Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Stainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02
Transféré par
pollux23Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Stainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02
Transféré par
pollux23Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BACTERIAL
STAINING
basic methods
Dr. T.V. Rao MD
1
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Microscopy helps to Measure
and Observe the Bacteria
Measurement
Microorganisms are very small
Use metric system
Metre (m) : standard unit
Micrometre (m) = 1 x10
-6
m
Nanometre (nm) = 1 x10
-9
m
Angstrom () = 1 x10
-10
m
2
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Why we should be Stain
Bacteria
Bacteria have nearly the same refractive
index as water, therefore, when they are
observed under a microscope they are
opaque or nearly invisible to the naked eye.
Different types of staining methods are used
to make the cells and their internal
structures more visible under the light
microscope.
.
3
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Staining helps in observation of
Bacteria
Microscopes are of
little use unless the
specimens for
viewing are prepared
properly.
Microorganisms must
be fixed & stained to
increase visibility,
accentuate specific
morphological
features, and
preserve them for
future use.
4
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Stains and Staining
Bacteria are slightly
negatively charged at
pH 7.0
Basic dye stains
bacteria
Acidic dye stains
background
Simple stain
Aqueous or alcohol
solution of single basic
dye
5
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
What is a Stain
A stain is a substance that adheres to a cell,
giving the cell color.
The presence of color gives the cells significant
contrast so are much more visible.
Different stains have different affinities for
different organisms, or different parts of
organisms
They are used to differentiate different types of
organisms or to view specific parts of organisms
6
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Staining Techniques
Staining is an auxiliary
technique used in
microscopy to enhance
contrast in the
microscopic image.
Stains and dyes are
frequently used in biology
and medicine to highlight
structures in biological
tissues for viewing, often
with the aid of different
microscopes.
7
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Smearing out of the
sample
8
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Fixation
Fixationwhich may
itself consist of
several stepsaims to
preserve the shape of
the cells or tissue
involved as much as
possible. Sometimes
heat fixation is used to
kill, adhere, and alter the
specimen so it will accept
stains
9
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Simple staining
simplest, the actual
staining process may
involve immersing the
sample (before or after
fixation and mounting)
in dye solution, followed
by rinsing and
observation.
The stain can be poured
drop by drop on the slide
10
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Simple staining
Methylene blue, Basic fuchsin
Provide the color contrast but impart the same
color to all the organisms in a smear
Loffler's ethylene blue: Sat. solution of M. blue
in alcohol - 30mlKoH, 0.01% in water -
100mlDissolve the dye in water, filter. For
smear: stain for 3. For section: stain
11
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Simple staining (cont..)
Dilute Carbol fuchsin:- Made by diluting Z-N
stain with 10- 15 times its volume of water- Stain
for 20-25 seconds, wash with water
Use: To demonstrate the morphology of Vibrio
cholera
Polychrome methylene blue:
Use: MFadyeans reaction - B. anthracis
12
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Simple Stains
13
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Bacterial arrangement
- Clusters
(group).
- Chains.
- Pairs (diploids).
- No special
arrangement.
14
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Simple Staining Easier to Perform
But has Limitations
Simple easy to use;
single staining agent
used; using basic and
acid dyes.
Features of dyes: give
coloring of
microorganisms; bind
specifically to various
cell structures
D i f f e r e n t i a l S t a i n s u s e t w o o r m o r e
s t a i n s a n d a l l o w t h e c e l l s t o b e
c a t e g o r i z e d i n t o v a r i o u s g r o u p s o r
t y p e s .
B o t h t e c h n i q u e s a l l o w t h e
o b s e r v a t i o n o f c e l l m o r p h o l o g y , o r
s h a p e , b u t d i f f e r e n t i a l s t a i n i n g
u s u a l l y p r o v i d e s m o r e i n f o r m a t i o n
a b o u t t h e c h a r a c t e r i s t i c s o f t h e c e l l
w a l l ( T h i c k n e s s ) .
T h e m o s t c o m m o n d i f f e r e n t i a l
s t a i n u s e d
15
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Differential Stains
Differential Stains use two or more stains
and allow the cells to be categorized into
various groups or types.
Both techniques allow the observation of
cell morphology, or shape, but differential
staining usually provides more
information about the characteristics of
the cell wall (Thickness).
16
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram staining
Named after Hans
Christian Gram,
differentiates
between Gram-
positive purple and
Gram-negative
pink stains and is
used to identify
certain pathogens.
17
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
18
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram staining - Principles
Gram staining is used to determine gram status to
classify bacteria broadly. It is based on the
composition of their cell wall. Gram staining uses
crystal violet to stain cell walls, iodine as a mordant,
and a fuchsin or safranin counterstain to mark all
bacteria. Gram status is important in medicine; the
presence or absence of a cell wall will change the
bacterium's susceptibility to some antibiotics.
Gram-positive bacteria stain dark blue or violet.
Their cell wall is typically rich with peptidoglycan
and lacks the secondary membrane and
lipopolysaccharide layer found in Gram-negative
bacteria
19
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram Staining Steps
1. Crystal violet acts as the primary stain. Crystal violet may
also be used as a simple stain because it dyes the cell wall
of any bacteria.
2. Grams iodine acts as a mordant (Helps to fix the
primary dye to the cell wall).
3. Decolorizer is used next to remove the primary stain
(crystal violet) from Gram Negative bacteria (those with
LPS imbedded in their cell walls). Decolorizer is
composed of an organic solvent, such as, acetone or
ethanol or a combination of both.)
4. Finally, a counter stain (Safranin), is applied to stain
those cells (Gram Negative) that have lost the primary
stain as a result of decolorization
20
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Stains differentiates different
groups of Bacteria
To distinguish
different kinds of
bacteria into
separate groups
based on staining
properties
Two types: Gram
stain & Acid-fast
stain.
21
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Differential Stains: Gram Stain
Color of
Gram + cells
Color of
Gram cells
Primary stain:
Crystal violet
Purple Purple
Mordant:
Iodine
Purple Purple
Decolorizing agent:
Alcohol-acetone
Purple Colorless
Counterstain:
Safranin
Purple Red
22
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram Staining technique
23
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram Staining Procedure
24
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram Staining technique
25
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Structure and Reactivity to
Gram Staining.
26
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
27
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Cell structure differentiates Gram
positive from Gram Negative
28
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gm+ve cocci & Gm-ve bacilli
29
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram-positive
Gram-positive bacteria are those that are
stained dark blue or violet by Gram staining.
This is in contrast to Gram-negative bacteria,
which cannot retain the crystal violet stain,
instead taking up the counter stain (safranin or
fuchsine) and appearing red or pink. Gram-
positive organisms are able to retain the crystal
violet stain because of the high amount of
peptidoglycan in the cell wall. Gram-positive cell
walls typically lack the outer membrane found in
Gram-negative bacteria.
30
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
GRAM-POSITIVE BACTERIA
GRAM-POSITIVE
BACTERIA are
characterized by having as
part of their cell wall
structure peptidoglycan as
well as polysaccharides
and/or teichoic acids. The
peptidoglycans which are
sometimes also called
murein are heteropolymers
of glycan strands, which are
cross-linked through short
peptides.
31
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
What are Gram Negative Bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are those bacteria that
do not retain crystal violet dye in the Gram
staining protocol. In a Gram stain test, a counter
stain (commonly safranin) is added after the crystal
violet, coloring all Gram-negative bacteria with a red
or pink color. The test itself is useful in classifying
two distinct types of bacteria based on the structural
differences of their cell walls. On the other
hand, Gram-positive bacteria will retain the crystal
violet dye when washed in a decolorizing solution.
32
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram negative bacteria
On most Gram-stained
preparations, Gram-negative
organisms will appear red or
pink because they are
counterstained. Due to
presence of higher lipid
content, after alcohol-
treatment, the porosity of the
cell wall increases, hence the
CVI complex (Crystal violet -
Iodine) can pass through.
Thus, the primary stain is not
retained.
33
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Structural Details of Gram ve
Bacteria
34
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Gram Negative Bacteria
Also, in contrast to
most Gram-positive
bacteria, Gram-
negative bacteria have
only a few layers of
peptidoglycan and a
secondary cell
membrane made
primarily of
lipopolysaccharide
35
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Common Questions
1 Principles of Gram Staining and its uses.
2 Name common/pathogenic Gram
positive and Gram negative Bacteria
3 Why some bacteria are Gram positive
and others Gram negative.
4 Why some bacteria cannot be stained by
Grams Method of staining.
5 What is the Use of Gram staining in your
future clinical practice.
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
36
ACID FAST
STAINING
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
37
Mycobacterium are Acid Fast
Bacilli
Mycobacterium are Gram-resistant (waxy cell
walls), non-motile, pleomorphic rods, related to the
Actinomyces. Most Mycobacteria are found in
habitats such as water or soil. However, a few are
intracellular pathogens of animals and humans.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, along with M. bovis,
M. africanum, and M. microti all cause the disease
known as tuberculosis (TB) and are members of the
tuberculosis species complex. Each member of the
TB complex is pathogenic, but M. tuberculosis is
pathogenic for humans while M. bovis is usually
pathogenic for animals.
38
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Acid-Fast Stain
Acid-fast cells contain a
large amount of lipids and
waxes in their cell walls
primarily mycolic
acid
Acid fast bacteria are
usually members of the
genus Mycobacterium or
Nocardia
Therefore, this stain is
important to identify
Mycobacterium or
Nocardia
39
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Ziehl-Neelsen stain
Ziehl-Neelsen staining is used to stain
species of Mycobacterium tuberculosis
that do not stain with the standard
laboratory staining procedures like Gram
staining.
The stains used are the red colored Carbol
fuchsin that stains the bacteria and a
counter stain like Methylene blue or
Malachite green.
40
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Acid-Fast Organisms
Primary stain binds cell wall mycolic
acids
Intense decolorization does not release
primary stain from the cell wall of AFB
Color of AFB-based on primary stain
Counterstain provides contrasting
background
41
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
AFB Staining Methods
Zeihl
Neelsens-hot
stain
Kinyouns-cold
stain
Modifications
42
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Ziehl- Neelsen Procedure
Make a smear. Air Dry. Heat Fix.
2. Flood smear with Carbol Fuchsin stain
Carbol Fuchsin is a lipid soluble, phenolic compound, which is
able to penetrate the cell wall
3. Cover flooded smear with filter paper
4. Steam for 10 minutes. Add more Carbol Fuchsin stain as
needed
5. Cool slide
6. Rinse with DI water
7. Flood slide with acid alcohol (leave 15 seconds). The acid
alcohol contains 3% HCl and 95% ethanol,
or you can declorase with 20% H2 S04
The waxy cell wall then prevents the stain from being removed
by the acid alcohol (decolorizer) once it has penetrated the cell
wall. The acid alcohol decolorizer will remove the stain from all
other cells.
43
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Ziehl- Neelsen Procedure
(continued)
8. Tilt slide 45 degrees over the sink and add acid
alcohol drop wise (drop by drop) until the red
color stops streaming from the smear
9. Rinse with DI water
10. Add Loefflers Methylene Blue stain (counter
stain). This stain adds blue color to non-acid fast
cells!! Leave Loefflers Blue stain on smear for 1
minute
11. Rinse slide. Blot dry.
12. Use oil immersion objective to view.
44
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Ziehl-Neelsen
stain
4 5 6
7
1 2 3
45
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
How the Acid fast bacteria
appear
46
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Fluorochrome AFB Microscopy
* More rapid and
sensitive
* Specificity : same
with sufficient
exprience
* Equipment cost ,
bulbs, technical
demands
* for busy labs
* External quality
assessment should
be done if this
method is performed
47
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Fluorescence and Bright-field
Microscopy
48
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Fluorochrome AFB Microscopy
Primary fluorochrome AFB fluoresces
Auramine O Green
Auramine O-Rhodamine B Yellow/orange
Acridine Orange Yellow/orange
Note: Color of AFB may vary with filter system on microscope
49
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Staining of M.lepra
M.lepra are less
acid fast than
M.tuberculosis
group of
organisms,
The concentration
of H2So4 is
reduced to 5 % for
decolorising
50
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
ALBERTS STAINING FOR
C.diptheria
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
51
Diphtheria is Serious Disease
When you suspect Diphtheria
In all cases of suspected
cases of Diphtheria, stain
one of the smears with
Gram stain
If Gram stained smear
shows morphology
suggestive of C.diptheria,
proceed to do Albert
staining which
demonstrates the
presence or absence of
metachromatic granules.
52
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Appearance of C.diptheria
C.diptheria are thin Gram positive bacilli,
straight or slightly curved and often enlarged
(clubbing) at one or both ends and are arranged
at acute angles giving shapes of Chinese letters
or V shape which is characteristic of these
organisms (Fig 1). Present in the body of the
bacillus are numerous metachromatic granules
which give the bacillus beaded or barred
appearance. These granules are best
demonstrated by Alberts stain.
53
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Albert staining
Albert stain I
Toluidine blue 0.15
gm
Malachite green 0.20
gm
Glacial acetic acid 1.0
ml
Alcohol(95%) 2.0 ml
Distilled water 100 ml
Albert stain II
Iodine 2.0 gm
Potassium
iodide 3.0 gm
Distilled water
300 ml
54
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Albert staining Procedure
Cover the heat-fixed smear with
Albert stain I. Let it stand for two
minutes.
Wash with water.
Cover the smear with Albert stain
II. Let it stand for two minutes.
Wash with water, blot dry and
examine.
55
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
How the C.diptheria appear
To demonstrate
metachromatic
granules in
C.diphtheriae. These
granules appear
bluish black whereas
the body of bacilli
appear green or
bluish green.
56
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Flagellar - staining
Flagella are usually invisible
under light microscopy, but
their identification and
anatomy are important in
determining some pathogens.
Certain chemicals that bind to
the flagella are used in the
staining process. The flagella
color may change or an
increase in contrast should
make them visible.
57
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Endospore staining
The cell walls of
endospores are
impermeable to most
chemicals, and being in
the genera Bacillus and
Clostridium, cause
diseases such as anthrax,
teatanus and gangrene.
The staining process
involves both a primary
stain and a counterstain.
58
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Capsule - Staining
A stain used to
reveal negatively
charged bacterial
capsules. The
encapsulated
cells will have a
halo appearance
under the
microscope.
59
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Negative staining
India Ink, Nigrosin
Organisms are not stained, only the
background is stained
Unstained organisms stand out in contrast
Use: To demonstrate the capsule of
Cryptococcus neoformans, Streptococcus
pneumoniae
60
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
61
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Nigrosin used for Negative
Staining
The negative stain is
particularly useful for
determining cell size
and arrangement. It
can also be used to
stain cells that are too
delicate to be heat-
fixed.
62
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
Programme designed by
Dr.T.V.Rao MD for e learning
in Microbiology for Medical and
Paramedical students in
Developing world
Email
doctortvrao@gmail.com
Dr.T.V.Rao MD
63
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Staining TechniquesDocument10 pagesStaining TechniquesJohn Emmanuel TayagPas encore d'évaluation
- Sputum Culture and SensitivityDocument8 pagesSputum Culture and SensitivityMarivic DianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hema I Chapter 11 - RBC IndicesDocument13 pagesHema I Chapter 11 - RBC Indiceseyoel80% (5)
- Physical Examination For Pregnant WomanDocument31 pagesPhysical Examination For Pregnant WomanFrancia ToledanoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2540Document7 pages2540pollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6200 PDFDocument12 pages6200 PDFpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- StainigDocument38 pagesStainigyuppie_raj2175Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic MacrocyticDocument1 pageAnemia Differential Diagnosis : Microcytic Normocytic Macrocyticمحمد عقيلي100% (1)
- 3500 PBDocument3 pages3500 PBpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blood TransfusionDocument5 pagesBlood TransfusionCla67% (3)
- Gram StainingDocument30 pagesGram StainingSolomon Fallah Foa Sandy100% (1)
- HANDOUT - Pathogen Most Wanted Poster - 2016Document2 pagesHANDOUT - Pathogen Most Wanted Poster - 2016Mazanda YalinduaPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Bank2Document85 pagesBlood Bank22131443Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3111 Metals by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 3111 ADocument10 pages3111 Metals by Flame Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 3111 Apollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotic Resistance: Audience-Senior Medical Officers Venue-Pune Date - 9 May 2011Document42 pagesAntibiotic Resistance: Audience-Senior Medical Officers Venue-Pune Date - 9 May 2011J NuchinPas encore d'évaluation
- 3112 Metals by Cold-Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectrometry : 1.00 MG Hg. G/L by Appropriate DilutionDocument2 pages3112 Metals by Cold-Vapor Atomic Absorption Spectrometry : 1.00 MG Hg. G/L by Appropriate Dilutionpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
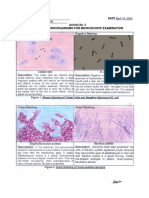
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2A. Microscopic Observation of Bacteria - Sep 13Document6 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 2A. Microscopic Observation of Bacteria - Sep 13Adrian MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Laboratory Exercise No. 2A. Microscopic Observation of Bacteria - Sep 13Document6 pagesLaboratory Exercise No. 2A. Microscopic Observation of Bacteria - Sep 13Adrian MiguelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram StainingDocument72 pagesGram Stainingtummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (2)
- Meningitis MENINGITIS Meningococcal MeningitisDocument46 pagesMeningitis MENINGITIS Meningococcal Meningitistummalapalli venkateswara raoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3030 Preliminary Treatment of Samples : 1. Filtration ProceduresDocument8 pages3030 Preliminary Treatment of Samples : 1. Filtration Procedurespollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electron Microscopy of Plant CellsD'EverandElectron Microscopy of Plant CellsC HawesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02Document63 pagesStainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02Herman CarinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Staining Guest Lecture JIPMER PondcherryDocument75 pagesGram Staining Guest Lecture JIPMER Pondcherrytummalapalli venkateswara raoPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Staing MethodDocument36 pagesDifferent Staing MethodAnik AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- Different Staing MethodDocument35 pagesDifferent Staing MethodAnik Alam100% (1)
- Gram StainDocument7 pagesGram StainYani ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Staining Skill Based LearningDocument61 pagesGram Staining Skill Based Learningtummalapalli venkateswara raoPas encore d'évaluation
- Staining MethodsDocument8 pagesStaining MethodsMd Arshad100% (1)
- Acivity 3 MicropharaDocument6 pagesAcivity 3 MicropharaDiane JaravataPas encore d'évaluation
- Staining and Mounting - Ms. HubillaDocument47 pagesStaining and Mounting - Ms. HubillaMaria Karina FerrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram StainingDocument2 pagesGram StainingJospes_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson-02 COMMON STAINING TECHDocument13 pagesLesson-02 COMMON STAINING TECHno1dubakoorPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.staining in MicrobiologyDocument65 pages4.staining in MicrobiologySubhi MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutDocument10 pagesLAB 2: Staining and Streaking: Series of Stains and Chemical Reagents To Increase Contrast and Reveal Information AboutrabkaPas encore d'évaluation
- تقريرDocument8 pagesتقريرcrtgyhujikPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Stain Lab (Keystone Anchor Bio.A.1.2.1) : PA StandardsDocument3 pagesGram Stain Lab (Keystone Anchor Bio.A.1.2.1) : PA StandardsNicole SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- Staining TechniquesDocument4 pagesStaining TechniquesAminat AdeolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn Microbiology Online Medical Microbiology Guide: News TickerDocument19 pagesLearn Microbiology Online Medical Microbiology Guide: News TickerCecilia MukototsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab CDocument3 pagesLab CEmmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Positive Vs Gram NegativeDocument9 pagesGram Positive Vs Gram NegativeOdior VictorPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Positive Vs Gram NegativeDocument10 pagesGram Positive Vs Gram NegativeOPSPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingDocument10 pagesGroup 5 - Experiment No.9 - Preparation of Bacterial Smear and Gram StainingPMG BrightPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Staining: The Simple StainDocument4 pagesCell Staining: The Simple StainAitlas KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exercise 6 SIMPLE STAININGDocument5 pagesLab Exercise 6 SIMPLE STAININGArianne Jans MunarPas encore d'évaluation
- MLT 415 Lab Report Gram Stain TechniquesDocument7 pagesMLT 415 Lab Report Gram Stain TechniquesYo YaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacterial Gram Staining (Experiment 3) : General Medical BiologyDocument8 pagesBacterial Gram Staining (Experiment 3) : General Medical BiologyRasan QadrPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Gram Stain.111Document6 pagesAssignment Gram Stain.111premium Shopping centrePas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Positive Vs Gram Negative 3Document5 pagesGram Positive Vs Gram Negative 3Octa SaktiantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Staining Methods (Simple, Gram and Acid-Fast Staining)Document26 pagesStaining Methods (Simple, Gram and Acid-Fast Staining)Gaurav MudaduPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple and Differential Staining of Bacteria: Figure1 Principles Behind Gram StainingDocument4 pagesSimple and Differential Staining of Bacteria: Figure1 Principles Behind Gram StainingNurulJazirohPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles and Types of StainingDocument42 pagesPrinciples and Types of StainingMthandeni KhumaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise 6 Postlab Discussion OutlineDocument3 pagesExercise 6 Postlab Discussion OutlineIrish Mae LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gramstaining 191127045807Document18 pagesGramstaining 191127045807AnjuPas encore d'évaluation
- Important of StainingDocument8 pagesImportant of StainingALI HASSANPas encore d'évaluation
- StainingDocument5 pagesStainingyuppie_raj2175Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report 3Document5 pagesLab Report 3nurul ainPas encore d'évaluation
- Stainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02Document62 pagesStainingbacteria 101004225924 Phpapp02Sunny jaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacte ReadingsDocument4 pagesBacte Readingssheilacastillo1222Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 3Document15 pagesLab 3maryamPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Lab Report - Experiment 2Document2 pagesMicrobiology Lab Report - Experiment 2Nida RidzuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Staining - Principles and Methods Microbial Staining - Principles and MethodsDocument33 pagesMicrobial Staining - Principles and Methods Microbial Staining - Principles and MethodsSELVI APas encore d'évaluation
- Skills in Medical: MicrobioloyDocument74 pagesSkills in Medical: MicrobioloyPhúc Võ ĐìnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram Stain MethodsDocument24 pagesGram Stain MethodsRasha MohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Post LabDocument3 pagesPost LabQueenie CalambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gram StainDocument13 pagesGram StainAnonymous RuHCQwo7Pas encore d'évaluation
- W4BACT211LABDocument1 pageW4BACT211LABJolo PascualPas encore d'évaluation
- Moyes 2009, Tinción de GramDocument8 pagesMoyes 2009, Tinción de GramVale rumazPas encore d'évaluation
- Stains NileDocument37 pagesStains NileNUBWA MEDUGUPas encore d'évaluation
- 54 Staining TechniquesDocument6 pages54 Staining TechniquesPrajakta GawadePas encore d'évaluation
- SBL 1023 Lab 9 Exp Gram Staining AsepticDocument10 pagesSBL 1023 Lab 9 Exp Gram Staining Asepticapi-384057570Pas encore d'évaluation
- Grams StainingDocument19 pagesGrams Stainingyixecix709Pas encore d'évaluation
- Staining - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFDocument15 pagesStaining - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia PDFNadiya AfifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Merhan, Kristine Mae M. (Lab Activity 5)Document5 pagesMerhan, Kristine Mae M. (Lab Activity 5)Kristine MerhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MCPC Agar (Vibrio) PDFDocument2 pagesMCPC Agar (Vibrio) PDFpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3120 Metals by Plasma Emission Spectroscopy 3120 ADocument7 pages3120 Metals by Plasma Emission Spectroscopy 3120 Apollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- V34n3a15 PDFDocument5 pagesV34n3a15 PDFpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3113 Metals by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocument8 pages3113 Metals by Electrothermal Atomic Absorption Spectrometrypollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3110 Metals by Atomic Absorption SpectrometryDocument1 page3110 Metals by Atomic Absorption Spectrometrypollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Significance: G/L) in A Variety ofDocument3 pagesSignificance: G/L) in A Variety ofpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3114 Arsenic and Selenium by Hydride Generation/Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 3114 ADocument7 pages3114 Arsenic and Selenium by Hydride Generation/Atomic Absorption Spectrometry 3114 Apollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3020Document2 pages3020pollux230% (1)
- B. Spectrophotometer Cells, 1 Cm. C. Filtering Apparatus and Filter: See 2120B.2cDocument4 pagesB. Spectrophotometer Cells, 1 Cm. C. Filtering Apparatus and Filter: See 2120B.2cpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadFile 3500 OsDocument1 pageDownloadFile 3500 Ospollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2720 Anaerobic Sludge Digester Gas Analysis : 1. Selection of MethodDocument5 pages2720 Anaerobic Sludge Digester Gas Analysis : 1. Selection of Methodpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2530Document4 pages2530pollux23100% (1)
- 2150 PDFDocument5 pages2150 PDFpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2160 PDFDocument4 pages2160 PDFpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6252Document9 pages6252pollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadFile 3500 THDocument1 pageDownloadFile 3500 THpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadFile 3500Mg PDFDocument2 pagesDownloadFile 3500Mg PDFpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- QUALITY ASSURANCE/QUALITY CONTROL (7020) /basic Quality Control Program 7-3Document6 pagesQUALITY ASSURANCE/QUALITY CONTROL (7020) /basic Quality Control Program 7-3pollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- Approved by Standard Methods Committee, 2001. Joint Task Group: James K. Edzwald (Chair), Penny J. Bristol, Brian A. Dempsey, Darren A. Lytle, David J. Pernitsky, Mike J. Sadar, Jeff ThrockmortonDocument1 pageApproved by Standard Methods Committee, 2001. Joint Task Group: James K. Edzwald (Chair), Penny J. Bristol, Brian A. Dempsey, Darren A. Lytle, David J. Pernitsky, Mike J. Sadar, Jeff Throckmortonpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2810 Dissolved Gas Supersaturation : 2-92 Physical & Aggregate Properties (2000)Document5 pages2810 Dissolved Gas Supersaturation : 2-92 Physical & Aggregate Properties (2000)pollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3125 Metals by Inductively Coupled Plasma/Mass SpectrometryDocument9 pages3125 Metals by Inductively Coupled Plasma/Mass Spectrometrypollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3020Document2 pages3020pollux230% (1)
- 1050 Expression of Results: 0. The Values Found From The Collaborative TestDocument3 pages1050 Expression of Results: 0. The Values Found From The Collaborative Testpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2710 Tests On Sludges : 1. General DiscussionDocument8 pages2710 Tests On Sludges : 1. General Discussionpollux23Pas encore d'évaluation
- 344-Malt Extract Agar-105398 PDFDocument1 page344-Malt Extract Agar-105398 PDFAlejandro Canaza JorgesPas encore d'évaluation
- Typhoid Fever Final 2Document28 pagesTyphoid Fever Final 2gAARaPas encore d'évaluation
- MICBIO GERM THEORY OF DSE and TERMINOLOGIES NOTESDocument3 pagesMICBIO GERM THEORY OF DSE and TERMINOLOGIES NOTESDemi Labawig100% (1)
- 40 Años de Microbiología ClínicaDocument6 pages40 Años de Microbiología ClínicaDennis Lorena Cárdenas LealPas encore d'évaluation
- FTRCDocument7 pagesFTRCTyler King0% (1)
- WhatsApp Image 2023-04-03 at 12.26.59 AMDocument1 pageWhatsApp Image 2023-04-03 at 12.26.59 AMjogendra ponnamandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation of BAP and CHOCDocument5 pagesPreparation of BAP and CHOCKenneth Jake BatiduanPas encore d'évaluation
- Primeasia University: A Mission With A VisionDocument2 pagesPrimeasia University: A Mission With A VisionNiamul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Salmonella JepangDocument6 pagesSalmonella JepangHanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medsurg (112) Rle: Care of Patients With Problems of The Hematologic SystemDocument5 pagesMedsurg (112) Rle: Care of Patients With Problems of The Hematologic SystemChelsea Faith SarandiPas encore d'évaluation
- CasestudyvaccinesDocument5 pagesCasestudyvaccinesapi-323720899Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 J Novoselac - Significance of Immunohematologic Testing in Mothe (Retrieved - 2023-07-12)Document4 pages2023 J Novoselac - Significance of Immunohematologic Testing in Mothe (Retrieved - 2023-07-12)DR.RAJESWARI SUBRAMANIYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Pathogens and Strategies For Combating Them - Science, Technology and Education (Table of Contents)Document17 pagesMicrobial Pathogens and Strategies For Combating Them - Science, Technology and Education (Table of Contents)Tahmina MonowarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lit ISOGRID Cat Page Overview 0901Document4 pagesLit ISOGRID Cat Page Overview 0901Cristian QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Kharkov National Medical University: Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology DepartmentDocument35 pagesKharkov National Medical University: Head of Microbiology, Virology and Immunology DepartmentAnisaFajarKumala100% (1)
- A&P Principles of Microbiology and Human Disease (Nursing) - PowerPointDocument47 pagesA&P Principles of Microbiology and Human Disease (Nursing) - PowerPointLinsey Bowen100% (2)
- DR - Thompsons CBC-RBC Indices Guide - A Guide To Red Blood Cell IndicesDocument54 pagesDR - Thompsons CBC-RBC Indices Guide - A Guide To Red Blood Cell IndicesYohana SetiawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity No. 7.1 BloodDocument2 pagesActivity No. 7.1 BloodRoselie Mae GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Test of Chapter 1 ScienceDocument4 pagesRevision Test of Chapter 1 ScienceYasoktaran AnanthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tas Kantung Darah BPS-Terumo-CatalogDocument4 pagesTas Kantung Darah BPS-Terumo-CatalogDoni VingkyPas encore d'évaluation