Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
08CLecture - Welding Codes Standards
Transféré par
David Huaman0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
445 vues15 pagesA standard can be defined as a set of technical definitions and guidelines. A Code becomes a Code when it has been adopted by one or more governmental bodies. One could say that welding-codes are essentially enforced specifications.
Description originale:
Titre original
08CLecture - Welding Codes Standards[1]
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentA standard can be defined as a set of technical definitions and guidelines. A Code becomes a Code when it has been adopted by one or more governmental bodies. One could say that welding-codes are essentially enforced specifications.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
445 vues15 pages08CLecture - Welding Codes Standards
Transféré par
David HuamanA standard can be defined as a set of technical definitions and guidelines. A Code becomes a Code when it has been adopted by one or more governmental bodies. One could say that welding-codes are essentially enforced specifications.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 15
1
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Standards, Codes and Specifications
1. Standard
A Standard can be defined as a set of technical definitions and guidelines
that function as instructions for designers, manufacturers, operators, or
users of equipment.
2. Code
A standard becomes a Code when it has been adopted by one or more
governmental bodies and is enforceable by law, or when it has been
incorporated into a business contract.
3. Specifications
Specifications cover requirements for voluntary adoption and no
enforcement is meant unless they are agreed upon between procuring
agency and contractor as spelled out in a Purchase Order. One could say
that Welding-codes are essentially enforced Specifications.
2
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Products Utilizing Welding Specifications
1. Pressure Vessels
2. Nuclear Reactor
3. Piping and Pipe lines
4. Buildings and bridges
5. Storage Tanks and vessels
6. Ships, barges, offshore drill rigs
7. Railroad rolling stock
8. Aircraft and spacecraft
9. Automotive and trucks
10. Construction and Agricultural Equipment
11. Industrial Machinery
12. Shipping Container
13. Ordnance Material
14. Non Structural Sheet Metal Components and systems
15. Miscellaneous Equipment
3
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Products Utilizing Welding Specifications
1. Pressure Vessels ASME Boiler & Pressure Vessel Code
i. Section I Rules for construction of Power Boilers
ii. Section II Material Specification (Four sub-sections)
iii. Section III Nuclear Power Plant Components
iv. Section IV Heating Boilers
v. Section V Non Destructive Examination
vi. Section VI Recommended Rules for care and operation of heating
boilers
vii. Section VII Recommended Rules for care of Power Boilers
viii. Section VIII Pressure Vessels (Div I and Div II)
ix. Section IX Welding and Brazing Qualifications
x. Section X Fiber Glass Reinforced plastic pressure vessel
xi. Section XI Rules for inservice inspection of nuclear reactor coolant
system
Code Symbol Stamps (N Nuclear Vessel, PP Pressure Piping, U Pressure
Vessel, S Power Boilers, H Heating Boilers)
4
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Products Utilizing Welding Specifications
2. Piping
i. B 31.1 Power Piping
ii. B 31.2 Fuel Gas Piping
iii. B 31.3 Process Piping
iv. B 31.4 Pipeline Transportation Systems for Liquid Hydrocarbons
and other Liquids
v. B 31.5 Refrigeration Piping and Heat Transfer Components
vi. B 31.8 Gas Transportation and Distribution Piping System
vii. B 31.8S Managing System Integrity of Gas Pipeline
viii. B 31.9 Building Services Pakistan
ix. B 31.11 Slurry Transportation Piping System
x. B 31G Manual for Determining Remaining Strength of Corroded
Pipelines
5
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Products Utilizing Welding Specifications
3. Nuclear Reactors
Section III ASME BPV code (Material Specification)
Quality Assurance Criteria for Nuclear Power Plants and Fuel Reprocessing Plants Code of
Federal Regulations, Section 10, Energy Part 50
Standard for welding of Reactor Coolant and Associated Systems and Components for
Naval Nuclear Power Plants, Department of defense Naval Ship Division
4. Building and Bridges
City Code and Specifications
AWS D1.1 Structural Welding Code Steel
AWS D1.2 Structural Welding Code Aluminum
AWS D1.4 Code for Welding Reinforcing Steel
AWS D1.5 Bridge Welding Code
AISC Manual of Steel Construction Allowable Stress Design (American Institute of Steel
Construction)
5. Storage Tanks and Vessel
AWS D5.2 Standard for Welded Steel Elevated Tanks, Stand Pipes and Reservoir for Water
Storage
API 650 Standard for Welded Steel Tanks for Oil Storage
6
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Products Utilizing Welding Specifications
6. Ships
AWS D3.5 Guide for Steel Hull Welding
AWS D3.7 Guide for Aluminum Hull Welding
US Coast Guard, Department of Transportation Marine Engineering Regulations
US Department of Navy, Naval Ship Systems Command, Fabrication, Welding and
Inspection of Ship Hulls
US Maritime Administration, Standard Specification for Merchant Ship Construction
7. Railroad Rolling Stock
Association of American Rail Roads Specification for Tank Cars
Association of American Rail Roads Specification for Design, Fabrication and Construction
of Freight Cars
AWS D15.1 Railroad Welding Specification
8. Aircraft and Spacecraft
SAE Aerospace Material Specifications
Aerospace Industries Association of America, National Aerospace Standards
MIL Standard MIL-T-1595A Qualification of Aircraft, Missile and Aerospace Fusion Welders
9. Automotive and Trucks
AWS D8.7Recommended Practices for Automotive Weld Quality Resistance Spot Quality
7
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Products Utilizing Welding Specifications
10. Construction Equipment
AWS D14.3 Specification for Welding Industrial and Mill Cranes and Other Material
Handling Equipment
11. Industrial Machinery
AWS D14.2 Specification for Welding Metal Cutting Machine Tool Weldments
AWS D14.4 Classification and Application of Welded Joints for Machinery and Equipment
AWS D14.5 Specifications for Welding Presses and Press Components
AWS D14.6 Specifications for Rotating Elements of Equipment
8
Reliability in Weldments Procedure and Performance Qulaifications
1. Refer to a relevant standard for
a. Type of tests required for qualification
b. Details of test coupons
c. Location and details of specimen etc
2. Common Standards providing such details are as under
a. ASME BPV code Section IX ie Welding and Brazing
Qualifications
b. AWS B3.0 Welding Procedure and Performance Qualification
c. AWS B4.0 Standard Methods for Mechanical Testing of Welds
3. Common Standards for Fabrication
a. ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel (BPV) Code
b. ASME B31 Pressure Piping Code
c. ASNI/AWS D1.1 Structural Welding Code
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
9
Procedure and Welder Qualifications
1. ASME SEC IX
i. Part QW - Welding
ii. Part QB - Brazing
2. Part QW - Welding
i. Article I Welding General Requirements
ii. Article II Welding Procedure Qualifications
iii. Article III Welding Performance Qualification
iv. Article IV Welding Data
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
10
A Review of ASME Sec IX Test Requirements
1. Article I Welding General Requirements
i. QW 120 Test Positions for Groove Welds
ii. QW 130 Test Positions for Fillet Welds
iii. QW 140 Types and Purpose of Tests and Examinations
iv. QW 150 ~190 Tension Tests, Bend Tests etc
*** Welding Variables & Acceptance Criteria
2. Article II Welding Procedure Qualifications
i. QW 200 General
ii. QW 210 Preparation of Test Coupons
iii. QW 250 Welding Variables
3. Article III Welding Performance Qualification
i. QW 310 Qualification Test coupons
ii. QW 320 Retests and Renewal of Qualifications
4. Article IV Welding Data
1. QW 450 Specimen
2. QW 460 Graphics
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
11
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Weld Reliability
1. Key to maintaining reliability in weldments (ASME Sec IX)
i. Welding Procedure Specifications : A WPS is a written qualified welding
procedure prepared to provide direction for making production welds to Code
requirements. The completed WPS shall describe all of the essential,
nonessential, and, when required, supplementary essential variables for each
welding process used in the WPS
ii. Procedure Qualification Record : A PQR is a record of the welding data used
to weld a test coupon. The PQR is a record of variables recorded during the
welding of the test coupons. It also contains the test results of the tested
specimens. Recorded variables normally fall within a small range of the actual
variables that will be used in production welding.
iii. Welder/Welding Operator Performance Qualification : the basic criterion
established for welder qualification is to determine the welders ability to deposit
sound weld metal. The purpose of the performance qualification test for the
welding operator is to determine the welding operators mechanical ability to
operate the welding equipment.
12
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Weld Reliability
1. Welding Variables:
i. Essential Variables. are those in which a change, as described in the
specific variables, is considered to affect the mechanical properties of the
weldment, and shall require requalification of the WPS.
ii. Supplementary essential variables are required for metals for which other
Sections specify notch-toughness tests and are in addition to the essential
variables for each welding process.
iii. Nonessential variables are those in which a change, as described in the
specific variables, may be made in the WPS without requalification.
13
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
14
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
15
A Review of ASME Sec IX Example Problem
1. You have finalized a contract with one of your customers for the fabrication
of a pressure vessel, design being provided by customer design department.
Design engineers have specified a 6 mm minimum thickness for plates. Both
groove and fillet welds are required. Under the terms of contract all
construction should conform to ASME BPV code.
i. Which sections you must refer to for qualification of welding procedure
and welders
ii. What type and number of tests are required
iii. Where do you get information about size of test of coupons and order of
removal for test specimen
iv. Where do you find the acceptance criteria for tested specimen
The customer concludes another contract for the fabrication of a pressure
vessel under BPV code, using similar material but a thickness of 8mm.
i. What types and number of tests you must perform
INTRODUCTION TO WELDING CODES, STANDARDS
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Presentation Asme Sec Ix Wps PQR WPQDocument177 pagesPresentation Asme Sec Ix Wps PQR WPQM A67% (3)
- Part 02 - Review of PWPS and WPSDocument9 pagesPart 02 - Review of PWPS and WPSYan FerizalPas encore d'évaluation
- Boliers and Pressure VesselsDocument33 pagesBoliers and Pressure VesselslourencePas encore d'évaluation
- Gtaw NC Ii TR PDFDocument62 pagesGtaw NC Ii TR PDFRocz RocoPas encore d'évaluation
- Piping Inspection Basics For The BeginnersDocument6 pagesPiping Inspection Basics For The Beginnersramyatan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Asme Viii 1 - PWHT PDFDocument1 pageAsme Viii 1 - PWHT PDFGANGADHAR SAHUPas encore d'évaluation
- Shielded Metal Arc WeldingDocument39 pagesShielded Metal Arc Weldingعزت عبد المنعم100% (1)
- Hydro Testing + Post Weld Heat TreatmentDocument20 pagesHydro Testing + Post Weld Heat TreatmentRafia ZafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Static Equipment in Oil and Gas IndustryDocument93 pagesStatic Equipment in Oil and Gas IndustryRaghavanPas encore d'évaluation
- تقنية اللحام نظريDocument104 pagesتقنية اللحام نظريmecherguiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To BoilersDocument25 pagesIntroduction To BoilersDamith Buddhika Sri WimalarathnaPas encore d'évaluation
- API653 Feb12Document4 pagesAPI653 Feb12Amair CoolPas encore d'évaluation
- 09 Sec 09 - ASME IX Summary-07revisedCCDocument38 pages09 Sec 09 - ASME IX Summary-07revisedCCamalhaj2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Earthing of Gas PipelinesDocument5 pagesEarthing of Gas PipelinesAnonymous YPpAb2KPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Year 3Document27 pagesChapter 4 Year 3Mohd SoufianPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding Codes, Standards & SpecificationsDocument62 pagesWelding Codes, Standards & SpecificationsSam100% (1)
- Flexpipe PDS FlexCord EnglishDocument2 pagesFlexpipe PDS FlexCord EnglishpsycopaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Asmepcc 2repairleaks Article 4Document23 pagesAsmepcc 2repairleaks Article 4amalhaj2013Pas encore d'évaluation
- Inspection of Heat ExchangerDocument83 pagesInspection of Heat ExchangerRaghavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Welcome To: Training Program On GUIDED TOUR OF Asme CodesDocument120 pagesWelcome To: Training Program On GUIDED TOUR OF Asme CodesDiego HenriquePas encore d'évaluation
- Hydro Test ProcedureDocument6 pagesHydro Test Procedurevijay padalePas encore d'évaluation
- Astm 890Document3 pagesAstm 890bsnegi111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 11 Corrosion CalculationsDocument33 pagesLesson 11 Corrosion Calculationsعزت عبد المنعمPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1.1.1 Boiler-General InspectionDocument46 pages2.1.1.1 Boiler-General InspectionSulistyo PujionoPas encore d'évaluation
- API 510-Kuwait PetroleumDocument392 pagesAPI 510-Kuwait PetroleumVijay Kumar100% (1)
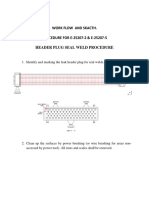
- Header Plug Seal Weld ProcedureDocument3 pagesHeader Plug Seal Weld ProcedureMohd Shafuaaz Kassim100% (1)
- PTI Piping Training Day 1 Rev.0Document84 pagesPTI Piping Training Day 1 Rev.0Karl Caudal100% (1)
- Wrapping MethodDocument5 pagesWrapping Methodnnuek67% (3)
- Trepanning Positioning Welding ManualDocument14 pagesTrepanning Positioning Welding ManualGovindan PerumalPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 6 B31.3 330 Preheating: Haward Technology Middle East 1 Section 6Document37 pagesSection 6 B31.3 330 Preheating: Haward Technology Middle East 1 Section 6Mohamed ElsayedPas encore d'évaluation
- QC Inspector (Offshore Pipeline Installation) Jobs in Propel Consult in UAE - United Arab Emirates - NaukrigulfDocument7 pagesQC Inspector (Offshore Pipeline Installation) Jobs in Propel Consult in UAE - United Arab Emirates - NaukrigulfAshif IqubalPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan For Training of Pipe Fitter & PlumberDocument116 pagesLesson Plan For Training of Pipe Fitter & PlumberAbu AnoopPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintanance of Spring Hanger by PTDocument2 pagesMaintanance of Spring Hanger by PTRagu NathanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reapir and Altertaion Section 8Document52 pagesReapir and Altertaion Section 8waqas pirachaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipework Pretest Checklist (Empty)Document1 pagePipework Pretest Checklist (Empty)Jorge GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Brochure API 570 Piping Inspector Preparation Xpress Course DescriptionDocument9 pagesBrochure API 570 Piping Inspector Preparation Xpress Course DescriptionINSTECH ConsultingPas encore d'évaluation
- Annealing (Metallurgy) WikiDocument4 pagesAnnealing (Metallurgy) WikiStephen MonteleprePas encore d'évaluation
- Asme Sec 9 - ADocument144 pagesAsme Sec 9 - Aروشان فاطمة روشانPas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Fittings and Piping AuxiliariesDocument38 pagesPipe Fittings and Piping Auxiliariesmsaad2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3 High Frequency WeldingDocument15 pagesLecture 3 High Frequency WeldingFaiz Ishak100% (1)
- Pressure Vessel InspectionsDocument8 pagesPressure Vessel InspectionsCepi Sindang KamulanPas encore d'évaluation
- Scope ASME Section Requirements For Boiler ASME StampDocument3 pagesScope ASME Section Requirements For Boiler ASME StampThineshraaj Naidu JayaramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pumps, Compressors, Turbines Operation, Maintenance & TroubleshootingDocument2 pagesPumps, Compressors, Turbines Operation, Maintenance & Troubleshootingm_alodat6144100% (1)
- Bolt Torquing SpecialistDocument2 pagesBolt Torquing SpecialistMarkus Landington100% (1)
- Rev00-Gasket Installation & Bolt Torquing ProcedureDocument24 pagesRev00-Gasket Installation & Bolt Torquing ProcedureHansel FrancisPas encore d'évaluation
- ASME BrochureDocument2 pagesASME BrochureumeshPas encore d'évaluation
- MNT-INTG-2007OP - Maintenance Welding InspectionDocument43 pagesMNT-INTG-2007OP - Maintenance Welding InspectionNatarajan MurugesanPas encore d'évaluation
- BPQ REV. 0 Interactive FormDocument2 pagesBPQ REV. 0 Interactive FormcosmicbunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction & Pipeline CoatingsDocument67 pagesConstruction & Pipeline CoatingsDi100% (1)
- 5.piping SeminarDocument85 pages5.piping Seminarvg100% (2)
- Rehabilitation of Yanbu South Terminal Projects BI # 10-00567Document12 pagesRehabilitation of Yanbu South Terminal Projects BI # 10-00567qazi12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bolt Torquing and - TensioningDocument22 pagesBolt Torquing and - TensioningDaniel Martinez100% (1)
- WeldingDocument23 pagesWeldingBilal TayyabPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding SupervisorDocument2 pagesWelding SupervisorSantosh Latake100% (1)
- Kumho ABS 750SWDocument3 pagesKumho ABS 750SWVu TranPas encore d'évaluation
- SMAW Electrode IdentificationDocument2 pagesSMAW Electrode IdentificationAsim AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Asme Sec Ix - Short NotesDocument20 pagesAsme Sec Ix - Short NotesParvee K NakwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation Asme Sec-Ix Wps PQR Wpq..Document176 pagesPresentation Asme Sec-Ix Wps PQR Wpq..Utkarsh GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Section IX WeldingDocument6 pagesSection IX WeldingAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 06B OxyAcetylene - CuttingDocument10 pages06B OxyAcetylene - CuttingDavid HuamanPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 BDissimilar Welds ReadingsDocument15 pages07 BDissimilar Welds ReadingsDavid HuamanPas encore d'évaluation
- 08BLecture - WeldTestingDocument28 pages08BLecture - WeldTestingDavid HuamanPas encore d'évaluation
- 08BLecture - WeldTestingDocument28 pages08BLecture - WeldTestingDavid HuamanPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 BDissimilar Welds ReadingsDocument15 pages07 BDissimilar Welds ReadingsDavid HuamanPas encore d'évaluation
- HBS - Zara Fast Fashion Case Write UpDocument4 pagesHBS - Zara Fast Fashion Case Write Upaaronhwalton100% (1)
- VRF Mv6R: Heat Recovery Outdoor UnitsDocument10 pagesVRF Mv6R: Heat Recovery Outdoor UnitsTony NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Expansions Meet Health Care Needs: Economists Question Trump Plan FiguresDocument10 pagesExpansions Meet Health Care Needs: Economists Question Trump Plan FiguresThe Daily Tar HeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Preliminary Voters ListDocument86 pagesPreliminary Voters Listمحمد منيب عبادPas encore d'évaluation
- Hotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahDocument2 pagesHotel Voucher: Itinerary ID Hotel Santika Taman Mini Indonesia IndahSyukron PribadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pe8 Mod5Document16 pagesPe8 Mod5Cryzel MuniPas encore d'évaluation
- Geography Paper 1Document7 pagesGeography Paper 1Sudhir TewatiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendicitis Case StudyDocument6 pagesAppendicitis Case StudyKimxi Chiu LimPas encore d'évaluation
- File 1) GRE 2009 From - Nov - 18 PDFDocument84 pagesFile 1) GRE 2009 From - Nov - 18 PDFhuyly34Pas encore d'évaluation
- Van Daley - Leadership ResumeDocument1 pageVan Daley - Leadership Resumeapi-352146181Pas encore d'évaluation
- Caterpillar Sis (01.2014) MultilanguageDocument10 pagesCaterpillar Sis (01.2014) MultilanguageTemmy Candra Wijaya100% (1)
- Dphs Freshman Course List 2024-25Document1 pageDphs Freshman Course List 2024-25api-337771649Pas encore d'évaluation
- Day 1 Training Material FlowDocument200 pagesDay 1 Training Material FlowGhazouani AymenPas encore d'évaluation
- COSO DefinEDDocument21 pagesCOSO DefinEDRefdy AnugrahPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer For Bookkeeping NCIIIDocument18 pagesReviewer For Bookkeeping NCIIIAngelica Faye95% (20)
- CE Laws L8 L15Document470 pagesCE Laws L8 L15Edwin BernatPas encore d'évaluation
- Shaft DeflectionDocument15 pagesShaft Deflectionfreek_jamesPas encore d'évaluation
- 28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsDocument14 pages28 ESL Discussion Topics Adult StudentsniallPas encore d'évaluation
- Norma Geral Astm Bronze Alumínio - b150b150m.19198Document7 pagesNorma Geral Astm Bronze Alumínio - b150b150m.19198EduardoPas encore d'évaluation
- 7273X 47 ITOW Mozart PDFDocument3 pages7273X 47 ITOW Mozart PDFAdrian KranjcevicPas encore d'évaluation
- Edug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - CompletedDocument37 pagesEdug 899 - Grade 2 Forces and Motion Unit - Completedapi-241358660Pas encore d'évaluation
- SmoothWall Express 2.0 Quick-Start GuideDocument6 pagesSmoothWall Express 2.0 Quick-Start Guideinfobits100% (1)
- Daewoo SJ-210H DSJ-6000LHMDocument44 pagesDaewoo SJ-210H DSJ-6000LHMMarco Antonio100% (5)
- Final Lab Manual Main Ars 200280705008Document6 pagesFinal Lab Manual Main Ars 200280705008shalini pathakPas encore d'évaluation
- THE Ketofeed Diet Book v2Document43 pagesTHE Ketofeed Diet Book v2jacosta12100% (1)
- (IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630Document43 pages(IGC 2024) 2nd Circular - 0630VictoriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper Format IJRDTDocument3 pagesPaper Format IJRDTrock starPas encore d'évaluation
- H I Ôn Thi Aptis & Vstep - Tài Liệu - Anna MaiDocument4 pagesH I Ôn Thi Aptis & Vstep - Tài Liệu - Anna Maihanh.mt2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stating Like and DislikesDocument2 pagesStating Like and DislikesDavid ArdiantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculate Breakeven Point in Units and Revenue Dollars: Intermediate Cost Analysis and ManagementDocument52 pagesCalculate Breakeven Point in Units and Revenue Dollars: Intermediate Cost Analysis and ManagementNavice Kie100% (1)