Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Immune System
Transféré par
LinaPurnamasariDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Immune System
Transféré par
LinaPurnamasariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INTRODUCTION
TO THE IMMUNE
SYSTEM
THE FUNCTION :
Distinguish sell from nonself antigen
Protect the organism from nonself
antigen
Necessary for survival in human
being and all animals
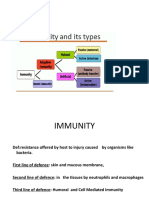
NONSPESIFIC IMMUNITY ( INNATE
IMMUNITY )
Inflammatory Response and Phagocytosis
Skin and mucosa barrier
SPESIFIC IMMUNITY ( ADAPTIVE
IMMUNITY )
Hummoral Immunity
Cellular Immunity
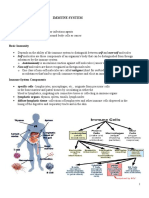
CELLS OF THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
A. LYMPHOCYTES
B. PHAGOCYTIC CELLS
C. BASOPHILS AND MAST CELLS
A. LYMPHOCYTES :
B lymphocytes
T lymphocytes
Null cells
B. PHAGOCYTIC CELLS :
Macrophages
Polymorphonuclear leucocytes
Eosinophils
C. BASOPHILS AND MAST CELLS
Development of the Immune System
A. PHYLOGENETIC DEVELOPMENT
B. ONTOGENETIC DEVELOPMENT
1. In mature mammals, the primary
lymphoid organs are the thymus and
bone marrow
2. Phagocytic cells
3. Complement components
Immune system functional
components
A. ANTIBODY-MEDIATED IMMUNITY
(Humoral Immunity)
1. Immunoglobulin structure
2. Antibody diversity
3. Structural functional correlates
4. Immunoglobulin classes
a. Immunoglobulin G
b. Immunoglobulin M
c. Immunoglobulin A
d. Immunoglobulin D
e. Immunoglobulin E
Difference between humoral and cell
mediated immunity
Humoral immunity Cell immunity
Antibody mediated Cell mediated
B lymphocyte T lymphocyte
Against bacterial Against viruses,
Infection fungi, intracellular
organisms, tumor
antigens, allograft
rejection
B. CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY
1. The T helper 1 / T helper 2 paradigm
2. T helper 1 and T helper 2 cells exhibit
functionally distinct characteristics
3. T helper 1 and T helper 2 cells regulate
cellular function
Phagocytic immuniy
CIRCULATING
FIXED
The steps of phagocytoses and destruction of foreign antigen
1. Random movement
2. Neutrophil adherence
3. Transmembrane migration (diapedesis)
4. Chemotoxis
5. Opsonization and fixation
6. Ingestion
7. Metabolic activation
8. Destruction
PHAGOCYTIC IMMUNITY
SPECIFIC FEATURES
A. Phagocytic cells migration
B. Opsonization
C. Phagocytosis
The Complement System
A. The classic activation pathway
B. Alternative pathway activation
C. Amplification
D. Effection mechanism
E. The membrane attack complex (MAC)
Antigen Antibody Interactions
ANTIGEN
ALLERGEN
IMMUNOGENICITY
ANTIGENICITY
HAPTEN
IMMUNOGENICITY
= Physical properties of the antigen
= Biologic system
= Route of administration
= Method of immunization
Classification of Immunologic
Reactions
Type I (Ig E Mediated)
Anaphylactic or immediate hypersensitivity :
- Early phase reaction
- Late phase reaction
Type II Cytotoxic Reactions
Binding of either Ig G or Ig M
antibody to cell bound antigens
Type III Immune Complex
Mediated Reactions
Type IV Cell Mediated,
Delayed Hypersensitivity
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of The Immune System 5th Edition Abbas Test BankDocument26 pagesBasic Immunology Functions and Disorders of The Immune System 5th Edition Abbas Test BankRussellFischerqxcj98% (55)
- Kathleen Langreo Notes FB (Feb6)Document27 pagesKathleen Langreo Notes FB (Feb6)Kaycee Ayo100% (4)
- Janeway's Immunobiology ReviewDocument2 pagesJaneway's Immunobiology ReviewPhillip McMullenPas encore d'évaluation
- Moorish Paradigm Book 8Document41 pagesMoorish Paradigm Book 8Perfecto Salaam-El100% (8)
- Immunology Flash CardsDocument46 pagesImmunology Flash CardsRickyNoviantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Hematoimun (Dr. Fakhri) - Immunity To Parasitic InfectionsDocument17 pagesModul Hematoimun (Dr. Fakhri) - Immunity To Parasitic InfectionsFajr Muzammil100% (1)
- Immune System DisorderDocument20 pagesImmune System Disorderkto12100% (1)
- Chap 14Document39 pagesChap 14Koby100% (4)
- Immunology: Benjie M. Clemente, RMT, Mls (Ascpi)Document30 pagesImmunology: Benjie M. Clemente, RMT, Mls (Ascpi)Meriam Juan100% (1)
- Immunology NotesDocument27 pagesImmunology Notescomputerlois88% (8)
- Immunology Micro D&R AgamDocument146 pagesImmunology Micro D&R AgamNirosha Arul100% (1)
- Basic ImmunologyDocument29 pagesBasic ImmunologyHema Duddukuri0% (1)
- ImmuneDocument12 pagesImmuneoldpenguinPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Endodontic Immunology 2Document4 pages8 Endodontic Immunology 2doctorgame085Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review Flash Card by Dr. Mitch Roy MaristelaDocument205 pagesReview Flash Card by Dr. Mitch Roy MaristelaMark Justin OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 10kapoyaDocument12 pages8 10kapoyaJeru Margareth TingsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology To InfectionDocument47 pagesImmunology To InfectionIndra ToshiwayPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic ImmunologyDocument57 pagesBasic ImmunologyRonalyn UgatPas encore d'évaluation
- Assoc. Prof. Ma. Jennifer R. Tiburcio, MSMT Department of Med Tech UST Faculty of PharmacyDocument27 pagesAssoc. Prof. Ma. Jennifer R. Tiburcio, MSMT Department of Med Tech UST Faculty of PharmacyJaellah MatawaPas encore d'évaluation
- Underwood: Chapter 7: Immunology and Immunopathology Defence Against InfectionDocument29 pagesUnderwood: Chapter 7: Immunology and Immunopathology Defence Against InfectionSAPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3a - Cells of The IS and Innate ImmunityDocument49 pagesChapter 3a - Cells of The IS and Innate ImmunityChezkah Nicole MirandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural ImmunityDocument20 pagesDiseases of Immunity: I-Innate or Natural Immunitymano343Pas encore d'évaluation
- Host Response To InfectionDocument36 pagesHost Response To InfectionFrancia Toledano100% (1)
- Unit-3 BTDocument27 pagesUnit-3 BTDhananjay KhadePas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Immunology Dr. Esra Hassan: 1-Innate Immune ResponseDocument7 pagesMicrobiology Immunology Dr. Esra Hassan: 1-Innate Immune ResponseMohammed R.HusseinPas encore d'évaluation
- Antigen, Antibody and Antigen-Antibody ReactionsDocument50 pagesAntigen, Antibody and Antigen-Antibody ReactionsAmbika Ghosh SenPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto ImmunityDocument23 pagesAuto Immunitymuneera salimPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology 1.1 Immunology - Dr. FontanillaDocument115 pagesMicrobiology 1.1 Immunology - Dr. FontanillaRyn ShadowPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology in Infectious Disease: Titin Andri Wihastuti Psik FkubDocument29 pagesImmunology in Infectious Disease: Titin Andri Wihastuti Psik Fkubminnie_ranger4763Pas encore d'évaluation
- Humoralimmunitylecture 091201050531 Phpapp02Document21 pagesHumoralimmunitylecture 091201050531 Phpapp02razikPas encore d'évaluation
- AntigensDocument33 pagesAntigensSandeep Pokhrel100% (2)
- Immunity - (Innate and Acquired)Document51 pagesImmunity - (Innate and Acquired)Okla HomaPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune DiseasesDocument101 pagesImmune DiseasesCarlo GriñoPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity in The BodyDocument2 pagesImmunity in The BodyMeow MeowPas encore d'évaluation
- Inmunidad y SepsisDocument6 pagesInmunidad y SepsisAmmarie SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewDocument87 pagesBasic Immunology From The Dermatologic Point of ViewnovelraaaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 and 3 ImmunologyDocument16 pagesChapter 2 and 3 ImmunologyRevathyPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunochemistry (1) KordofanDocument34 pagesImmunochemistry (1) KordofanDr. Atif Hassan KhirelsiedPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionDocument56 pagesImmunity: Innate Defenses Specific Immunity Cell Mediated Immunity Self RecognitionMiranda sekar arumPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology 1 2Document32 pagesImmunology 1 2Jacky Junaedi100% (1)
- Lesson 6 ImmunologyDocument24 pagesLesson 6 ImmunologyVictor Z. DyPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityDocument191 pages19 - Lecture - PPT Lymphatic ImmunityGwyneth Adrienne Leigh VillapandoPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunityDocument31 pagesImmunityFahad NiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology and MicrobiologyDocument91 pagesImmunology and MicrobiologyB.simhachalamPas encore d'évaluation
- IMMUNITYDocument58 pagesIMMUNITYkamala 123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Modul Hematoimun (Dr. Fakhri) - Immunity To Parasitic InfectionsDocument17 pagesModul Hematoimun (Dr. Fakhri) - Immunity To Parasitic InfectionsAfdaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesDocument2 pagesChapter 21 - The Immune System: Innate and Adaptive Body DefensesChryza Faith QuicoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Definitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemDocument5 pagesDefinitions and Outline Structure of The Immune SystemanonymousPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 ImmunologyDocument66 pages05 Immunologytemesgen.girma0906Pas encore d'évaluation
- DR A.Aziz Djamal MSC - DTM&H.SPMK (K)Document27 pagesDR A.Aziz Djamal MSC - DTM&H.SPMK (K)Irfan GhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune System of HumanbodyDocument49 pagesImmune System of Humanbodysayan27.sikdarPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunityDocument190 pagesImmunityFathima100% (1)
- Isabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Document8 pagesIsabela State University: Immunology (Bs Psych 2)Charlz ZipaganPas encore d'évaluation
- 13i Immunologic DisordersDocument73 pages13i Immunologic DisordersDjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Immunology Batch 11Document28 pagesFinal Immunology Batch 11botet_2306Pas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Immunology Lecture 2Document53 pagesClinical Immunology Lecture 2jibril channelPas encore d'évaluation
- Humoral & Celullar ImmunityDocument60 pagesHumoral & Celullar ImmunityHaziq KamardinPas encore d'évaluation
- Adaptive Immunity: DR Arsalan Uqaili M.Phil (Physiology)Document37 pagesAdaptive Immunity: DR Arsalan Uqaili M.Phil (Physiology)USAMA AHMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology and Serology SolutionDocument17 pagesImmunology and Serology Solutionzakaria hossainPas encore d'évaluation
- How Do B Cells Produce Antibodies?Document165 pagesHow Do B Cells Produce Antibodies?Sharmaine TrangiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jenis Dan Bagian Antibodi Aktivitas Dan Spesifitas Tiap Antibodi Ikatan Antara Antibodi Dan AntigenDocument26 pagesJenis Dan Bagian Antibodi Aktivitas Dan Spesifitas Tiap Antibodi Ikatan Antara Antibodi Dan AntigenJundy RabbaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988D'EverandImmunointervention in Autoimmune Diseases: Papers Based on an International Meeting in Paris, France, in June 1988J. F. BachPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityD'EverandImmunology Unveiled: A Comprehensive Journey through the Human Immune System: Guardians of the Body: The Unseen Heroes of ImmunityPas encore d'évaluation
- Preclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1D'EverandPreclinical Immunology and Microbiology Review 2023: For USMLE Step 1 and COMLEX-USA Level 1Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE) : Lina PurnamasariDocument13 pagesJapanese Encephalitis (JE) : Lina PurnamasariLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- IBS, Dyspepsia, MigrainDocument20 pagesIBS, Dyspepsia, MigrainLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Receptors and Transduction 2: Dr. MV HejmadiDocument18 pagesReceptors and Transduction 2: Dr. MV HejmadiLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisDocument3 pages16 Tenses Dalam Bahasa InggrisOrion SihombingPas encore d'évaluation
- PMTCT 2010 PDFDocument116 pagesPMTCT 2010 PDFLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti Retro Viral TherapyDocument156 pagesAnti Retro Viral TherapyMubiru Sylvia100% (2)
- Urtika IV RevisiDocument27 pagesUrtika IV RevisiLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument37 pagesChronic Renal FailureLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Alergi Dasar IVDocument57 pagesAlergi Dasar IVLinaPurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- EBVDocument70 pagesEBVminerva_stanciuPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Fluids and Blood - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGYDocument29 pagesBody Fluids and Blood - HUMAN PHYSIOLOGYSodeinde SimeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Fi HemaDocument7 pagesPre Fi HemaRoyPintorPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseDocument43 pages6.3 Defence Against Infectious DiseaseAlacrity Xenoion SpadesPas encore d'évaluation
- Human Health and DiseaseDocument15 pagesHuman Health and DiseaseBiju MylachalPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 Natural Remedies For Epstein Barr VirusDocument40 pages7 Natural Remedies For Epstein Barr VirusalbinutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Geriatric AssessmentDocument58 pagesComprehensive Geriatric Assessmentrisa astriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Cellular AberrationDocument11 pagesIntroduction To Cellular AberrationAdiel CalsaPas encore d'évaluation
- محاضرة دكتورة ايمانDocument9 pagesمحاضرة دكتورة ايمانMsikvPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Report - AS90926Document4 pagesBiological Report - AS90926Kyra ElderPas encore d'évaluation
- Haematology NotesDocument184 pagesHaematology NotesJason royPas encore d'évaluation
- Koller 1980Document11 pagesKoller 1980..Pas encore d'évaluation
- Immuno-Virology-Bacteriology Book Version 103Document332 pagesImmuno-Virology-Bacteriology Book Version 103Goose ChapmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Blood Cell BiochemistryDocument19 pagesRed Blood Cell BiochemistryPrincewill SeiyefaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oppenheim J.J., Feldmann M. - Introduction To The Role of Cytokines in Innate Host Defense and Adaptive Immunity (2000) PDFDocument18 pagesOppenheim J.J., Feldmann M. - Introduction To The Role of Cytokines in Innate Host Defense and Adaptive Immunity (2000) PDFHesbon MomanyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyDocument14 pagesPediatric Kidney Transplantation - Background, History of The Procedure, EpidemiologyNovi BaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Sri Chaitanya Educational Institutions, India: Health and DiseaseDocument11 pagesSri Chaitanya Educational Institutions, India: Health and DiseaseBat ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema 2 WBCDocument30 pagesHema 2 WBCAngge Aquino OfficialPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebook Clinical Immunology Principles and Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Clinical Immunology Principles and Practice PDF Full Chapter PDFrobert.wheat692100% (23)
- Cell Mediated and Humoral Immunity. Cytokines & The Immune Responses, Hypersensitivity ReactionsDocument40 pagesCell Mediated and Humoral Immunity. Cytokines & The Immune Responses, Hypersensitivity ReactionsAjaga RuqayyahPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 12 Lymphatic-SystemDocument126 pagesCH 12 Lymphatic-SystemAntonio Calleja II100% (1)
- Chapter 11 Specific Host Defense MechanismDocument5 pagesChapter 11 Specific Host Defense MechanismEanna ParadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune System: Basic ImmunityDocument14 pagesImmune System: Basic ImmunityPLANARIAPas encore d'évaluation
- HUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE NEET OBT 2023 - Compressed-1-150Document10 pagesHUMAN HEALTH AND DISEASE NEET OBT 2023 - Compressed-1-150Nirmal ChakravarthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of The Spleen, Thymus, and White Blood Cells: PathologyDocument7 pagesDiseases of The Spleen, Thymus, and White Blood Cells: PathologyAbi SulitPas encore d'évaluation
- MUST To KNOW in Immunology and SerologyDocument18 pagesMUST To KNOW in Immunology and SerologyRona Salando50% (2)