Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Conduction
Transféré par
taguiam_jera0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
16 vues15 pagesThe normal electrical conduction of the heart originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node and travels through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node, causing the atria to contract. It then passes through the bundle of His to stimulate contraction of the ventricles. The electrocardiogram (ECG) represents this cardiac cycle through specific waveforms, obtained via electrodes placed on the skin. The standard 12-lead ECG is used to diagnose arrhythmias and conduction abnormalities.
Description originale:
heart conduction
Titre original
conduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe normal electrical conduction of the heart originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node and travels through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node, causing the atria to contract. It then passes through the bundle of His to stimulate contraction of the ventricles. The electrocardiogram (ECG) represents this cardiac cycle through specific waveforms, obtained via electrodes placed on the skin. The standard 12-lead ECG is used to diagnose arrhythmias and conduction abnormalities.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
16 vues15 pagesConduction
Transféré par
taguiam_jeraThe normal electrical conduction of the heart originates in the sinoatrial (SA) node and travels through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node, causing the atria to contract. It then passes through the bundle of His to stimulate contraction of the ventricles. The electrocardiogram (ECG) represents this cardiac cycle through specific waveforms, obtained via electrodes placed on the skin. The standard 12-lead ECG is used to diagnose arrhythmias and conduction abnormalities.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 15
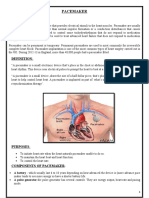
HEART CONDUCTIONS
Normal electrical conduction of the
heart
- the electrical impulse that stimulates
and paces the cardiac muscle normally
originates in the SA node.
- the electrical impulse quickly travels
from the sinus node through the atria
to the atrioventricular (AV) node, this
process is known as conduction.
- The electrical stimulation of the
muscle cells of the atria causes them
to contract. The structure of the AV
node slows the electrical impulse,
giving the atria time to contract and fill
the ventricles with blood. This part of
the atrial contraction is frequently
referred to as the atrial kick.
- The electrical impulse then travels very
quickly through the bundle of His to the
right and left bundle branches and the
Purkinje fibers, located in the ventricular
muscle.
-the electrical stimulation cells of the
ventricles in turn causes the mechanical
contraction of the ventricle (systole). The
cell repolarize and the ventricles then
relax (diastole).
- The process from sinus node
electrical impulse generation
through ventricular repolarization
completes the electromechanical
circuit, and the cycle begins again.
Electrocardiogram
- is a graphic representation of the
electrical currents of the heart. The
ECG is obtained by placing disposable
electrodes in standard positions on the
skin of the chest wall and extremities.
- Each phase of the cardiac cycle is
reflected by specific waveforms on
the screen of a cardiac monitor or
on a strip of ECG graph paper.
Components of Electrodes
1. an adhesive substances that
attaches to the skin to secure the
electrode in place.
2. a substance that reduces the
skins electrical impedance and
promotes detection of the
electrical current.
Lead
- is a specific view of the electrical
activity of the heart.
-the standard ECG is composed of
12 leads or 12 different views,
although it is possible to record 15
or 18 leads.
12 lead ECG
-is used to diagnose:
-Dysrhythmias
-Conduction abnormalities
-Chamber enlargement
-Myocardial ischemia
-Injury / Infarction
15 lead ECG
- adds three additional chest leads
across the right precordium and is
used for early diagnosis of right
ventricular and left posterior
(ventricular) infarction.
18 lead ECG
- adds three posterior leads to the
15 lead ECG and is useful for early
detection of myocardial ischemia
and injury.
Obtaining an Electrocardiogram
-an ECG machine placed at the
patients side for an immediate
recording (standard 12-lead ECG)
-a cardiac monitor at the patients
bedside for continuous reading; this
kind of monitoring, usually called
hardwire monitoring, is used in ICU.
-a small box that the patient carries that
continuously transmit the ECG
information by radiowaves to a central
monitor called telemetry.
- a small, lightweight tape recorder-like
machine (ambulatory ECG monitoring or
a Holter monitor) that the patient wears
and that continuously records the ECG on
a tape, which later views and analyzed
with a scanner.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document53 pagesElectrocardiogram (ECG)eric100% (1)
- Understanding The 12 Lead ECGDocument7 pagesUnderstanding The 12 Lead ECGccbrown7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationDocument10 pagesBasis of ECG and Intro To ECG InterpretationKristin SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- EKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!D'EverandEKG Interpretation: Making EKG/ECG Interpretation Easy!Pas encore d'évaluation
- EKG Basics HandoutDocument8 pagesEKG Basics HandoutDuy JzPas encore d'évaluation
- TestDocument46 pagesTestmohammed faqihPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg / EkgDocument10 pagesEcg / EkgSilver Villota Magday Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNDocument34 pagesBasic Ecg Interpretation and Arrhythmia Recognition By: Ma. Victoria E. Martinez Er - RNMavic Martinez BuntalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Principles of ECGDocument53 pagesBasic Principles of ECGSmita Jain100% (1)
- EKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationD'EverandEKG | ECG Interpretation. Everything You Need to Know about 12-Lead ECG/EKG InterpretationÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Pacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingDocument57 pagesPacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingAhmad Khalil Ahmad Al-SadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrocardiography (ECG)Document11 pagesElectrocardiography (ECG)Hassan AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordination and ResponseDocument21 pagesCoordination and ResponseAisya Omeira60% (5)
- Cardiac DysrhythmiasDocument9 pagesCardiac DysrhythmiasMandy JameroPas encore d'évaluation
- 118a - CardiomyopathyDocument10 pages118a - CardiomyopathyJoanna TaylanPas encore d'évaluation
- Blue Book PediatricsDocument126 pagesBlue Book PediatricsKoricho Mengistu100% (1)
- Care Plan BronchitisDocument3 pagesCare Plan BronchitisYousef JafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrocardiogram IntroductionDocument20 pagesElectrocardiogram IntroductionGajendra TodakarPas encore d'évaluation
- Everything You Need To Know About High Blood PressureDocument10 pagesEverything You Need To Know About High Blood PressureEmanuelPredescuPas encore d'évaluation
- EcgDocument52 pagesEcgعبد الله الحربيPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg PDFDocument6 pagesEcg PDFzezoo egPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Interpretation: Prepared byDocument16 pagesECG Interpretation: Prepared bypipoahmed51Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionDocument12 pagesA Review On Pacemakers: Device Types, Operating Modes and Pacing Pulses. Problems Related To The Pacing Pulses DetectionsdekapurePas encore d'évaluation
- EkgppDocument93 pagesEkgppLindsay WishmierPas encore d'évaluation
- The HeartDocument10 pagesThe HeartNabil Magdi HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is EcgDocument5 pagesWhat Is EcgLeeyan MeePas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrocardiographyDocument4 pagesElectrocardiographyJho BuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Document46 pagesPacemaker Learning Package: Paula Nekic CNE Liverpool Hospital ICU January 2016Deepak BhatPas encore d'évaluation
- Conduction SystemDocument2 pagesConduction SystemMalik Asif HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG Monitoring in TheatreDocument17 pagesECG Monitoring in TheatrePhani NadellaPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Biophysical Basics of Electrocardiography and Blood Pressure Measurement Techniques Time: 2 HoursDocument5 pagesTopic: Biophysical Basics of Electrocardiography and Blood Pressure Measurement Techniques Time: 2 Hoursnamar13766Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Lora ECGDocument53 pagesDr. Lora ECGAhmed HeshamPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cardiac Electrical System and How The HeartDocument26 pagesThe Cardiac Electrical System and How The HeartZoe Jisel LuzadasPas encore d'évaluation
- RRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRDocument2 pagesRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRRSaginesh MkPas encore d'évaluation
- ECGfinalDocument10 pagesECGfinalSarah FerguzonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg + Ventricular Tachycardia and FibrillationDocument9 pagesEcg + Ventricular Tachycardia and Fibrillationsakkiyy154Pas encore d'évaluation
- 6heart Sound PacemakerDocument28 pages6heart Sound PacemakerJack OnePas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderDocument7 pagesExperiment No.: 06: Title: Study and Simulation of ECG RecorderVISHWESH KULKARNIPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseDocument4 pagesWhat Is An ECG?: Heart DiseaseAjay Pal NattPas encore d'évaluation
- FBA Unit-2Document37 pagesFBA Unit-2bathula hariniPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Project Phase 1 Report CloudDocument35 pagesMajor Project Phase 1 Report CloudPraj CPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic:: Performing and Interpreting Electrocardiogram (ECG)Document137 pagesTopic:: Performing and Interpreting Electrocardiogram (ECG)Tiffany AdriasPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgDocument38 pagesGroup 4 - Baseline Heart Rate & EcgTimothy John Bautista100% (2)
- Ekg Ecg Interpretation by DR Jason Lowe PDF Bb3 DR NotesDocument79 pagesEkg Ecg Interpretation by DR Jason Lowe PDF Bb3 DR NotesGuru RewriPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacemaker Physics ResearchDocument6 pagesPacemaker Physics ResearchJose Rene BerliozPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg FinalDocument61 pagesEcg Finalmahes2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- Electrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument18 pagesElectrocardiography - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediapayments8543Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Wiring Diagram of The HeartDocument4 pagesThe Wiring Diagram of The Heartgurneet kourPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosisDocument38 pagesElectrocardiogram: Electrocardiogram EKG Heart Heart's Electrical Activity DiagnosislorhenzsoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Conduction System of The HeartDocument27 pagesElectrical Conduction System of The HeartAnonymous gUjimJKPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)Document12 pagesElectrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)श्रीकृष्ण हेङ्गजूPas encore d'évaluation
- Ecg Review: Ecgs Made Easy: Section IDocument11 pagesEcg Review: Ecgs Made Easy: Section ISewyel GarburiPas encore d'évaluation
- #Dr. Lora Ecg PDFDocument53 pages#Dr. Lora Ecg PDFمحمد زينPas encore d'évaluation
- Special Conductive System of Heart: By: Azher SyedDocument14 pagesSpecial Conductive System of Heart: By: Azher SyedAzhersyedPas encore d'évaluation
- PACEMAKERDocument5 pagesPACEMAKERPoonam ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Ghid Ekg USADocument68 pagesGhid Ekg USAmorfopatologiePas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Lead EKG 101Document84 pages12 Lead EKG 101Clarke KrugmanPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrocardiographyDocument11 pagesElectrocardiographysohan.ghosh23-25Pas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledmostafa5050Pas encore d'évaluation
- ECG-EKG Presentation - Gunda GDocument21 pagesECG-EKG Presentation - Gunda GGadzikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy & Function of Conducting SystemDocument22 pagesAnatomy & Function of Conducting SystemhalayehiahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacemaker Physics Research - High SchoolDocument7 pagesPacemaker Physics Research - High SchoolJose Rene BerliozPas encore d'évaluation
- The Heart'S Conduction System and "Natural Pacemaker "Document8 pagesThe Heart'S Conduction System and "Natural Pacemaker "merin sunilPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyDocument27 pagesUnit 5 Basic of ElectrocardiographyJack TomarPas encore d'évaluation
- NCM116 Module 3 Cerebrovascular Disease QuizDocument5 pagesNCM116 Module 3 Cerebrovascular Disease QuizIvan FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Resusitasi Jantung ParuDocument31 pagesResusitasi Jantung ParuJohan100% (1)
- Abbraviation New1Document26 pagesAbbraviation New1remjith rajendranPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC 2086 Review Ex1 VCDocument3 pagesBSC 2086 Review Ex1 VCGreter AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- M.SC Questions PaperDocument2 pagesM.SC Questions Paperkhela Ram SorenPas encore d'évaluation
- NeurocheatsheetDocument2 pagesNeurocheatsheetsameeryousuf6830Pas encore d'évaluation
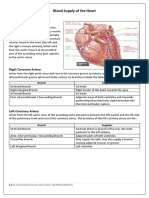
- Blood Supply of The HeartDocument5 pagesBlood Supply of The HeartMohammed EljackPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG ProjectDocument58 pagesECG Projectد. سعد قاسم الاجهزة الطبيةPas encore d'évaluation
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 11Document7 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 11Atabuddin MondalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Document37 pagesNutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Trishia BonPas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0020.Document32 pagesWa0020.Safura IjazPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulatory SystemDocument14 pagesCirculatory Systemsmbdy tbhhhPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Note Asas Psikologi (The Biological Perspective)Document66 pagesLecture Note Asas Psikologi (The Biological Perspective)Muhammad FaizPas encore d'évaluation
- The Definitions of The Skill Related Fitness ComponentsDocument4 pagesThe Definitions of The Skill Related Fitness ComponentsrainPas encore d'évaluation
- RenalDocument4 pagesRenalCourtneyPas encore d'évaluation
- T P R B P: Vital SignsDocument20 pagesT P R B P: Vital SignsEla 15Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab ResultsDocument3 pagesLab ResultsKristal Cyril PolzPas encore d'évaluation
- Aimst University Physiology Unit: Dr.P.SunithaDocument50 pagesAimst University Physiology Unit: Dr.P.SunithaYaashinii PeriathambyPas encore d'évaluation
- Science F3 Chap 2-Blood Circulation and TransportDocument34 pagesScience F3 Chap 2-Blood Circulation and TransportRebecca Choong Xin Hui93% (15)
- Assessment of Hematologic Function and Treatment Modalities Assessment of Hematologic Function and Treatment ModalitiesDocument26 pagesAssessment of Hematologic Function and Treatment Modalities Assessment of Hematologic Function and Treatment ModalitiesEdelweiss Marie CayetanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesDocument34 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and Physiology - Study Guide For NursesMarie ParksPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Circulatory System)Document12 pagesScience Vi-Quarter 2 Module (Week 1-2 Circulatory System)Denver TamayoPas encore d'évaluation
- EPILEPSYDocument5 pagesEPILEPSYIffa NooramPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Control and CoordinationDocument27 pagesPresentation On Control and CoordinationKunal TolaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 6 Lect1 Control of Body TemperatureDocument40 pagesWeek 6 Lect1 Control of Body Temperaturesjames20032312Pas encore d'évaluation