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Materials and ProcessesbrotaccristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Neral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Seals, Gaskets, ValvesDocument37 pagesNeral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Seals, Gaskets, ValvesbrotaccristianPas encore d'évaluation
- Neral Notes On Engineering Hardware - FastenersDocument45 pagesNeral Notes On Engineering Hardware - Fastenersbrotaccristian100% (1)
- Part 6 Power Transmission ElementsDocument56 pagesPart 6 Power Transmission ElementsBasem Al-HajPas encore d'évaluation
- Zurada - Introduction To Artificial Neural Systems (WPC, 1992)Document764 pagesZurada - Introduction To Artificial Neural Systems (WPC, 1992)Rohan Singh93% (14)
- Global Environmental ConcernsDocument17 pagesGlobal Environmental Concernsirvan82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Management: Syllabus Financial Management: Investment-Need, Appraisal and Criteria, Financial Analysis TechDocument13 pagesFinancial Management: Syllabus Financial Management: Investment-Need, Appraisal and Criteria, Financial Analysis TechNiket KawalePas encore d'évaluation
- ECAM5Document28 pagesECAM5Niket KawalePas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Monitoring and Targeting: 8.1 DefinitionDocument12 pagesEnergy Monitoring and Targeting: 8.1 DefinitionNiket KawalePas encore d'évaluation
- Project Management: SyllabusDocument16 pagesProject Management: SyllabusNiket KawalePas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Audit ChapterDocument25 pagesEnergy Audit ChapterGourav JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Material and Energy BalanceDocument23 pagesMaterial and Energy BalanceSaurabh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- w14 Mounting PDFDocument7 pagesw14 Mounting PDFBasem Al-HajPas encore d'évaluation
- Forms of EnergyDocument18 pagesForms of EnergyJAYESHPas encore d'évaluation
- Energy Scenario: Syllabus Energy Scenario: Commercial and Non-Commercial Energy, Primary Energy ResourcesDocument36 pagesEnergy Scenario: Syllabus Energy Scenario: Commercial and Non-Commercial Energy, Primary Energy ResourcesCelestino Montiel MaldonadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Analisis de Vibraciones Mecanicas SKFDocument31 pagesAnalisis de Vibraciones Mecanicas SKFJhonathan GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech7350 05 Balancing PDFDocument5 pagesMech7350 05 Balancing PDFBasem Al-HajPas encore d'évaluation
- Combo PDFDocument209 pagesCombo PDFBasem Al-HajPas encore d'évaluation
- 400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9 VibrationDocument4 pages400 Bad Request 400 Bad Request Nginx/1.2.9 VibrationmghgolPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech7350 14 Condition MonitoringDocument12 pagesMech7350 14 Condition Monitoringkwakwa4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bearing Isolator Interchange2005 PDFDocument60 pagesBearing Isolator Interchange2005 PDFBasem Al-HajPas encore d'évaluation
- Coding System of Strain Gauges-AGS-TECH VersionDocument8 pagesCoding System of Strain Gauges-AGS-TECH VersionsergiojgsPas encore d'évaluation
- Waterproofing TunnelsDocument12 pagesWaterproofing TunnelsSharifah Normala100% (1)
- Nordipipe BrochureDocument8 pagesNordipipe BrochureLuis13956353Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cold WeldingDocument2 pagesCold Weldingpramod_kPas encore d'évaluation
- EU FlowerDocument2 pagesEU FlowerabeesPas encore d'évaluation
- Geniosil W180Document3 pagesGeniosil W180Locer2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Hy-RibDocument20 pagesNotes On Hy-RibMohd Faizal100% (1)
- BS 6100-6-2Document10 pagesBS 6100-6-2Leed ENPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Characteristics PDFDocument4 pagesMaterial Characteristics PDFELTIPAZOPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Junction Box and Fitting PDFDocument5 pagesElectrical Junction Box and Fitting PDFhendrabudimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electroplating of JewelryDocument13 pagesElectroplating of JewelrymobsivacPas encore d'évaluation
- BS 5493Document143 pagesBS 5493Muhammad Irfan Butt88% (8)
- Flanges General - Materials According To ASTMDocument2 pagesFlanges General - Materials According To ASTMthinkwell_10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Penguard ProDocument6 pagesPenguard ProvoidfirezPas encore d'évaluation
- ManufacturingDocument6 pagesManufacturingTeEbhan ChAnthira SeEkaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Textiles MidtermDocument38 pagesTextiles MidtermcamiayoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Alloy 6moDocument2 pagesAlloy 6moqshaath100% (1)
- On Veneer and Laminates ArchitecturalDocument14 pagesOn Veneer and Laminates ArchitecturalBhargPatelPas encore d'évaluation
- FKM 1Document13 pagesFKM 1itee0510Pas encore d'évaluation
- CSI Estimating CategoriesDocument8 pagesCSI Estimating CategoriesAnonymous 0oQHdzb7pvPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Chapter 9 AlloysDocument13 pagesChemistry Chapter 9 AlloysJian Jet LeePas encore d'évaluation
- GRG Technical SpecificationDocument6 pagesGRG Technical SpecificationHarsh AsthanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bill Qty. For Main Road of Bashmakh-PenjwenDocument12 pagesBill Qty. For Main Road of Bashmakh-PenjwenChalakAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- NE01 103RevACDocument25 pagesNE01 103RevACMarlene Yuriserll Ruiz MuñozPas encore d'évaluation
- CIP 6 Joints in Concrete Slaabs On Grade PDFDocument2 pagesCIP 6 Joints in Concrete Slaabs On Grade PDFAli ParvezPas encore d'évaluation
- Marvin ADM Construction DetailsDocument17 pagesMarvin ADM Construction DetailsJulius 'Julez' MorrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe SpecificationsDocument5 pagesPipe Specificationsbabar.muetPas encore d'évaluation
- Fosroc CatalogueDocument298 pagesFosroc CatalogueGeorge Tsiamtsouris75% (4)
- Brochure DowDocument8 pagesBrochure DowLucas Bissoli100% (1)
- Window Shutters by Shutter SmartDocument18 pagesWindow Shutters by Shutter SmartViken OhenasianPas encore d'évaluation