Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bluetooth Overview
Transféré par
Sumit KhilariDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bluetooth Overview
Transféré par
Sumit KhilariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bluetooth
Presenters: Group 6
Allan Alarcon, Ingrid Anderson, Bhupesh Kapoor, Shi-Wu Lee
- Name given to this new technology, set
to commercially come out this year
- It is a cable-replacement technology
- Technically, is a chip to be plugged
into computers, printers, mobile phones,
etc. Designed by taking the information
normally carried by the cable, and
transmitting it at a special frequency to a
receiver Bluetooth chip which will then
give information received to these
mobile devices.
History
History
The Bluetooth Special Interest Group
(SIG) was founded by Ericsson, IBM,
Intel, Nokia and Toshiba in February
1998 to develop as open specification for
short-range wireless connectivity.
Key Features:
Robustness, low complexity, low power
and low cost
Main Strength:
Ability to simultaneously handle
both data and voice transmissions such
as headset for voice calls.
Usage
Home: Having multiple PCs and need
for networks that are simple to install
and maintain
Commercially: Handhelds and other
mobile devices
Some System requirements:
- Universal framework to access
information across a diverse set of
devices
- Should offer similar protection as in
cables. There should not be any
compromises on security
- It should be simple, small and power
efficient for easy mobile usage
The standard requirement :
- must enable the devices to
establish ad hoc connections.
Wireless connectivity over Bluetooth
Works with: Any laptop, handheld PC or PDA with a spare Type II
PCMCIA slot
Operating Systems: Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows 98,
Windows 95 or Windows CE
Bluetooth Components
Four major components:
Radio Unit (radio transceiver)
Baseband Unit (flash memory
& CPU)
Software Stack (driver
software)
Application Software (user
interface)
Bluetooth Radio
Radio transceiver supports spectrum spreading and operates at a
frequency between 2.402 GHz - 2.480 GHz ISM band.
Spectrum spreading is accomplished by frequency hopping in 79
hops displaced by 1MHz. (maximum of 1600 hops/sec.)
Each device can optionally vary its transmitted antenna power
Device Power
Class
Max Output
Power (mW)
Max Output
Power (dBm)
Expected Range
(?Obstructed
Environment?)
Class 1 100mW 20dBm 100m
Class 2 2.5mW 4dBm 10m
Class 3 1mW 0dBm 10cm
Bluetooth Baseband
Better term: Link Controller Unit
Actual hardware unit which enables the physical link between devices
Implements baseband protocols and Link Manager (LM) routines.
link connection and power control
asynchronous and synchronous links
handles packets, paging and inquiry
applies a time-division duplex scheme (alternate transmit and
receive)
Connection Establishment
All devices are in Standby Mode by default, unconnected and
periodically scan for messages.
2 types of scans:
Page Scan - device is listening for Data Access Code (DAC)
used for set up connection
Inquiry Scan - device is listening for Inquiry Access Code (IAC)
used to discover which units are in range
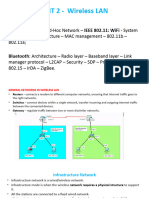
Bluetooth Network Topology
capable of point to point & point to multi-point connections
Piconet:
a master device
one to seven active slave units
a piconet channel
Scatternet:
a group of piconets, up to maximum of ten
a way of connecting a device to multiple masters
Full-duplex rate of more than 6Mb/s.
Link and Packet Types
2 types of physical links
Synchronous Connection-Oriented (SCO)
voice and data transmission, a point to point connection between a
master and a specific slave
Asynchronous Connection-Less (ACL)
data transmission only, a point to multi-point connection between a
master and all the active slaves
Bluetooth Capacities
Bluetooth can support:
one asynchronous data channel
asymmetric link of 723.2 kb/s in either direction while permitting
57.6 kb/s in the return direction
symmetric link of 433.9 kb/s
up to three simultaneous synchronous voice channels
each supports 64 kb/s in each direction
one channel which simultaneously supports asynchronous data and
synchronous voice
Note: D stands for Data , M stands for Medium rate , H stands for High rate
(All rates are in Kbits/sec)
Packet Type
Max Symmetric rate
(two way)
Max Forward
(Assymetric) rate
Max Reverse
(Assymetric) rate
DM1 108.8 108.8 108.8
DH1 172.8 172.8 172.8
DM3 258.1 387.2 54.4
DH3 390.4 585.6 86.4
DM5 286.7 477.8 36.3
DH5 433.9 723.2 57.6
AUX1 185.6 185.6 185.6
Connection Modes
4 Connection Modes
Active Mode: device is actively participating in a channel. Its
assigned an Active Member Address (AM_ADDR)
Hold Mode: maintains AM_ADDR. Supports synchronous but not
asynchronous packets
Sniff Mode: maintains AM_ADDR. Supports both synchronous and
asynchronous packets
Park Mode: no activity within a channel but remains synchronized to
a channel
Security Features
specification includes security features at the link level.
supports authentication (unidirectional or mutual) and
encryption.
devices transmit on the heavily used, unlicensed 2.45 GHz
radio band ( the same used by microwaves.)
to keep transmission from breaking up, frequency hopping
is employed.
Security Features contd
Each Bluetooth device has a unique address
Associating the ID with a person facilitates tracking
i.e. individuals can be traced and their activities easily logged.
For Bluetooth devices to communicate, an initialization process uses a
PIN.
While some devices allow users to punch in an ID number, the PIN
can also be stored in the non-volatile memory of the device
Security Modes
Bluetooth security is divided into three
modes:
Security Mode 1: non-secure
Security Mode 2: service level enforced security
Security Mode 3: link level enforced security
Security Architecture
Security Implementation within the Architecture
Two possible security
modes for devices:
Trusted Device
Such a device would have
access to all services for which
the trust relationship has been
set.
Untrusted Device
Such a device would have
restricted access to services.
Three levels of security for
services:
Authorisation Required
access granted to trusted
devices
Authentication Required
the remote device must be
authenticated
Encryption Required
The link must be changed to
encrypted mode, before access
to the service is possible
Potential Weaknesses
PIN code problems
Spoofing due to non-secret link key
Spoofing Bluetooth device addresses
Limited transport in 2.4 GHz band.
Mbps for BlueTooth. Need higher
rate for Local Area Networks.
(sending graphics to be printed)
mutual perturbation (cross-talk) of
corresponding office equipment
within a same building
frequency hopping provides some
level of security, confidentiality
may be compromised via currently
available decoder technology.
Bluetooth is WPAN (Wireless
Personal Area Network) not LAN
replacement. low cost, low profile,
low power wireless link for
convenience
BT not designed for large file nor
fast transfer; for mobility and
convenience
wireless devices always have
security issues, but BTs range is
10 meters need to be within this
range to pick up transmission
Drawbacks Benefits
Higher frequency 60GHz:
a. free world wide
b. less cross talk thus more
confidentiality of transmitted
information
c. larger bandwidth than 2.4 GHz
60 GHz - Not Cost Effective
(potentially higher cost of
necessary adapters. Power drain
and may be larger in size.
BlueTooth designed to circumvent
these issues. Cheap, low power,
and convenient.
Drawbacks Benefits
Compatibility of BlueTooth: Upgrade to BT
PC's quite easy. Bluetooth PCMCIA cards, USB connectors etc. are
developed at this stage, thus only a matter of installing the device, and
loading up some bluetooth software
Upgrade PDAs with BlueTooth add-on chips or buy PDAs with chip
already in place
current Mobile Phones may not be upgraded , due to their cheap cost
and relativity limited complexity, and lack an interface for any kind of
bluetooth device (such as a USB port). Although Ericsson will be
offering a bluetooth chip add-on.
Future : Is it already here?
Bluetooth vs Airport (802.11)
1MB/sec, 10 meters, 7 active
devices
can be used wherever you are
home, office or on the move.
(PDA, mobile phone)
Cheap; various applications to
drive the price down
(electronics, telecoms,
automotive and computing)
BT future revision may be as a
high speed network solution
10 MB/sec, 50 meters, 10 active
devices
wireless networking only
pricer
higher speed wireless
networking solution
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument72 pagesBluetooth SecurityPalash BalaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth SecurityDocument72 pagesBluetooth Securityabhi_badPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Voice Communication Interference With Ieee 802.11 ModelingDocument72 pagesBluetooth Voice Communication Interference With Ieee 802.11 ModelingHaruna TofaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth 121219060937 Phpapp01Document15 pagesBluetooth 121219060937 Phpapp01Rit HoanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch3. ConnectivityDocument70 pagesCh3. ConnectivityMohan RajPas encore d'évaluation
- BluetoothDocument23 pagesBluetoothjaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 BluetoothDocument75 pagesUnit 6 BluetoothHimaBindu ValivetiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooh Based Smart Sensor Networks - PresentationDocument27 pagesBluetooh Based Smart Sensor Networks - PresentationTarandeep Singh100% (7)
- Bluetooth Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument50 pagesBluetooth Based Wireless Sensor NetworksDegusa PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology PresentationDocument29 pagesBluetooth Technology PresentationMihai BogdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology Prepared By: SunilDocument32 pagesBluetooth Technology Prepared By: SunilSurya6556Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth PresentatioDocument17 pagesBluetooth PresentatioCHPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology Seminar Report PDFDocument21 pagesBluetooth Technology Seminar Report PDFSuvankar DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument24 pagesBluetooth TechnologyAbhishekPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth TechnologiesDocument21 pagesBluetooth TechnologiespoojaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetoothtechnology 1Document26 pagesBluetoothtechnology 1Rahul NairPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth: Wire Less TechnologyDocument13 pagesBluetooth: Wire Less Technologykrishna495Pas encore d'évaluation
- BT TECHNOLOGY SECURITYDocument34 pagesBT TECHNOLOGY SECURITYGanesh KwaradiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology How It WorksDocument12 pagesBluetooth Technology How It WorksnitsugaeugenePas encore d'évaluation
- BLUETOOTH SECURITY BY Jim BurleyDocument11 pagesBLUETOOTH SECURITY BY Jim BurleyHanmanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch3. BluetoothDocument18 pagesCh3. BluetoothAnkita MitraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument23 pagesBluetooth TechnologyBittuPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth 1Document10 pagesBluetooth 1Aparna JindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth TechDocument23 pagesBluetooth Techapi-3746880100% (1)
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument13 pagesBluetooth TechnologysneharachPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology ExplainedDocument26 pagesBluetooth Technology ExplainedSayan RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of Award of Degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science and EngineeringDocument22 pagesSubmitted in Partial Fulfillment of Award of Degree of Bachelor of Technology in Computer Science and EngineeringAmol ChaudhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Wireless Personal Area NetwoksDocument40 pagesWireless Personal Area NetwoksRanjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology in Wireless CommunicationsDocument8 pagesBluetooth Technology in Wireless CommunicationsVignesh SbPas encore d'évaluation
- WINSEM2022-23 CSE3009 ETH VL2022230503000 2023-02-02 Reference-Material-IDocument54 pagesWINSEM2022-23 CSE3009 ETH VL2022230503000 2023-02-02 Reference-Material-IArvind KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- 1hk17is072 Technical SeminarDocument24 pages1hk17is072 Technical SeminarSheba BegumPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth TechnologyDocument17 pagesBluetooth TechnologyAbhinay GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project On Bluetooth Technology: Presented ByDocument9 pagesProject On Bluetooth Technology: Presented BySanjeev Kumar SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- BluetoothDocument39 pagesBluetoothਗੁਰਪਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘ ਸੂਰਾਪੁਰੀPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 15networking DevicesDocument33 pagesLec 15networking DevicesJyoti SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology: A Wireless RevolutionDocument29 pagesBluetooth Technology: A Wireless RevolutionHonest ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technology Seminar ReportDocument23 pagesBluetooth Technology Seminar ReportAbhinav KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lect56ccs312cct306 Feb2023Document57 pagesLect56ccs312cct306 Feb2023maryallaine02Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Vs ZigbeeDocument20 pagesBluetooth Vs ZigbeeZarnigar AltafPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Based Sensor Network: A Technical Seminar Presentation OnDocument17 pagesBluetooth Based Sensor Network: A Technical Seminar Presentation OnDipak AryalPas encore d'évaluation
- BluetoothDocument7 pagesBluetoothmritunjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Blah Blah VlamDocument15 pagesBlah Blah VlambikuttanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth CiaDocument4 pagesBluetooth CiaMegha LakhawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth: Quote of The DayDocument8 pagesBluetooth: Quote of The DayShahid MehmoodPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar TopicsDocument15 pagesSeminar TopicsUsha MarigoudarPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth DelatorreDocument11 pagesBluetooth DelatorreGinu Rodavia Dela TorrePas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Tutorial: Center For Wireless TelecommunicationsDocument46 pagesBluetooth Tutorial: Center For Wireless TelecommunicationsCristna UllfigPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth Technical Report SummaryDocument13 pagesBluetooth Technical Report SummaryK.Rohit GoudPas encore d'évaluation
- MN - Unit 2Document50 pagesMN - Unit 212c04gokulsboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bluetooth PrakashDocument18 pagesBluetooth PrakashLoverboy6556Pas encore d'évaluation
- BluetoothDocument10 pagesBluetoothHOD-DCE PSG-PTCPas encore d'évaluation
- WlanDocument8 pagesWlanLibya ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1D'EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Cisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewD'EverandCisco Network Administration Interview Questions: CISCO CCNA Certification ReviewÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (6)
- India. A STUDY ON CONSUMER PREFERENCES FOR COCA COLADocument43 pagesIndia. A STUDY ON CONSUMER PREFERENCES FOR COCA COLADoru PosticaPas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile IndustryDocument31 pagesAutomobile IndustrySumit KhilariPas encore d'évaluation
- Capital Budgeting Case Study of Heavy-Duty TractorsDocument4 pagesCapital Budgeting Case Study of Heavy-Duty TractorsSumit KhilariPas encore d'évaluation
- New Microsoft Office Word Document Auto Saved)Document3 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word Document Auto Saved)Sumit KhilariPas encore d'évaluation
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentSumit KhilariPas encore d'évaluation
- DMDocument45 pagesDMSumit KhilariPas encore d'évaluation
- Venus X1 User Manual GuideDocument109 pagesVenus X1 User Manual GuideRodrigoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Arinc 818Document4 pagesWhat Is Arinc 818Prasanna RamamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Antares Articulator Setup Manual How ToDocument23 pagesAntares Articulator Setup Manual How ToPete Mills100% (2)
- Class 4 ComputerDocument3 pagesClass 4 ComputerumeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Samsung Printer and Toner May Price List - DealerDocument8 pagesSamsung Printer and Toner May Price List - DealerYu PohChu100% (1)
- Konica Minolta Bizhub 600 BrochureDocument8 pagesKonica Minolta Bizhub 600 BrochureToñito MedranoPas encore d'évaluation
- AVTech DR046Document2 pagesAVTech DR046Elena Carmen StoicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet Barcode Scanners BCP 8000Document2 pagesDatasheet Barcode Scanners BCP 8000Arif Saeed BhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Communication and Computer Networks: CSC339 by Faiza AkramDocument26 pagesData Communication and Computer Networks: CSC339 by Faiza AkramHack MafiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Auto Script BrochureDocument24 pagesAuto Script BrochureMalay K GhoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Arabsat Channels PDFDocument14 pagesArabsat Channels PDFPapa MouhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Want To Obtain Optimum Picture Quality With Your SAMSUNG Ultra HD Blu-Ray Player?Document2 pagesWant To Obtain Optimum Picture Quality With Your SAMSUNG Ultra HD Blu-Ray Player?fuilkjPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networks: NameDocument1 pageComputer Networks: NameHafizPradanaGemilangPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is VoIPDocument3 pagesWhat Is VoIPkazitamjidaliPas encore d'évaluation
- USB Mass Storage Implmnt ARM7 CoresDocument8 pagesUSB Mass Storage Implmnt ARM7 CoresVaseem AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Registrar of Voters OfficesDocument8 pagesRegistrar of Voters OfficesJimTuckerforLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Layering Scenario and Network ProtocolsDocument51 pagesLayering Scenario and Network ProtocolsAkhila VeerabommalaPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Network Operating SystemDocument5 pagesWhat Is A Network Operating Systemvolaa100% (1)
- Google Hacking Database Finds Various Online DevicesDocument4 pagesGoogle Hacking Database Finds Various Online Devicesworkmumbai3870Pas encore d'évaluation
- Take Better People Pictures!: ExclusiveDocument166 pagesTake Better People Pictures!: Exclusiveapi-3808225Pas encore d'évaluation
- MHP GuideDocument215 pagesMHP Guidemark.minnoye100% (3)
- HP System Diagnostics Failure Code GuideDocument11 pagesHP System Diagnostics Failure Code GuideAlcyoneSpiral100% (1)
- Akai LCD TV Lct3201td - Service MasnualDocument108 pagesAkai LCD TV Lct3201td - Service MasnualMario Rodriguez JuradoPas encore d'évaluation
- TP Link TD-W8968 - V3 User GuideDocument115 pagesTP Link TD-W8968 - V3 User GuideKaran Singh BaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Get Free Office 365 ProPlus for StudentsDocument3 pagesGet Free Office 365 ProPlus for Studentsallkhusairy6tuansiPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer POST / Beep Codes: IT AlleyDocument8 pagesComputer POST / Beep Codes: IT AlleyEko Putra SentosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Top 100 best-selling consumer electronics productsDocument21 pagesTop 100 best-selling consumer electronics productsAgustín Antonio Sulgati GrillPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 1 DCNDocument3 pagesQuiz 1 DCNAakif BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Canon Pixma Ip8500 Printer Service ManualDocument38 pagesCanon Pixma Ip8500 Printer Service Manualbutch_phelps100% (1)