Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Foreign Exchange Rate Determination: Expectations and The Asset Market Model
Transféré par
Irfan Khazi0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues20 pagesforexx
Titre original
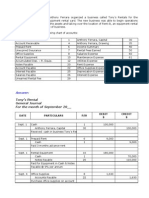
Forex Determination.st
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentforexx
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues20 pagesForeign Exchange Rate Determination: Expectations and The Asset Market Model
Transféré par
Irfan Khaziforexx
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 20
1
Foreign Exchange Rate Determination:
Expectations and the Asset Market
Model
International Financial
Management
Dr. A. DeMaskey
2
Learning Objectives
What are the determinants of exchange rates?
Are changes in exchange rates predictable?
What factors affect the equilibrium exchange
rate?
What is the role of expectations?
How do central banks intervene in the foreign
exchange market?
3
Potential Foreign Exchange Rate
Determinants
Parity Conditions
1. Relative inflation rates
2. Relative interest rates
3. Forward exchange rates
4. Exchange rate regimes
5. Official monetary reserves
Infrastructure
1. Strength of banking system
2. Strength of securities markets
3. Outlook for growth and profitability
Speculation
1. Currencies
2. Securities
3. Uncovered interest arbitrage
4. Real estate
5. Commodities
Cross-Border Investment
1. Foreign direct investment
2. Portfolio investment
Political Risk
1. Capital controls
2. Black market in currencies
3. Exchange rate spreads
4. Risk premium on securities
and FDI
Spot Exchange Rate
4
Measuring Exchange Rate
Movements
Appreciation
Depreciation
Percent Change in the Foreign
Currency Value
Percent Change in the Home
Currency Value
5
Exchange Rate Equilibrium
Demand
Supply
Equilibrium Exchange Rate
6
Equilibrium Exchange Rate
S
D
$1.50
Dollar Value of
Quantity of
7
Macro-Economic Factors
Influencing Exchange Rates
Relative Inflation Rates
Relative Interest Rates
Relative Income Levels
8
Impact of Rising U.S. Inflation on the
Equilibrium Value of the British Pound
S
D
$1.50
Dollar Value of
Quantity of
9
Impact of Rising U.S. Interest Rates on
the Equilibrium Value of the British Pound
S
D
$1.50
Dollar Value of
Quantity of
10
Impact of Rising U.S. Income on the
Equilibrium Value of the British Pound
S
D
$1.50
Dollar Value of
Quantity of
11
Government Controls
Foreign Exchange Barriers
Foreign Trade Barriers
Government Intervention in Foreign
Exchange Market
Affecting macro variables, such as
inflation, interest rates, and income
levels
12
Expectations
Foreign exchange markets react to any news
that may have a future effect.
Institutional investors often take currency
positions based on anticipated interest rate
movements in various countries.
Because of speculative transactions, foreign
exchange rates can be very volatile.
13
Role of Expectations
Signal Impact on $
Poor U.S. economic indicators
Fed chairman suggests Fed is
unlikely to cut U.S. interest rates
A possible decline in German
interest rates
Central banks expected to
intervene to boost the euro
14
Interaction of Factors
Trade-Related Factors
Financial Factors
Trade-related factors and financial
factors sometimes interact.
15
Factors Affecting Exchange
Rates
Inflation Differential
Income Differential
Govt Trade Restrictions
Interest Rate Differential
Capital Flow Restrictions
U.S. Demand
For Foreign Goods
Foreign Demand
For U.S. Goods
U.S. Demand
For FC
Supply of FC
For Sale
U.S. Demand
For Foreign
Securities
Foreign Demand
For U.S. Securities
U.S. Demand
For FC
Supply of FC
For Sale
Exchange Rate
Between the
Foreign Currency
And the Dollar
16
Government Intervention
Reasons
Direct
Sterilized
Non-Sterilized
Indirect
Government Policy
Government Barriers
17
Central Bank Intervention
Nonsterilized Intervention
To Strengthen the C$
Federal Reserve
Banks Participating
In the Foreign
Exchange Market
C$ $
Sterilized Intervention
To Strengthen the C$
Federal Reserve
Banks Participating
In the Foreign
Exchange Market
Financial
Institutions
That Invest
In Treasury
Securities
$ C$
Treasury Securities
$
18
Impact of Currency Value
Government Deficit
Government Policy Tool
Weak Home Currency
Strong Home Currency
19
Effect of Expectations
Currency values are determined by:
Inflation
Interest rates
Economic and political stability
GDP growth
Reputation of central bank
In reality, however, exchange rates are
affected by expectations of these
variables.
20
Central Bank Behavior
Reputable central banks:
Are trusted by markets to maintain a
currencys purchasing power through sound
monetary policy.
Tend to be independent.
Have currencies that are more highly valued
than those issued by less reputable banks.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Exchange RatesDocument32 pagesExchange RatesStuti BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 101 Consulting FrameworkDocument205 pagesTop 101 Consulting FrameworkWilmer Chacón100% (2)
- Fundamental Analysis of Forex Markets ExplainedDocument13 pagesFundamental Analysis of Forex Markets ExplainedAar Rageedi0% (1)
- Determination of Exchange RateDocument14 pagesDetermination of Exchange RateAshish Tagade100% (2)
- The Foreign Exchange Matrix: A new framework for understanding currency movementsD'EverandThe Foreign Exchange Matrix: A new framework for understanding currency movementsÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- CH 04 - Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument24 pagesCH 04 - Exchange Rate DeterminationadamPas encore d'évaluation
- FA - Assignment - 01Document17 pagesFA - Assignment - 01Rehan Mehmood63% (8)
- Effects of Foreign Exchange Rates On Indian EconomyDocument43 pagesEffects of Foreign Exchange Rates On Indian EconomyMohamed Rizwan0% (1)
- Quiz - Merchandising BSA 101 2015-2016 With SolutionDocument7 pagesQuiz - Merchandising BSA 101 2015-2016 With SolutionNia BranzuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Exchange RateDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange RateTikitaka TitiPas encore d'évaluation
- International Trade of Goods and Services And: Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange Rates 1. Inflation RatesDocument5 pagesInternational Trade of Goods and Services And: Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange Rates 1. Inflation RatesUtkarsh GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange Ratesanish-kc-8151Pas encore d'évaluation
- Report On Multilevel MarketingDocument27 pagesReport On Multilevel MarketingCincinnatiEnquirerPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Affecting Exchange RatesDocument9 pagesFactors Affecting Exchange RatesAnoopa NarayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Accounting AnalysisDocument15 pagesAccounting AnalysisMonoarul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Meeting ScriptDocument4 pagesBusiness Meeting Scriptroshelle100% (3)
- ch07 Godfrey Teori AkuntansiDocument34 pagesch07 Godfrey Teori Akuntansiuphevanbogs100% (2)
- Summary MKI Chapter 4Document4 pagesSummary MKI Chapter 4DeviPas encore d'évaluation
- RizwanDocument9 pagesRizwanRizwan BashirPas encore d'évaluation
- The Determination of Exchange Rate: BY Annisa Ramadhani Bertha Muhammad Karina Fitri Zahira SalsabellaDocument25 pagesThe Determination of Exchange Rate: BY Annisa Ramadhani Bertha Muhammad Karina Fitri Zahira SalsabellaRatu ShaviraPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument2 pagesExchange Rate DeterminationafniPas encore d'évaluation
- International Finance: Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange RatesDocument8 pagesInternational Finance: Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Ratesvan_1234100% (1)
- (Determination of Exchange Rates) PDFDocument24 pages(Determination of Exchange Rates) PDFEdward Joseph A. RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document24 pagesChapter 4Manjunath BVPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors That Influence Exchange RatesJoelene ChewPas encore d'évaluation
- Case C8Document6 pagesCase C8Việt Tuấn TrịnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Financial System: International InstitutionsDocument21 pagesGlobal Financial System: International Institutionsapi-265248190% (1)
- Exchange Rate Determination: Chapter ObjectivesDocument18 pagesExchange Rate Determination: Chapter Objectiveschauhan ShivangiPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Factors That Influence Exchange Rate.: 1. InflationDocument9 pagesMain Factors That Influence Exchange Rate.: 1. InflationHiren GanganiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document14 pagesChapter 9Cindy permatasariPas encore d'évaluation
- International Monetary and Financial Systems - Chapter-4 MbsDocument62 pagesInternational Monetary and Financial Systems - Chapter-4 MbsArjun MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Global Financial System: 1.1 International InstitutionsDocument25 pages01 Global Financial System: 1.1 International Institutionsapi-26524819Pas encore d'évaluation
- Key Factors Affecting Exchange Rate ChangeDocument3 pagesKey Factors Affecting Exchange Rate ChangeyzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Global Financial System: International InstitutionsDocument15 pagesGlobal Financial System: International Institutionsapi-26524819Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Factors That Influence Exchange RatesDocument2 pages6 Factors That Influence Exchange RatesfredsvPas encore d'évaluation
- IfDocument3 pagesIfAman MalviyaPas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadDocument4 pagesDownloadmanirajpoot45Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preprints202106 0240 v1Document5 pagesPreprints202106 0240 v1Kenzy Waleed SolimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Written Prompt Macro 4Document4 pagesWritten Prompt Macro 4Douglas ArisiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange Rate Determination: South-Western/Thomson Learning © 2006Document24 pagesExchange Rate Determination: South-Western/Thomson Learning © 2006Praveen JaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Currency Fluctuation Team - QuatreDocument18 pagesCurrency Fluctuation Team - Quatrejignesh143347Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fin 444Document22 pagesFin 444mrinmoy royPas encore d'évaluation
- Inflation. Interest Rates. Balance of Payments. Government Intervention. Other FactorsDocument2 pagesInflation. Interest Rates. Balance of Payments. Government Intervention. Other FactorsEmmanuelle RojasPas encore d'évaluation
- How Would You Characterize The International Monetary System Since Collapse of Bretton WoodsDocument6 pagesHow Would You Characterize The International Monetary System Since Collapse of Bretton Woodsmario32323243Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 9 International MarketsDocument27 pagesTopic 9 International MarketsKelly Chan Yun JiePas encore d'évaluation
- FIN 422 (Chapter 2)Document9 pagesFIN 422 (Chapter 2)Sumaiya AfrinPas encore d'évaluation
- CH - 4 - Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument23 pagesCH - 4 - Exchange Rate DeterminationAwsaf bin hashemPas encore d'évaluation
- Factor Affect Currency ValueDocument1 pageFactor Affect Currency Valueshibashish PandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fin 444 CHP 4 SlidesDocument24 pagesFin 444 CHP 4 SlidesBappi MahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 Wed Bsacore6Document4 pagesModule 4 Wed Bsacore6Kryzzel JonPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange RatesDocument2 pages8 Key Factors That Affect Foreign Exchange RatesdhitalkhushiPas encore d'évaluation
- Money in AssigmentDocument6 pagesMoney in AssigmentMussa AthanasPas encore d'évaluation
- Determining Exchange Rate: TopicDocument24 pagesDetermining Exchange Rate: TopicGreeshma SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentedby: Shaily Srivastava Sneha Kumari Manjunath Anamika SrivastavaDocument57 pagesPresentedby: Shaily Srivastava Sneha Kumari Manjunath Anamika SrivastavaSneha SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Part 1: The International Financial Environment Chapter 4 Exchange Rate DeterminationDocument32 pagesPart 1: The International Financial Environment Chapter 4 Exchange Rate DeterminationAbdelrahman HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- FIM AssignmentDocument5 pagesFIM AssignmentNoor AliPas encore d'évaluation
- ProjectDocument7 pagesProjectRajeshwari ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Report International Financial System: Group MembersDocument6 pagesFinal Report International Financial System: Group MembersmohsinPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange RateDocument2 pagesExchange RateJosh Lander MatugasPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Influencing Exchange RatesDocument2 pagesFactors Influencing Exchange RatesPravin Kumar PPas encore d'évaluation
- BMGC L6 2022-2023Document59 pagesBMGC L6 2022-2023Bianca KangPas encore d'évaluation
- Weekly Market Commentary 10/22/2012Document3 pagesWeekly Market Commentary 10/22/2012monarchadvisorygroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Exchange Rate Movements: Changes in ExportsDocument11 pagesExchange Rate Movements: Changes in ExportsamitPas encore d'évaluation
- Narrative Report For FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, PedrosaDocument3 pagesNarrative Report For FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT, PedrosaAlfredJoshuaMirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 4 Exchange Rate Determination 11edDocument42 pagesCH 4 Exchange Rate Determination 11edNazmul HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- The Effects of Currency Fluctuations On The EconomyDocument3 pagesThe Effects of Currency Fluctuations On The EconomyKhairun NisyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rational Market Economics: A Compass for the Beginning InvestorD'EverandRational Market Economics: A Compass for the Beginning InvestorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Defining Marketing For The 21st CenturyDocument25 pagesChapter 1 Defining Marketing For The 21st CenturyMisbahSyedPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 15Document2 pagesCase 15AdrtyPas encore d'évaluation
- Classes Document 1346855496Document18 pagesClasses Document 1346855496Tony Peterz KurewaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco-10 em PDFDocument11 pagesEco-10 em PDFAnilLalvaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment On MAXIS: Segi MbaDocument18 pagesAssignment On MAXIS: Segi MbaSharmiLa RajandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions Manual: Introduction To AccountingDocument5 pagesSolutions Manual: Introduction To AccountingAlison JcPas encore d'évaluation
- Cost and Management Accounting I For 3rd Year Business Education StudentsDocument86 pagesCost and Management Accounting I For 3rd Year Business Education StudentsAmir Kan100% (2)
- Case Study 2Document2 pagesCase Study 2jagseer25% (4)
- Schedule For ConferenceDocument9 pagesSchedule For ConferenceSagar SanganiPas encore d'évaluation
- BL2 Module 2 Topics 5-8Document17 pagesBL2 Module 2 Topics 5-8Vinsmoke KaidoPas encore d'évaluation
- Daftar Isi ISADocument4 pagesDaftar Isi ISADedi PramonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Môn QU Ản Trị Chiến Lược (Strategic Management) L ớp học phần: Th ời lượng: 75 phútDocument2 pagesMôn QU Ản Trị Chiến Lược (Strategic Management) L ớp học phần: Th ời lượng: 75 phútThanh Hiếu Trần ThịPas encore d'évaluation
- SWOT Analysis of Shemu Edible Oil FactoryDocument11 pagesSWOT Analysis of Shemu Edible Oil FactoryEyael ShimleasPas encore d'évaluation
- Rahul Das-21810052, Project Parivartan AssignmentDocument2 pagesRahul Das-21810052, Project Parivartan AssignmentRAHUL DASPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 1Document11 pagesTest 1VânAnh Nguyễn100% (1)
- Materi UTS Manajemen Stratejik S1 Akt April2021Document12 pagesMateri UTS Manajemen Stratejik S1 Akt April2021AthayaSekarNovianaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Relative - Valuation QuestionsDocument3 pages4 Relative - Valuation Questionselianamacedo1720Pas encore d'évaluation
- DDT - Chapter 1Document47 pagesDDT - Chapter 1Suba ChaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Ias 8Document7 pagesIas 8Jan Joshua Paolo GarcePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Recording Business Transactions: Acid)Document29 pagesChapter 2 Recording Business Transactions: Acid)Farhan Osman ahmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Econenv536 Lecture4 - 51 12 07Document36 pagesEconenv536 Lecture4 - 51 12 07Ingrid FariasPas encore d'évaluation
- I CPADocument2 pagesI CPAHydeePas encore d'évaluation
- CBLM Bookkeeping Nciii PDF FreeDocument52 pagesCBLM Bookkeeping Nciii PDF FreeJhonalyn Jaranilla-mahino TamposPas encore d'évaluation