Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Doctors' Role in Tackling Organ Trade
Transféré par
Bruno0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
129 vues70 pagesRenal Transplants, Liver Transplants, Heart Transplants - How TN Reversed the Trend
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentRenal Transplants, Liver Transplants, Heart Transplants - How TN Reversed the Trend
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
129 vues70 pagesDoctors' Role in Tackling Organ Trade
Transféré par
BrunoRenal Transplants, Liver Transplants, Heart Transplants - How TN Reversed the Trend
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 70
Doctors Role
in Tackling Organ Trade
Bruno Mascarenhas JMA
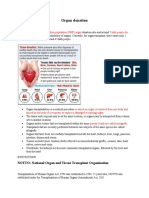
Kidneys
When One Kidney fails . . .
The other kidney does the work
Rarely Symptomatic
When Both Kidneys Fail
Acute Renal Failure
Chronic Renal Failure
Acute Renal Failure
Chronic Renal Failure. . .
How to get the other Kidney
Relatives of a Patient whose Brain
Stem is Dead agree to donate the
patients kidneys
A Live Relative or Some one with an
emotional bond Donates one of his
kidney
A stranger sells for money (This is
ILLEGAL)
Unfortunately . . .
The least preferred route was being
widely used
http://photography.nationalgeographic.co.in/photography/enlarge/kidney-
donors_pod_image.html
Villivakkam kidneyvakkam
Not limited to one locality .
How to tackle this
Multidisciplinary Approach
Legal
Lawmakers
Judiciary
Police
From Health Point of View
Kidneys Needed
+ Patients with Renal Failures
Number of Kidneys Available
+ Kidneys donated by live donors
+ Kidneys donated from Brain Stem Dead
Patient
Rearrange this
Chronic Renal Failure = Live Donor +
Cadavers
Live Donors = Chronic Renal Failure -
Cadavers
Reduce Live Donors
Reduce the Need by reducing Renal
Failure
Increase Donation from Brain Stem
Dead Patients
Reduce Demand
Reduce Renal Failure
Life Style Modifications
What is meant by
Brain Stem Death
A Dead Brain stem in body whose
heart is still beating is what is
Brain Stem Dead in simple terms
This has become a reality because of
advancement in intensive care /
pharmacotherapy etc.
Brain Stem Death
Do all human beings who die pass
through this stage?
No. Only 1% of all death pass
through this stage
The state of brain Death is a brief
period in minutes
Donation from Brain Stem Dead
Patients . . . . . .
March 2007
March 2007
Four Working Groups:
Cadaver organ donation
Cadaver organ transplantation
Coordinating Organization for organ
sharing
Live donation and transplantation
33 recommendations for follow up
action.
Lack of proper mechanism for
identifying the recipients
Trauma Centres
Transplant Centres
Lack of Co ordination Mechanism
After March 2007
The participants felt that there were many
grey areas in the Transplantation of
Human Organs Act.
In particular, no guidelines on who will
get the donated cadaver organ
The Government followed up with a series
of consultative meetings held with groups
of doctors by Mr.P.W.C.Davidar
Series of Government Orders in
2008
Brain death Declaration of brain death
made mandatory in Government Medical
College Hospitals in Chennai Orders Issued.
Brain death Declaration of brain death made
mandatory in Government Medical College
Hospitals in Chennai Procedure for
declaration of brain death orders issued.
Health & Family Welfare Department Organ
Transplant Authorization Committee
Procedures Additional responsibilities
Detailed instructions orders issued.
Series of Government Orders in
2008
Health & Family Welfare Department
Organ Transplant Cadaver Organ
Transplant Program Procedure to be
adopted for cadaver transplant by the
Government and Private Hospitals
approved for organ transplant by the
Appropriate Authority orders issued.
Health and Family Welfare Department
Organ Transplant Responsibilities
of Transplant centers in hospitals
Detailed instructions Orders issued.
Cadaver Transplant Programme,
Government of Tamil Nadu
Prof Dr J Amalorpavanathan, Professor of
Vascular Surgery, MMC & RGGGH
appointed as Convenor, Cadaver
Transplant Programme in honorary
capacity
Office space provided at the Government
General Hospital
Advisory Committee headed by Health
Secretary, GoTN
Mr Davidar,
DMS, DME, TNMSC,
Police Dept, 2 NGOs, 1 Medical Ethicist,
3 Government Hospitals, 4 Private Hospitals
Tamil Nadu Network for Organ
Sharing
Initiatives for forming Tamil Nadu
Network for Organ Sharing and
maintaining a common online waitlist
for all potential recipients in all
hospitals who choose to come under
this network in Tamil Nadu and
allotment of organs by the Network
Common Waiting List (based Blood
Group) visible to all stakeholders
Allocation based on waiting List
Initiatives for Transplantation
from Deceased Donors
Transplant co ordinators
Elective Operation theatre to be
used at the Night Time and Odd
Hours for Organ harvesting and
Transplants
20th September, 2008
2008 : Turning Point
8 Government Orders
Noble Gesture of Dr. Ashokan (Alumni
of Chengalpet Medical College 1980
Batch) and Dr. Pushpanjali,
Thirukazhukundram,
More Brain Dead Certification
More Donation
More recipients benefited
From 2008
Convenor runs the CTP
Overseen and supported by the
Advisory Committee which keeps
watch and amends Guidelines as
needed
Participating hospitals to keep
providing inputs to improve the
Guidelines
CoTP - GoTN
Register willing transplant hospitals in
the organ sharing network
Keep them posted of the regulatory
framework
Convene meetings of the Advisory
Committee and take follow up action
CoTP - GoTN
Take calls 24X7 from donor hospitals,
allocate organs and co-ordinate till
transplants take place
Send periodic reports
Maintain database of cadaveric and
live donor transplants
Maintain website www.dmrhs.org
Convene meetings of hospitals for
ideas on improving the framework
CoTP - GoTN
Hospitals treating patients with End
Stage Organ Failure (Kidney failure or
liver failure or heart failure) register
those willing for transplant at the
online database www.tnos.org
Waiting List is maintained online and
is watched by all hospitals in the
programme
One Master List for each Blood
Group and based on it, lists for
Each hospital
All Government hospitals combined
All private hospitals combined and
All Hospitals Combined
Donated at Government
Hospital
1st priority - List of the Government Hospital
where the deceased donor is located, for liver,
heart and one kidney. The other kidney world be
allocated to:
2nd priority - combined Government Hospitals list
3rd priority - combined Private Hospitals list
4th priority - Government Hospitals outside the
State,
5th priority - Private Hospitals outside the State
Finally, if the organ(s) remains unutilized by the
above criteria, it may be offered to a foreign
national registered in a Government or Private
hospital within and then outside state. (This is to
ensure that there is no wastage of organs
donated)
Donated at Private Hospital
1st priority - the list within the Private Hospital
where the deceased donor is located, for liver,
heart and one kidney. The other kidney world be
allocated to:
2nd priority - the combined list of Government and
Private Hospitals
3rd priority - Government / private hospitals
outside the state
Finally, if the organ(s) remains unutilized by the
above criteria, it may be offered to a foreign
national registered in Government or private
hospital within and then outside the state,
provided earlier information and such a request
has been registered with the Advisory committee
/Convenor, Cadaver Transplant Program, Tamil
Nadu.
From 2008 Till Jul 31,2013
374 Donors From Tamil Nadu
58 Heart
24 Lung
339 Liver
689 Kidney
1110 Major organs
390 Heart Valve
578 Cornea
1 Skin
2079 Total Organs
689 Kidneys donated means
689 Patients with Chronic Renal
Failure have been benefitted
+
689 Healthy patients were not
operated
4 Heart Transplants in
RGGGH
Only State Government Hospital to do
Heart Transplants
And Totally Free of Cost
Liver Transplants in Stanley
Medical College Hospital
Only State Government Hospital to do
Liver Transplants
And Totally Free of Cost
10 times National Average
Deceased Donation (ie Donation from
Braid Stem Dead patients) Rate in TN
is 1.3/million/year which is 10 times
the national average
WHO
In July 2010, a 14 nation WHO meet
in Geneva to establish a blue print to
improve organ donation in UN
Countries, put in TN Experience as a
key point in the blue print prepared
Many states have followed TN Model
Hindu Op-Ed article,
25/10/2010
New lives out of deaths
V.K. Subburaj, P.W.C. Davidar, J.
Amalorpavanathan and C.E. Karunakaran Tamil
Nadu shows the way in organ transplantation.
If your liver has failed and you need a
functioning organ to be transplanted for
you to survive then go to Chennai: this is
the buzz among liver-failure patients across
India The State has done 110 deceased
donor liver transplantations in a period of
less than two years. All other States put
together have not done even half this
number.
British Medical Journal
HOW DECEASED DONOR TRANSPLANTATION
IS IMPACTING A DECLINE IN COMMERCIAL
TRANSPLANTATION - THE TAMIL NADU
EXPERIENCE TRANSPLANTATION JOURNAL
Yuvaram N V Reddy(1), Milly Matthew(1), Saravanan S(1),
Amalorpavanathan(3), Georgi Abraham(1,2), Sunil Shroff(4)
Abstract
India with a population of 1.2 billion has a renal transplantation rate
of 3.25 per million population. The major cause of chronic kidney
disease is hypertension and diabetes. The crude and age adjusted
incidence rates of ESRD are estimated to be 151 and 232 per million
population respectively in India. There was a remarkable lack of
knowledge in the public about deceased organ donation until a
decade ago. However, the role played by the media and Non
Governmental Organizations in partnership with the government has
emphasized and implemented deceased donor transplantation in
certain states in India - to mention particularly, the Tamil Nadu
model. In the last two years, deceased organ donation has reached
1.3 per million population in Tamil Nadu thereby effectively
eliminating commercial transplantation. There is no religious bar for
organ donation. A central transplant coordinator appointed by the
government oversees legitimate and transparent allocation of
deceased organs both in the public and private facilities as per the
transplant waiting list. This model also takes care of the poor
sections of society by conducting donation and transplantation
through government run public facilities free of cost. In the last two
years, deceased donor transplantation has been performed through
this network procuring organs such as the heart, heart valves, lung,
liver, kidneys, cornea and skin. The infrastructural lack of
immunological surveillance - including donor specific antibody
monitoring, HLA typing, panel reactive antibody except in a few
tertiary care centres - prevents allocation according to the
immunological status of the recipient. This private-public partnership
promoting deceased donor transplantation has effectively eliminated
commercialization in transplantation in the state of Tamil Nadu with
a population of 72 million which is a model for other regions of South
Asia and developing countries.
CADAVER TRANSPLANT PROGRAM, TAMIL NADU
News Articles
CADAVER TRANSPLANT PROGRAM, TAMIL NADU
Take Home Message
Any Surgery Carries a Risk,
Lets not subject a healthy human to
a risk by being a donor
Discourage Live Donors
Encourage Registration in TNOS
and wait for Cadaver Donor
Take Home Message
Deceased Donor Transplant will eradicate
women slavery where more than 90% of
living related Kidney Donors are women
This is a social responsibility of the
Doctors for the Society from which they
should not shy away
Though Tamilnadu is way ahead other
states in Deceased Donor Transplant we
still have to work hard to move forward in
other states and centres
We gratefully acknowledge
Extremely dedicated Neuro
consultants
Intensivists who are willing to
manage the patients with severe
Brain Stem Dysfunction
Anaesthesiologists who are willing to
do Apnea testing
Administration who are willing to
support this programme
We gratefully acknowledge
The contributions made by all the
patients
The relatives who took the noble,
valiant, gallant decision of donating
the organs of the deceased
We gratefully acknowledge
Officials in Government
Thiru.V.K.Subburaj I.A.S.,
Secretary to Government, Health and Family Welfare
Department, Government of Tamilnadu
Dr.GIRIJA VAIDYANATHAN, I.A.S.,
Secretary to Government, Health and Family Welfare
Department, Government of Tamilnadu
Dr.J. RADHAKRISHNAN, I.A.S.,
Secretary to Government, Health and Family Welfare
Department, Government of Tamilnadu
Thiru.P.W.C.Davidar IAS,
Principle Secretary, P & AR, GoTN
Dr.J.Amalorpavanathan
Convenor, Cadaver Transplant Programme
Prof.Dr.K.Deiveegan MS MCh
Professor of Neurosurgery and Head, Institute of
Neurology, Madras Medical College and Rajiv Gandhi
Government General Hospital
Prof.Surendran MS MCh
Former Professor of Surgical
Gasteroenterology, Stanley Medical College
NGOs
Dr.Shroff Mr.CE Karunakaran
Future . . .
Split Liver : Single Liver for an Adult
and one more child
Utilize More Hearts
Study the Outcome of Transplant
Recipients
Increasing awareness of whole body
donation
One of the Oldest Hospitals . .
Road Safety
Government General Hospital
Established in 16 Nov 1664
Road Safety
Now in its 350
th
Year
Now named Rajiv Gandhi Government
General Hospital
06-Jan-2012 Road Safety 66
67
Madras Medical College
Established in 1835
Road Safety
Now in its 179
th
year
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NEET PG 2013 Rank List of Eligible CandidatesDocument256 pagesNEET PG 2013 Rank List of Eligible CandidatesBruno75% (8)
- Prof DR Amit Gupta AITSC Trauma Registry & Trauma Quality Improvement in IndiaDocument77 pagesProf DR Amit Gupta AITSC Trauma Registry & Trauma Quality Improvement in IndiaBruno50% (2)
- DR - Rajesh CMO (RGGGH) In-Hospital Care of Trauma Patients in Tamil Nadu - Current Systems For Management of AdultsDocument32 pagesDR - Rajesh CMO (RGGGH) In-Hospital Care of Trauma Patients in Tamil Nadu - Current Systems For Management of AdultsBruno100% (1)
- C2013 Criminal Law II Compiled DigestsDocument202 pagesC2013 Criminal Law II Compiled DigestsMaria Myrna Mercado-navarro100% (4)
- Need of Organ Donation in IndiaDocument12 pagesNeed of Organ Donation in IndianishaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation Research PaperDocument6 pagesOrgan Donation Research PaperMihir MorePas encore d'évaluation
- Document Ngo - JeevandeepDocument33 pagesDocument Ngo - JeevandeepPrachikarambelkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation 3.24Document26 pagesOrgan Donation 3.24Yongjie ShenPas encore d'évaluation
- India's Organ Donation ChallengeDocument4 pagesIndia's Organ Donation Challengesid 0596Pas encore d'évaluation
- REDCOPDocument4 pagesREDCOPIzhra MargatePas encore d'évaluation
- The Organ Donor ProgramDocument12 pagesThe Organ Donor ProgramLisette BalabarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- BuzzleDocument4 pagesBuzzledobosionelaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8organ DonationDocument14 pages8organ DonationLoikan JosuePas encore d'évaluation
- Organ TransplantationDocument33 pagesOrgan TransplantationAyyagariKathyayani100% (1)
- Organ Donation Knowledge StudyDocument85 pagesOrgan Donation Knowledge StudyAmit PasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Kidney Donor Awarness ProgrammDocument27 pagesKidney Donor Awarness Programmswap58warPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOT6003 - TermPaper EDITEDDocument21 pagesBIOT6003 - TermPaper EDITEDLana DayaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Market For KidneysDocument11 pagesMarket For Kidneysapi-605344411Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ethic of Organ TransplantationDocument48 pagesEthic of Organ TransplantationHusnawaty Dayu100% (1)
- Law of Emerging TechnologiesDocument8 pagesLaw of Emerging TechnologiesNaman JainPas encore d'évaluation
- DebateDocument3 pagesDebateTulbanos KenPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation Final Presentation B2Document8 pagesOrgan Donation Final Presentation B2Fro NarvaezPas encore d'évaluation
- Transplantation: Treatment Methods For Kidney FailureDocument28 pagesTransplantation: Treatment Methods For Kidney FailurecopiimeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5Document72 pagesLecture 5gokulkrishnayadhavPas encore d'évaluation
- University Kidney EducationDocument7 pagesUniversity Kidney EducationJwaltzPadlanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ TransplantDocument2 pagesOrgan Transplantapi-392813642Pas encore d'évaluation
- In Defense of A Regulated Market in Kidneys From Living VendorsDocument35 pagesIn Defense of A Regulated Market in Kidneys From Living VendorssemelusePas encore d'évaluation
- The Development of Science and Organ Donation - Abin AndrewsDocument4 pagesThe Development of Science and Organ Donation - Abin AndrewsABIN ANDREWS BPas encore d'évaluation
- The Meat MarketDocument4 pagesThe Meat Marketasha328Pas encore d'évaluation
- Materi Presantations 13Document3 pagesMateri Presantations 13AlyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation: An Important DecisionDocument2 pagesOrgan Donation: An Important DecisionAntonio BereberePas encore d'évaluation
- Farhana Syed Nokman: More Than 21,000 Malaysians On Waiting List For Organ Donors by - December 4, 2017 at 3:46pmDocument3 pagesFarhana Syed Nokman: More Than 21,000 Malaysians On Waiting List For Organ Donors by - December 4, 2017 at 3:46pmAfiqah IndrawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation AnalysisDocument11 pagesOrgan Donation AnalysisAmit PasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Research PaperDocument7 pagesResearch Paperapi-366892152Pas encore d'évaluation
- Durham College Presentation From AnatDocument21 pagesDurham College Presentation From Anatapi-456469027Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Transplant Laws in IndiaDocument7 pagesOrgan Transplant Laws in IndianamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Q4 PT Final DraftDocument10 pagesBio Q4 PT Final DraftToka OthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eurotransplant: Zoë Daudey - Biology - 11-12-2017 - A1EDocument10 pagesEurotransplant: Zoë Daudey - Biology - 11-12-2017 - A1Eapi-390089783Pas encore d'évaluation
- Updates On Organ DonationDocument61 pagesUpdates On Organ DonationAnusha VerghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Organ TransplantationDocument6 pagesOrgan TransplantationFares SamirPas encore d'évaluation
- National Organ Tissue Cell Transplan PolicyDocument76 pagesNational Organ Tissue Cell Transplan Policyyus97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Awareness of Legislation Moderates The Effect of Opt-Out Consent On Organ Donation IntentionsDocument6 pagesAwareness of Legislation Moderates The Effect of Opt-Out Consent On Organ Donation IntentionsVictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Answers To Section 3.7 Organ TransplantationDocument2 pagesAnswers To Section 3.7 Organ TransplantationbrownieallennPas encore d'évaluation
- Health FinalDocument13 pagesHealth Finalamulya anandPas encore d'évaluation
- IntroDocument4 pagesIntroSanjeet DuhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ transplantationsDocument5 pagesOrgan transplantationsSakunthala RajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Dissertation Organ DonationDocument5 pagesDissertation Organ DonationBestCollegePaperWritingServiceMobile100% (1)
- Liver TransplantsDocument6 pagesLiver Transplantssadaq84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Death Donor Transplants Key to Saving LivesDocument3 pagesBrain Death Donor Transplants Key to Saving LivesFuraya FuisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Opt in or Opt OutDocument3 pagesOpt in or Opt OutIrina IonescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation Saves LivesDocument24 pagesOrgan Donation Saves LivesSuraj SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Transplantation-FinalDocument4 pagesOrgan Transplantation-Finalbaby_ssPas encore d'évaluation
- Running Head: Proposal Argument EssayDocument7 pagesRunning Head: Proposal Argument EssayPoet CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Adoption of An Opt-Out Model For Cadaveric Organ DonationDocument2 pagesAdoption of An Opt-Out Model For Cadaveric Organ DonationEulaArias JuanPabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation - An Investigation Into The Hurdles Faced in Making Organ Donation A Stream Lined and Commonplace Process in IndiaDocument3 pagesOrgan Donation - An Investigation Into The Hurdles Faced in Making Organ Donation A Stream Lined and Commonplace Process in IndiaPratika NagpalPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation AwarenessDocument44 pagesOrgan Donation AwarenessKlause Kenze Kabil50% (2)
- Ethical Issues in Organ DonationDocument28 pagesEthical Issues in Organ Donationytkl72Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organ TransplantationDocument25 pagesOrgan Transplantationb29ondPas encore d'évaluation
- Englishorganpaper 1Document6 pagesEnglishorganpaper 1api-302390891Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cash For Kidneys: The Case For A Market For OrgansDocument5 pagesCash For Kidneys: The Case For A Market For OrganssepulPas encore d'évaluation
- Internal Practices of Organ DonationDocument8 pagesInternal Practices of Organ DonationhkdawnwongPas encore d'évaluation
- The Global Organ Shortage: Economic Causes, Human Consequences, Policy ResponsesD'EverandThe Global Organ Shortage: Economic Causes, Human Consequences, Policy ResponsesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ending the Waiting Game: Increasing Kidney Transplants in CanadaD'EverandEnding the Waiting Game: Increasing Kidney Transplants in CanadaPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Raja S Vignesh (Thoothukudi Medical College) in Hospital Care of Patient by NeurosurgeonDocument25 pagesDR - Raja S Vignesh (Thoothukudi Medical College) in Hospital Care of Patient by NeurosurgeonBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology and Pathology of Physical and Psychological StressDocument60 pagesPhysiology and Pathology of Physical and Psychological StressBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof - Dr.Indumathy Santhanam (ICH) In-Hospital Care of Trauma Patients in Tamil Nadu - Current Systems For Management of ChildrenDocument40 pagesProf - Dr.Indumathy Santhanam (ICH) In-Hospital Care of Trauma Patients in Tamil Nadu - Current Systems For Management of ChildrenBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof Gita Krishnan Ramadurai Use of RADAMS and 108 Avasaram App in Trauma CareDocument21 pagesProf Gita Krishnan Ramadurai Use of RADAMS and 108 Avasaram App in Trauma CareBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof Venkatesh Balasubramanian Current State Road Accident Database and Requirements For Integration of A Trauma RegistryDocument37 pagesProf Venkatesh Balasubramanian Current State Road Accident Database and Requirements For Integration of A Trauma RegistryBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ms Ellaine Boo Role of Trauma NursingDocument35 pagesMs Ellaine Boo Role of Trauma NursingBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof DR Mark Fitzgerald Integrated In-Hospital Trauma Care - Building Blocks That Save LivesDocument42 pagesProf DR Mark Fitzgerald Integrated In-Hospital Trauma Care - Building Blocks That Save LivesBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hub and Spoke Model For STEMI Management - Tamil Nadu ModelDocument16 pagesHub and Spoke Model For STEMI Management - Tamil Nadu ModelBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Thambaiah (Cuddalore GH) in Hospital Care of Patients by OrthopaedicianDocument36 pagesDR - Thambaiah (Cuddalore GH) in Hospital Care of Patients by OrthopaedicianBruno100% (1)
- DR Joseph Mathew Designation of Trauma Hospitals in A Trauma SystemDocument29 pagesDR Joseph Mathew Designation of Trauma Hospitals in A Trauma SystemBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Joseph Mathew: Trauma Units and Team WorkDocument39 pagesDR - Joseph Mathew: Trauma Units and Team WorkBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mrs. Sulochana (RGGGH) Current Status of Trauma Nursing in TNDocument11 pagesMrs. Sulochana (RGGGH) Current Status of Trauma Nursing in TNBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- TAEI NTRI WorkshopDocument16 pagesTAEI NTRI WorkshopBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Ramana Rao Pre-Hospital Services in Tamil NaduDocument73 pagesDR - Ramana Rao Pre-Hospital Services in Tamil NaduBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- DR - Darez Ahamed Vision For Tamil NaduDocument6 pagesDR - Darez Ahamed Vision For Tamil NaduBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof DR Peter Cameron Measuring The Quality of Trauma Systems and In-Hospital Trauma CareDocument46 pagesProf DR Peter Cameron Measuring The Quality of Trauma Systems and In-Hospital Trauma CareBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ian Patrick Pre-Hospital Systems in Australia Key Components of The Pre-Hospital System in Australia and Best Buys For Tamil NaduDocument26 pagesIan Patrick Pre-Hospital Systems in Australia Key Components of The Pre-Hospital System in Australia and Best Buys For Tamil NaduBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- How Tamil Nadu Eradicated Organ SaleDocument108 pagesHow Tamil Nadu Eradicated Organ SaleBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Prof DR Mark Fitzgerald What Is A Trauma System and Trauma System ComponentsDocument36 pagesProf DR Mark Fitzgerald What Is A Trauma System and Trauma System ComponentsBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mr. Dayanand Kataria, IAS Transport Commissioner Road Safety StatusDocument25 pagesMr. Dayanand Kataria, IAS Transport Commissioner Road Safety StatusBruno100% (1)
- Why Tamil Nadu Model Works Better in Eradicating Organ SaleDocument52 pagesWhy Tamil Nadu Model Works Better in Eradicating Organ SaleBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurosurgeon For A Social CauseDocument55 pagesNeurosurgeon For A Social CauseBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurology, Neurosurgery MCQ PointsDocument32 pagesNeurology, Neurosurgery MCQ PointsBruno86% (7)
- TN Gazette 47 of 2013 Part VI Section 4Document84 pagesTN Gazette 47 of 2013 Part VI Section 4BrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- AR Rahman PDFDocument405 pagesAR Rahman PDFPitchai BalaPas encore d'évaluation
- HMIS - Health Management Information System - Government of Tamil NaduDocument12 pagesHMIS - Health Management Information System - Government of Tamil NaduBruno100% (1)
- MUST To KNOW in Histopathology 1Document34 pagesMUST To KNOW in Histopathology 1Noven Brix DeguitPas encore d'évaluation
- Brain Death Testing Protocol (Rev220605) PDFDocument2 pagesBrain Death Testing Protocol (Rev220605) PDFRei Irinco100% (1)
- Legal Med Identification & Death AspectsDocument4 pagesLegal Med Identification & Death AspectsBea SamontePas encore d'évaluation
- Neuroimaging Clinics - Imaging of Head TraumaDocument184 pagesNeuroimaging Clinics - Imaging of Head TraumaSimion Iulian100% (1)
- Doctors' Role in Tackling Organ TradeDocument70 pagesDoctors' Role in Tackling Organ TradeBrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventanas para Doppler TranscranealDocument2 pagesVentanas para Doppler TranscranealKarlistenPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Transplant in IslamDocument17 pagesOrgan Transplant in IslamMichael WestPas encore d'évaluation
- Coma and Brain DeathDocument24 pagesComa and Brain DeathDean AccountPas encore d'évaluation
- Annual Report For Organ Transplantation in Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaDocument201 pagesAnnual Report For Organ Transplantation in Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaAhmed QannitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosing death criteria in medicineDocument13 pagesDiagnosing death criteria in medicineYosselin Doroteo AntonioPas encore d'évaluation
- Medico-Legal Aspects of Death: By: Paula Grace V. VillegasDocument21 pagesMedico-Legal Aspects of Death: By: Paula Grace V. VillegasPau VillegasPas encore d'évaluation
- The Healthy FoodDocument13 pagesThe Healthy Foodayabouhsini24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Transplant Laws in IndiaDocument7 pagesOrgan Transplant Laws in IndianamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurology Lectures 1 4 DR - RosalesDocument20 pagesNeurology Lectures 1 4 DR - RosalesMiguel Cuevas DolotPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Guide Questions - 4.5 Page UrgDocument6 pagesCase Study Guide Questions - 4.5 Page UrgRanzo FranqPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4Document80 pagesChapter 4Dever GeronaPas encore d'évaluation
- Behavior and Ethics QuestionsDocument26 pagesBehavior and Ethics QuestionsRahul VadlapatlaPas encore d'évaluation
- Halakhic BioethicDocument171 pagesHalakhic BioethicShalom SpiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Forensic MedicineDocument11 pagesForensic MedicineMikaelGo-OngPas encore d'évaluation
- Organ Donation: From Diagnosis To Transplant: ReviewDocument10 pagesOrgan Donation: From Diagnosis To Transplant: ReviewFIA SlotPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs of Death: One Is Declared Dead WhenDocument2 pagesSigns of Death: One Is Declared Dead WhenMohammid PadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Crimin 2013 BDocument20 pagesCrimin 2013 BMa Tiffany Cabigon100% (1)
- Understanding Brain Death, Coma, and StrokeDocument21 pagesUnderstanding Brain Death, Coma, and StrokeDrGasnasPas encore d'évaluation
- INSTAGRAM: DR - Jams - N - Food Follow For More USMLE Tips and FOODDDDD!Document12 pagesINSTAGRAM: DR - Jams - N - Food Follow For More USMLE Tips and FOODDDDD!usmlePas encore d'évaluation
- Histology and HistopathologyDocument42 pagesHistology and HistopathologyDreyden HaloPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 2 - Ethics in Pharmacy PracticeDocument15 pagesCHAPTER 2 - Ethics in Pharmacy PracticeMona GhazyPas encore d'évaluation
- Redefinition of DeathDocument9 pagesRedefinition of DeathKarla Mae Smiley XdPas encore d'évaluation
- Medico-Legal Aspects of Death DeterminationDocument7 pagesMedico-Legal Aspects of Death DeterminationthehonestcentavoPas encore d'évaluation
- Kamala KannanDocument103 pagesKamala KannanshrikantPas encore d'évaluation