Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction of Managerial Economics
Transféré par
Sandesh ShettyCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Introduction of Managerial Economics
Transféré par
Sandesh ShettyDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Concept of Economics
Economics is the science of choice in the face of unlimited ends and scarce
resources which have alternative uses. Since resources are scarce and the
uses to which they can be put to are unlimited, one is required to choose the
best amongst the available alternatives. The crux of the problem which
economics tries to address is the choice of the best uses of resources among
the alternative uses.
Generally, economics can be divided into two broad categories:
microeconomics and macroeconomics.
Macroeconomics is the study of the economic system as a whole. It
includes techniques for analyzing changes in total output, total
employment, the consumer price index, the unemployment rate, and
exports and imports. Only aggregate levels of these variables are
considered.
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Concept of Economics (contd.)
But concealed in the aggregate data are countless changes in the output
levels of individual firms, the consumption decisions of individual
consumers, and the prices of particular goods and services. These all fall
under the domain of microeconomics.
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of the individual actors on the
economic stage, that is, firms and individuals and their interaction in
markets.
2
Origin of Managerial Economics
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Like every other individual a manger of a business firm has to take decisions
in the face of scarcity and alternative uses of resources. In fact success of a
business firm largely depends upon the efficiency in utilization of limited
resources remaining in the disposal of the business firm.
Thus managerial economics is evolved as an important tool kits which is
useful in the decision making for the manager.
The development of managerial economics as a separate discipline has a
recent origin. Joel Deans book Managerial Economics published in 1951 is
taken as the pioneer in this discipline.
Due to wide recognition of the uses of economic theories in the decision
making of the business this subject is rich in literature in these days.
3
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Concept of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics is the discipline that deals with the application of
economic concepts, theories and methodologies to the practical problems
of businesses/firms in order to formulate rational managerial decisions for
solving those problems.
It uses the tools and techniques of Economic analysis to solve managerial
problems or to achieve the firms desired objective. It is that branch of
economics, which serves as a link between abstract theories and
managerial practices. It is based on economic analysis for identifying
problems, organizing information and evaluating alternatives.
Managerial economics borrows theories from traditional economics i.e.
microeconomics where as it borrows tools from decision science i.e.
mathematics and statistics and it tries to find out optimum solution of
business problems.
Thus Spencer and Seligman defined Managerial economics as The
integration of economic theory and business practice for the purpose of
facilitating decision-making and forward planning by management.
4
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Concept of Managerial Economics (contd.)
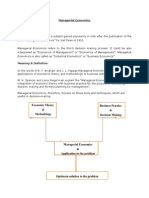
Following diagram shows how does the managerial economics provide the
link between traditional economics and decision sciences
Management
Problems
Economic Theory Decision Sciences
Managerial
Economics
Economic Methodology:
Descriptive Model
Prescriptive Model
Study of Functional Areas:
Accounting, Finance, and
Marketing
Optimal
Decision
5
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Concept of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Managerial economics is by nature goal oriented and prescriptive which
may be viewed as economics applied in decision making at the level of firm.
Like an individual most of the problems of the firm emerge in allocation of
scarce resources.
We can trace different ideas given by scholars in this subject.
Managerial economics is the price theory in service of business executive.
-D.J. Watson
Managerial economics can be viewed as an application of that part of
microeconomics that focuses on such topics as risk, demand, production,
cost, pricing, and market structure. -Petersen and Lewis
Managerial economics is concerned with the ways in which managers
should make decisions in order to maximize the effectiveness or performance
of the organizations they manage. - Edwin Mansfield
6
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Concept of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Managerial economics is the study of allocation of resources available to
a firm among the activities of that unit. - Hynes
Use of economic analysis in formulating policies is known as managerial
economics - Joel Dean
Managerial economics is the application of economic theory and the tools
of decision science to examine how an organization can achieve its aims or
objectives most efficiently. - Dominic Salvatore
Managerial economics is the application of economic theory and
methodology to business administration practice.
- Pappas and Brigham
From these ideas it can be concluded managerial economics is the discipline,
which deals with the application of economic theory to business
management. Thus it lies on the borderline between economics and
business management and serves as a bridge between these two disciplines.
7
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Distinction between Managerial Economics and
Traditional Economics
There are some differences between managerial economics and traditional
economic theory because managerial economics seeks the help of other
disciplines such as statistics, mathematics, accounting, management to get
optimal solution to the managerial decision-making problems.
Differences between managerial economics and traditional economics which are
outlined below:
i. Managerial economics concerns with the application of economic
principles to the problems of the firm but the traditional economics deals
with the body of principles itself.
ii. Managerial economics is highly microeconomics in character. It studies the
problems of a firm but does not study the macroeconomic phenomenon.
But traditional economics consist of both micro and macro economics.
8
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Distinction between Managerial Economics and Traditional
Economics (contd.)
iii. Traditional economics is a study of both firm and an individual, whereas
managerial economics is a study of the problem of a firm only.
iv. Managerial economics focuses its attention in the study of profits
because it has great influence primarily on entrepreneurial decision and
value theory of the firm. In traditional economics, the microeconomics is
a branch under which all the theories of factor pricing such as rent,
wages, interest and profit are studied.
v. Traditional economics studies human behavior on the basis of certain
assumptions, but these assumptions may not be true in managerial
economics because managerial economics is concerned with practical
problems.
9
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Features of Managerial Economics
Even if there are some differences among scholars on the subject of features
of managerial economics, here some of the commonly agreed
characteristics of managerial economics are introduced. They are:
i. Microeconomics character: - Managerial economics is microeconomics
in character because its unit of study is firm. However, it always takes
the help of macroeconomics to understand and adjust to the
environment in which the firm operates.
ii. Choice and Allocation: - Managerial economics is concerned with
decision-making of economic nature. This implies that managerial
economics deals with identification of economic choices and allocation
of scarce resources on the best alternative.
iii. Goal Oriented: - Managerial economics is goal-oriented and
prescriptive. It deals with how decisions should be formulated by
managers to achieve the organizational goals.
10
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Features of Managerial Economics (contd.)
iv. Conceptual and Metrical: - Managerial economics is both Conceptual
and Metrical. A rational/logical application of quantitative techniques to
business decision-making considers hard and careful thinking about the
nature of the particular problem to be solved. Managerial economics
provides necessary conceptual tools to achieve this.
v. Pragmatic: - Managerial economics is more pragmatic than traditional
economics. Hence, it is called applied microeconomics. It ignores the
complex concepts of the traditional economics.
vi. Normative: - Managerial economics belongs to normative economics
rather than positive economics. Positive economics studies economic
behavior without making judgments. Normative economics, on the
other hand, makes value judgments and prescribes what should be
done to solve economic problems.
vii. Multi-disciplinary: - Managerial economics is an integration of different
academic disciplines.
11
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics
Managerial economics can be used to explain and understand almost all
business problems. Though it has late origin, due to applicability nature this
subject is turned to be an area continuous research and innovation. Thus
there is no unanimous way of explaining scope of managerial economics.
The most common way is explaining its areas of study, which covers all
those economic concepts, theories and tools of analysis which can be used
to analyze issues related to demand projection, production and cost,
market structure, level of competition and general environment. Mostly,
these topics are rooted in economic theory (i.e., micro- and macro
economics).
12
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Microeconomics Applied to Operational Issues:
Operational issues of firms are of internal nature. Internal issues include all
those problems which arise within the business organization and fall within
the control of the management. Some of the basic internal issues are:
a) Choice of business and the nature of products, that is, what to produce,
b) Choice of size of the firm, that is, how much to produce,
c) Choice of technology, that is, choosing the factor-combination
(technique of production)
d) Choice of price, that is, how to price the commodity,
e) How to promote sales,
f) How to face competition,
g) How to decide on new investments,
h) How to manage profit and capital,
i) How to manage an inventory, that is, stock of both finished goods and
raw materials.
13
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Microeconomics deals with such questions confronted by managers. The
following microeconomic theories deal with most of these questions.
Microeconomics Applied to Operational Issues:
a) Demand Analysis and Forecasting: - An understanding of the forces
behind demand is a powerful tool for managers. Such knowledge
provides the background needed to make pricing decisions, forecast
sales and formulate marketing strategies. A forecast of future sales is
essential before employing resources.
b) Theory of Production and Production Decisions: - Production theory
explains the relationship between inputs and output. It also explains
under what conditions costs increase or decrease; how total output
behaves when use of inputs is changed; and how can output be
maximized from a given quantity of resources. Thus, it helps the
managers in determining the size of the firm, and the amount of capital
and labour to be employed keeping in view the objectives of the firm.
14
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Microeconomics Applied to Operational Issues:
c) Market Structure and Pricing Theory: - Price theory explains how prices
of outputs and inputs are determined under different market
conditions; when price discrimination is desirable, feasible and
profitable; and to what extent advertising can be helpful in expanding
sales in a competitive market. Hence, price theory can be helpful in
determining the price policy of the firm.
d) Analysis of Cost: - Estimates of cost are essential for planning purposes.
The factors determining costs are not always known or controllable
which gives rise to cost uncertainty. Factors of production are scarce
and they have alternative uses. Factors of production may be allocated
in a particular way to get maximum output. Thus the analysis of costs
and their links to output are also importance in managerial economics.
15
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Microeconomics Applied to Operational Issues:
e) Profit and Capital Management (Investment Decisions): - Profit
provides the index of success of a business firm. Profit analysis is
difficult, because the uncertainty of expectations makes realization of
profit planning and measurement difficult and these areas are covered
in the study of managerial economics.
Capital management means planning and control of capital
expenditures. Hence, it is very important for a firm to manage required
capital through proper investment planning. The main topics covered
are: cost of capital, types of investment decisions, and evaluation and
selections of investment projects.
16
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Microeconomics Applied to Operational Issues:
f) Inventory Management: - Inventory refers to a stock of raw materials
or finished goods which a firm keeps. Management of inventory is very
important for a firm to keep intact of its current production and supply
capacity and to meet the challenges arising from change in market and
other conditions. In this regard, a major question that arises is: how
much of the inventory is the ideal stock? If it is high, capital is
unproductively tied up, and that might be useful for other productive
purposes if the stock of inventory is reduced. On the other hand, if the
level of inventory is low, production will be hampered. Hence,
managerial economics uses different methods which are helpful in
minimizing the inventory cost.
17
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Scope of Managerial Economics (contd.)
Macroeconomics Applied to Business Environment:
Macroeconomic issues relate to the general business environment in which a
business operates. The factors which constitute economic environment of a
country include the following.
a. Types of economic system in the country;
b. General trends in national income, employment, prices, saving and
investment, etc;
c. Trend in labour supply and strength of the capital market;
d. Governments economic policies: industrial policy, fiscal policy, monetary
policy, price and foreign trade policies;
e. Social factors like value system of the society, property rights, customs and
habits;
f. Socio-economic organization like trade unions, consumers associations, and
producers unions
g. The degree of globalization of the economy and the influence on the
domestic markets.
18
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Uses and Significance of Managerial Economics in Business
Decision Making
Every management system is related with decision-making. Decision-
making requires a balance between simplification of analysis of
management problems and complications of handling a numbers of factors
and tools to attain predetermined objectives. In this context managerial
economics occupies important place. The uses or significance of
managerial economics can be outlined as:
i. Provide Tools and Techniques: It selects those economic theories,
concepts, and techniques of analysis, which have a bearing on the
decision-making process. These are, if necessary, modified with a view to
enable the manager take better decisions. Thus, managerial economics
accomplished the objective of building a suitable tool kit from traditional
economics.
19
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Uses and Significance of Managerial Economics in Business
Decision Making (contd.)
ii. Adopts Ideas from Other Subjects: Managerial economics also takes the
aid of other academic disciplines having a bearing upon the business
decisions of a manager in view of the various explicit and implicit
constraints subject to which resource allocation is to be optimized.
iii. Decision Making: Managerial economics helps in reaching a variety of
business decisions in a complicated environment such as what to
produce, what inputs and production techniques should be applied,
how much output should be produced and at what prices it should be
sold, what should be the product-mix, what are the best sizes and
locations of new plants, when should equipment be replaced and how
should the available capital be allocated, etc.
20
INTRODUCTION OF MANAGERIAL ECONOMICS
Uses and Significance of Managerial Economics in Business
Decision Making (contd.)
iv. Managerial Competency: Managerial economics makes a manager a
more competent model builder. Thus s/he can capture the essential
relationship, while leaving out the cluttering details and peripheral
relationships. It means managerial economics helps in model building
depicting the relationship between essential variables.
v. Serve as an Integrating Agent: When size of a firm expands its activities
are undertaken by more specializing departments or functional areas like
finance, marketing, personnel, production, etc. Managerial economics
serves as an integrating agent by coordinating the different areas. The
significance of which lies in the fact that the functional departments
often enjoy considerable autonomy and aspire conflicting goals, and
coordination of goals of different units is must to achieve the goals of
the firm as a whole.
21
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Advanced MGTDocument136 pagesAdvanced MGTShawn MehdiPas encore d'évaluation
- CBC Heo (Wheel Loader) NC IIDocument58 pagesCBC Heo (Wheel Loader) NC IIJohn JamesPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Management ReviewerDocument7 pagesRisk Management ReviewerPhoebe WalastikPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Global HRMDocument12 pagesStrategic Global HRMJanan GulPas encore d'évaluation
- Handling & Liquidation of Cash AdvancesDocument84 pagesHandling & Liquidation of Cash AdvancesMinnie JulianPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mooring Pattern Study For Q-Flex Type LNG Carriers Scheduled For Berthing at Ege Gaz Aliaga LNG TerminalDocument6 pagesThe Mooring Pattern Study For Q-Flex Type LNG Carriers Scheduled For Berthing at Ege Gaz Aliaga LNG TerminalMahad Abdi100% (1)
- Economic OptimizationDocument22 pagesEconomic Optimizationraja_maqsood_jamaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Good Governance SyllabusDocument5 pagesGood Governance SyllabusMariya BhavesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa 214 Human Resource Management ReportDocument29 pagesPa 214 Human Resource Management ReportMarielle Dindero ArcinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Managerial Economics Chapter 3 PresentationDocument34 pagesManagerial Economics Chapter 3 PresentationtarekffPas encore d'évaluation
- Organizing: I. Nature of OrganizationsDocument6 pagesOrganizing: I. Nature of OrganizationsNicole Andrea TuazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit III-structure of OrganizationDocument15 pagesUnit III-structure of OrganizationAnirudhaRudhraPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 - Governance and Social ResponsibilityDocument25 pagesModule 1 - Governance and Social ResponsibilityPrecious Pearl manatoPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument21 pages1.introduction To Managerial Economicsneha chauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Memo 1 - Submission of Rank and File IPCR SLIPR For 2016 Sem 2Document4 pagesMemo 1 - Submission of Rank and File IPCR SLIPR For 2016 Sem 2Sam LagoPas encore d'évaluation
- CII Sohrabji Godrej GreenDocument30 pagesCII Sohrabji Godrej GreenRITHANYAA100% (2)
- DBM CSC Form No. 1 Position Description FormDocument2 pagesDBM CSC Form No. 1 Position Description FormJodina FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Noe HRM 11e IM Ch01Document8 pagesNoe HRM 11e IM Ch01Māhmõūd ĀhmēdPas encore d'évaluation
- New Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: A Global PerspectiveDocument33 pagesNew Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies: A Global PerspectiveLakshmikanthBalasubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Resource - Accounting and The Business EnvironmentDocument109 pagesLearning Resource - Accounting and The Business EnvironmentCrystal Castor LabraguePas encore d'évaluation
- Topic Two Planning FunctionDocument4 pagesTopic Two Planning Functionstill earvin100% (2)
- 07 2018 WP JOsCoS PDFDocument23 pages07 2018 WP JOsCoS PDFLoise EnglesPas encore d'évaluation
- Sla At&tDocument2 pagesSla At&tCésar Lainez Lozada TorattoPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus in Acctg. 13 Management Consultancy BSADocument10 pagesSyllabus in Acctg. 13 Management Consultancy BSAAnonymous Vng49z7hPas encore d'évaluation
- III. The Nature of People and OrganizationDocument16 pagesIII. The Nature of People and OrganizationKhristina Anne Ama67% (3)
- Characteristics of Organizational Change: Organizational Development Finals ReviewerDocument4 pagesCharacteristics of Organizational Change: Organizational Development Finals ReviewerMarvin OngPas encore d'évaluation
- 4.performance Management SystemDocument28 pages4.performance Management SystemRosemin VirjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Motivation Theories - Lec 1Document11 pagesMotivation Theories - Lec 1Tharushi DiyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Q1 Functional Organization Has Been Divided To Put The Specialists in The Top Position Throughout The EnterpriseDocument7 pagesQ1 Functional Organization Has Been Divided To Put The Specialists in The Top Position Throughout The EnterpriseSneha ShadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4.1-Perception and Personality in OrganizationsDocument20 pagesModule 4.1-Perception and Personality in OrganizationsBenjamin Codilla Gerez, Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- MBE Unit IDocument36 pagesMBE Unit Istandalonemba50% (2)
- Course Outline For Managerial EconomicsDocument2 pagesCourse Outline For Managerial EconomicsZerihunPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview of Human Behavior in OrganizationsDocument6 pagesAn Overview of Human Behavior in OrganizationsCaroline SolomonPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Analysis & Design HRM IDocument38 pagesJob Analysis & Design HRM IRaja Shahryar Ayub KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- First Quiz in Management AccountingDocument7 pagesFirst Quiz in Management AccountingEumell Alexis PalePas encore d'évaluation
- Responsibility Accounting1Document14 pagesResponsibility Accounting1Sujeet GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction-Business LawDocument12 pagesIntroduction-Business LawAmirul Hakim Nor AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Accountancy Notes PDFDocument11 pagesAccountancy Notes PDFSantosh ChavanPas encore d'évaluation
- IAS-16 (Property, Plant & Equipment)Document20 pagesIAS-16 (Property, Plant & Equipment)Nazmul HaquePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1 - Introduction To Strategic Management AccountingDocument11 pagesChapter - 1 - Introduction To Strategic Management AccountingNusrat Islam100% (1)
- 01 - Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument23 pages01 - Introduction To Managerial Economicscdkalpita80% (5)
- Chapter 4 (Separtion of Administrative and Other Powers)Document1 pageChapter 4 (Separtion of Administrative and Other Powers)Vanessa Salvador100% (1)
- Cost Benefit AnalysisDocument2 pagesCost Benefit AnalysisGarvitJainPas encore d'évaluation
- TQMDocument5 pagesTQMJASMINE REGIPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical Decision Making ProcessDocument4 pagesEthical Decision Making ProcessRathin BanerjeePas encore d'évaluation
- ECON13B Managerial EconomicsDocument3 pagesECON13B Managerial EconomicsTin Portuzuela100% (1)
- 112 KCSRDocument6 pages112 KCSRm a zubairPas encore d'évaluation
- Accouting PrinciplesDocument5 pagesAccouting PrinciplesPriyanka RawoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Managerial Economics 02Document35 pagesManagerial Economics 02shihab285Pas encore d'évaluation
- My Presentation About PayRoll SystemDocument3 pagesMy Presentation About PayRoll SystemAzeem Asim MughalPas encore d'évaluation
- (Assignment) Planning and ManagementDocument6 pages(Assignment) Planning and ManagementaadiljohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Shagun Verma Attitude & Job SatisfactionDocument56 pagesShagun Verma Attitude & Job SatisfactionShagun VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Goal Congruence MCS Form ProcessDocument9 pagesGoal Congruence MCS Form Processmukeshkumar91Pas encore d'évaluation
- Promotion Transfer SeparationsDocument22 pagesPromotion Transfer SeparationssambitacharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Program Development: Zuhaira U. EbrahimDocument23 pagesProgram Development: Zuhaira U. Ebrahimlang0510Pas encore d'évaluation
- Scope of Management AccountingDocument2 pagesScope of Management Accountingbaba3674100% (1)
- Autocratic ModelDocument5 pagesAutocratic ModelVenkatesh KesavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Job Analysis Is Conducted To Determine TheDocument14 pagesJob Analysis Is Conducted To Determine TheMarkmarilynPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument19 pagesCase StudyxyzPas encore d'évaluation
- New - OBTL-Governance, Ethics, Internal Control, MGMT Risk - First-Semester-AY2020-2021Document5 pagesNew - OBTL-Governance, Ethics, Internal Control, MGMT Risk - First-Semester-AY2020-2021rebecca lisingPas encore d'évaluation
- JAIBB SyllabusDocument5 pagesJAIBB Syllabusmuhit jishanPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Managerial EconomicsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Managerial EconomicsamitasamPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 Introduction of Managerial EconomicsDocument21 pages02 Introduction of Managerial Economicssubroto36Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction of Managerial EconomicsDocument12 pagesIntroduction of Managerial EconomicsS TMPas encore d'évaluation
- Img 20201010 0005Document1 pageImg 20201010 0005Tarek SalehPas encore d'évaluation
- (20836104 - Artificial Satellites) Investigation of The Accuracy of Google Earth Elevation DataDocument9 pages(20836104 - Artificial Satellites) Investigation of The Accuracy of Google Earth Elevation DataSunidhi VermaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diogenes Laertius-Book 10 - Epicurus - Tomado de Lives of The Eminent Philosophers (Oxford, 2018) PDFDocument54 pagesDiogenes Laertius-Book 10 - Epicurus - Tomado de Lives of The Eminent Philosophers (Oxford, 2018) PDFAndres Felipe Pineda JaimesPas encore d'évaluation
- USER MANUAL ABRITES Commander For Nissan PDFDocument20 pagesUSER MANUAL ABRITES Commander For Nissan PDFBosi GashiPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Perceptions and Treatment of Mental Illness in EthiopiaDocument7 pagesTraditional Perceptions and Treatment of Mental Illness in EthiopiaifriqiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER IV The PSYCHOLOGY of YOGA Yoga, One Among The Six Orthodox Schools of Indian ... (PDFDrive)Document64 pagesCHAPTER IV The PSYCHOLOGY of YOGA Yoga, One Among The Six Orthodox Schools of Indian ... (PDFDrive)kriti madhokPas encore d'évaluation
- Iguard® LM SeriesDocument82 pagesIguard® LM SeriesImran ShahidPas encore d'évaluation
- A Content Analysis of SeabankDocument13 pagesA Content Analysis of SeabankMarielet Dela PazPas encore d'évaluation
- 444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 16-16Document1 page444323735-Chem-Matters-Workbook-2E-Teacher-s-Edn-pdf 16-16whatisPas encore d'évaluation
- Pioneer 1019ah-K Repair ManualDocument162 pagesPioneer 1019ah-K Repair ManualjekPas encore d'évaluation
- Acting White 2011 SohnDocument18 pagesActing White 2011 SohnrcegliePas encore d'évaluation
- The Ovation E-Amp: A 180 W High-Fidelity Audio Power AmplifierDocument61 pagesThe Ovation E-Amp: A 180 W High-Fidelity Audio Power AmplifierNini Farribas100% (1)
- John DrydenDocument3 pagesJohn DrydenDunas SvetlanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Federalist Papers 10 51 ExcerptsDocument2 pagesFederalist Papers 10 51 Excerptsapi-292351355Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sample CVFormat 1Document2 pagesSample CVFormat 1subham.sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Contemporary Strategic ManagementDocument2 pagesContemporary Strategic ManagementZee Dee100% (1)
- W.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueDocument2 pagesW.C. Hicks Appliances: Client Name SKU Item Name Delivery Price Total DueParth PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- 0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andDocument20 pages0012 Mergers and Acquisitions Current Scenario andJuke LastPas encore d'évaluation
- Borges, The SouthDocument4 pagesBorges, The Southdanielg233100% (1)
- Colfax MR Series CompresorDocument2 pagesColfax MR Series CompresorinvidiuoPas encore d'évaluation
- DirectionDocument1 pageDirectionJessica BacaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Information Systems and Supply Chain ManagementDocument2 pagesInformation Systems and Supply Chain Managementvipinkandpal86Pas encore d'évaluation
- Simran's ResumeDocument1 pageSimran's ResumesimranPas encore d'évaluation
- PlateNo 1Document7 pagesPlateNo 1Franz Anfernee Felipe GenerosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Total Physical Response (G4)Document3 pagesTotal Physical Response (G4)Aq Nadzrul LarhPas encore d'évaluation
- Very Narrow Aisle MTC Turret TruckDocument6 pagesVery Narrow Aisle MTC Turret Truckfirdaushalam96Pas encore d'évaluation