Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Chickenpox in Pediatrics
Transféré par
Eman Khammas0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues7 pagesppt
Titre original
Chickenpox in pediatrics ppt
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentppt
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
46 vues7 pagesChickenpox in Pediatrics
Transféré par
Eman Khammasppt
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 7
Chickenpox
It is an acute febrile illness caused by
Varicella-Zoster virus. It is characterized
by variable constitutional symptoms and
characteristic skin rash and sudden onset.
The skin rash starts as maculopapular and
changes to vesicular in due course of the
disease.
It is distributed mainly on the trunk
(centripetal) and polymorphic( more than
one type of rash exist at any time).
The importance of chickenpox lies in two
points:
1. Its differentiation from smallpox, which
was common and serious disease.
2. The complications: Atypical
pneumonia in adults and encephalitis
in children. Neonates of non immune
mothers are at special risk of
complication when they contract
infection during or within few days of
delivery. The same is true for those
with leukaemia and those on
corticosteroids.
Reservoir: Man
Incubation period: 2-3 weeks
Mode of transmission: Direct
contact, droplet infection or
indirectly through freshly
contaminated articles.
Period of communicability: From
5 days before the appearance of
rash till 6 days after the
appearance of the last crop of
rash.
Susceptibility: General. Natural
infection is followed by life-long
immunity.
Prevention: No specific
preventive measure is
available.
Control:
1. Notification to health authorities.
2. Isolation and concurrent
disinfection.
3. Immuniglobulins with 4 days of
exposure are of value in people on
corticosteroids and neonates of
non-immune mothers
4. Exclude smallpox through careful
differentiation as follows:
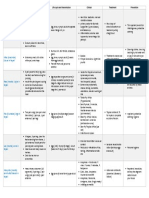
Chickenpox Smallpox Characteristic
Prodromal symptoms severe Mild until just
for 2-4 days before rash before rash
Skin rash
Type One crop and appears Several crops over
Within 1-2 days several days
Distribution Same stage and centrifugal Polymorphic and
centripetal
Individual lesions -Axilla spared Axilla involved
-Palms and soles Palms and soles
Involved spared oftenly
-Circular Oval
-Deep Superficial
- Vesicle are mutilocular Vesicles are unilocula
Scar Depressed Superficial
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Diversity in Living Organisms - : Homo SapiensDocument2 pagesDiversity in Living Organisms - : Homo Sapiensexcaliber4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arthropods of Medical ImportanceDocument6 pagesArthropods of Medical ImportanceMarlon Ursua BagalayosPas encore d'évaluation
- IGCSE Biology NotesDocument50 pagesIGCSE Biology NotesSandra AtefPas encore d'évaluation
- Orientation on OLTRAP: Understanding Dengue Vector ControlDocument53 pagesOrientation on OLTRAP: Understanding Dengue Vector ControlLaurel S. MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Measles - German Measles - ChickenpoxDocument3 pagesMeasles - German Measles - Chickenpoxd3mooz13Pas encore d'évaluation
- Phylum Nematoda 13Document132 pagesPhylum Nematoda 13Iseth ISeth100% (1)
- A Brief Note On: Chicken PoxDocument29 pagesA Brief Note On: Chicken PoxRemesh ChandranPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 2 Extraintestinal NematodesDocument5 pagesLesson 2 Extraintestinal NematodesCDPas encore d'évaluation
- Vectors PSM ParksDocument36 pagesVectors PSM ParksAshish RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Nematodes (Round Worms) Lec 7 Fall 2021 PDFDocument12 pagesNematodes (Round Worms) Lec 7 Fall 2021 PDFMk KassemPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Eye Diseases 2022Document33 pagesCommon Eye Diseases 2022Shia LevyPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitology ReviewerDocument36 pagesParasitology ReviewerMark Justin OcampoPas encore d'évaluation
- The 7 Signs of LifeDocument25 pagesThe 7 Signs of LifeOmar FaourPas encore d'évaluation
- TicksDocument5 pagesTickskebaridukePas encore d'évaluation
- General Study Guide - 2: - For Each Insect/pathogen CombinationDocument20 pagesGeneral Study Guide - 2: - For Each Insect/pathogen CombinationHerold Riwaldo SPas encore d'évaluation
- Life Sciences Reproduction in Vertebrates 22 February 2024Document24 pagesLife Sciences Reproduction in Vertebrates 22 February 2024finnhyacinthPas encore d'évaluation
- SpirochetesDocument6 pagesSpirochetesEarl John SepayaPas encore d'évaluation
- (PARA) 2.04 - Intestinal Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoDocument4 pages(PARA) 2.04 - Intestinal Flukes - Dr. AlvaradoMarlon BauagPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument16 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesKirstin Jan LuibPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitology-Lec 7 Lung FlukesDocument5 pagesParasitology-Lec 7 Lung Flukesapi-3743217100% (1)
- Veterinary Helminthology MidtermsDocument4 pagesVeterinary Helminthology Midtermshumanupgrade100% (1)
- Field Crops Diseases Bringher Shalom Part 1 2016Document49 pagesField Crops Diseases Bringher Shalom Part 1 2016carreonrosellejoy8Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2 MosquitoDocument8 pages2 Mosquito173Swapnaneil BujarbaruahPas encore d'évaluation
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Document1 pageTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument4 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesAliana RaymundoPas encore d'évaluation
- Antiprotozoal Drugs ResistanceDocument4 pagesAntiprotozoal Drugs Resistance111techie999Pas encore d'évaluation
- EctoparasiteDocument1 pageEctoparasiteBishal JB KunworPas encore d'évaluation
- Far Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BDocument15 pagesFar Eastern University - Nicanor Reyes Medical Foundation: Pedia 3B: Virology BHarlyn MagsinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Pox: A Child Infected With SmallpoxDocument5 pagesSmall Pox: A Child Infected With SmallpoxJavee_Viccent__5618Pas encore d'évaluation
- Significance of ReproductionDocument11 pagesSignificance of ReproductionCandy OpsadPas encore d'évaluation
- NATSCI002 Botany Lab Virtual Lab Roots Stem MidtermDocument4 pagesNATSCI002 Botany Lab Virtual Lab Roots Stem MidtermAnthonete NuñezPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn About Ascaris And Other Important RoundwormsDocument3 pagesLearn About Ascaris And Other Important RoundwormsSARA50% (2)
- Mosquitoes 131019090213 Phpapp01Document92 pagesMosquitoes 131019090213 Phpapp01Aparna KinginiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unicellular and Multicellular OrganismDocument14 pagesUnicellular and Multicellular OrganismDekfa MiefaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational ServicesDocument2 088 pagesBiology-A Complete Solution For - V. Educational Servicesteamindian gamersPas encore d'évaluation
- Albugo: White Rust of CrucifersDocument34 pagesAlbugo: White Rust of CrucifersMuhammad MushtaqPas encore d'évaluation
- FungiDocument3 pagesFungikrystal TortolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Stage 6 Syllabus 2017Document6 pagesBiology Stage 6 Syllabus 2017LilyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nematodes and Their Life CyclesDocument4 pagesNematodes and Their Life CyclesAneezaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7 How Do Organisms ReproduceDocument27 pagesChapter 7 How Do Organisms Reproducefortwitt18Pas encore d'évaluation
- DICOT SEED EMBRYO DEVELOPMENTDocument3 pagesDICOT SEED EMBRYO DEVELOPMENTSamantha Jesi Shania EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- CLMDocument13 pagesCLMBhica Wrahty AdetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality Time with Scale Insects and Their Natural EnemiesDocument172 pagesQuality Time with Scale Insects and Their Natural Enemiesmetbijay100% (1)
- Chapter 13 Arthropods-TorresDocument20 pagesChapter 13 Arthropods-TorresRiven TrucePas encore d'évaluation
- VARICELLADocument1 pageVARICELLAWendy Laura Sanchez FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Parasitic Protozoans of Farmed Fish and CrustaceansDocument11 pagesParasitic Protozoans of Farmed Fish and CrustaceansPaulyn ZamudioPas encore d'évaluation
- 3) Bacterial Skin Infections Semi NotesDocument2 pages3) Bacterial Skin Infections Semi NotesIssa MoodPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Intstinal HelminthesDocument27 pages3-Intstinal Helminthesademabdella38Pas encore d'évaluation
- Trematodes: 2. MiracidiaDocument3 pagesTrematodes: 2. MiracidiaBikram ChohanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Intestinal NematodesDocument9 pagesThe Intestinal NematodesdhaineyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 BIO3243 Lecturer4 RiverblindnessDocument18 pages9 BIO3243 Lecturer4 RiverblindnessNGOGA NISINGIZWE NESTORPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Reproduction in OrganismsDocument9 pages1 Reproduction in OrganismsTanya PasrichaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 12 MicroDocument4 pagesLec 12 MicroTamim Al-TamimiPas encore d'évaluation
- SCABIESDocument14 pagesSCABIESNom Kumar Naik Rathod100% (1)
- Mycology W1-3Document22 pagesMycology W1-3joseadreannes.pinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- [C-02] The NematodesDocument25 pages[C-02] The NematodesNick BatumbakalPas encore d'évaluation
- Enterobius Vermicularis) : Hawri H. Mohammed H.D., M.Sc. ParasitologyDocument9 pagesEnterobius Vermicularis) : Hawri H. Mohammed H.D., M.Sc. ParasitologyHawre NajmaddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical+Parasitology-Module+9Document10 pagesClinical+Parasitology-Module+9Geresh MagsinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology Lecture 1 ObjectivesDocument27 pagesEpidemiology Lecture 1 ObjectivesEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Vitamins L5Document22 pagesVitamins L5Eman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Epidemiology: Dr. Eman Khammas Al-Sadi Chief of Community DepartmentDocument23 pagesAnalytical Epidemiology: Dr. Eman Khammas Al-Sadi Chief of Community DepartmentEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology Lectures 3,4: Dr. Eman Khammas Al-Sadi Assistant Prof. in Pediatrics Chief of Community Medicine DepartmentDocument20 pagesEpidemiology Lectures 3,4: Dr. Eman Khammas Al-Sadi Assistant Prof. in Pediatrics Chief of Community Medicine DepartmentEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Assistant Prof. D. Eman Khammas AI-sadi Pediatrician /community Medicine DepartmentDocument20 pagesAssistant Prof. D. Eman Khammas AI-sadi Pediatrician /community Medicine DepartmentEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiological Data: Dr. Eman Khammas Alsadi Head of Community Medicine DepartmentDocument23 pagesEpidemiological Data: Dr. Eman Khammas Alsadi Head of Community Medicine DepartmentEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cho L2Document23 pagesCho L2Eman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein L4Document24 pagesProtein L4Eman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition: Assistant Prof. D. Eman Khammas AI-sadi Pediatrician /community Medicine DepartmentDocument25 pagesNutrition: Assistant Prof. D. Eman Khammas AI-sadi Pediatrician /community Medicine DepartmentEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Descriptive Epidemiology PPTDocument19 pagesDescriptive Epidemiology PPTEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Managing complications of infants of diabetic mothersDocument60 pagesManaging complications of infants of diabetic mothersEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Epidemiology Lecture 1 ObjectivesDocument27 pagesEpidemiology Lecture 1 ObjectivesEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Parathyroid GlandsDocument14 pagesPathology Parathyroid GlandsEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- 6 Adrenocortical NeoplasmDocument22 pages6 Adrenocortical NeoplasmEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical HazardsDocument18 pagesPhysical HazardsEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Anaemia Blood QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesAnaemia Blood QuestionnaireEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Understand Diabetes Mellitus Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument22 pagesUnderstand Diabetes Mellitus Types, Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- ChickenpoxDocument7 pagesChickenpoxEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- MumpsDocument8 pagesMumpsEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lebnan GuidlinesDocument36 pagesLebnan GuidlinesEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- 23rd EarDocument23 pages23rd EarEman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- 25th Lecture 25 Integumentary System-1Document24 pages25th Lecture 25 Integumentary System-1Eman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Nam1Document2 pagesStudent Nam1Eman KhammasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Examination AnswersDocument205 pagesPathophysiology Examination AnswersFırat Güllü67% (6)
- Measles Basic Info EnglishDocument2 pagesMeasles Basic Info EnglishSinclair Broadcast Group - EugenePas encore d'évaluation
- Raw 2 LawsDocument17 pagesRaw 2 LawsRed HalePas encore d'évaluation
- Vims-Vas Biyong 1-12-2022Document122 pagesVims-Vas Biyong 1-12-2022Julia JacoboPas encore d'évaluation
- Cepheid GeneXpert System Menu Flyer CE IVD 0293 EnglishDocument2 pagesCepheid GeneXpert System Menu Flyer CE IVD 0293 EnglishTchouala DentrishPas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Test CovidDocument2 pagesRapid Test CovidYuzia Birthdie C UPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutor Imun HBsAg KuantitatifDocument27 pagesTutor Imun HBsAg Kuantitatifv_mayasari100% (1)
- Needle Prick InjuryDocument20 pagesNeedle Prick InjuryThirugnanaThiruPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN Immunization NotesDocument9 pagesCHN Immunization NotesJustin AncogPas encore d'évaluation
- Administering Blood TransfusionDocument10 pagesAdministering Blood Transfusionkatz_hotchickPas encore d'évaluation
- Pamphlet AmoebiasisDocument3 pagesPamphlet AmoebiasisAristotel Cabais100% (1)
- Plot No.428, Phase-IV, Udyog Vihar, Gurgaon, Haryana - 122 015Document3 pagesPlot No.428, Phase-IV, Udyog Vihar, Gurgaon, Haryana - 122 015Asit APas encore d'évaluation
- COVID-19: Myths and TruthsDocument3 pagesCOVID-19: Myths and TruthsWrhaeyna Marie SalesPas encore d'évaluation
- RT-PCR Test Report: Kanyakumari Government Medical College and Hospital, KanyakumariDocument2 pagesRT-PCR Test Report: Kanyakumari Government Medical College and Hospital, KanyakumariAnithaPas encore d'évaluation
- About Tattoos What Is A Tattoo?Document2 pagesAbout Tattoos What Is A Tattoo?Çağatay SarıkayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Understanding Autoimmune UveitisDocument5 pagesGuide to Understanding Autoimmune UveitisHitesh ParmarPas encore d'évaluation
- ReportsDocument5 pagesReportsguptaaarushi528Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Effect of Inflammation On BoneDocument14 pagesThe Effect of Inflammation On BoneKelas CPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Notes On Disease and EpidemiologyDocument4 pagesLecture Notes On Disease and EpidemiologyDiane Princess SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs or Symptoms of Acute HIV InfectionDocument3 pagesSigns or Symptoms of Acute HIV InfectionAndrea LunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reducing Malaria Infections in Sub-Saharan AfricaDocument2 pagesReducing Malaria Infections in Sub-Saharan AfricaStansa SeniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: David Hough MSIII Penn State College of MedicineDocument33 pagesNecrotizing Fasciitis: David Hough MSIII Penn State College of Medicineaaz220Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Mothers' Compliance with Vaccination ProgramsDocument68 pagesUnderstanding Mothers' Compliance with Vaccination ProgramsEden NatividadPas encore d'évaluation
- ABO Blood TypesDocument4 pagesABO Blood TypesKBS100% (1)
- Certificate for COVID-19 Vaccination in IndiaDocument1 pageCertificate for COVID-19 Vaccination in IndiaRam Sumer TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Leishmaniasis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical SymptomsDocument12 pagesReview of Leishmaniasis: Epidemiology, Pathogenesis, Clinical SymptomsJaison Enrique Torres PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) : Paediatric Department CMEDocument25 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) : Paediatric Department CMENurul Syazwani Ramli67% (3)
- Amare Thesis Proposal1Document39 pagesAmare Thesis Proposal1ናታኔም ናታኔምPas encore d'évaluation
- Lista DiagnosticeDocument566 pagesLista DiagnosticeGeanina MireaPas encore d'évaluation
- CSF & Body FluidDocument42 pagesCSF & Body FluidlopaPas encore d'évaluation






















































![[C-02] The Nematodes](https://imgv2-1-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/723587188/149x198/eccae51023/1713275217?v=1)