Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Animal Development: Cell Biology October 23, 2013
Transféré par
RustEdDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Animal Development: Cell Biology October 23, 2013
Transféré par
RustEdDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Animal Development
Cell Biology
October 23, 2013
Gastrulation: Universal Features of
Animal Development
Important classes of proteins for
animal development
Two classes of proteins are especially
important for multicellular organization
- transmembrane molecules used for cell
adhesion and cell signaling (cellcell
interactions)
- gene regulatory proteins (DNA binding
proteins: differential gene expression)
Regulatory DNA defines the program of development
Embryo manipulation reveals the
interactions between its Cells
Descriptive Embryology describe the anatomical
changesthe patterns of cell division, growth,
and movementthat convert the egg into the
mature organism
Experimental embryology aims to understand
development in terms of the ways in which cells
and tissues interact to generate the multicellular
structure.
Developmental genetics analyzes development in
terms of the actions of genes.
Experimental embryology
In experimental embryology, cells and tissues from developing
animals are removed, rearranged, transplanted, or grown in
isolation, in order to discover how they influence one another.
Examples:
- An early embryo cut in half, for example, may yield two complete
and perfectly formed animals.
- A small piece of tissue transplanted to a new site may reorganize
the whole structure of the developing body.
Such experiments can help understanding of the underlying cell
cell interactions and rules of cell behavior.
Most widely used species have been birdsespecially the chick
and amphibiansparticularly the African frog Xenopus laevis.
(A), an early amphibian embryo is split almost into two parts with a hair
loop. (B), an amphibian embryo at a somewhat later stage receives a graft of a
small cluster of cells from another embryo at that stage. The two quite different
operations both cause a single embryo to develop into a pair of conjoined (Siamese)
twins.
Mutational studies on animals identify
genes that control development
Developmental genetics
Parent animals are treated with a chemical mutagen or
ionizing radiation to induce mutations in their germ
cells, and large numbers of their progeny are
examined.
Those rare mutant individuals that show some
interesting developmental abnormalityaltered
development of the eye, for exampleare picked out
for further study.
It is possible to discover genes that are required
specifically for the normal development of any chosen
feature.
Genetic approach
The genetic approach is easiest in small
animals with short generation times that can
be grown in the laboratory
- fruit fly, Drosophila melanogaster
- nematode worm, Caenorhabditis elegans
- zebrafish, Danio rerio
- mouse, Mus musculus
A cell makes developmental decisions
long before it shows a visible change
Cells have memory that reflect their
location in the body
In many systems, long before cells become
committed to differentiating as a specific cell
type, they become regionally determined: that is,
they switch on and maintain expression of genes
that can best be regarded as markers of position
or region in the body.
This position-specific character of a cell is called
its positional value, and it shows its effects in the
way the cell behaves in subsequent steps of
pattern formation
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Cell Biology NotesDocument18 pagesCell Biology NotesZara100% (2)
- Acne Scars Nu PDFDocument315 pagesAcne Scars Nu PDFCristina Pop100% (2)
- Dihybrid ProblemsDocument7 pagesDihybrid Problemsbrenden chapmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Topic 3 Student RoomDocument10 pagesBio Topic 3 Student RoomFaizan SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Astrological e Magazine - April 2018Document44 pagesThe Astrological e Magazine - April 2018RustEd100% (2)
- Genomic Equivalence: DefinitionDocument5 pagesGenomic Equivalence: Definitionjgfjhf arwtrPas encore d'évaluation
- The Astrological e Magazine January 2018Document44 pagesThe Astrological e Magazine January 2018RustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- CADD and Molecular ModelingDocument54 pagesCADD and Molecular ModelingRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- CMT Lesson 2Document14 pagesCMT Lesson 2Pam SyPas encore d'évaluation
- 8.introduction To EmbryologyDocument63 pages8.introduction To EmbryologyAhmed OrabyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Project On Study of Rate of Fermentation of JuicesDocument6 pagesChemistry Project On Study of Rate of Fermentation of Juicesyash dongrePas encore d'évaluation
- BIOLOGY - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY - Science Notes For End of Year 9 AssessmentJenny DavidsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Organization of Genome in Prokaryotes and EukaryotespptDocument24 pagesOrganization of Genome in Prokaryotes and EukaryotespptRamesh BeniwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Trans - Patten's Foundations of Embryology Chapters 1-7Document21 pagesTrans - Patten's Foundations of Embryology Chapters 1-7Lorenzo Daniel Antonio0% (1)
- BIOL 1110 Midterm Review - RoughDocument32 pagesBIOL 1110 Midterm Review - RoughJ100% (1)
- Cell Biology Ch21 Part 1 05222023 강의자료Document32 pagesCell Biology Ch21 Part 1 05222023 강의자료조형윤Pas encore d'évaluation
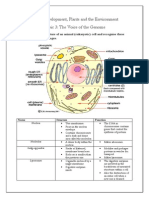
- Topic 3: Voice of The Genome: SpecificationDocument12 pagesTopic 3: Voice of The Genome: SpecificationPratham SavjaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Lab - Activity 1 Cell BioDocument32 pagesPost Lab - Activity 1 Cell Bioraphael100% (1)
- Revised TERM PAPERDocument15 pagesRevised TERM PAPERVikal RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 1Document6 pagesBio 1zachharveyneilPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Siti Suri Lecture 1: Animal Cell CultureDocument41 pagesDR Siti Suri Lecture 1: Animal Cell CultureBiotechnology IIUM Kuantan80% (5)
- Cell Commitment N DeterminationDocument41 pagesCell Commitment N DeterminationShampa SenPas encore d'évaluation
- Zoology: The Scientific Study of Animal LifeDocument9 pagesZoology: The Scientific Study of Animal LifeShobithaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib-Bio1.1 - Cell IntroductionDocument30 pagesIb-Bio1.1 - Cell IntroductionZeineb AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Diversity: Zarah Alaska-VillalonDocument68 pagesAnimal Diversity: Zarah Alaska-VillalonGabrielle Salamanca CastuloPas encore d'évaluation
- All Bio Topic 1Document13 pagesAll Bio Topic 1Trisha Faith BuckPas encore d'évaluation
- Senior Science Revision SheetDocument28 pagesSenior Science Revision Sheetd alwadhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Role of Cytoplasm in Cell DifferentiationDocument7 pagesRole of Cytoplasm in Cell DifferentiationJ LALPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Bio Learning GuideDocument50 pagesCell Bio Learning GuideMichaela DereloPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Grade 9 and 10 Revision Short NotesDocument17 pagesBiology Grade 9 and 10 Revision Short Notesdawitdesta2022Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Classx Bio ReproductionDocument13 pagesNotes Classx Bio Reproductionvaibhav4gamePas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesDocument12 pagesClass 10 Science Chapter 8 Revision NotesMuzafar ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- BIO125ZusammenfassungLF 3Document43 pagesBIO125ZusammenfassungLF 399rnbccdr8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Asexual Repro NotesDocument23 pagesAsexual Repro NotesMs ZoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Koret Munguldar - Km2753@nyu - Edu - Office Hours by Appointment - MEYR 261Document35 pagesKoret Munguldar - Km2753@nyu - Edu - Office Hours by Appointment - MEYR 261Ayesha HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Cells Development Biodiversity and ConservationDocument47 pagesUnit 2 Cells Development Biodiversity and ConservationKevir Man100% (1)
- An Introduction To Evo Devo: by Nabeel MohammedDocument32 pagesAn Introduction To Evo Devo: by Nabeel Mohammednabeelfrom95Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and ConservationDocument47 pagesUnit 2 Cells, Development, Biodiversity and ConservationEllane leePas encore d'évaluation
- Students Copy - Chapter 2 - The Cellular Basis of LifeDocument51 pagesStudents Copy - Chapter 2 - The Cellular Basis of LifeKate Nicole EjercitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Biological Science: Licensure Examination For TeachersDocument6 pagesBiological Science: Licensure Examination For TeachersJennyPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Cell CultureDocument33 pagesAnimal Cell CultureMd. Babul AktarPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Differentiation Cmtut - 6305Document9 pagesCell Differentiation Cmtut - 6305rkblsistem100% (1)
- Stem Cell Therapy Hope or HypeDocument45 pagesStem Cell Therapy Hope or HypeSiddharth DhanarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Genetics/ Classical GeneticsDocument3 pagesTransmission Genetics/ Classical GeneticsAidyl ChuPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviewer in Science BasteDocument5 pagesReviewer in Science BasteDHAINE LOUIS GENEVIEVE DE VILLAPas encore d'évaluation
- Genes Development FinalDocument59 pagesGenes Development FinalJennifer ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction & Overview: Developmental BiologyDocument52 pagesIntroduction & Overview: Developmental BiologyArtika Muliany TindaonPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 BiologyDocument14 pagesChapter 1 BiologyMarina ArvanitopoulouPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary Notes - Topic 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms - CIE Biology IGCSEDocument3 pagesSummary Notes - Topic 1 Characteristics and Classification of Living Organisms - CIE Biology IGCSEaswin sivakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Pdf&rendition 1Document7 pagesPdf&rendition 1KARTIK PRATAP SHAHIPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Theory: Functions of LifeDocument12 pagesCell Theory: Functions of LifeSeila MoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Fate Maps: Course: B.Sc. (H) Zoology VI Semester Paper: Developmental Biology Faculty: Dr. Priya GoelDocument17 pagesFate Maps: Course: B.Sc. (H) Zoology VI Semester Paper: Developmental Biology Faculty: Dr. Priya GoelSusmita PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology-Unit 1Document13 pagesCell Biology-Unit 1Kazo SaŋPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytogenetics, Mitosis and MeiosisDocument17 pagesCytogenetics, Mitosis and MeiosisdomeniclwandilePas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of LearningDocument4 pagesSummary of LearningJr YansonPas encore d'évaluation
- Experimental EmbryologyDocument14 pagesExperimental Embryologygurjit20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Heredity SyllabusDocument13 pagesHeredity SyllabusCharlie BarkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Teacher: DR Gouri Course: Zoology Hons. 6 Sem Paper: Developmental BiologyDocument17 pagesTeacher: DR Gouri Course: Zoology Hons. 6 Sem Paper: Developmental BiologyApratim SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Booktext ID 104548024&PLACEBO IEDocument103 pagesBooktext ID 104548024&PLACEBO IEajaypatidar001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Practica 2 - InmunologíaDocument9 pagesPractica 2 - InmunologíaDante Huitron HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Tansgensis ApplicationDocument17 pagesTansgensis Applicationdishika1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bio 152 Lab 10 Animal Developemnt Worksheet PDFDocument18 pagesBio 152 Lab 10 Animal Developemnt Worksheet PDFHyena100% (1)
- Subject: Biology Chapter 8: How Do Organisms Reproduce?: Q.1 What Is Reproduction?Document16 pagesSubject: Biology Chapter 8: How Do Organisms Reproduce?: Q.1 What Is Reproduction?AadiveerPas encore d'évaluation
- B1. Cells OAA TrilogyDocument2 pagesB1. Cells OAA Trilogypixoxis263Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsDocument11 pages2.1 Cell Theory: Topic 2: CellsMorgan LockePas encore d'évaluation
- Camp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.D'EverandCamp's Zoology by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3.cancer AwarenessAndManagement SarahforOEDocument52 pages3.cancer AwarenessAndManagement SarahforOERustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Some Problems in Adsorption and Calorimetric Studies of The Steps of Catalytic ProcessesDocument25 pagesSome Problems in Adsorption and Calorimetric Studies of The Steps of Catalytic ProcessesRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Frames Data Frames: Row - Names Read - Table Read - CSV Data - MatrixDocument2 pagesData Frames Data Frames: Row - Names Read - Table Read - CSV Data - MatrixRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Factors Factors: LM GLMDocument3 pagesFactors Factors: LM GLMRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading in Larger Datasets With Read - Table Reading in Larger Datasets With Read - TableDocument4 pagesReading in Larger Datasets With Read - Table Reading in Larger Datasets With Read - TableRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Shanmuga Arts, Science, Technology & Research AcademyDocument3 pagesShanmuga Arts, Science, Technology & Research AcademyRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- M A SanskritDocument7 pagesM A SanskritRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 1 AnswersDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 AnswersRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein-Ligand Docking: Dr. Noel O'Boyle University College Cork N.oboyle@ucc - IeDocument39 pagesProtein-Ligand Docking: Dr. Noel O'Boyle University College Cork N.oboyle@ucc - IeRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- 15 MicrobiologyDocument19 pages15 MicrobiologyRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 IitDocument6 pages9 IitRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 SuccessDocument5 pages7 SuccessRustEdPas encore d'évaluation
- Mark BartlettDocument40 pagesMark BartlettbenedickPas encore d'évaluation
- Donat - Leaching PDFDocument18 pagesDonat - Leaching PDFMilenko Matulic RíosPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology - Lab 5 - Collection and Preservation of AnimalsDocument6 pagesBiology - Lab 5 - Collection and Preservation of AnimalsBeyonce SkekelPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyDocument20 pagesUNIT 1 Introduction To Food Microbiology MicrobiologyHarsh DwivediPas encore d'évaluation
- Diffusion EssayDocument2 pagesDiffusion Essayapi-242424506Pas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Enzymes: 0610 BiologyDocument9 pages5 Enzymes: 0610 BiologyAbdul HadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviews: Epidemiology, Definition and Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument15 pagesReviews: Epidemiology, Definition and Treatment of Complicated Urinary Tract InfectionsPutu AdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Escherichia Coli DH10BDocument2 pagesEscherichia Coli DH10BSecc. 2 Marco Antonio Aviles RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Twincubator Use and Maintenance: Document Type: SOPDocument4 pagesTwincubator Use and Maintenance: Document Type: SOPfelix bazanPas encore d'évaluation
- State of The Apes Volume4 EndpagesDocument95 pagesState of The Apes Volume4 EndpagesAlifanda CahyanantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading-Renaissance Learning and Unlocking Your PotentialDocument6 pagesReading-Renaissance Learning and Unlocking Your PotentialHoneyLopesPas encore d'évaluation
- Stafford & Golightly - LSDDocument102 pagesStafford & Golightly - LSDPicior de LemnPas encore d'évaluation
- Douluo Dalu V20 - Slaughter CityDocument102 pagesDouluo Dalu V20 - Slaughter Cityenrico susantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Aesculus Hippocastanum in Europe: Distribution, Habitat, Usage and Threats by Ravazzi and Caudullo, EAFS 2016Document1 pageAesculus Hippocastanum in Europe: Distribution, Habitat, Usage and Threats by Ravazzi and Caudullo, EAFS 2016Cesare RavazziPas encore d'évaluation
- Vegetative Propagation Cape BiologyDocument11 pagesVegetative Propagation Cape BiologyOrlanda EllisPas encore d'évaluation
- Immunotherapy in Bladder Cancer: Present and Future: Inmunoterapia en Cáncer Vesical. Presente y FuturoDocument19 pagesImmunotherapy in Bladder Cancer: Present and Future: Inmunoterapia en Cáncer Vesical. Presente y FuturoIrvin SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Burn NCPDocument4 pagesBurn NCPregPas encore d'évaluation
- Mercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three CommerciallyDocument7 pagesMercury, Cadmium and Lead Levels in Three Commerciallypasindu bambarandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solving Material Balance Problems For Single Units Without ReactionsDocument24 pagesSolving Material Balance Problems For Single Units Without ReactionsVanessa Arrieta HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- AMICON Ultra Centrifuge DevicesDocument9 pagesAMICON Ultra Centrifuge Devicesdjass1804Pas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis CourseworkDocument7 pagesPhotosynthesis Courseworkcjzarbkef100% (2)
- LASA Blood SamplingDocument4 pagesLASA Blood SamplinggursinPas encore d'évaluation
- Metamorphosis Rock, Paper, Scissors: Teacher Lesson PlanDocument6 pagesMetamorphosis Rock, Paper, Scissors: Teacher Lesson Planriefta89Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical Organic ChemistryDocument2 pagesPharmaceutical Organic ChemistryPankaj KushwahPas encore d'évaluation
- Nanotechnology - Volume 5 - NanomedicineDocument407 pagesNanotechnology - Volume 5 - NanomedicineArrianna WillisPas encore d'évaluation
- Silent Sound Technology: AbstractDocument3 pagesSilent Sound Technology: AbstractMegha MaturPas encore d'évaluation