Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
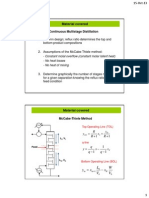
Fundamentals of Distillation
Transféré par
mujeebtalib0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
235 vues51 pagesFundamentals of distillation
Titre original
Fundamentals of distillation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentFundamentals of distillation
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
235 vues51 pagesFundamentals of Distillation
Transféré par
mujeebtalibFundamentals of distillation
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 51
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
Faculty
M Elamaran
PNM-CG
Prepared by
Production-CG Team
CONTENTS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Introduction
Basics of distillation
History of distillation
Types of distillation
Videos
Fractionating equipments
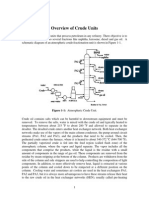
INTRODUCTION TO REFINERY
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Hydrocarbon molecules in crude do NOT meet customer needs
SEPARATION PROCESSES
(Primary Processes)
CONVERSION PROCESSES
(Secondary Processes)
FINISHING PROCESSES
(Secondary Processes)
Segregate the molecules
Rearrange the molecules
Remove Contaminants
MARKETABLE PRODUCTS
UNIT OPERATIONS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
1.Fluid flow processes, including fluids transportation, filtration, and solids
fluidization.
2. Heat transfer processes, including evaporation, condensation, and heat
exchange.
3. Mass transfer processes, including gas absorption, distillation, extraction,
adsorption, and drying.
4.Thermodynamic processes, including gas liquefaction, and refrigeration.
5.Mechanical processes, including solids transportation, crushing and
pulverization, and screening and sieving.
UNIT OPERATIONS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
1. Combination.
2. Separation Distillation comes under this.
3. Reaction.
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
EVAPORATION
ORDINARY EVAPORATION IS A SURFACE PHENOMENON - SOME MOLECULES
HAVE ENOUGH KINETIC ENERGY TO ESCAPE FROM THE LIQUID.
THE PROCESS OF EVAPORATION IN A CLOSED CONTAINER WILL PROCEED
UNTIL THERE ARE AS MANY MOLECULES RETURNING TO THE LIQUID AS
THERE ARE ESCAPING.
AT THIS POINT THE VAPOUR IS SAID TO BE SATURATED AND THE PRESSURE
OF THAT VAPOUR (EXPRESSED IN mmHg) IS CALLED SATURATED VAPOUR
PRESSURE.
IF THE LIQUID IS OPEN TO THE AIR, THEN THE VAPOUR PRESSURE IS SEEN AS
PARTIAL PRESSURE ALONG WITH OTHER CONSTITUENTS OF THE AIR.
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
THE TEMPERATURE AT WHICH VAPOUR PRESSURE IS EQUAL TO THE
ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE IS CALLED THE BOILING POINT.
SINCE THE VAPOUR PRESSURE IS LOW IN ORDINARY EVAPORATION AND THE
PRESSURE INSIDE THE LIQUID IS EQUAL TO ATMOSPHERIC PRESSURE PLUS
THE LIQUID PRESSURE, BUBBLES OF VAPOUR CAN NOT FORM INSIDE THE
BULK LIQUID.
AT BOILING POINT, VAPOUR PRESSURE IS EQUAL TO ATMOSPHERIC
PRESSURE, BUBBLES FORM AND VAPORIZATION BECOMES A VOLUME
PHENOMENA.
SINCE THE MOLECULAR KINETIC ENERGY IS GREATER AT HIGHER
TEMPERATURE, MORE MOLECULES CAN ESCAPE THE SURFACE AND THE
SATURATED VAPOUR PRESSURE IS CORRESPONDINGLY HIGHER.
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
VAPOUR PRESSURE OF A LIQUID AT A PARTICULAR TEMPERATURE IS THE
EQUILIBRIUM PRESSURE EXERTED BY MOLECULES LEAVING AND ENTERING
THE LIQUID SURFACE.
SOME IMPORTANT POINTS REGARDING VAPOUR PRESSURE:
ENERGY INPUT RAISES VAPOUR PRESSURE
VAPOUR PRESSURE IS RELATED TO BOILING
A LIQUID IS SAID TO BOIL WHEN ITS VAPOUR PRESSURE EQUALS THE
SURROUNDING PRESSURE
THE EASE WITH WHICH A LIQUID BOILS DEPENDS ON ITS VOLATILITY
LIQUIDS WITH HIGH VAPOUR PRESSURES (VOLATILE LIQUIDS) WILL BOIL AT
LOWER TEMPERATURES
THE VAPOUR PRESSURE AND HENCE THE BOILING POINT OF A LIQUID MIXTURE
DEPENDS ON THE RELATIVE AMOUNTS OF THE COMPONENTS IN THE MIXTURE
DISTILLATION OCCURS BECAUSE OF THE DIFFERENCES IN THE VOLATILITY OF
THE COMPONENTS IN THE LIQUID MIXTURE
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
THE BOILING POINT DIAGRAM SHOWS
HOW THE EQUILIBRIUM COMPOSITIONS OF
THE COMPONENTS IN A LIQUID MIXTURE
VARY WITH TEMPERATURE AT A FIXED
PRESSURE.
CONSIDER AN EXAMPLE OF A LIQUID
MIXTURE CONTAINING 2 COMPONENTS (A
AND B) - A BINARY MIXTURE.
IN THIS EXAMPLE, A IS THE MORE VOLATILE
COMPONENT AND THEREFORE HAS A
LOWER BOILING POINT THAN B.
THE DEW-POINT IS THE TEMPERATURE AT
WHICH THE SATURATED VAPOUR STARTS
TO CONDENSE.
THE BUBBLE-POINT IS THE TEMPERATURE
AT WHICH THE LIQUID STARTS TO BOIL.
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
FOR EXAMPLE, WHEN A SUBCOOLED LIQUID
WITH MOLE FRACTION OF A=0.4 (POINT A) IS
HEATED, ITS CONCENTRATION REMAINS
CONSTANT UNTIL IT REACHES THE BUBBLE-
POINT (POINT B), WHEN IT STARTS TO BOIL.
THE VAPOURS EVOLVED DURING THE BOILING
HAS THE EQUILIBRIUM COMPOSITION GIVEN
BY POINT C, APPROXIMATELY 0.8 MOLE
FRACTION A.
THIS IS APPROXIMATELY 50% RICHER IN A
THAN THE ORIGINAL LIQUID.
THIS DIFFERENCE BETWEEN LIQUID AND
VAPOUR COMPOSITIONS IN EQUILIBRIUM IS
THE BASIS FOR DISTILLATION OPERATIONS.
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
DISTILLATION IS ACHIEVED BY THE APPLICATION AND REMOVAL OF HEAT.
THE SEPARATION OF COMPONENTS FROM A MIXTURE BY DISTILLATION DEPENDS ON
THE DIFFERENCE IN BOILING POINTS OF THE INDIVIDUAL COMPONENTS, CALLED
RELATIVE VOLATILITY.
WHEN A MIXTURE OF TWO OR MORE LIQUIDS IS HEATED AND BOILED, THE VAPOR HAS
A DIFFERENT COMPOSITION THAN THE LIQUID. FOR EXAMPLE, IF 10% MIXTURE OF
ETHANOL IN WATER IS BOILED, THE VAPOR WILL CONTAIN OVER 50% ETHANOL.
DISTILLATION IS BASED ON THE FACT THAT THE VAPOUR OF A BOILING MIXTURE WILL
BE RICHER IN THE COMPONENTS THAT HAVE LOWER BOILING POINTS. THE
CONDENSATE WILL CONTAIN MORE VOLATILE COMPONENTS.
AT THE SAME TIME, THE ORIGINAL MIXTURE WILL CONTAIN MORE OF THE LESS
VOLATILE MATERIAL.
BASICS OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
THE VAPOR CAN BE CONDENSED AND BOILED AGAIN, WHICH WILL RESULT IN AN
EVEN HIGHER CONCENTRATION OF ETHANOL. DISTILLATION OPERATES ON THIS
PRINCIPLE.
REPEATED BOILING AND CONDENSING IS A CLUMSY PROCESS, HOWEVER, THIS CAN
BE DONE AS A CONTINUOUS PROCESS IN A DISTILLATION COLUMN.
IN THE COLUMN, RISING VAPORS WILL STRIP OUT THE MORE VOLATILE
COMPONENT, WHICH WILL BE GRADUALLY CONCENTRATED AS THE VAPOR CLIMBS
UP THE COLUMN
DISTILLATION CONSUMES ENORMOUS AMOUNTS OF ENERGY . BOTH IN TERMS OF
COOLING AND HEATING REQUIREMENTS IT CAN CONTRIBUTE TO MORE THAN 50%
OF PLANT OPERATING COSTS.
HISTORY OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
USE OF DISTILLATION DATES BACK IN RECORDED HISTORY TO ABOUT 50 B.C.
INDUSTRIAL EXPLOITATION OF THIS SEPARATION PROCESS STARTED IN 12TH
CENTURY WHEN IT WAS USED TO PRODUCE ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES.
BY THE 16TH CENTURY, DISTILLATION WAS BEING USED IN THE MANUFACTURE OF
VINEGAR, PERFUMES, OILS AND OTHER PRODUCTS.
EARLY DISTILLATION WAS BASICALLY BATCH STILLS TO PRODUCE ETHANOL.
NEXT WAS A SERIES OF STILLS WITH A CONTINUOUS FEED THAT FLOWED THROUGH
THE SERIES.
HISTORY OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
HISTORY OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
HISTORY OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
THE NEXT PROGRESSION WAS TO PLACE THE STILLS IN A COLUMN AND
INTERCHANGE THE VAPOUR AND LIQUID TO IMPROVE RECOVERY.
EARLY SMALL TOWERS HAD ONE OR TWO LARGE BUBBLE CAPS PER
TRAY.
THE LIQUID AND VAPOUR TRAVELLED THROUGH THE CENTRE OF
COLUMN AND MIXED ON THE OUTER RING OF BUBBLE CAP.
LATER WHEN THE TRAY EFICIENCY BECAME MORE IMPORTANT, FLOW
ON THE TRAY BEGAN TO BE STUDIED AND SEVERAL TYPES OF TRAYS
AND CHANGED FLOW PATTERNS WERE DEVELOPED.
TRAY COLUMNS APPEARED IN THE SCENE IN THE 1820s ALONG WITH
FEED PREHEATING AND USE OF INTERNAL REFLUX.
HISTORY OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
TYPES OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Based on system composition:
Binary distillation
Multi component distillation
Based on Operation Mode:
Batch distillation
Continuous distillation
TYPES OF DISTILLATION
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Based on Extra feed:
Extractive distillation: Extra feed component leaves with the
bottom product.
Azeotropic distillation: Extra feed component leaves with the top
product.
Based on Separation:
Stripping Removes lighter from heavier component
Rectification Removes heavier from lighter component
Fractionation Separates lighter and heavier.
Complex fractionation separates into 3 or more components.
VIDEOS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
Faculty
M Elamaran
PNM-CG
Prepared by
Production-CG Team
COMPONENTS OF FRACTIONATION EQUIPMENT
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Distillation columns are made up of several components, each of which
is used either to transfer heat energy or enhance material transfer. A
typical distillation contains several major components:
A vertical shell where the separation of liquid components is carried out.
Column internals such as trays/plates and/or packings which are used to
enhance component separations.
A reboiler to provide the necessary vaporization for the distillation
process .
A condenser to cool and condense the vapour leaving the top of the
column
A reflux drum to hold the condensed vapour from the top of the column
so that liquid (reflux) can be recycled back to the column
COMPONENTS OF FRACTIONATION EQUIPMENT
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
COMPONENTS OF FRACTIONATION EQUIPMENT
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
The liquid mixture that is to be processed is known as the feed and
this is introduced usually somewhere near the middle of the column
to a tray known as the feed tray. The feed tray divides the column
into a top (enriching or rectification) section and a bottom
(stripping) section. The feed flows down the column where it is
collected at the bottom in the reboiler.
COMPONENTS OF FRACTIONATION EQUIPMENT
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
The condenser, reboiler and the column internal are termed as
Stages, where ideally vapour and liquid equilibrium is established, if
given enough residence time.
A vessel filled with a mixture of two components is said to be in
equilibrium if the number of light molecules escaping from the
liquid is equal to the number returning to the liquid.
REBOILER
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Heat is supplied to the reboiler to generate
vapour. The source of heat input can be any
suitable fluid, although in most chemical
plants this is normally steam. In refineries,
the heating source may be the output
streams of other columns. The vapour
raised in the reboiler is re-introduced into
the unit at the bottom of the column. The
liquid removed from the reboiler is known
as the bottoms product or simply, bottoms.
REBOILER TYPES
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Types of Reboiler:
1. Vertical Thermo-Syphon Reboiler.
2. Horizontal Thermo-Syphon Reboiler
3. Kettle Reboiler.
4. Furnace
CONDENSER
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
The vapour moves up the column, and as it
exits the top of the unit, it is cooled by a
condenser. The condensed liquid is stored
in a holding vessel known as the reflux
drum. Some of this liquid is recycled back
to the top of the column and this is called
the reflux. The condensed liquid that is
removed from the system is known as the
distillate or top product.
CONDENSER TYPES
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
A. Partial Condenser
The partial condenser is best used when there is a
large difference in the overhead vapour composition.
For e.g. when there is a small amount of methane
and hydrogen mixed in a gasoline stream, the partial
condenser condenses the gasoline and leaves the
methane and hydrogen as a vapour to be vented
from the overhead reflux drum.
B. Total Condenser
The total condenser is best used when there is small
difference in the overhead vapour composition. The
overhead vapour can be condensed at approximately
same temperature.
CONDENSER TYPES
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
C. Hot vapour bypass condenser
The hot vapour bypass condenser is best utilized
when there is a potential for large changes in the
overhead vapour composition. The vapour
bypass can be used to maintain the pressure in
the tower system when the light components are
lower than design.
COLUMN INTERNALS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
TRAYS PACKINGS
TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Trays
A tray essentially acts as a mini-column, each
accomplishing a fraction of the separation
task.
The more trays there are, the better is the
degree of separation .
Overall separation efficiency will depend
significantly on the design of the tray.
Trays are designed to maximize vapour-liquid
contact by considering the liquid distribution
and vapour distribution.
TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Vapour and liquid mixes to form a froth.
Mass transfer occurs within the froth.
The froth overflows across a weir.
The vapour disengages and move to the
tray above.
The bulk liquid flows down the down
comer to next tray.
The steps are repeated in the next tray.
LIQUID AND VAPOR FLOW IN TRAY COLUMN
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Each tray has 2 conduits called down
comers: one on each side. Liquid falls
by gravity through the down comers
from one tray to the tray below.
A weir ensures there is always some
liquid (holdup) on the tray and is
designed such that the holdup is at a
suitable height, e.g. such that the
bubble caps are covered by liquid.
Vapour flows up the column and is
forced to pass through the liquid via
the openings on each tray. The area
allowed for the passage of vapour on
each tray is called the active tray area.
LIQUID FLOW
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Single pass Double Pass
TRAY TYPES
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
1. BAFFLE TRAYS
2. SIEVE TRAYS
3. VALVE TRAYS
4. BUBBLE CAP TRAYS
5. HIGH EFFICIENCY TRAYS
TRAY TYPES- BAFFLE TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Baffle Tray
Baffle trays are trays of low fouling
potential with low efficiency. They have
open areas approaching 50 % where a
high efficiency tray will have open area
less than 15 %.
Three major types of baffle trays are
A. Shed decks
B. Side to side trays
C. Disc and Donut trays
TRAY TYPES- SIEVE TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Flat perforated plate
Vapor issues from holes to give
multi-orifice effect
Simple in structure easy to
fabricate
Turn down ratio is around 2:1
Pressure drop is moderate
Not suitable for operation under
variable loads
TRAY TYPES- VALVE TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Valve can be round or rectangular
with or without caging structure
Vary high capacity tray
Turndown ratio5:1
pressure drop Moderate (earlier
designs somewhat higher recent
design same as sieve tray)
Around 20%higher cost then sieve
tray
TRAY TYPES- VALVE TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
CAGED VALVE
FIXED VALVE FLOATING VALVE
TRAY TYPES- BUBBLE CAP TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Perforated plate with riser around
the hole
Cap in the form of inverted cups
over the riser
excellent turn down ratio
Good at extreme low liquid rates
Pressure drop is high
TRAY TYPES- BUBBLE CAP TRAYS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
PACKED COLUMNS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Random and structured Packed columns generate a mass transfer area by providing
a large surface area over which the liquid can transfer heat and mass to the vapour.
Packing utilizes a continuous contacting principle to separate products. A major
advantage to packed column is the reduction in pressure across the column.
Typically the column pressure drop for a packed column is less than that of a trayed
column because of % open area.
Typical percent open area of a trayed column is 8 to 15 %, whereas a packed column
can approach 50 %. Liquid accumulation for a packed column is lower than a trayed
column.
Another advantage of packed column is reduced foaming. Packing generates thin
films instead of fine droplets for mass and heat transfer, reducing entrainment when
foaming agents are present.
The introduction of vapour and liquid to the packing is very important. Trays will
normally equalize whatever mal-distribution is developed by vapour and liquid feeds.
PACKED COLUMNS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
TRAY VS PACKED COLUMNS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Sl. No Description Trays Random
Packing
Structured
Packing
1 Pressure Drop High Low Lower
2 Fouling Service Yes No No
3 Feed Point Flexibility Yes Difficult Difficult
4 Liquid Hold up Considerable Small Small
5 Cleaning Easy Difficult difficult
6 Cost Low Low/Medium High
COLUMN PROBLEMS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Foaming
Foaming refers to the expansion of liquid due to passage of
vapour or gas. Although it provides high interfacial liquid-vapour
contact, excessive foaming often leads to liquid buildup on trays.
In some cases, foaming may be so bad that the foam mixes with
liquid on the tray above. Whether foaming will occur depends
primarily on physical properties of the liquid mixtures, but is
sometimes due to tray designs and condition. Whatever the
cause, separation efficiency is always reduced.
COLUMN PROBLEMS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Entrainment
Entrainment refers to the liquid carried by vapour up to the tray
above and is again caused by high vapour flow rates. It is
detrimental because tray efficiency is reduced: lower volatile
material is carried to a plate holding liquid of higher volatility. It
could also contaminate high purity distillate. Excessive
entrainment can lead to flooding.
COLUMN PROBLEMS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Weeping/Dumping
This phenomenon is caused by low vapour flow. The pressure
exerted by the vapour is insufficient to hold up the liquid on the
tray. Therefore, liquid starts to leak through perforations.
Excessive weeping will lead to dumping. That is the liquid on all
trays will crash (dump) through to the base of the column (via a
domino effect) and the column will have to be re-started.
Weeping is indicated by a sharp pressure drop in the column and
reduced separation efficiency.
COLUMN PROBLEMS
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Flooding
Flooding is brought about by excessive vapour flow, causing liquid
to be entrained in the vapour up the column. The increased
pressure from excessive vapour also backs up the liquid in the
down comer, causing an increase in liquid holdup on the plate
above. Depending on the degree of flooding, the maximum
capacity of the column may be severely reduced. Flooding is
detected by sharp increases in column differential pressure and
significant decrease in separation efficiency.
QUERIES
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
PARADEEP REFINERY PROJECT
A Sunrise Project for a Sunshine Future
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Hot High Pressure SeparatorDocument2 pagesHot High Pressure SeparatorKhai NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- CDU Training Powerpoint PDFDocument144 pagesCDU Training Powerpoint PDFnefoussi100% (1)
- A Students Guide To RefineryDocument16 pagesA Students Guide To RefineryManisha RatheePas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Gas FractionationDocument28 pagesNatural Gas Fractionationmohamed100% (1)
- Tower Tray Oil and Gas IndustryDocument11 pagesTower Tray Oil and Gas IndustryHeet PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation TowwerDocument154 pagesDistillation TowwerAmmar HashimPas encore d'évaluation
- Significance of Debutanizer Reflux RatioDocument2 pagesSignificance of Debutanizer Reflux RatioMuhammadUsmanSaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- CPE 601 Distillation - Topic 5 Design of Other EquipmentDocument70 pagesCPE 601 Distillation - Topic 5 Design of Other EquipmentRosa SinensisPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Catalytic Cracking Unit (FCCU)Document1 pageFluid Catalytic Cracking Unit (FCCU)Billy BlinksPas encore d'évaluation
- Desalter OperationDocument19 pagesDesalter OperationmohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation Column Basics PDFDocument4 pagesDistillation Column Basics PDFck19654840Pas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Oil DesalterDocument3 pagesCrude Oil DesalterStaherPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation Tray Types Operation TRBSHTDocument38 pagesDistillation Tray Types Operation TRBSHTGary JonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation in RefineryDocument4 pagesDistillation in RefineryMuhammad SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar - Sulfur RecoveryDocument18 pagesSeminar - Sulfur RecoverySourav Sikdar100% (1)
- Lecture 4 Reflux Ratio and Column DesignDocument13 pagesLecture 4 Reflux Ratio and Column DesignMohammedTalib100% (1)
- 08 HydroprocessingDocument52 pages08 HydroprocessingThaiyalNayakiPas encore d'évaluation
- Atmospheric & Vacuum Distillation ProcessesDocument22 pagesAtmospheric & Vacuum Distillation ProcessesNikhil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Reforming and Naphtha SplitterDocument32 pagesReforming and Naphtha Splittercedric100% (5)
- Petroleumrefining2of3 190124033941 PDFDocument247 pagesPetroleumrefining2of3 190124033941 PDFsuman mukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- Refinery 3Document53 pagesRefinery 3Patel AshokPas encore d'évaluation
- Desalting of Crude Oil in RefineryDocument3 pagesDesalting of Crude Oil in RefineryKmt_AePas encore d'évaluation
- Treatment of Effluent From RefineriesDocument26 pagesTreatment of Effluent From RefinerieskalaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Heavy Oil HydrotreatingDocument15 pagesHeavy Oil HydrotreatingSIMON LIUPas encore d'évaluation
- Fractional DistillationDocument17 pagesFractional DistillationSubash KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Crude Distillation PosterDocument1 pageCrude Distillation Postervivek_rec100% (1)
- Petroleum Fractionation-Overview PDFDocument35 pagesPetroleum Fractionation-Overview PDFRiyad AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Gas Dehydration by Molecular SievesDocument16 pagesNatural Gas Dehydration by Molecular SievesSneha PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 HydrotreatingDocument31 pages8 HydrotreatingAmroKasht100% (2)
- Debottlenecking Refineries Through Comprehensive Feedstock PretreatmentDocument20 pagesDebottlenecking Refineries Through Comprehensive Feedstock PretreatmentAnonymous msVFzaPas encore d'évaluation
- ED ProcessDocument9 pagesED ProcesskhanasifalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Refining Water Best PracticesDocument60 pagesRefining Water Best Practicesarini_aristia_sPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro To DistillationDocument33 pagesIntro To Distillationcallielizza100% (1)
- Optimisation of SRUDocument12 pagesOptimisation of SRUHuzefaFDPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Chemistry of Crude-FinalDocument39 pagesLecture 1 Chemistry of Crude-FinalNaval Koralkar Chemical Engg. Dept.Pas encore d'évaluation
- T Basak AromaticsDocument41 pagesT Basak AromaticsDP PurwadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Desalter EfficiencyDocument3 pagesDesalter Efficiencykronos39zeusPas encore d'évaluation
- AspenHYSYS YourveryfirstHYSYSSimulationDocument60 pagesAspenHYSYS YourveryfirstHYSYSSimulationkiranchemenggPas encore d'évaluation
- Refinery Definitions - FAQDocument7 pagesRefinery Definitions - FAQbalajiupesPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Distillation: V. K. KapoorDocument62 pagesBasics of Distillation: V. K. Kapoorstardeepakrati100% (1)
- Gas Processing MethodsDocument27 pagesGas Processing MethodsHammad AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation StartupDocument4 pagesDistillation StartupsundharPas encore d'évaluation
- Packed Distillation ColumnDocument5 pagesPacked Distillation ColumnaziziPas encore d'évaluation
- AlkyDocument37 pagesAlkyMỹ PhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmed Deyab: Senior Process Engineer Process Simulation ConsultantDocument154 pagesAhmed Deyab: Senior Process Engineer Process Simulation ConsultantHamza AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Presented By: Anas SaleemDocument21 pagesPresented By: Anas SaleemAnas Saleem100% (2)
- Distillation ColumnsDocument40 pagesDistillation ColumnsSantiagoOrtizLdsPas encore d'évaluation
- Internship Presentation Indian Oil (IOCL)Document36 pagesInternship Presentation Indian Oil (IOCL)Dhrubajyoti DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Choosing Column InternalsDocument7 pagesChoosing Column Internalspetrolhead1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-02 Petroleum Process I-IVDocument143 pagesUnit-02 Petroleum Process I-IVMayank KoparkarPas encore d'évaluation
- S 344 Sour Water Prf4Document4 pagesS 344 Sour Water Prf4Elshad MirzayevPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety in Chemical Process IndustriesDocument40 pagesSafety in Chemical Process IndustriesDevendra SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Filling The Propylene Gap On Purpose TechnologiesDocument12 pagesFilling The Propylene Gap On Purpose Technologiesvajidqc100% (1)
- Reactor and Catalyst DesignDocument19 pagesReactor and Catalyst Designbakhtyar21100% (1)
- Amine Treatment/ Regeneration UnitDocument17 pagesAmine Treatment/ Regeneration UnitSyed Abdul RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Safety Talk: Fired HeatersDocument58 pagesSafety Talk: Fired HeatersSaleem ChohanPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Title: Heat ExchangerDocument19 pagesProject Title: Heat ExchangerHan SanPas encore d'évaluation
- Double Pipe Heat Exchanger Based On Nano FluidDocument14 pagesDouble Pipe Heat Exchanger Based On Nano Fluiddhanshri kolekarPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Transfer Lab Presentation: By-Shubham Sachan Rajdeep Singh Shashwat Tiwari Sahil YadavDocument21 pagesMass Transfer Lab Presentation: By-Shubham Sachan Rajdeep Singh Shashwat Tiwari Sahil Yadavbadshah sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- How Is Fresh Water Different From Sea Water ?Document17 pagesHow Is Fresh Water Different From Sea Water ?Atif NaumanPas encore d'évaluation
- Paradeep Refinery Project: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine FutureDocument79 pagesParadeep Refinery Project: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine Futuremujeebtalib50% (2)
- Introduction To Heat ExchangersDocument44 pagesIntroduction To Heat ExchangersmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator Operation and ProtectionDocument52 pagesGenerator Operation and Protectionmujeebtalib100% (4)
- Pump Regular ChecksDocument3 pagesPump Regular ChecksmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of CompressorsDocument43 pagesTheory of Compressorsmujeebtalib100% (3)
- Introduction To Storage Tanks & Tank InternalsDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Storage Tanks & Tank Internalsmujeebtalib80% (5)
- Primitive Checkpoints Before Login Into E-Tendering Portal: TroubleshootingDocument5 pagesPrimitive Checkpoints Before Login Into E-Tendering Portal: TroubleshootingmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Field InstrumentationDocument89 pagesField Instrumentationmujeebtalib100% (6)
- Offsite FacilitiesDocument44 pagesOffsite FacilitiesmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Oil SPill ManagementDocument39 pagesOil SPill Managementmujeebtalib100% (4)
- ON Delayed Coker Unit: Prepared byDocument42 pagesON Delayed Coker Unit: Prepared bymujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- AVU Critical EquipmentsDocument55 pagesAVU Critical EquipmentsmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Hazards in A RefineryDocument25 pagesHazards in A Refinerymujeebtalib100% (1)
- Pump BasicsDocument54 pagesPump BasicsmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical SafetyDocument58 pagesElectrical Safetymujeebtalib100% (5)
- Furnace Start-Up and ShutdownDocument47 pagesFurnace Start-Up and Shutdownmujeebtalib100% (3)
- Tank OperationDocument18 pagesTank Operationmujeebtalib100% (1)
- GT PresentaionDocument98 pagesGT Presentaionmujeebtalib100% (5)
- Aum Shree Sainathaya NamahDocument52 pagesAum Shree Sainathaya NamahmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Disaster ManagementDocument39 pagesDisaster ManagementmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Generator Operation and ProtectionDocument52 pagesGenerator Operation and Protectionmujeebtalib100% (4)
- Handling of Hazardous Chemicals: Haldia RefineryDocument34 pagesHandling of Hazardous Chemicals: Haldia RefinerymujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Coker Ball Valve of Velan PDFDocument8 pagesCoker Ball Valve of Velan PDFmujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Properties:: Haldia RefineryDocument43 pagesPhysical Properties:: Haldia Refinerymujeebtalib100% (3)
- Fundamentals of Refining Products and PropertiesDocument46 pagesFundamentals of Refining Products and Propertiesmujeebtalib100% (1)
- Paradeep Refinery Project: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine FutureDocument35 pagesParadeep Refinery Project: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine Futuremujeebtalib80% (5)
- Use of Personal Protective Equipments: Manoj Kr. Ray SM (F&S)Document33 pagesUse of Personal Protective Equipments: Manoj Kr. Ray SM (F&S)mujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Fire TriangleDocument50 pagesFire TrianglemujeebtalibPas encore d'évaluation
- Captive Power Plant - Encon Measures: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine FutureDocument20 pagesCaptive Power Plant - Encon Measures: A Sunrise Project For A Sunshine Futuremujeebtalib100% (1)
- Grade 8 Science Text Book 61fb9947be91fDocument289 pagesGrade 8 Science Text Book 61fb9947be91fNadarajah PragatheeswarPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGL102 Othello Act 3 Discussion QuestionsDocument2 pagesENGL102 Othello Act 3 Discussion QuestionsDaniel DenningPas encore d'évaluation
- TOPIC 2 - Fans, Blowers and Air CompressorDocument69 pagesTOPIC 2 - Fans, Blowers and Air CompressorCllyan ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Classroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalDocument1 pageClassroom Activty Rubrics Classroom Activty Rubrics: Total TotalMay Almerez- WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Section ADocument7 pagesSection AZeeshan HaiderPas encore d'évaluation
- Bridging The Divide Between Saas and Enterprise Datacenters: An Oracle White Paper Feb 2010Document18 pagesBridging The Divide Between Saas and Enterprise Datacenters: An Oracle White Paper Feb 2010Danno NPas encore d'évaluation
- KKS Equipment Matrik No PM Description PM StartDocument3 pagesKKS Equipment Matrik No PM Description PM StartGHAZY TUBePas encore d'évaluation
- A Quick Guide To Artificial IntelligenceDocument41 pagesA Quick Guide To Artificial IntelligenceFrancis Violet Raymond100% (2)
- Hydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsDocument28 pagesHydraulic Excavator: Engine WeightsFelipe Pisklevits LaubePas encore d'évaluation
- Alexander Fraser TytlerDocument4 pagesAlexander Fraser Tytlersbr9guyPas encore d'évaluation
- IBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Document80 pagesIBM Thinkpad Z61 Quanta BW2Abubakar SidikPas encore d'évaluation
- Inglês - Advérbios - Adverbs.Document18 pagesInglês - Advérbios - Adverbs.KhyashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Microcal P20Document2 pagesMicrocal P20ctmtectrolPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizal Noli Me TangereDocument35 pagesRizal Noli Me TangereKristine Cantilero100% (2)
- Probset 3 KeyDocument7 pagesProbset 3 KeyhoneyschuPas encore d'évaluation
- Instruction Manual Il-Obct-R1: Slip-Over Current Transformer ObctDocument2 pagesInstruction Manual Il-Obct-R1: Slip-Over Current Transformer Obctبوحميدة كمالPas encore d'évaluation
- Interventional Studies 2Document28 pagesInterventional Studies 2Abdul RazzakPas encore d'évaluation
- BIR REliefDocument32 pagesBIR REliefJayRellvic Guy-ab67% (6)
- QFW Series SteamDocument8 pagesQFW Series Steamnikon_fa50% (2)
- Quiz EditedDocument6 pagesQuiz EditedAbigail LeronPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Stress InterventionsDocument5 pagesJob Stress InterventionscocaralucamihaelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Coping Mechanism and Academic Performance Among FiDocument14 pagesCoping Mechanism and Academic Performance Among FiMary Margaret MorillaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of IT in TQM L'Oreal Case StudyDocument9 pagesThe Role of IT in TQM L'Oreal Case StudyUdrea RoxanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hot Aishwarya Rai Wedding and Her Life.20130105.040216Document2 pagesThe Hot Aishwarya Rai Wedding and Her Life.20130105.040216anon_501746111100% (1)
- Subtotal Gastrectomy For Gastric CancerDocument15 pagesSubtotal Gastrectomy For Gastric CancerRUBEN DARIO AGRESOTTPas encore d'évaluation
- 555 TimerDocument25 pages555 TimerDr-Muhammad Aqeel AslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology: DR - Wasfi Dhahir Abid AliDocument9 pagesPathophysiology: DR - Wasfi Dhahir Abid AliSheryl Ann PedinesPas encore d'évaluation
- Project 2 Analysis of Florida WaterDocument8 pagesProject 2 Analysis of Florida WaterBeau Beauchamp100% (1)
- Operaciones UnitariasDocument91 pagesOperaciones UnitariasAlejandro ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- VDA Volume Assessment of Quality Management Methods Guideline 1st Edition November 2017 Online-DocumentDocument36 pagesVDA Volume Assessment of Quality Management Methods Guideline 1st Edition November 2017 Online-DocumentR JPas encore d'évaluation