Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 06 IC Fabrication - An Introduction
Transféré par
Udai Singh0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues37 pagesIC Fabrication - an introduction jau-wen lin, ph.d. Explains the fabrication process. A logic circuit diagram is drawn to determine the electronic circuit required for the requested function. The photomask is a copy of the circuit pattern, drawn on a glass plate coated with a metallic film.
Description originale:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentIC Fabrication - an introduction jau-wen lin, ph.d. Explains the fabrication process. A logic circuit diagram is drawn to determine the electronic circuit required for the requested function. The photomask is a copy of the circuit pattern, drawn on a glass plate coated with a metallic film.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
24 vues37 pagesChapter 06 IC Fabrication - An Introduction
Transféré par
Udai SinghIC Fabrication - an introduction jau-wen lin, ph.d. Explains the fabrication process. A logic circuit diagram is drawn to determine the electronic circuit required for the requested function. The photomask is a copy of the circuit pattern, drawn on a glass plate coated with a metallic film.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 37
IC Fabrication An Introduction
Jau-Wen Lin, Ph. D.
Integrated circuit showing
memory blocks, logic and
input/output pads around
the periphery
Six Level of
Interconnection
drain
IC device
Silicon chip
High lead solder die attach
Tin/lead plated copper
leadframe
Semiconductor Applications
3C : Computer--- /Communication / Consumables
Personal Computer--- Desktop Computer (DT) /
Notebook (NB)
Communication---
ADSL / Cable Modem /
IEEE802.11X / Bluetooth / VoIP
Consumables---
Game / DVD / Digital Camera
3C merge--- Digital Home
Types of Chips
Dynamic Random Access Memory chips
(DRAMs) - serve as the primary memory for
computers
Microprocessors (MPUs) - act as the brains of
computers.
Application Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs)
- are custom semiconductors designed for very specific
functions
Digital Signal Processors (DSPs) - process signals,
such as image and sound signals or radar pulses.
Programmable memory chips (EPROMs,
EEPROMs, and Flash) - are used to perform
functions that require programming on the chip.
Front-End Processing (Wafer fabrication)
Back-End Processing (Assembly and
Testing)
Semiconductor Fabrication
Processes
A logic circuit diagram is drawn to determine the
electronic circuit required for the requested function.
Once the logic circuit diagram is complete,
simulations are performed multiple times to test the
circuits operation.
Logic Circuit Design / Layout
Design
Photomask Creation
The photomask is a copy of the circuit pattern,
drawn on a glass plate coated with a metallic film.
The glass plate lets light pass, but the metallic film
does not.
Due to increasingly high integration and
miniaturization of the pattern, the size of the
photomask is usually magnified four to ten times
the actual size.
The
photomask
of a RF IC
Chip
Wafer Fabrication
A high-purity, single-crystal silicon called
"99.999999999% (eleven-nine)" is grown from a
seed to an ingot.
The wafers are generally available in diameters of
150 mm, 200 mm, or 300 mm, and are mirror-
polished and rinsed before shipment from the
wafer manufacturer.
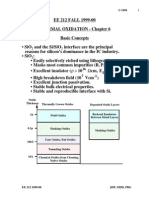
Deposition
the wafer is placed in a high-temperature furnace to
make the silicon react with oxygen or water vapor, and
to develop oxide films on the wafer surface (thermal
oxidation).
To develop nitride films and polysilicon films, the
chemical vapor deposition (CVD) method is used, in
which a gaseous reactant is introduced to the silicon
substrate, and chemical reaction produce the deposited
layer material.
The metallic layers used in the wiring of the circuit are
also formed by CVD, spattering (PVD: physical vapor
deposition)
Photoresist Coating
A resin called "photoresist" is coated over the
entire wafer. (~1m thick coating.)
Photoresist is a special resin similar in
behavior to photography films that changes
properties when exposed to light.
Masking/Exposure
Placed over the photoresist-coated wafer, which
is then irradiated to have the circuit diagram
transcribed onto it.
An irradiation device called the "stepper" is used
to irradiate the wafer through the mask with
ultraviolet (UV) light.
Lithography area in clean room
Patterning: Development
The photoresist chemically reacts and dissolves in the
developing solution, only on the parts that were not
masked during exposure (positive method).
Development is performed with an alkaline
developing solution.
After the development, photoresist is left on the
wafer surface in the shape of the mask pattern.
Etching
"Etching" refers to the physical or chemical etching
of oxide films and metallic films using the resist
pattern as a mask.
Etching with liquid chemicals is called "wet
etching" and etching with gas is called "dry
etching".
Photoresist Stripping
The photoresist remaining on the wafer surface
is no longer necessary after etching is complete.
Ashing by oxygen plasma or the likes is
performed to remove the residual photoresist.
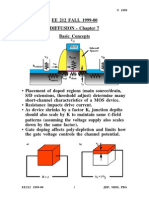
Device Insulation Layer (Field-
Oxide Film) Formation
After the oxide film and nitride film are
developed, a resist pattern is formed on the
regions that will become the device
insulation layer.
Ion implantation is performed on the wafer,
forming a p-type diffusion layer.
Next, the oxide film and nitride film on the
diffusion layer are etched.
Using the nitride film pattern as the mask,
the oxide film that will become the device
insulation layer is developed.
Transistor Formation
A transistor is a semiconductor device with a
switching function and three terminals:
source, drain, and gate.
An insulation layer called "gate oxide" is first
formed on the wafer surface.
A polysilicon film is deposited onto the gate
oxide, and a polysilicon gate for controlling
the flow of electrons between the source
region and the drain region is formed by
lithography and etching.
After the polysilicon gate is formed, an n-
type diffusion layer consisting of both the
source and the drain regions is formed by
implantation of impurities
Polysilicon Gate
Cross-Section Image
Metallization
Interconnecting the devices, such as transistors,
formed on the silicon wafer completes the circuit.
the wafer is first covered with a thick and flat
interlayer insulation film (oxide film). Next, contact
holes are drilled by lithograph and etching, through
the interlayer insulation film, above the devices to
be connected.
Nine-layer Copper Interconnect Architecture
Wafer Inspection
Each IC on the completed wafer is electronically
tested by the tester.
After this inspection, the front-end processing is
complete.
Dicing
In back end processing, a wafer completed in
front end processing is cut into individual IC
chips and encapsulated into packages.
Mounting
After the IC chips are cut apart, they
are sealed into packages. The IC
chips must first be attached to a
platform called the "lead frame.
Wire bonding
The mounted IC chips are connected to the
lead frames.
Encapsulation
The IC chips and the lead frame islands are
encapsulated with molding resin for
protection.
Characteristic Selection
The packaged IC chips are tested and
selected.
Printing and Lead Finish
The final step of IC chip manufacturing is the
printing onto the package surface and the
finishing of leads. After this step, the IC
chips are complete.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Deliveroo Tablet PDFDocument52 pagesDeliveroo Tablet PDFAnonymous ZRbij0qPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Photovoltaics - Planar and Nanostructured DevicesDocument111 pagesInorganic Photovoltaics - Planar and Nanostructured DevicesUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 - Chapter 1 PDFDocument37 pages08 - Chapter 1 PDFDeepak Chauhan100% (1)
- Semiconductor Physics Part II GATE Problem PDFDocument19 pagesSemiconductor Physics Part II GATE Problem PDFUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Jalcom S 18 03001Document28 pagesJalcom S 18 03001Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Electronics PDFDocument224 pagesDigital Electronics PDFSruthy Arun100% (1)
- Multiple Choice Questions PNJunctionDocument2 pagesMultiple Choice Questions PNJunctionANkit JAinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mcq7 Ed MosfetDocument3 pagesMcq7 Ed MosfetparimalaseenivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee 547 Homework3 Answers PDFDocument5 pagesEee 547 Homework3 Answers PDFUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Semicondutcto Physics GATE Problems PDFDocument14 pagesSemicondutcto Physics GATE Problems PDFUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- P N JUNCTION DIODE Multiple Choice Questions - 2Document2 pagesP N JUNCTION DIODE Multiple Choice Questions - 2Ssgn SrinivasaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee 547 Homework4 Answers PDFDocument4 pagesEee 547 Homework4 Answers PDFUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 7 Lithography Chapter5Document3 pagesLecture 7 Lithography Chapter5Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Peter ZeitzoffDocument34 pagesPeter ZeitzoffUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 8 Lithography Chapter5Document3 pagesLecture 8 Lithography Chapter5Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document38 pagesChapter 9Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Eee 547 Homework5 Answers PDFDocument4 pagesEee 547 Homework5 Answers PDFUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document14 pagesChapter 3Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Handout #10 © 1999: Thermally Grown Oxides Deposited Oxide Layers Oxide ThicknessDocument22 pagesClass Handout #10 © 1999: Thermally Grown Oxides Deposited Oxide Layers Oxide ThicknessUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7Document28 pagesChapter 7Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 10Document22 pagesChapter 10Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 01 Fundamental OperationsDocument3 pages11 01 Fundamental OperationsUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8Document25 pagesChapter 8Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document17 pagesChapter 2Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Handout #7 © 1999: Cu Particles NaDocument12 pagesClass Handout #7 © 1999: Cu Particles NaUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document10 pagesChapter 1Udai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Eamcet PB Physics JR Inter Physics 01 01units and DimensionsDocument9 pagesEamcet PB Physics JR Inter Physics 01 01units and DimensionsUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Compound Angles WSDocument5 pagesCompound Angles WSUdai SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- LEON3 SPARC Processor, The Past Present and FutureDocument41 pagesLEON3 SPARC Processor, The Past Present and FutureBonnie ThompsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Philips fwm35-21 21m 22 30 Ver1.0Document66 pagesPhilips fwm35-21 21m 22 30 Ver1.0Daniel Corento MarinPas encore d'évaluation
- 12 Phy Syllabus 21-22Document1 page12 Phy Syllabus 21-22Ashish TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Communication Lab Manual GuideDocument45 pagesCommunication Lab Manual GuideRaja DuduluPas encore d'évaluation
- Libros. Caso Alcasser. Blanco, Juan Ignacio. Que Paso en AlcacerDocument12 pagesLibros. Caso Alcasser. Blanco, Juan Ignacio. Que Paso en AlcacerMiguel Angel García-SánchezPas encore d'évaluation
- FSW25N50A InPowerSemiconductor PDFDocument9 pagesFSW25N50A InPowerSemiconductor PDFyya tpgPas encore d'évaluation
- NIKO-SEM Power MOSFET Selection GuideDocument5 pagesNIKO-SEM Power MOSFET Selection GuideroozbehxoxPas encore d'évaluation
- T-2424 FerdigDocument6 pagesT-2424 FerdigNishant PandyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1: Combinational Logic Design: A. ObjectivesDocument4 pagesLab 1: Combinational Logic Design: A. ObjectivesSimon ElysiumPas encore d'évaluation
- Guided By:-R.B Patel Professer of Electronics & Communication Department. Ganpat University. Presented By: - Salim PanjwaniDocument23 pagesGuided By:-R.B Patel Professer of Electronics & Communication Department. Ganpat University. Presented By: - Salim PanjwaniSalim PanjwaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to OLED DisplaysDocument12 pagesIntroduction to OLED DisplaysMANISHA BHURIAPas encore d'évaluation
- TE FusionDocument8 pagesTE Fusionculeros1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acer Aspire 6530Document44 pagesAcer Aspire 6530Vad SheckPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet SHT25Document14 pagesDatasheet SHT25Rafael BenitezPas encore d'évaluation
- UNITROL 6000 Medium - ABB UNITROL Indirect Excitation Systems (ABB Solutions For Excitation and Synchronization)Document3 pagesUNITROL 6000 Medium - ABB UNITROL Indirect Excitation Systems (ABB Solutions For Excitation and Synchronization)lxd.hepPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar Mobile Charger Project ReportDocument16 pagesSolar Mobile Charger Project ReportKumaran SgPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.10 Input Module, 24Vdc Pos/Neg, 16-Point IC694MDL645Document3 pages6.10 Input Module, 24Vdc Pos/Neg, 16-Point IC694MDL645Omar Alfredo Del Castillo QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- C Sensors: Item Code: 570000447 Part Number:10 LDR 10mmDocument2 pagesC Sensors: Item Code: 570000447 Part Number:10 LDR 10mmAeFondevillaPas encore d'évaluation
- GEK91774 Events and CountersDocument74 pagesGEK91774 Events and CountersTorredoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sanken Regulator-ICs-Catalog PDFDocument119 pagesSanken Regulator-ICs-Catalog PDFJoseni FigueiredoPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical Work 2 - CMOS + Rubric PDFDocument12 pagesPractical Work 2 - CMOS + Rubric PDFRiki SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- MB Manual Ga-Ma78lmt-S2 (H) eDocument100 pagesMB Manual Ga-Ma78lmt-S2 (H) emallikaarjjunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lumped-Element System Dynamics: Joel Voldman Massachusetts Institute of Technology (With Thanks To SDS)Document69 pagesLumped-Element System Dynamics: Joel Voldman Massachusetts Institute of Technology (With Thanks To SDS)Nguyen Thanh KhuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet: Gigabit Passive Optical NetworkDocument14 pagesDatasheet: Gigabit Passive Optical NetworkTazar phyo waiPas encore d'évaluation
- Precise Speed Control of BDC Motor Using KeyboardDocument6 pagesPrecise Speed Control of BDC Motor Using KeyboardAravind SampathPas encore d'évaluation
- Pickup Booster Pedal User Manual by Seymour DuncanDocument8 pagesPickup Booster Pedal User Manual by Seymour DuncanMarcos El maloPas encore d'évaluation
- Innomed Medical: Top-X High Frequency X-Ray GeneratorsDocument1 pageInnomed Medical: Top-X High Frequency X-Ray GeneratorszPas encore d'évaluation
- AQU4518R14v06: Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesAQU4518R14v06: Antenna SpecificationsRaluca Roxana SzaszPas encore d'évaluation
- Redstone PDF Word Version 1.2Document27 pagesRedstone PDF Word Version 1.2Johnny PowersPas encore d'évaluation