Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Slide Constructism
Transféré par
Ina Ina0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
29 vues24 pagesCONSTRUCTIVISM encourages construction of knowledge by the pupils. A person never really knows the world as it is. Each person constructs beliefs about what is real. Constructivist learners need to learn to plan, evaluate and reflect on their learning.
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentCONSTRUCTIVISM encourages construction of knowledge by the pupils. A person never really knows the world as it is. Each person constructs beliefs about what is real. Constructivist learners need to learn to plan, evaluate and reflect on their learning.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
29 vues24 pagesSlide Constructism
Transféré par
Ina InaCONSTRUCTIVISM encourages construction of knowledge by the pupils. A person never really knows the world as it is. Each person constructs beliefs about what is real. Constructivist learners need to learn to plan, evaluate and reflect on their learning.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 24
CONSTRUCTIVISM
I HEAR AND I FORGET
I SEE AND I REMEMBER
I DO AND I UNDERSTAND
Synthesis of
Cognitive learning process by Piaget
Discovery learning through hands-on and
minds-on activities by Bruner
Formation of meaningful mental structures
by Ausubel
Emphasis on the five learning domains by
Gagne
WHAT IS CONSTRUCTIVISM
Constructivism
Encourages
Construction of Knowledge
by the Pupils
By comparing
Prior
learning
New
learning
In
Social Context
Implication
Learning of Science
Manipulative
resources
Discovery
activities
Cooperative
Processes
Curriculum
Integration
Choosing
Needhams
Model
Five-phase
Learning
Orientation
Eliciting
Ideas
Restructuring
of Ideas
Application
of Ideas
Reflection
United by
Hands-on Minds-on
WHAT IS CONSTRUCTIVISM
About how people learn
Emphasizes the importance of building
knowledge actively as a result of
interaction between prior learning and
new learning
Constructivist learners are actively
involved in their own process of learning
Constructivist learners needs to learn to
plan, evaluate and reflect on their learning
Three principles in theory of constructivism
A person never really knows the world as it is.
Each person constructs beliefs about what is
real
What a person already believes, what a
person brings to new situations, filters out or
changes the information that the persons
senses deliver
People create a reality based on their previous
beliefs, their own abilities to reason, and their
desire to reconcile what they believe and
what they actually observe
CONSTRUCTIVISM
Models
Needhams 5 Phase
Osborne Generative Model
Interactive Model
Cooperative Learning
Technique Approach
STS
Learning Cycle
Strategies
(Inquiry)
Experiment
Simulation
Project
Field Work
Concept Mapping
Roles of the Teacher
Presenter
Not a lecturer but a person who
demonstrates, provides examples, and
presents activities or alternatives to pupils so
that they will experiences the process of
learning
Observer
A person who identifies the pupils ideas,
interacts with the pupils and provides
learning alternatives formally or informally
Question Master and Problem Initiator
One who stimulates the formation of ideas,
testing of ideas, and building of concepts by
asking questions and posing problems that are
related to the observation made
Organiser of Environment
A person who organises carefully and clearly
what needs to be done by the pupils, by giving
enough freedom to the pupils to carry out
realistics investigation; a person who organises
the teaching-learning process from the
perspective of the children
Roles of the Teacher
Public Relations Coordinators
A person who encourages co-operation,
development of public relations, and patience so
that multiculturalism prevails in the class; and a
person who defends the practice of these values
and teaches the children the advantages of
practising these values outside the classroom
Learning Assessor
A person who assess the progress of each childs
constructivist development in terms of
knowledge construction and development of
scientific skills
Roles of the Teacher
Theory Builder
A person who helps pupils to make
associations between ideas and building
meaningful patterns to represent the
knowledge constructed
Roles of the Teacher
TRADITIONAL CLASS CONSTRUCTIVIST CLASS
Teachers disseminate information
to students and students are
recipients of knowledge
Teachers have discuss with their
students and help them construct
their own knowledge
Teachers role is directive, rooted
in authority
Teachers role is interactive, rooted
in negotiation
Knowledge is seen as inert Knowledge is seen as dynamic
ever changing with our
experiences
Students work primarily alone Students work primarily in groups
Assessment is through testing
correct answers
Assessment includes students
works, observations, and points of
view, as well as tests. Process is
an important as product
PHASE PURPOSE METHODS
Orientation To attract students attention and
interest
Experiment, video and
film show,
demonstration,
problem solving
Generation of ideas To be aware of the students
prior knowledge
Experiment, small
group discussion,
concept mapping and
presentation
Restructuring of ideas
(i) Explanation and
exchanging ideas
(ii) Exposure to conflict
Ideas
(iii) Development of new
ideas
(iv) Evaluation
To realize the existence of
alternative ideas, ideas needs to
be improved, to be developed or
to be replaced with scientific
ideas
To determine the alternative
ideas and critically assess the
present ideas
To test the validity of present
ideas
To improvise, develop or to
replace with new ideas
To test the validity of the new
ideas
Small group discussion
and presentation
Discussion, reading,
and teachers input
Experiment, project
and demonstration
NEEDHAMS FIVE PHASE CONSTRUCTIVIST MODEL
Cont. NEEDHAMS FIVE PHASE CONSTRUCTIVIST MODEL
PHASE PURPOSE METHODS
Application of ideas To apply the new ideas
to a different situation
Writing of individuals
report on the project
work
Reflection To accommodate ones
idea to scientific ideas
To be aware of the
change in the thinking of
the pupils
Pupils can make their
own reflection on how
far their original ideas
have changed
Writing of individuals
report on the project
work, group discussion,
personal notes
Example of Lesson Plan
Science Concept : Investigating Living Things
Year : 6
Brief Description of the Science Concept :
Bread mould gets its food from grains, fruit and vegetables . The mould begins as a
tiny spore that lands on a food source like bread. Spores can be found in the air, on
the ground the air and you
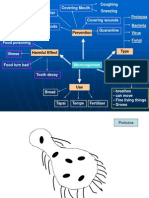
Prevalent Misconceptions
Pupils think that fungus reproduce out of nowhere when bread turns stale.
Lesson Objectives
(i) To identify ways to take care (protect) our food
(ii) To state that bacteria and fungus can spoil food
Materials needed
Fresh bread, Stale Bread, 5 post- boxes, Mahjong paper, Water, Microscope, Glass
dish
No Step Teaching and Learning
Activities
Scientific
Skills
Criteria
1 Orientation Teachers shows mouldy
bread and a piece of fresh
bread.
Teacher ask :
a) What can you observe
from these two pieces of
bread?
Student answer the
question from
observation
b) Why are they different ?
Teacher gives them
exercises
(refer to Appendix )
Observation
Inferences
Observation
by using
senses
Observation
Explaining
No Step Teaching and Learning
Activities
Scientific
Skills
Criteria
2 Generation
of ideas
a) The pupils are divided
into a few groups
b) They discuss in groups
how pieces of bread can
become mouldy
c) Children are asked to
tick their inferences
from the boxes provided
d) After choosing, their
inferences, they carry
out Post-box activity
e) Pupils will analyse
inferences from Post-box
activity
f) After Post-box activity,
teacher asks each group
to do a concept map to
generate ideas
Communication
Questioning
technique
Inferences
Communication
Cooperative
Learning
(team-work)
No Step Teaching and Learning
Activities
Scientific
Skills
Criteria
3 Restructuring
of Ideas
Experiment
a) Each group will be given a
piece of bread, some water
and two glass dish
b) Students are required to
carry out the experiment to
make fungus grow on the
bread
c) Each day student will
observe and record the
observation for a week
d) Pupils are required to draw
daily what they saw from
their observation for a week
e) A few days later, teacher
asks the pupils to take a
sample of fungus and
observe it under a
microscope
f) Ask children to draw the
fungus
Investigating
Observation
Observation
Acitivities are
carried out by
following
procedure
To record
information
from the
experiment
No Step Teaching and Learning
Activities
Scientific
Skills
Criteria
3 Restructuring
of Ideas
Using Internet
a) Teacher asks the
students to find more
information through the
internet about
production of fungus eg.
http://www.sci.mus.mn.us/
sin/tf/b/bread/bread.html
b) Search the cause that
encourage the growth of
fungus
Library, paper cutting and
magazine
Pupils can use these
materials for restructuring
of ideas
Communication
No Step Teaching and Learning
Activities
Scientific
Skills
Criteria
4 Application of
Ideas
From the information and
ideas they received through
the internet and the exp.
they had carry out.
a) Pupils record observation on
mahjong paper
b) The pupils can state the
causes of fungus growing
on the bread
c) The pupils can relate the
importance of bacteria or
fungus in the decaying of
rubbish
d) The pupils will know how
fungus is used in our food
such as fermented rice,
bread and others
Communication
Hypothesis
Reporting
the
observation
No Step Teaching and Learning
Activities
Scientific
Skills
Criteria
5 Reflection Students are required to
conclude on how fungus
can spoil the bread
Students can give
suggestions on how to
protect the bread from
fungus
Post-Box Activity
Observe the two pieces of bread given to you. One of the bread has black spot on it.
Why ? Each group is given two choices .
A The bread was spoil because it was not
in an air tight container
B The bread was spoil because of fungus
C The bread was spoil because it has
been left unattended
D It spoils by water in air
E Sunrays have spoiled the bread
F Bacteria have spoiled the bread
G The bread is stale
Discussion
Learning Objectives
The names of different parts of plants
Some thing float and some things sink
Make a complete circuit
Pushing and pulling can change the shape of
the shape of objects
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- b1dl1 E1, b1dl1 E2Document2 pagesb1dl1 E1, b1dl1 E2Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jadual Taklimat BIG PPG 2014Document2 pagesJadual Taklimat BIG PPG 2014Izam SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Visit and Field WorkDocument4 pagesVisit and Field Workhany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acid and Alkali-9Document2 pagesAcid and Alkali-9Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fungus Algae Lichen Conifer Moss Fern: Non-Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesFungus Algae Lichen Conifer Moss Fern: Non-Flowering Plantshany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- G11 Task1Document11 pagesG11 Task1Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength & Stability-G12Document2 pagesStrength & Stability-G12Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Penyediaan Larutan KimiaDocument11 pagesPenyediaan Larutan KimiaIna InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ele3102 CWK Tasks-1Document2 pagesEle3102 CWK Tasks-1hany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- A. Circle The Correct Answer. (20 Marks)Document9 pagesA. Circle The Correct Answer. (20 Marks)Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- First Aid For Various Injuries and Accidents.Document25 pagesFirst Aid For Various Injuries and Accidents.Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet 2 B 1 (A) : Match The Seeds To The PlantDocument4 pagesWorksheet 2 B 1 (A) : Match The Seeds To The Planthany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preparation of Chemical SolutionsDocument12 pagesPreparation of Chemical SolutionsIna InaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Day'S Excursion To The Malacca Zoo Project: Fair TestDocument10 pagesA Day'S Excursion To The Malacca Zoo Project: Fair TestIna InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Minggu 8 & 9 Amali Jantung 3Document26 pagesMinggu 8 & 9 Amali Jantung 3Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lawatan Sambil BelajarDocument13 pagesLawatan Sambil BelajarIna InaPas encore d'évaluation
- MindMap (MicroveOven) g1Document5 pagesMindMap (MicroveOven) g1Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Visit and Field WorkDocument4 pagesVisit and Field Workhany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz AnimalsDocument1 pageQuiz Animalshany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Historical Development of Science in MalaysiaDocument1 pageHistorical Development of Science in Malaysiahany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Minggu 8 & 9 Amali Jantung 5Document45 pagesMinggu 8 & 9 Amali Jantung 5Ina InaPas encore d'évaluation
- Amali Jantung 4Document33 pagesAmali Jantung 4Busrah TaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Inquiry NotesDocument16 pagesScience Inquiry Noteshany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fungus Algae Lichen Conifer Moss Fern: Non-Flowering PlantsDocument3 pagesFungus Algae Lichen Conifer Moss Fern: Non-Flowering Plantshany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Designer Animal-Ice BreakingDocument1 pageDesigner Animal-Ice Breakinghany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Science Inquiry Notes OriginalDocument25 pagesScience Inquiry Notes Originalhany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Name The Parts of A Plant by Filling in The BlanksDocument1 pageName The Parts of A Plant by Filling in The Blankshany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Group 8Document1 pageGroup 8hany3688_519912007Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Chapter 2 The Development of EspDocument4 pagesChapter 2 The Development of EspK wong100% (1)
- Reading & Writing Stage 3-Question PaperDocument13 pagesReading & Writing Stage 3-Question PaperSheryl HarrisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Statistics: Statistical TestsDocument42 pagesStatistics: Statistical TestsMichael WelkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Philisophy and Logic - AristotleDocument21 pagesPhilisophy and Logic - AristotleRalphPas encore d'évaluation
- Debate THBT Technology Decreases Creativity Online 2020Document5 pagesDebate THBT Technology Decreases Creativity Online 2020kbr8246Pas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic LeadershipDocument27 pagesStrategic Leadershiphss601100% (4)
- Of The Sublime Presence in QuestionDocument263 pagesOf The Sublime Presence in QuestionMax GreenPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 7 Differential Loneliness Scale For Non-Student PopulationsDocument3 pagesTest 7 Differential Loneliness Scale For Non-Student PopulationsdorinmertPas encore d'évaluation
- Task2 Educ.2Document5 pagesTask2 Educ.2HONEYLYN CASINGPas encore d'évaluation
- 1.3 Social Norms and OtheringDocument32 pages1.3 Social Norms and OtheringPhantomscar181Pas encore d'évaluation
- AIML UNit-1Document42 pagesAIML UNit-1harish9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ethical CommunicationDocument8 pagesEthical CommunicationConstance BandaPas encore d'évaluation
- G5. Improvisation in Various Art FormsDocument21 pagesG5. Improvisation in Various Art FormsEa YangPas encore d'évaluation
- SLHR501 PDFDocument3 pagesSLHR501 PDFNeha AhlawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Int 2 Unit 7 Day 2Document21 pagesInt 2 Unit 7 Day 2Tienda AfuroshoppuPas encore d'évaluation
- DAILY LESSON LOG in HEALTH For CLASS OBSERVATION - JEDDAHLYN A. RAMOSDocument3 pagesDAILY LESSON LOG in HEALTH For CLASS OBSERVATION - JEDDAHLYN A. RAMOSJeddahlyn Atienza RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Eye Gaze Communication SystemDocument22 pagesEye Gaze Communication SystemsrujanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abuse Workshop WS5Document72 pagesAbuse Workshop WS5krumkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Roz Mexted Sabbatical Report 1Document35 pagesRoz Mexted Sabbatical Report 1api-300545887Pas encore d'évaluation
- Metaethics Geoff Sayre-McCordDocument13 pagesMetaethics Geoff Sayre-McCordJaviera FargaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan PDFDocument7 pagesLesson Plan PDFtaneastefanita100% (1)
- Introduction To OBDocument14 pagesIntroduction To OBIshaan Sharma100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Week 2 (Nadhirah)Document19 pagesLesson Plan Week 2 (Nadhirah)Nadhirah AfendiPas encore d'évaluation
- Modes of LearningDocument5 pagesModes of LearningJossy Liz García PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapeh Health 7Document3 pagesMapeh Health 7glazegamoloPas encore d'évaluation
- Contoh ProposalDocument16 pagesContoh ProposalEylah FadilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Rhetorical Analysis FinalDocument6 pagesRhetorical Analysis Finalapi-40517138450% (2)
- Mind Maps For BooksDocument20 pagesMind Maps For BooksScribdAskanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aveva PID Diagram Process Design Ensuring Consistency Between A Piping Instrumentation Diagram 3D Model Throiugh Aveva PID Diagram PDFDocument136 pagesAveva PID Diagram Process Design Ensuring Consistency Between A Piping Instrumentation Diagram 3D Model Throiugh Aveva PID Diagram PDFbalajivangaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Significance of The StudyDocument2 pagesWriting Significance of The StudyKate BandohanPas encore d'évaluation