Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Cosmids
Transféré par
Rachu Raj0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues8 pagesjkb
Titre original
10-19-05
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentjkb
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
12 vues8 pagesCosmids
Transféré par
Rachu Rajjkb
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPT, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 8
Cosmids:
Plasmids that contain l cos sites.
This allows them to be packaged into l particles.
But dont have l genes, therefore can clone larger
insert fragments; 35-45 kb.
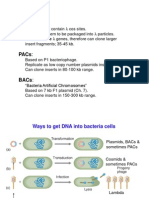
PACs:
Based on P1 bacteriophage.
Replicate as low copy number plasmids inside E. coli.
Can clone inserts in 80-100 kb range.
BACs:
Bacteria Artificial Chromosomes
Based on 7 kb F1 plasmid (Ch. 7).
Can clone inserts in 150-300 kb range.
Ways to get DNA into bacteria cells
Plasmids, BACs &
sometimes PACs
Cosmids &
sometimes PACs
Lambda
Recombinant DNAs
Recombinant DNA Libraries
Collection of many clones derived from a single DNA source.
Genomic Libraries:
Many clones, each of which contains a fragment of
chromosomal DNA from a particular species.
Complete genomic library: Entire genome is
represented in at least one clone.
Making a Genomic Library
1. Digest chromosomal DNA & vector DNA with restriction
enzyme(s).
2. Isolate desired size range of chromosomal DNA fragments.
(Gel Electrophoresis)
3. Ligate chromosomal restriction fragments with vector DNA.
4. Either package clones (l and cosmids) or use DNA to
transform E. coli (PACs and BACs).
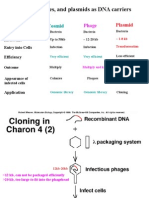
Lambda Bacteriophage Vectors
cos cos
cos
Selection:
Only recombinant phage produce plaques.
1. Size limits of DNA that fits into phage particle.
left l arm (15kb) + right l arm (10kb) +
insert (~15kb) = 40kb
2. Requirement for l genetic information:
cos sites & genes in right & left l arms.
Library
Complete Genomic Library
Entire genome is represented
Mininum number of clones (genome equivalent) needed depends
on size of genome & vector used.
Example: Human genome = 3 x 10
6
kb
Average sizes of inserts
l: ~15 kb Cosmids: ~35 kb
Human genome equivalents
~2 x 10
5
l clones ~8.6 x 10
4
cosmid clones
10
4
BAC clones (~300 kb/clone)
Recombinant DNA Libraries
Collection of many clones derived from a single DNA source.
Genomic Libraries:
Many clones, each of which contains a fragment of
chromosomal DNA from a particular species.
Complete genomic library: Entire genome is
represented in at least one clone.
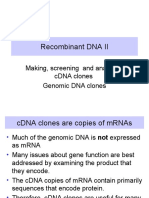
cDNA Libraries:
cDNAs = DNA copies of RNA molecules.
cDNA libraries: Each clone contains DNA copy of an
individual mRNA.
Very useful for studying just the part of a gene that is
present in mRNA.
Making a cDNA Library
1. Prepare poly(A)+ RNA from
desired source.
2. Synthesize cDNAs:
Anneal oligo(dT) primers to
mRNAs.
Synthesize 1st cDNA strand
using Reverse Transcriptase.
Degrade RNA with NaOH.
Synthesize 2nd cDNA strand
using DNA polymerase I.
Nick hairpin loop using S1
nuclease.
3. Ligate with vector.
(plasmid or l)
1st cDNA strand
2nd cDNA strand
3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cloning VectorsDocument161 pagesCloning Vectorssubhash nayak100% (2)
- VectorsDocument6 pagesVectorsAssad MustafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recombinant DNA Cloning TechnologyDocument71 pagesRecombinant DNA Cloning TechnologyRajkaran Moorthy100% (1)
- DNA LibrariesDocument37 pagesDNA LibrariesMansoor KhalidPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical BiotechnologyDocument36 pagesPharmaceutical BiotechnologyHussein Talal KenaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Peter John M.Phil, PHD Assistant ProfessorDocument25 pagesDr. Peter John M.Phil, PHD Assistant ProfessorMehak ToorPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of Genomic and cDNA Libraries-AmitDocument10 pagesConstruction of Genomic and cDNA Libraries-AmitPrashant BajpaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Elements Life and Design: Boris M. Klebanov David M. Barlam Frederic E. NystromDocument5 pagesMachine Elements Life and Design: Boris M. Klebanov David M. Barlam Frederic E. NystromRachu Raj100% (1)
- 5.library ProductionDocument53 pages5.library Productionshruti shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Cloning - Biotech 509Document33 pagesGene Cloning - Biotech 509Tarhima JahanPas encore d'évaluation
- Yac Bac PacDocument30 pagesYac Bac PacRahmama100% (1)
- Cosmids, Phages, and Plasmids As DNA Carriers: CosmidDocument12 pagesCosmids, Phages, and Plasmids As DNA Carriers: CosmidDukum RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of Genomic Library - The Idea of Amplifying Very Large Mixtures of DNA Fragments andDocument18 pagesConstruction of Genomic Library - The Idea of Amplifying Very Large Mixtures of DNA Fragments andPrabhjot Brar100% (1)
- A Genomic LibraryDocument5 pagesA Genomic LibraryPabloPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene LibrariesDocument14 pagesGene Librariessharmamaddy32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Genetics Lect 2 2011 Colour 2 Slides Per PageDocument9 pagesGenetics Lect 2 2011 Colour 2 Slides Per Pageyr0668Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Cloning StrategiesDocument35 pagesGene Cloning Strategiesnishit1990100% (2)
- Uneeb GreatDocument21 pagesUneeb Greatusman azeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Genomic and CDNA LibrariesDocument15 pagesGenomic and CDNA LibrariesPrabhleen KaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of Genomic LibraryDocument16 pagesConstruction of Genomic Librarysivagurunathan.P80% (5)
- Molecular Techniques in Human GeneticsDocument31 pagesMolecular Techniques in Human GeneticsBabak NamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Library ConstructionDocument8 pagesLibrary ConstructionVinay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Recombinant DNA II: Making, Screening and Analyzing cDNA Clones Genomic DNA ClonesDocument23 pagesRecombinant DNA II: Making, Screening and Analyzing cDNA Clones Genomic DNA Clonessri murniati naibahoPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Cloning: Molecular Biology Techniques #1 Recombinant DNADocument16 pagesDNA Cloning: Molecular Biology Techniques #1 Recombinant DNAmohamedtnsPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Construction of DNA LibrariesDocument6 pagesUnit 2 Construction of DNA LibrariesvijikalkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Choosing A Cloning VectorDocument9 pagesChoosing A Cloning VectorJudit JàkimPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Cloning Vectors PDFDocument44 pages1 - Cloning Vectors PDFUsman ShamshadaliPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA LibraryDocument18 pagesDNA LibraryworknehbethanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Recombinant Dna Tech SaswatDocument8 pagesRecombinant Dna Tech SaswatSaswat Anurag RoutPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Cloning, Vectors and Cloning StrategiesDocument93 pagesPrinciples of Cloning, Vectors and Cloning StrategiesEmmanuel OcanseyPas encore d'évaluation
- By, BIRAC Innovation Fellow University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadDocument12 pagesBy, BIRAC Innovation Fellow University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadTabada NickyPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Lec.8 Dr. Sddiq Recombinant DNA 20200414030255 PDFDocument7 pages08 Lec.8 Dr. Sddiq Recombinant DNA 20200414030255 PDFحسن الأسديPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloning Vector: BY: Dr. Mukesh Kumar BhardwajDocument23 pagesCloning Vector: BY: Dr. Mukesh Kumar Bhardwajمحمود محمدPas encore d'évaluation
- BOCM 3714: T: +27 (0) 51 401 9111 - Info@ufs - Ac.za - WWW - Ufs.ac - ZaDocument30 pagesBOCM 3714: T: +27 (0) 51 401 9111 - Info@ufs - Ac.za - WWW - Ufs.ac - ZaNthabeleng NkaotaPas encore d'évaluation
- The cDNA Library (Notes)Document9 pagesThe cDNA Library (Notes)sharadmore211Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Year Recombinant DNADocument42 pages3rd Year Recombinant DNAReazul Islam ShantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mod3 PDFDocument65 pagesMod3 PDFRAKISHO WORLD100% (1)
- 4.1 Finger Prints and MapsDocument12 pages4.1 Finger Prints and MapsFadhili DungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene LibraryDocument5 pagesGene LibraryRajeswari NarayanappaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 3A - CloningDocument19 pagesLecture 3A - Cloningctiey_hudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Selection of Suitable Vector: Step IiDocument45 pagesSelection of Suitable Vector: Step IiDhruv PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Tech Essay PDFDocument4 pagesGene Tech Essay PDFdev_nakomPas encore d'évaluation
- Genomic DNA LibraryDocument15 pagesGenomic DNA Libraryplastioid4079Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture of Genetic Engineering (Principals and Applications)Document66 pagesLecture of Genetic Engineering (Principals and Applications)Rawan KhalafPas encore d'évaluation
- cDNA Libraries and Gene CloningDocument8 pagescDNA Libraries and Gene CloningRoberto RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Aula BMol 4Document34 pagesAula BMol 4Diogo MadalenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gene LibrariesDocument14 pagesGene LibrariesShikha YashveerPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloning Vectors Part1Document56 pagesCloning Vectors Part1NIKHIL YEMULPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised TERM PAPERDocument19 pagesRevised TERM PAPERVikal RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Block II Lecture 1: Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument42 pagesBlock II Lecture 1: Recombinant DNA TechnologyRitesh Chandrakant SuryawanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Cloning-revised-Unit 1 (Portion)Document56 pagesIntroduction To Cloning-revised-Unit 1 (Portion)akshayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ilovepdf MergedDocument73 pagesIlovepdf MergedakshayaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Cloning Techniques and Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument41 pagesDNA Cloning Techniques and Recombinant DNA TechnologyTanveer KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- I Am Sharing 'Biochemistry (1) ' With YouDocument16 pagesI Am Sharing 'Biochemistry (1) ' With YouAhmed MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT7 016f18rec11Document8 pagesMIT7 016f18rec11Shubham singhPas encore d'évaluation
- History of Genetic Manipulation: Recombinant DNA TechnologyDocument69 pagesHistory of Genetic Manipulation: Recombinant DNA TechnologyBagus WijayaPas encore d'évaluation
- cDNA Library - WikipediaDocument4 pagescDNA Library - WikipediaHkr GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Recombinant DNA Technology !: Molecular Cloning Genomic Libraries cDNA Libraries "Sub-Cloning"Document26 pagesRecombinant DNA Technology !: Molecular Cloning Genomic Libraries cDNA Libraries "Sub-Cloning"burnitdownPas encore d'évaluation
- Cdna and Bac LibraryDocument14 pagesCdna and Bac LibraryNoman AnwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Make The Number.: SmallestDocument10 pagesMake The Number.: SmallestRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Make The Number.: SmallestDocument10 pagesMake The Number.: SmallestRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Make The Number.: SmallestDocument10 pagesMake The Number.: SmallestRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Make The Number.: SmallestDocument10 pagesMake The Number.: SmallestRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Make The Number.: SmallestDocument10 pagesMake The Number.: SmallestRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Make The Number.: SmallestDocument10 pagesMake The Number.: SmallestRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- A Strategy For Performance ExcellenceDocument32 pagesA Strategy For Performance ExcellencebhogbhogaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 SDocument15 pages5 SViswanathan SrkPas encore d'évaluation
- CosmidsDocument8 pagesCosmidsRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- New Doc 10Document1 pageNew Doc 10Rachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- A Strategy For Performance ExcellenceDocument32 pagesA Strategy For Performance ExcellencebhogbhogaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 SDocument15 pages5 SViswanathan SrkPas encore d'évaluation
- Yeast Shuttle VectorsDocument5 pagesYeast Shuttle VectorsraphiaPas encore d'évaluation
- CccutilDocument1 pageCccutilJose Enrique Flores GonzalezPas encore d'évaluation
- (Office Copy. Please Attach With The Application) : Page 1/1Document1 page(Office Copy. Please Attach With The Application) : Page 1/1Rachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Moleculkbnoknlo Ughiufvbik IouhgDocument26 pagesMoleculkbnoknlo Ughiufvbik IouhgRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- IijjkDocument2 pagesIijjkRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- (Office Copy. Please Attach With The Application) : Page 1/1Document1 page(Office Copy. Please Attach With The Application) : Page 1/1Rachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2: Vectors, cDNA Libraries, & Plasmid MiniprepsDocument39 pagesLecture 2: Vectors, cDNA Libraries, & Plasmid MiniprepsRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- PG Ccss2407ljbhDocument11 pagesPG Ccss2407ljbhRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- IijjkDocument2 pagesIijjkRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- File WWWDocument1 pageFile WWWRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- PG Ccss2407ljbhDocument11 pagesPG Ccss2407ljbhRachu RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Yeast Shuttle VectorsDocument5 pagesYeast Shuttle VectorsraphiaPas encore d'évaluation
- First: Elevation Section On BBDocument1 pageFirst: Elevation Section On BBBoppineti Naga RajuPas encore d'évaluation
- B Tech Scheme Revised Syllabus Equivalent Subjects-1Document23 pagesB Tech Scheme Revised Syllabus Equivalent Subjects-1Rachu RajPas encore d'évaluation