Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
HTTP Versus HTTPS
Transféré par
dang2327Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HTTP Versus HTTPS
Transféré par
dang2327Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Maroti Deshmukh
12MCMB02
Introduction to HTTP
Limitations to HTTP
Introduction to HTTPS
Implementation of HTTPS
HTTPS Encryption
Identify secure connection
Disadvantages of HTTPS
HTTP vs. HTTPS
Conclusion
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) is the set
of rules for transferring files (text, graphic
images, sound, video, and other multimedia
files) on the world wide web.
HTTP uses default port 80.
The client submits an HTTP request message
to the server. The server, which provides
resources such as HTML files and other
content, or performs other functions on
behalf of the client, returns a response
message to the client.
Unsecured
Does not use certificates
Privacy
Integrity
Authentication
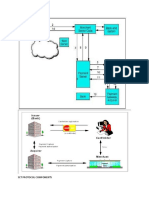
HTTPS = HTTP + SSL
HTTPS stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol
over Secure Socket Layer, or HTTP over SSL.
HTTPS by default uses port 443.
URL's beginning with HTTPS indicate that the
connection is encrypted using SSL.
HTTPS is implemented using Secure Sockets
Layer (SSL).
HTTPS by purchasing an SSL Certificate.
SSL certificates becomes the "passport" or the
digital document that verify that the security
and authenticity of the interaction.
The SSL certificate is installed on a web server
to identify the business using it to encrypt
sensitive data such as credit card
information.
SSL Certificates give a website the ability to
communicate securely with its web
customers.
An SSL Certificate enables encryption of
sensitive information during online
transactions.
Each SSL Certificate contains unique,
authenticated information about the
certificate owner.
A Certificate Authority verifies the identity of
the certificate owner when it is issued.
Each SSL Certificate consists of a Public key
and a Private key.
So during a secure communication, the
browser encrypts the message using the
public key and sends it to the server. The
message is decrypted on the server side
using the Private key.
In Internet Explorer, you will see a lock icon
in the Security Status bar. The Security Status
bar is located on the right side of the Address
bar. You can click the lock to view the identity
of the website.
If the information does not match or the
certificate has expired, the browser displays
an error message or warning and the status
bar may turn RED.
HTTPS is slightly slower than HTTP
HTTPS adds computational overhead as well
as network overhead.
URL begins with http://" in case of HTTP while
the URL begins with https:// in case of HTTPS.
HTTP is unsecured while HTTPS is secured.
HTTP uses port 80 for communication while
HTTPS uses port 443 for communication.
HTTP operates at Application Layer while HTTPS
operates at Transport Layer.
No encryption is there in HTTP while HTTPS uses
encryption.
No certificates required in HTTP while certificates
required in HTTPS.
The HTTP network protocol is fundamental to
the way the World Wide Web works, and the
encryption involved in HTTPS adds an
essential layer if confidential information or
sensitive data are to be exchanged over the
public internet.
Murizah Kassim1, 2, Mohamed Ismail1,
Kasmiran Jumari1 and Mat Ikram Yusuf
21Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia
Kefei Cheng, Meng Gao, Ruijie Guo College of
Computer Science Chongqing University of
Posts and Telecommunications Chongqing,
China
http://www.101hacker.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Concise Guide to SSL/TLS for DevOpsD'EverandThe Concise Guide to SSL/TLS for DevOpsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Securing .NET Web Services with SSL: How to Protect “Data in Transit” between Client and Remote ServerD'EverandSecuring .NET Web Services with SSL: How to Protect “Data in Transit” between Client and Remote ServerPas encore d'évaluation
- CCN Case StudyDocument13 pagesCCN Case StudyGaurang Gawas100% (1)
- HTTP Secure (HTTPS) - Encrypted Communication ProtocolDocument6 pagesHTTP Secure (HTTPS) - Encrypted Communication ProtocolFRANCESCO222Pas encore d'évaluation
- www_instantsslDocument2 pageswww_instantsslazariamorakePas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Communication Channels: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)Document5 pagesSecure Communication Channels: Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)Mani ShankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL) : Divey Gupta Sunny Gajjar B.Tech-IV Computer Engg. NIT-SuratDocument22 pagesSecure Socket Layer (SSL) : Divey Gupta Sunny Gajjar B.Tech-IV Computer Engg. NIT-SuratSunny Kishorbhai GajjarPas encore d'évaluation
- Test BytesDocument18 pagesTest Bytesraghunandhan.cvPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit3 Part2Document4 pagesUnit3 Part2ENGINEERING EXTRACTSPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTP Vs HttpsDocument2 pagesHTTP Vs HttpsRajesh100% (1)
- Chapter 17 - HTTPSDocument14 pagesChapter 17 - HTTPSnsd8681Pas encore d'évaluation
- HTTP Vs HttpsDocument6 pagesHTTP Vs HttpsEduardo MarquesPas encore d'évaluation
- DocumentDocument1 pageDocumentHassan AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- 165 TY B KenilSeminarDocument30 pages165 TY B KenilSeminarB K EnterprisePas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Socket Layer: M S.Bhiogade Patni Computer Services, Mumbai, IndiaDocument6 pagesSecure Socket Layer: M S.Bhiogade Patni Computer Services, Mumbai, Indiadidiey87Pas encore d'évaluation
- SSL Tls HttpsDocument32 pagesSSL Tls HttpsShivansh PundirPas encore d'évaluation
- Protocol World Wide Web Web Servers Browsers URL Web Page HTMLDocument3 pagesProtocol World Wide Web Web Servers Browsers URL Web Page HTMLSumathi SelvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTPS - WikipediaDocument12 pagesHTTPS - WikipediaLea AcamPas encore d'évaluation
- NSC Unit - 3 - 221210 - 134942Document29 pagesNSC Unit - 3 - 221210 - 134942SurenderPas encore d'évaluation
- IT Assignment On: Protocols For Secure Online BankingDocument16 pagesIT Assignment On: Protocols For Secure Online BankingSuveer MalhotraPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is HTTPS?: White PaperDocument7 pagesWhat Is HTTPS?: White Paperlai khoiPas encore d'évaluation
- What is an SSL/TLS X.509 CertificateDocument48 pagesWhat is an SSL/TLS X.509 CertificatePaul KatemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trusted.: o o o o oDocument7 pagesTrusted.: o o o o orajavijayakanth9Pas encore d'évaluation
- CNS 4Document7 pagesCNS 4Nikhil BompellyPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTP and HttpsDocument2 pagesHTTP and HttpsHaseeb Abdul RaufPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL)Document47 pagesSecure Socket Layer (SSL)Wasif ImranPas encore d'évaluation
- SSL and TLS: Privacy & IntegrityDocument4 pagesSSL and TLS: Privacy & IntegrityVishesh TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.3 Secure Socket Layer (SSL)Document4 pages5.3 Secure Socket Layer (SSL)Aryan PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- How SSL Works: Web Browser SSL CertificateDocument3 pagesHow SSL Works: Web Browser SSL CertificateSamrah QamarPas encore d'évaluation
- ETIT NotesDocument14 pagesETIT NotesAniket BinewalePas encore d'évaluation
- Owasp: Hanushini A/P Lachemykanden (MC 180606656)Document9 pagesOwasp: Hanushini A/P Lachemykanden (MC 180606656)Heenisha LachemykandenPas encore d'évaluation
- TLS/SSL Secures Data Transmission and AuthenticationDocument3 pagesTLS/SSL Secures Data Transmission and Authenticationfawas hamdiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is HTTPSDocument2 pagesWhat Is HTTPSNMU CEISSAFPPas encore d'évaluation
- Difference Between HTTP and Https 30Document2 pagesDifference Between HTTP and Https 30honraw abdullaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Design and Implementation of A SSL Proxy For Content SwitchDocument4 pagesThe Design and Implementation of A SSL Proxy For Content SwitchTania MitkovaPas encore d'évaluation
- SSL - Secure Sockets LayerDocument12 pagesSSL - Secure Sockets LayerAli. RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTPS ResearchDocument2 pagesHTTPS ResearchThe Great AlliancePas encore d'évaluation
- SSL - Secure Sockets LayerDocument15 pagesSSL - Secure Sockets Layerhareem100Pas encore d'évaluation
- TLS/SSL Secured Hosting GuideDocument4 pagesTLS/SSL Secured Hosting GuideHammy MohPas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Socket LayerDocument4 pagesSecure Socket LayerAkhilJaanuPas encore d'évaluation
- Security in e - CommerceDocument4 pagesSecurity in e - CommerceAlex T BinoyPas encore d'évaluation
- DiniDocument20 pagesDiniiraj shaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Beginners Guide To Tls SSL Certificates Whitepaper en 2019Document7 pagesBeginners Guide To Tls SSL Certificates Whitepaper en 2019viswatejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Benefits of SSL: Why Use SSL? To Encrypt Sensitive InformationDocument6 pagesBenefits of SSL: Why Use SSL? To Encrypt Sensitive InformationNishu KprPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is An SSL CertificateDocument1 pageWhat Is An SSL CertificaterraskoPas encore d'évaluation
- ASSESSMENT TASK 3.editedDocument7 pagesASSESSMENT TASK 3.editedAritra ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of the World Wide WebDocument19 pagesOverview of the World Wide WebM Joshua AlfredPas encore d'évaluation
- Name Any Three Client Applications To Connect With FTP ServerDocument5 pagesName Any Three Client Applications To Connect With FTP ServerI2414 Hafiz Muhammad Zeeshan E1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Secure Socket Layer: Barnali Gupta BanikDocument35 pagesSecure Socket Layer: Barnali Gupta BanikbarnaliguptabanikPas encore d'évaluation
- 4 Communication ProtocolDocument14 pages4 Communication ProtocolMay MyatPas encore d'évaluation
- SSL CertificationDocument9 pagesSSL Certificationraktim4uPas encore d'évaluation
- A Quick Guide To: SSL/TLS CertificatesDocument9 pagesA Quick Guide To: SSL/TLS CertificatesGrandy DadderPas encore d'évaluation
- Surf Jacking: "HTTPS Will Not Save You"Document11 pagesSurf Jacking: "HTTPS Will Not Save You"ArondeParon100% (1)
- CryptographyDocument2 pagesCryptographyrsoni soniPas encore d'évaluation
- 17.2.7 Lab - Certificate Authority StoresDocument7 pages17.2.7 Lab - Certificate Authority StoresntutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Document 376700.1 PDFDocument26 pagesDocument 376700.1 PDFChristiam NiñoPas encore d'évaluation
- E-Commerce Security Best PracticesDocument19 pagesE-Commerce Security Best PracticesNess Wadia College of Coomerce PunePas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS?Document1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between HTTP and HTTPS?Sanat KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- U4 4 Secured Socket LayerDocument22 pagesU4 4 Secured Socket LayerNeetishPas encore d'évaluation
- HTTP The Protocol Every Web Developer Must Know - Part 2Document10 pagesHTTP The Protocol Every Web Developer Must Know - Part 2David Lee100% (1)
- GPUs for OFDM SDR Prototyping: A Comparative StudyDocument4 pagesGPUs for OFDM SDR Prototyping: A Comparative Studydang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless OFDMDocument45 pagesWireless OFDMdang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yetis Et Al. - Implementation Aspects For Interference Alignment - 2015Document5 pagesYetis Et Al. - Implementation Aspects For Interference Alignment - 2015dang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zhao Et Al. - A Spectrum Adaptive NC-CI OFDM System - 2015Document6 pagesZhao Et Al. - A Spectrum Adaptive NC-CI OFDM System - 2015dang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Generation of Streaming Sorting NetworksDocument9 pagesComputer Generation of Streaming Sorting Networksdang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Generation of Streaming Sorting NetworksDocument9 pagesComputer Generation of Streaming Sorting Networksdang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Generation of Streaming Sorting NetworksDocument9 pagesComputer Generation of Streaming Sorting Networksdang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- PDF DisplayDocument3 pagesPDF Displaydang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- PDF DisplayDocument3 pagesPDF Displaydang2327Pas encore d'évaluation
- FulltextDocument123 pagesFulltextAAYUSH VARSHNEYPas encore d'évaluation
- Aklan State University study on staff perceptions of biometricsDocument11 pagesAklan State University study on staff perceptions of biometricsDizabelle Anteojo Delos ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- how-generative-ai-can-help-banks-manage-risk-and-complianceDocument8 pageshow-generative-ai-can-help-banks-manage-risk-and-complianceLuciana BritoPas encore d'évaluation
- GM HR PoliciesDocument16 pagesGM HR PoliciesVahab HasiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Etoken 7300 PBDocument1 pageEtoken 7300 PBJustino Rivera PazPas encore d'évaluation
- CryptogrophyDocument37 pagesCryptogrophyFarah EssidPas encore d'évaluation
- Web Security, XSS, InjectionDocument137 pagesWeb Security, XSS, InjectionMenberu MunyePas encore d'évaluation
- Email Security 11 Labs v11 New-2Document115 pagesEmail Security 11 Labs v11 New-2enco123encoPas encore d'évaluation
- PCNSA-Exam-Dumps (2020) PDFDocument15 pagesPCNSA-Exam-Dumps (2020) PDFgurungePas encore d'évaluation
- The Security Risk Management GuideDocument121 pagesThe Security Risk Management Guidedansguardian123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Improper Assets Management: Gavin Johnson-LynnDocument16 pagesImproper Assets Management: Gavin Johnson-LynnOluwaseun OgunrindePas encore d'évaluation
- Atm Theft Detection Using Sensors and Email CommunicationDocument5 pagesAtm Theft Detection Using Sensors and Email CommunicationBhanu B PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- FINALMSc DISSERTATIONFAISALALIGARBADocument144 pagesFINALMSc DISSERTATIONFAISALALIGARBAFaisal AliPas encore d'évaluation
- AZ 104T00A ENU PowerPoint - 01Document22 pagesAZ 104T00A ENU PowerPoint - 01thijscreamPas encore d'évaluation
- Intrusion and Tools....Document35 pagesIntrusion and Tools....saqlain abbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of ComputerDocument2 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of ComputerClark Lopez100% (3)
- Certified Information Security Expert (CISE Level 1 v2) Detailed Course ModuleDocument18 pagesCertified Information Security Expert (CISE Level 1 v2) Detailed Course ModuleAmila KulathungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist 1 After Recon - Beginner Friendly ChecklistDocument2 pagesChecklist 1 After Recon - Beginner Friendly Checklistsidhant TechPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyber Red TeamDocument49 pagesCyber Red TeamLalo LandaPas encore d'évaluation
- SSCWN Winter2015 PDFDocument112 pagesSSCWN Winter2015 PDFJacksonPas encore d'évaluation
- Intruders and intrusion techniquesDocument18 pagesIntruders and intrusion techniquesNikhil NerkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure Network Security ENDocument19 pagesBrochure Network Security ENRanneela Sri PurusothmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Fortune 500 Cyber Security CompanyDocument49 pagesFortune 500 Cyber Security CompanyMsAbdulLatifPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Vmax Security ConceptsDocument76 pages2 Vmax Security ConceptspeymanPas encore d'évaluation
- Test QuestionsDocument18 pagesTest QuestionsWilliam HopsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 Security Engineering 1 12/11/2014Document72 pagesChapter 13 Security Engineering 1 12/11/2014Ask NamePas encore d'évaluation
- Fortinet Managed IPS Rules For AWS Network Firewall: Data SheetDocument2 pagesFortinet Managed IPS Rules For AWS Network Firewall: Data SheetJohnPas encore d'évaluation
- News - HCA Healthcare Reports Data Security Incident - FINALDocument2 pagesNews - HCA Healthcare Reports Data Security Incident - FINALDan LehrPas encore d'évaluation
- SSL TLS Decryption Uncovering SecretsDocument30 pagesSSL TLS Decryption Uncovering SecretsfanvantanPas encore d'évaluation
- Obscurity Labs 2020 InfoSheetDocument8 pagesObscurity Labs 2020 InfoSheetAlexander Rymdeko-HarveyPas encore d'évaluation