Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Antibody Identification
Transféré par
hamaadaDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Antibody Identification
Transféré par
hamaadaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Unit Immunohematologi
PDN
Antibody Identification
Determined the specificity & significance
of RBC antibodies.
Selecting blood for transfusion.
Monitoring potential cases of HDN
IgG Antibody
IgM Antibody
When we do antibody identification?
Antibody screening positive
Incompatible crossmatch
Discrepancy in serum grouping
Patients History
Age,Sex,Race.
Diagnosis.
H/O transfusion,pregnancies& medication.
Provides clue in antibody identification
especially in complex cases.
Transfusion History
DCT positive in recently transfused pt may
indicate DHTR ( within 3 months )
Antigens typing not conclusive.
Interpretation of results should be careful
Basic Rules for Antibody
Identification.
Always include the original reactive cells.
Always include the patients own cells.
Always use a variety of techniques.
Always record results quantitatively.
Include group A
1
,group A
2
and cord blood
where appropriate.
continues
Interpret results by considering negative
results first.
Confirmation of antibody identification.
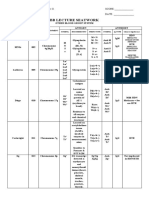
Evaluation of Panel Results.
1. Is the auto control positive or negative ?
Negative : alloantibody present
Positive : Present of autoantibody or
both.
Phases and strength of
reactions
IgM antibodies react at saline RT after IS.
IgG Antibodies react at AHG phase .
Multiple antibodies react at various phases
and strength.
Exclusion of antibody
Antibody fail to react with cell known to
have the corresponding antigen.
Only cells that gave negative reactions
in all phases of testing should used for
ruling out antibodies.
Does the serum reactivity match
the remaining specificities ?
Pattern of single antibody usually match
the antigram.
Reactivity not matched a
specific pattern.
Multiple antibodies.
Cold reactive auto antibody.
Antibody showing dosage effect.
Antibody directed against high & low
frequency antigens.
Are all commonly encountered
RBC antibodies ruled out ?
Serum may contain more than one
antibody.
May masked the presence of another .
Patients Antigen
Should lack the antigen to the
alloantibody produced.
Antigens typing is useful in
resolution of complex cases.
Eliminates many possibilities.
Problems in Antibody
Identification.
A. Multiple Antibodies.
2 or more antibodies difficult to
interpret results.
Reactions of Multiple Antibodies
Does not fit pattern of single antibody.
Reactions of red cells panels at different
phase. Should be evaluate differently.
Unexpected results are obtained when
antibody specificity is confirmed.
Antibodies to high incidence
antigen
React with all red cells panel with equal
strength.
Auto control negative.
E.g. Anti Jk
3
k.
Antibodies to low incidence
antigens
Pts serum react with the particulars donor
unit only.
Screening & panel cells negative.
E.g Anti Mia ,
Cold Autoantibodies
React with all cells, including A/C .
Prewarmed technique.
Monospecific anti IgG.
Cold auto adsorption.
Selection of blood for
transfusion
Red cells chosen for transfusion to a
patient with an antibody should be
negative for the corresponding antigen.
Even if the antibody no longer detectable.
To prevent a secondary immune
response.
Continues
The blood bank must maintain records of
all patients whom antibody have been
detected.
An antiglobulin crossmatch procedure is
required if the serum contain or previously
contained a significant antibody.
Special Serologic Techniques
Enzim enhances the reactivity e.g ( Rh,
Kidd, Lewis) but eliminates others eg.(
Duffy, MNS
Elution- dissociate IgG antibody
Adsorption- process of removing antibody
from serum by combining a serum with
appropriate RBCs.
Neutralization
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Approach To Antibody IdentificationDocument4 pagesApproach To Antibody IdentificationMohamed ElmasryPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Cell Antibody PanelsDocument40 pagesRed Cell Antibody Panelsrube10000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Current Aspects in Blood BankingDocument134 pagesCurrent Aspects in Blood BankingDr. Madhuvan GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of ImmunohematologyDocument28 pagesBasics of ImmunohematologyAkhil ChaudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- Autoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaDocument55 pagesAutoimmune Hemolytic AnemiaNicky SebastianPas encore d'évaluation
- Fast Facts: Measurable Residual Disease: A clearer picture for treatment decisionsD'EverandFast Facts: Measurable Residual Disease: A clearer picture for treatment decisionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Essentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationD'EverandEssentials of ABO -Rh Grouping and Compatibility Testing: Theoretical Aspects and Practical ApplicationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Transfusion Medicine and Hemostasis: Clinical and Laboratory AspectsD'EverandTransfusion Medicine and Hemostasis: Clinical and Laboratory AspectsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (9)
- ImmunoassayD'EverandImmunoassayEleftherios P. DiamandisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Blood Banking: RH Blood Group SystemDocument2 pagesBlood Banking: RH Blood Group SystemRomie Solacito100% (1)
- Immunohematology Review ASCLSGA 2015 PDFDocument49 pagesImmunohematology Review ASCLSGA 2015 PDFSheanalene CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 ABO Discrepancies Other ProblemsDocument65 pages3 ABO Discrepancies Other ProblemsRuel Maddawin100% (2)
- Correctly: IncorrectlyDocument70 pagesCorrectly: IncorrectlyDjdjjd Siisus100% (1)
- BOC Study Guide: The MostDocument17 pagesBOC Study Guide: The MostDeanne LambanPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument7 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentDocAxi Maximo Jr AxibalPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunohematologyDocument4 pagesImmunohematologyosama1381971Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pre Transfusion TestingDocument57 pagesPre Transfusion TestingDominic Bernardo100% (4)
- Immunohematology & Blood Bank: Alyazeed Hussein, BSCDocument58 pagesImmunohematology & Blood Bank: Alyazeed Hussein, BSCVijay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- C1 IH Lab L3 ABO Forward Reverse Typing Manual and Gel MethodDocument8 pagesC1 IH Lab L3 ABO Forward Reverse Typing Manual and Gel MethodDIVINA KYLE YGOPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical ChemistryDocument10 pagesClinical ChemistryChristina AtefPas encore d'évaluation
- HeamatologyDocument45 pagesHeamatologypikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Incorrectly: CorrectlyDocument25 pagesIncorrectly: CorrectlypikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank 4 DiscpDocument20 pagesBlood Bank 4 DiscpHector de la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Banking Chapter 1Document9 pagesBlood Banking Chapter 1throwawyPas encore d'évaluation
- GeneralDocument31 pagesGeneralpikachu100% (1)
- Recall 1Document4 pagesRecall 1pikachuPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank Guy Blood GroupsDocument19 pagesBlood Bank Guy Blood GroupsJessica TuPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank Case StudyDocument17 pagesBlood Bank Case StudyMelissa Harding33% (3)
- Clinical Chemistry IDocument8 pagesClinical Chemistry IMariel AbatayoPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood BankDocument32 pagesBlood Bankpikachu100% (1)
- Antibody ScreeningDocument57 pagesAntibody ScreeningSebastian Jake John100% (1)
- COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideDocument9 pagesCOMPLETE BLOOD COUNT Lecture GuideKaycee Gretz LorescaPas encore d'évaluation
- Typing, Screening and Crossmatching of BloodDocument55 pagesTyping, Screening and Crossmatching of BloodAsad MirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Banking Course BookDocument2 pagesBlood Banking Course BookShukr Wesman BlbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Abs Elu HandoutDocument6 pagesAbs Elu HandoutSiti Fadhilla TsabithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mtap - Immunohema Transfusion MedicineDocument9 pagesMtap - Immunohema Transfusion MedicineMoira Pauline LibroraniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alloimmunisation To Blood Group AntigensDocument34 pagesAlloimmunisation To Blood Group AntigensbloodbankPas encore d'évaluation
- Slle Examination Content Guideline - March 05 PDFDocument16 pagesSlle Examination Content Guideline - March 05 PDFYahya Alkamali100% (1)
- Flashcards in Abo Blood GroupDocument10 pagesFlashcards in Abo Blood GroupVincent ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices Ed6 Harmening-235-257Document23 pagesModern Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices Ed6 Harmening-235-257ivanlchPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank QuizDocument13 pagesBlood Bank Quizdimalawang.af100% (1)
- Other Blood Group System AssignmentDocument5 pagesOther Blood Group System AssignmentMary ChristellePas encore d'évaluation
- Hematology QuizDocument5 pagesHematology Quizkep1313100% (1)
- Study Stack - MLT Table ReviewDocument3 pagesStudy Stack - MLT Table Review장주연Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank TypingDocument34 pagesBlood Bank TypingSkylarPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Discrepancy Assignment Spring 2021Document5 pagesABO Discrepancy Assignment Spring 2021Ciarra AsuncionPas encore d'évaluation
- 1358453842.3856hematology Question BankDocument182 pages1358453842.3856hematology Question BankKay BristolPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO DiscrepanicesDocument12 pagesABO DiscrepanicesGlenn PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Toaz - Info Recalls March PRDocument8 pagesToaz - Info Recalls March PRNyeinlinn Maung100% (1)
- Resolution of Abo DiscrepanciesDocument4 pagesResolution of Abo DiscrepanciesPatrick MabugatPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic HaematologyDocument32 pagesBasic HaematologyAhtshamtaeiq AhtshamtariqPas encore d'évaluation
- ImmunohematologyDocument11 pagesImmunohematologydtimtiman100% (1)
- Compatibility Testing: Dr. Mohammed H Saiem Aldahr Blood Bank 3 Medical TechnologyDocument44 pagesCompatibility Testing: Dr. Mohammed H Saiem Aldahr Blood Bank 3 Medical TechnologyAnne Lorraine Margarette DulayPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 2 CH 29 Review QuestionsDocument2 pagesCHEM 2 CH 29 Review QuestionsthrowawyPas encore d'évaluation
- 22 - ImmunohematologyDocument6 pages22 - Immunohematologyhamadadodo7Pas encore d'évaluation
- RH BLOOD GROUPDocument23 pagesRH BLOOD GROUPWho KnowsPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhesus PhenotypingDocument3 pagesRhesus PhenotypinghamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- 24 HR FFPDocument4 pages24 HR FFPhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- SalineDocument6 pagesSalinehamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nilai University College Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology MPAD 1221 Practical 5Document2 pagesNilai University College Diploma in Medical Laboratory Technology MPAD 1221 Practical 5hamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cryoprecipitate: CompositionDocument3 pagesCryoprecipitate: CompositionhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Special tests:) ١) ﺕﺎﻧﻮﺑﺮﻜﻴﺒﻟﺍ (Bicarbonate (Document4 pagesSpecial tests:) ١) ﺕﺎﻧﻮﺑﺮﻜﻴﺒﻟﺍ (Bicarbonate (hamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paked CellsDocument3 pagesPaked CellshamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Home ADocument11 pagesHome AhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhesus Grouping ProcedureDocument1 pageRhesus Grouping ProcedurehamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Immune ToleranceDocument7 pagesImmune TolerancehamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Grouping ProcedureDocument2 pagesABO Grouping ProcedurehamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Direct Antiglobulin Test (DAT)Document2 pagesDirect Antiglobulin Test (DAT)hamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Use A BalanceDocument1 pageHow To Use A BalancehamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Subgroups and Bombay GroupDocument15 pagesABO Subgroups and Bombay GrouphamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Reversing TestDocument2 pagesABO Reversing TesthamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood TherapyDocument21 pagesBlood TherapySandra Ag Ariodere KeonyediPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross-Matching: To Meet Wikipedia'sDocument5 pagesCross-Matching: To Meet Wikipedia'shamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibody DetectionDocument7 pagesAntibody DetectionhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood CellsDocument7 pagesBlood CellshamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chitungwiza Central Hospital Laboratory DepartmentDocument2 pagesChitungwiza Central Hospital Laboratory DepartmenthamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibody DetectionDocument7 pagesAntibody DetectionhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Forward TestingDocument2 pagesABO Forward TestinghamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ab IdentificationDocument4 pagesAb IdentificationhamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Haemolytic AnaemiaDocument11 pagesHaemolytic AnaemiahamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Grouping ProcedureDocument2 pagesABO Grouping ProcedurehamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Abo Blood GroupDocument26 pagesAbo Blood GrouphamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Collection & ProcessingDocument29 pagesBlood Collection & ProcessinghamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Group SystemsDocument7 pagesBlood Group SystemshamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- 129 Goljan Rapid Review Blood Banking and Transfusion Disorders FlashcardsDocument21 pages129 Goljan Rapid Review Blood Banking and Transfusion Disorders FlashcardshamaadaPas encore d'évaluation
- BMJOpen 2013 LerouxDocument12 pagesBMJOpen 2013 LerouxadityaPas encore d'évaluation
- ID Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Derajat VDocument10 pagesID Penyakit Ginjal Kronik Derajat VNinaSakina AttamimiPas encore d'évaluation
- PTB Case-StudyDocument64 pagesPTB Case-StudyBeverly DatuPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Prefixes and Suffixes and English Roots - 2003Document28 pagesMedical Prefixes and Suffixes and English Roots - 2003Nada SaviraPas encore d'évaluation
- Reducing Hospital Readmissions: by Jenny MinottDocument12 pagesReducing Hospital Readmissions: by Jenny MinottRr.Tutik SRi HariyatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pleural Effusion: Etiology: Pleural Fluid Formation AbsorptionDocument16 pagesPleural Effusion: Etiology: Pleural Fluid Formation AbsorptionitsirenePas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical Legal Assign 3Document7 pagesEthical Legal Assign 3Armie CapinpinPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 - CIR V Philippine Health Care ProvidersDocument2 pages17 - CIR V Philippine Health Care ProvidersCamille AngelicaPas encore d'évaluation
- You Are Dangerous To Your Health CRAWFORDDocument18 pagesYou Are Dangerous To Your Health CRAWFORDGonzalo PaezPas encore d'évaluation
- HYPERALDOSTERONISMDocument7 pagesHYPERALDOSTERONISMMarnee Justine ColladoPas encore d'évaluation
- Crash Cart ICU EMRDocument5 pagesCrash Cart ICU EMRRetteri KUMARANPas encore d'évaluation
- Jessica Horsley ResumeDocument2 pagesJessica Horsley Resumeapi-238896609Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Folic AcidDocument2 pagesDrug Study Folic Acid6fq2cmfgn4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aplikasi Brief Pain Inventory Bpi Indonesian VersiDocument12 pagesAplikasi Brief Pain Inventory Bpi Indonesian Versixiongmao2389Pas encore d'évaluation
- Degloving Injuries of The Extremities and TorsoDocument20 pagesDegloving Injuries of The Extremities and TorsoRommy Shandy Saputra100% (1)
- Handwashing BoothDocument8 pagesHandwashing Boothapi-284180001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental TeratogensDocument14 pagesEnvironmental TeratogensAbdul bariPas encore d'évaluation
- Choking/TercekikDocument17 pagesChoking/Tercekiksakpn2000Pas encore d'évaluation
- Health Income and Poverty - Where We Are and What Could HelpDocument1 pageHealth Income and Poverty - Where We Are and What Could Helpapi-466415791Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Pain in BiliodigestiDocument19 pagesPathophysiology of Pain in Biliodigestiprabowoaji12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Head Trauma: PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesPediatric Head Trauma: Pathophysiologyherman76Pas encore d'évaluation
- Magnesium SulphateDocument9 pagesMagnesium SulphateNatália A. OliveiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Anesthesia in The FutureDocument11 pagesAnesthesia in The FuturesayednourPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheumatology Handout - c2fDocument1 pageRheumatology Handout - c2fapi-195799092Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Smart Chiropractor A Guide To Marketing Your PracticeDocument43 pagesThe Smart Chiropractor A Guide To Marketing Your PracticeAaron DriverPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Calculations For Nurses A Step-by-Step Approa... - (Chapter 8 Infusion Rate Calculations)Document22 pagesDrug Calculations For Nurses A Step-by-Step Approa... - (Chapter 8 Infusion Rate Calculations)HarjotBrarPas encore d'évaluation
- MED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021Document2 pagesMED2 Tut1 Inflammation Healing Quiz NG 2021joshPas encore d'évaluation
- Anal AbscessDocument5 pagesAnal AbscessFernia StevaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cervical CytologyDocument3 pagesCervical CytologyLim Min AiPas encore d'évaluation
- SalesDocument1 pageSalesapi-77587316Pas encore d'évaluation