Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Enzymes 2
Transféré par
Norshamsiah SamsudinDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Enzymes 2
Transféré par
Norshamsiah SamsudinDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
enzymes
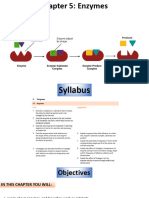
Enzymes
are biological catalyst
that
regulate
almost
all the
cellular
reactions
Text book
Thingking process: describing ocntext
Biochemical
reactions occur
simultaneously in a
cell and in a series
of linked reactions
Enzymes act as
biological catalysts
Different type of
enzymes can only
catalyst one
particular reaction
Enzymes regulate
almost all the cellular
reactions
Enzymes control
the speed of
chemical reactions
in human body
Enzymes are
synthesised by
living organisms
Enzymes are
proteins
This is because
enzymes are not used
up but released at the
end of the reaction
The same enzymes
molecules can process
a large molecules of
substrate molecules
Enzymes are
needed in small
amount
Enzymes are not affected
by the reactions they
catalyse
This means enzymes are
not changed or destroyed
by the reactions
Enzymes speed up
biochemical
reactions
Most enzymes can catalyse
specific reactions both in the
forward and in the reverse
direction
Reversible
Examples of inhibitors
are heavy metals such as
lead and mercury
Can be slowed down
by inhibitors
Each enzyme can usually catalyse
only a single reaction or one kind or
substrate
Enzymes have specific sites called
active sites which bind to specific
substrate. For example, only starch
molecules (substrate) can fit into the
active sites of salivary amylase
(enzyme) while protein molecules
cannot
Highly specifc
Cofactors binds to the
enzymes and help to
weaken the bonds in
the substrate
molecules.
Examples of inorganic
cofactors are iron and
copper. Organic
cofactors or coenzymes
include water-soluble
vitamins such as
vitamin B comples.
Require
confactors to
function
Since enzymes are higly specific in their actions, the
names of the most enzymes are derived by adding
suffix -ase to the name of the substrates they
hydrolyse. For example,
Subtrates Enzyme
Lactose Lactase
Sucrose Sucrase
Lipid Lipase
The name of the enymes is written above the
reaction arrow. For example, sucrase hyrolyses the
breakdown of sucrase to glucose and fructose.
Sucrose + water glucose + fructose
However, there are some enzymes that were named before a
systematic way of naming enzymes was formulated. For
example, pepsin, trypsin and rennin.
hydrolysis
The nucleus contains DNA which carries the information
for the synthesis of enzymes
Proteins that are synthesised at the ribosomes are
transported through the space within the rough
endoplasmic reticulum
Proteins that are from rough ER
wrapped in vesicles that bud off from
the membranes of the rough ER
These tansport vesicles then fuse with
the membranes of the Golgi apparatus
and empty their contents into the
membranuos space
The proteins are further modified
in the Golgi apparatus.
Secretory vesicles containing these
enzymes bud off them from the Golgi
apparatus and travel to plasma
membrane
These vesicles will then fuse with
the plasma membrane before
releasing the enzymes outside
the cell as enzymes
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsD'EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (5)
- ENZYMESDocument39 pagesENZYMESDhaya VPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme: Ayesha Shafi Pharm-D, (P.U.), M. Phil. Pharmaceutical Chemistry (P.U.)Document34 pagesEnzyme: Ayesha Shafi Pharm-D, (P.U.), M. Phil. Pharmaceutical Chemistry (P.U.)Shafaqat Ghani Shafaqat Ghani100% (2)
- EnzymesDocument40 pagesEnzymesAmal100% (2)
- EnzymeDocument192 pagesEnzymeKishorePas encore d'évaluation
- S5 Bio (Enzymes)Document16 pagesS5 Bio (Enzymes)juniormugarura5Pas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument36 pagesEnzymesAyush GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme and Enzyme KineticsDocument61 pagesEnzyme and Enzyme KineticsNaiomiPas encore d'évaluation
- CHY 47 Enzymes 2nd Semester 2021-2022Document156 pagesCHY 47 Enzymes 2nd Semester 2021-2022Shakira AntiquinaPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument15 pagesEnzymesJun MinPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes in Food IndustryDocument67 pagesEnzymes in Food Industryamrutha tkPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme: An IntroductionDocument14 pagesEnzyme: An IntroductionVishnu SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme StructureDocument2 pagesEnzyme StructurePrince OycoPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument19 pagesEnzymesKimCharlsO. EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes 1Document54 pagesEnzymes 1Mayuri DhanushwarPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument53 pagesEnzymesMayuri DhanushwarPas encore d'évaluation
- Biomolecules (Enzymes)Document17 pagesBiomolecules (Enzymes)Shareza TalattadPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument23 pagesEnzymesBalram NeupanePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 EnzymeDocument37 pagesChapter 5 Enzymejzdf2d9nnvPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument5 pagesEnzymeseyosiyas tekleweyinPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.4 Exploring EnzymesDocument17 pages2.4 Exploring EnzymesIsaacPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument3 pagesEnzymesDavid PetalcurinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Enzyme Action PowerpointDocument18 pagesLesson 1 Enzyme Action Powerpointtbrook2017Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter5 Bio f5Document8 pagesChapter5 Bio f5JiayingPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes - Molecular Devices That Determines The Course of Chemical ReactionsDocument27 pagesEnzymes - Molecular Devices That Determines The Course of Chemical ReactionsTARIQPas encore d'évaluation
- BMS131 Lec05Document19 pagesBMS131 Lec05mariam tarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 5 - Enzymes and CoenzymesDocument7 pagesLecture 5 - Enzymes and CoenzymesDoreenPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymeDocument15 pagesEnzymeSheena Mhae LopeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes - BiochemistryDocument40 pagesEnzymes - Biochemistrysunil patelPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument28 pagesEnzymesGautamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes L1 2023 2024Document33 pagesEnzymes L1 2023 20249829c7fchsPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes PPTDocument40 pagesEnzymes PPTJaisy PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme 1Document115 pagesEnzyme 1fikaduPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Chapter 4 Bio NotesDocument6 pagesForm 4 Chapter 4 Bio NotesCharnita Vinosha VenudranPas encore d'évaluation
- History Enzymes - 6Document40 pagesHistory Enzymes - 6AndyPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes (As Biology)Document42 pagesEnzymes (As Biology)Muhtasim FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument44 pagesEnzymesYumul, Jewel B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Động Hoá Học Duoc-32-112Document81 pagesĐộng Hoá Học Duoc-32-112Nguyễn Đình TrườngPas encore d'évaluation
- PhmarmacogDocument8 pagesPhmarmacogMichelle CasilangPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymologyDocument47 pagesEnzymologyTererai Lalelani Masikati Hove100% (1)
- Module 11: EnzymesDocument3 pagesModule 11: EnzymesMariam EskandariPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument11 pagesEnzymesAmjad AshrafiPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio G11 Unit 3 Enzymes PPXDocument14 pagesBio G11 Unit 3 Enzymes PPXBereket NetsanetPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4-IDocument40 pagesChapter 4-ISifan MotumaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Metabolism and EnzymesDocument8 pagesChapter 5 Metabolism and Enzymes绿谷出久Pas encore d'évaluation
- BT1301 NolDocument131 pagesBT1301 NolJanani RipplingrythmPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport Mechanisms in EnzymesDocument17 pagesTransport Mechanisms in EnzymesBrasa Y. de AlmiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes PPTDocument39 pagesEnzymes PPTsunil patelPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes As Biological CatalystsDocument23 pagesEnzymes As Biological CatalystsLailatul BadriyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme: Jahangirnagar UniversityDocument34 pagesEnzyme: Jahangirnagar UniversityShanian AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- AlgebraDocument28 pagesAlgebrahadeelPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-Ii: Chemical BiologyDocument16 pagesUnit-Ii: Chemical BiologySurya Prakash KabiPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzym HappyDocument47 pagesEnzym HappyAnggitsb NainggolanPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes NPDocument25 pagesEnzymes NPBharatShethPas encore d'évaluation
- "Helper" Protein Molecules: EnzymesDocument7 pages"Helper" Protein Molecules: EnzymesMuhammad Junaid IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem 1 - NOMENCLATURE OF ENZYMESDocument51 pagesBiochem 1 - NOMENCLATURE OF ENZYMESNyasha Peter ManamikePas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 4.5 EnzymesDocument11 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 4.5 EnzymesSatpal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- ENZYMESDocument32 pagesENZYMESREECH BOL KUOL REECHPas encore d'évaluation
- EnzymesDocument71 pagesEnzymesSaran DPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio t4 KSSM Chap 5 DLPDocument34 pagesBio t4 KSSM Chap 5 DLPRayniePas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Science Form 1 2020Document29 pagesRPT Science Form 1 2020Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- P2 Bio Workshop, 2017Document12 pagesP2 Bio Workshop, 2017Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Coordination and Responses: Bab 3: Koordinasi Dan Gerak BalasDocument2 pagesChapter 3: Coordination and Responses: Bab 3: Koordinasi Dan Gerak BalasNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Answering Technique Questions 2019Document6 pagesAnswering Technique Questions 2019Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton NewmanDocument2 pagesNewton NewmanNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY 2013 MODUL E: CHAPTER 4, 5, 6 Form 5 (Group II) : Diagram 2Document14 pagesBIOLOGY 2013 MODUL E: CHAPTER 4, 5, 6 Form 5 (Group II) : Diagram 2Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Question 1 (SPM 2015) : Paper 2, Biology SPM Structure (Section A)Document9 pagesQuestion 1 (SPM 2015) : Paper 2, Biology SPM Structure (Section A)Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestion of Carbohydrates, Proteins and LipidsDocument1 pageDigestion of Carbohydrates, Proteins and LipidsNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul DC Emer LangDocument13 pagesModul DC Emer LangNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology SPM Modul A: Chapter 2, 3 & 4 (Form 4) GROUP IDocument9 pagesBiology SPM Modul A: Chapter 2, 3 & 4 (Form 4) GROUP INorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- I Believe I Can Fly ExerciseDocument1 pageI Believe I Can Fly ExerciseNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mangrove SwampDocument1 pageMangrove SwampNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Hormones f5 c3Document12 pagesPlant Hormones f5 c3Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Kota Samarahan Gantt Chart Form 5 Biology 2015: XXXXX X XXDocument1 pageSMK Kota Samarahan Gantt Chart Form 5 Biology 2015: XXXXX X XXNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Kota Samarahan Gantt Chart Form 5 Biology 2015Document2 pagesSMK Kota Samarahan Gantt Chart Form 5 Biology 2015Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Kota Samarahan English Language: Scheme of Work Form 4 First Semester 2015Document10 pagesSMK Kota Samarahan English Language: Scheme of Work Form 4 First Semester 2015Norshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 3Document23 pagesCase Study 3Norshamsiah Samsudin100% (1)
- A Wedding EssayDocument1 pageA Wedding EssayNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Outcome: To Carry Out Metabolic Processes To Be Digested Complex SubstancesDocument6 pagesLearning Outcome: To Carry Out Metabolic Processes To Be Digested Complex SubstancesNorshamsiah SamsudinPas encore d'évaluation
- USMLE 1 Hematology BookDocument368 pagesUSMLE 1 Hematology BookPRINCEPas encore d'évaluation
- Lagging DNA Strand SynthesisDocument2 pagesLagging DNA Strand SynthesisBio SynthesisPas encore d'évaluation
- Overproduction of Geraniol by Enhanced Precursor Supply in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae PDFDocument6 pagesOverproduction of Geraniol by Enhanced Precursor Supply in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae PDFSilvia Juliana Sanabria UribePas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 BookDocument229 pages2020 BookGhazala AmbrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Nebulization Buffer 454 SequencingDocument34 pagesNebulization Buffer 454 SequencingAndres S. EspindolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Antigen and AntibodyDocument40 pagesAntigen and Antibodydrdhirenvet100% (1)
- Cellular Respiration 1Document28 pagesCellular Respiration 1Maria Flor PabeloniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017Document32 pagesBiological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017AGM EBPas encore d'évaluation
- @ebookmedicin 2019 Epigenetics andDocument215 pages@ebookmedicin 2019 Epigenetics andKevin S100% (1)
- Elisa - PCR - Electrophoresa: Dr. Malayana R Nasution, SPPKDocument30 pagesElisa - PCR - Electrophoresa: Dr. Malayana R Nasution, SPPKfgrehPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzymes ProbsDocument21 pagesEnzymes ProbsAnonymous sVNvV7Q100% (1)
- 6nucleic Acids PDFDocument52 pages6nucleic Acids PDFNica Lyca MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Chemistry ImmunoassaysDocument23 pagesClinical Chemistry ImmunoassaysVincent ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Plant Root Growth, Architecture and FunctionDocument36 pagesPlant Root Growth, Architecture and Functionbrainhub50Pas encore d'évaluation
- Virus MorphologyDocument28 pagesVirus MorphologypoojasolPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Diah Rumekti hadiatiAPCGS JogjaDocument25 pagesDr. Diah Rumekti hadiatiAPCGS JogjacirerererePas encore d'évaluation
- XXXXXXXXDocument17 pagesXXXXXXXXRicardo LazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Translational ModificationDocument4 pagesPost Translational ModificationSaira DogarPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Phospholipase A Receptor IIFT: A Milestone in The Diagnosis of IMNDocument1 pageAnti-Phospholipase A Receptor IIFT: A Milestone in The Diagnosis of IMNnbiolab6659Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5616Document275 pages5616RmartdedPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology 1 First QuarterDocument10 pagesGeneral Biology 1 First QuarterAnjhiene CambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology CHP 1 To CHP 5 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ'S)Document9 pagesBiology CHP 1 To CHP 5 Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ'S)Usman RiazPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsDocument19 pages15 Quarter 1 Module 15-light-INDEPENDENT-reactionsMah Jane Divina0% (1)
- 50 TOP DNA STRUCTURE Questions and Answers PDF 2019Document7 pages50 TOP DNA STRUCTURE Questions and Answers PDF 2019kassaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1 Principles of EndocrinologyDocument82 pagesLecture 1 Principles of EndocrinologyHomeground entertainmentPas encore d'évaluation
- Jada Cumberbatch 816010507 BIOC2162 Secretory and Circulatory Systems Tutorial #2Document14 pagesJada Cumberbatch 816010507 BIOC2162 Secretory and Circulatory Systems Tutorial #2amyPas encore d'évaluation
- MDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample MaterialsDocument232 pagesMDS Postal Coaching Synopsis Sample Materialsbrihaspathiacademy100% (1)
- Designing An Epitope Vaccine Against Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus An in Silico StudyDocument9 pagesDesigning An Epitope Vaccine Against Dermatophagoides Pteronyssinus An in Silico StudyHina BatoolPas encore d'évaluation
- Mutation (Gene Mutation) NotesDocument13 pagesMutation (Gene Mutation) Notesaini azzahraPas encore d'évaluation
- Metabolic Reprogramming 2Document13 pagesMetabolic Reprogramming 222194Pas encore d'évaluation