Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Cardiac Electrophysiology
Transféré par
Nik-Othman C. Abdullah II0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
194 vues18 pagesElectrophysiology is the study of the electrical nature of tissues and cells. Arrhythmias are the abnormal rate or rhythm of the heart's beat. A person's heart rate can be affected by a number of factors.
Description originale:
Titre original
Introduction to Cardiac Electrophysiology
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentElectrophysiology is the study of the electrical nature of tissues and cells. Arrhythmias are the abnormal rate or rhythm of the heart's beat. A person's heart rate can be affected by a number of factors.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
194 vues18 pagesIntroduction To Cardiac Electrophysiology
Transféré par
Nik-Othman C. Abdullah IIElectrophysiology is the study of the electrical nature of tissues and cells. Arrhythmias are the abnormal rate or rhythm of the heart's beat. A person's heart rate can be affected by a number of factors.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PPTX, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 18
By: Nik-Othman Abdullah
Electrophysiology is the study of the electrical nature
of tissues and cells.
It involves the movement and measurement of voltage
and current coursing through the tissues through the
ion channel proteins;
It also includes the movement and adverse effects of
currents in whole organs such as the heart
In medicine, an Electrophysiology study (EP Test) is
used to study abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmia)
and other related cardiophysiological functions that
involves movement (tachycardia, bradycardia etc.)
Cardiac dysrhythmia or arrhythmia is the abnormal rate or
rhythm of the hearts beat
An irregular heartbeat must not be confused with an irregular
heart rate. Arrhythmias, irregular heart beating, may occur
during regular and irregular heart rates
It can either cause the heart to beat faster, slower or irregularly
Though most arrhythmias are harmless, some could be
serious and life-threatening; the heart may not be able to
pump enough blood throughout the body, which can be fatal
for vital organs that requires sufficient blood flow eg. brain,
lungs, liver etc.
During a heartbeat, the electrical impulses travel in a specific and organized pathway. When the
impulses are interrupted this causes the heart to produce an irregular heartbeat
Coronary artery diseases such as atherosclerosis (artery hardening), ischemia (blood-supply
restriction to tissues) and angina (chest pain due to restriction of blood-supply to muscles)
Blood electrolyte imbalance (lack of sodium and potassium in the diet, hyponatrimia etc.)
Smoking, drinking and use of CNS-acting drugs such as cocaine, methamphetamine, cannabis etc.
Strong emotional stress such as anger, depression or even surprise
Genetic or congenital heart defects
The phrase heart skipped a beat refers to arrhythmia, which occurs when seeing or experiencing
something staggering. This is caused by the elevated hormone levels produced by the body, which in
turn causes the heart to work profusely in an unexpected manner; this sudden surge of hormones
may trigger an arrhythmia
DRUGS
SMOKING
SMOKING
STRONG EMOTIONAL STRESS
STRONG EMOTIONAL STRESS
STRONG EMOTIONAL STRESS
STRONG
EMOTIONAL
STRESS
DRINKING
ARRYTHMIA
An Intracardiac electrophysiological study (EPS)
is a test to measure if the hearts electrical signals
are properly functioning
In the course of an average human lifespan, the
possibility of having one or more abnormal heart
functions is relatively high
An EPS is a minimally invasive procedure that helps
physicians and specialists, such as cardiologist,
determine heart rhythm problems and abnormal heart
function
Wire electrodes will be placed in the heart.
These electrodes measure the electrical
activity in the heart
The groin or neck area will be cleansed and
a topical anesthetic will be applied
IV sheaths will then be inserted through the
groin or the neck area
The physician then uses a fluoroscope
(moving x-ray images) to guide the catheter
to the heart, placing the electrodes in the
right places
The electrodes pick up the hearts electrical
impulses for measurement
The electrodes may produce controlled
impulses to induce arrhythmia. This will
help the physician understand the causes
and location of the abnormalities lie.
Living things are composed of electrical
properties running through our cells and
tissues. They are transferred and run across
different parts of our bodies through the ion
channels of the cells
The study of electrophysiology involves
measuring these electrical charges to
determine whether a part of the tissue, or
even a whole organ is working and functioning
properly
Electrophysiology measures the bioelectricity of living things
In neuroscience, it includes the electrical properties of neurons
Involves the measurement of voltage and current across
the protective membrane of a cell
The tip of a fine microelectrode will be inserted into the
cell so that the membrane potential can be measured
The tips have a diameter of less than 1 micrometer and
a resistance of 7 megaohms
A typical membrane potential of a healthy cell is -60 to -
80 mV and the action potential +40 mV
This technique allows the physiologist to
clamp, or hold onto a desired cell
potential value
This allows easier measurement of how
much ionic current crosses a cells
membrane at a specific voltage
Many of the ion channels in the membrane
of a neuron are voltage-gated ion
channels, which only opens at a specific
voltage range
This is made possible by the near-
simultaneous currents that passes as the
recording electrode are charged to alter
the cell potential
This technique records the membrane potential by injecting a specifically measured
current through the electrode
The electrode then records and transmits the current. Unlike voltage clamp, the
current clamp has the freedom in varying, and the amplifier records the voltage
This is used to study how a cell responds when current enters a cell, which is
important in understanding how neurons respond to neurotransmitters
As we know, the body requires electricity or bioelectricity in order to contract
and expand muscles, which in turn results to movements
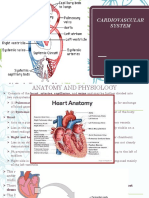
The hearts electrical system controls the rate and rhythm of the heart
In each and every heartbeat, an electrical signal spreads from the top part of the
heart and surges through the bottom. This causes the heart to contract and
expand, hence, the pumping mechanism of our heart, also, the heartbeat
These electrical signal begins in the sinoatrial node and travels to and fro via
the ion-channels, which is located in the right atrium
As the current travel from the right atrium to the left atrium, the atria contracts
causing blood to be pumped into the ventricles
The current then moves downward the atrioventricular node, sited in between
atria and ventricles. The signals here slows down a tad allowing the ventricles to
be filled with blood
As the electrical signal leaves the AV node or the bundle of His, the signal
causes a contraction action which allows the heart to pump blood into the lungs
and the rest of the body
Cardiac electrophysiology is the science in diagnosing and treatment of the electrical
activities of the heart
It is usually done by using invasive catheters with electrodes to either record and
induce programmed electrical stimulation (PES)
When the signals arise in the SA node and stimulates
the atria to contract, which then travels to the AV
node, stimulus is conducted through the bundle of
His to the Purkinje fibers.
It travels towards the endocardium at the hearts apex
and finally rests at the ventricular epicardium
On a microscopic point of view, the wave
depolarization propagates and travels through
adjacent cells via the gap junctions
The heart, being a functional syncytium, freely
allows propagation of electrical impulse in all
direction, which results in a single contractile function
The cardiac muscles are similar to neurons and skeletal
muscles
A myocardial cell has a negative membrane potential at rest,
the same as a neuron
During a stimulation above the treshold value, the voltage-
gated ion channels open up and allows flooding of cations
into the cell
The positively charged ions entering the cell causes
depolarization of an action potential
Similar to skeletal muscles, depolarization causes the opening
of calcium channels and release of Ca
2+
This causes calcium-calcium induction release from the
sarcoplasmic reticulum, hence, causes muscle contraction
Potassium channels then reopen, allowing potassium to flood
out of the cells causing repolarization
Electrical activity is spontaneously
generated by the SA node
The SA node is the physiological
pacemaker, responsible for the hearts
mechanism
Electrical impulses are propagated
throughout the right atrium all the way
to the left atrium, stimulating the
myocardium of the atria to contract
The activity of the electrical impulse
throughout the atria is visualize as the
P wave in an ECG
Electrical charges spreads throughout
the atria via intermodal tracts, from the
SA node to the AV node
An electrocardiogram is used to examine the electrical
conduction of the heart
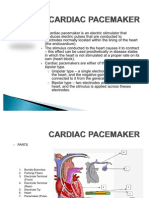
A pacemaker is used to stabilize the hearts rhythm. It is
surgivally placed and inserted into the hearts conduction
system
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Swan Ganz CatheterDocument40 pagesSwan Ganz CatheterRobertson Sliva100% (3)
- Heart Catheterization & AngioplastyDocument25 pagesHeart Catheterization & AngioplastyRifa'atul MahmudahPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodynamic Drug InfusionsDocument45 pagesHemodynamic Drug InfusionsDawit MuchePas encore d'évaluation
- Defibrillation and Cardioversion PDFDocument12 pagesDefibrillation and Cardioversion PDFmadePas encore d'évaluation
- Percutaneous InterventionsDocument55 pagesPercutaneous InterventionsShannon Bellamy-FoggPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Catheterization and Coronary AngiographyDocument5 pagesCardiac Catheterization and Coronary Angiographyedem100% (1)
- (GYNE) 3.05 Gestational Trophoblastic Disease - Co-HidalgoDocument7 pages(GYNE) 3.05 Gestational Trophoblastic Disease - Co-HidalgoMeg MisaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Physiology PDFDocument17 pagesCardiac Physiology PDFAli Aborges Jr.Pas encore d'évaluation
- CH17 Cardiovascular Assessment - Nk07Document69 pagesCH17 Cardiovascular Assessment - Nk07Abdiel Tobii SanchezPas encore d'évaluation
- AdrenalDocument7 pagesAdrenalryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac PacemakerDocument6 pagesCardiac Pacemakervin_sore100% (1)
- Cardiac Surgery Post-Op Care PDFDocument12 pagesCardiac Surgery Post-Op Care PDFHazel100% (1)
- Intra Aortic Balloon PumpDocument5 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon PumpZainal 'babeh' Arifin100% (1)
- Prehospital Rsi ManualDocument20 pagesPrehospital Rsi ManualMiguel XanaduPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingDocument57 pagesPacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingAhmad Khalil Ahmad Al-SadiPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiovascularDocument36 pagesCardiovascularShield Mae BalanlayPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Pacemakers NewDocument108 pagesCardiac Pacemakers NewAlif Fanharnita BrilianaPas encore d'évaluation
- CABG PresentationDocument55 pagesCABG Presentationnmaykanathan100% (7)
- Basics of Mechanical VentilationDocument63 pagesBasics of Mechanical VentilationDiem KhuePas encore d'évaluation
- The SOMATID - A Pleomorphic, Ultra-Microsopic Subcellular Living and Reproducing EntityDocument55 pagesThe SOMATID - A Pleomorphic, Ultra-Microsopic Subcellular Living and Reproducing EntityMarkMadMunkiPas encore d'évaluation
- MVR CabgDocument57 pagesMVR CabgRoshani sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Stress TestingDocument24 pagesCardiac Stress TestingRhoda Dela Torre ContrerasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Interventional Cath Lab Tech v4. Study GuideDocument2 pagesCardiac Interventional Cath Lab Tech v4. Study GuideRoric Thomas100% (1)
- Icu OrientationDocument9 pagesIcu OrientationKshayna 1234Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Output and Hemodynamic MeasurementDocument29 pagesCardiac Output and Hemodynamic Measurementdeepa100% (1)
- Cardiac PacingDocument4 pagesCardiac PacingmrygnvllPas encore d'évaluation
- Embriologi 1Document15 pagesEmbriologi 1Suhail UmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Simple Office SpirometryDocument42 pagesSimple Office SpirometryRoberto Merza III100% (4)
- Seminar On Hemodynamic Monitoring: BY UMA Iind Year MSC NursingDocument52 pagesSeminar On Hemodynamic Monitoring: BY UMA Iind Year MSC NursingAyen AlingPas encore d'évaluation
- Perioperative Care For CABG PatientsDocument32 pagesPerioperative Care For CABG PatientsAya EyadPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity and ExerciseDocument30 pagesActivity and ExerciseSIVA KRISHNA PRASAD ARJAPas encore d'évaluation
- Intra Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) BasicsDocument35 pagesIntra Aortic Balloon Pump (IABP) BasicsvamshidhPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic CathlabDocument26 pagesBasic CathlabwiwingPas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of Cardiac SurgeryDocument46 pagesComplications of Cardiac SurgeryRuffaeelJabr100% (2)
- Temporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 PrimerDocument51 pagesTemporary Pacemakers-SICU's 101 Primerwaqas_xsPas encore d'évaluation
- ECG .DR Ayalew EthiopiaDocument60 pagesECG .DR Ayalew EthiopiaAyalew Zewdie100% (2)
- Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument44 pagesHemodynamic Monitoringinvisigoth17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adult Cardiac Surgery - Nursing Care and ManagementDocument225 pagesAdult Cardiac Surgery - Nursing Care and ManagementOsama Elsayed AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal AnemiaDocument22 pagesNeonatal AnemiaFebrina Utami Putri100% (4)
- Aortic Root FinalDocument82 pagesAortic Root FinalMustafa KamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Hemodynamics in The Cath Lab 2Document45 pagesHemodynamics in The Cath Lab 2usfcards100% (1)
- Ventricular Assist DeviceDocument4 pagesVentricular Assist DevicemariakristinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Care of The Patient With A Cardiac Mechanical DisorderDocument8 pagesCare of The Patient With A Cardiac Mechanical DisorderthubtendrolmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Op CardiacDocument7 pagesPost Op CardiacsimplyputmonicPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandCardiac Tamponade, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacing Week PresentationsDocument54 pagesPacing Week PresentationsjoejenningsPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAbnormal Slow Heart Beats, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Cytogenetics, FISH and Molecular Testing in Hematologic Malignancies, 2008, p.334 PDFDocument334 pagesCytogenetics, FISH and Molecular Testing in Hematologic Malignancies, 2008, p.334 PDFJorge Santos100% (1)
- Holter Monitor: 'Ambulatory Electrocardiography Device''Document22 pagesHolter Monitor: 'Ambulatory Electrocardiography Device''Rachel PeredaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pacemaker NotesDocument7 pagesPacemaker Notesrohit860Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac MonitoringDocument5 pagesCardiac MonitoringAmit Kl100% (1)
- Enterobacter Spp.Document32 pagesEnterobacter Spp.ntnquynhpro100% (1)
- Nursing Responsibilities For The Patient Will Undergo Cardiac CatheterizationDocument4 pagesNursing Responsibilities For The Patient Will Undergo Cardiac CatheterizationCharlene Jacobe Cornista100% (1)
- Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument62 pagesCardiopulmonary BypassNidya Putri100% (1)
- Procedure For Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Device ClosureDocument13 pagesProcedure For Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) Device ClosurejaganjaggiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction Definition: Types of PacemakersDocument8 pagesIntroduction Definition: Types of PacemakersPrasann RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Low Delay Dual Chamber Pacemaker Using VerilogDocument4 pagesImplementation of Low Delay Dual Chamber Pacemaker Using VerilogMeghanand KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Selected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With DysrhythmiasDocument19 pagesSelected Nursing Diagnoses and Interventions For Patients With Dysrhythmiaslanie_jecielPas encore d'évaluation
- Arterial LinesDocument9 pagesArterial LinesRei IrincoPas encore d'évaluation
- 3730 Monitoring Hemodinamik-2019Document52 pages3730 Monitoring Hemodinamik-2019ojika olandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acls Course HandoutsDocument8 pagesAcls Course HandoutsRoxas CedrickPas encore d'évaluation
- FinalDocument56 pagesFinalvamshidhPas encore d'évaluation
- Sedation in The IcuDocument4 pagesSedation in The Icuprashsubbu100% (1)
- AGT Applied Anatomy Notes1.1Document69 pagesAGT Applied Anatomy Notes1.1Akshay ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung Protective Mechanical Ventilation StrategiesDocument4 pagesLung Protective Mechanical Ventilation StrategiesAnne Julia AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Ventilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials An Educational Review 2016Document7 pagesVentilator Weaning and Spontaneous Breathing Trials An Educational Review 2016Tarran PhagooPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Monitor, ECG and CauterizationDocument28 pagesCardiac Monitor, ECG and CauterizationGlaiza Mae Olivar-ArguillesPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Natural Compounds As Substitutive Antimicrobial Agents History of Medicine and Efficiency of Natural CompoundsDocument28 pagesUse of Natural Compounds As Substitutive Antimicrobial Agents History of Medicine and Efficiency of Natural CompoundsNik-Othman C. Abdullah IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction and Literature Review: - HippocratesDocument26 pagesIntroduction and Literature Review: - HippocratesNik-Othman C. Abdullah IIPas encore d'évaluation
- BBT 2033 Biopharmaceutical Technology PaperDocument27 pagesBBT 2033 Biopharmaceutical Technology PaperNik-Othman C. Abdullah IIPas encore d'évaluation
- BBT 2033 Biopharmaceutical Technology PaperDocument27 pagesBBT 2033 Biopharmaceutical Technology PaperNik-Othman C. Abdullah IIPas encore d'évaluation
- An Opinion On Earth's PopulationDocument1 pageAn Opinion On Earth's PopulationNik-Othman C. Abdullah IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Private TutorialDocument6 pagesPrivate TutorialHoàngQuýPhiPas encore d'évaluation
- IdmDocument46 pagesIdmht8zwk946sPas encore d'évaluation
- FinasterideDocument2 pagesFinasterideSyokoyolanting DondonPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Research Fact SheetDocument5 pagesPost Traumatic Stress Disorder Research Fact SheetSofia MarcelinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulating The Cell Cycle: Lesson SummaryDocument7 pagesRegulating The Cell Cycle: Lesson SummaryKayPas encore d'évaluation
- Case StudyDocument10 pagesCase Studysabrown109Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Books For Class 11 BiotechnologyDocument336 pagesNCERT Books For Class 11 BiotechnologyPiyush MohapatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Tura KuDocument104 pagesTura KuFitzgerald BillyPas encore d'évaluation
- Abbot, Diabetes ManagementDocument1 pageAbbot, Diabetes ManagementMelissa Grace DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Frog OrgansDocument25 pagesFrog OrgansKen RubioPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology 1Document15 pagesBiology 1maielsherif2020Pas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide, 112, Exam# 1, Ch. 1 - 4 PDFDocument1 pageStudy Guide, 112, Exam# 1, Ch. 1 - 4 PDFRichard ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- 5Document3 pages5Nidhi JaisPas encore d'évaluation
- Swyer SyndromeDocument1 pageSwyer SyndromeHaPas encore d'évaluation
- Addiction AND Upregulation BUISSON 2002Document7 pagesAddiction AND Upregulation BUISSON 2002Andra SilvaPas encore d'évaluation
- Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms Interfere With Macrophage AntimicrDocument175 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus Biofilms Interfere With Macrophage AntimicrshalusinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurse Writing 003 OET Practice Letter by PASS OETDocument26 pagesNurse Writing 003 OET Practice Letter by PASS OETNajad Salahudeen50% (2)
- Hyperparathyrodism Hypoparathyrodism: Dr. A. Wahyudi Pababbari, SPPD, FinasimDocument48 pagesHyperparathyrodism Hypoparathyrodism: Dr. A. Wahyudi Pababbari, SPPD, FinasimKahfiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Four Major Drug TargetsDocument34 pagesFour Major Drug TargetsFlowerPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 12Document9 pagesCH 12lalitPas encore d'évaluation
- Peripheral Neuropathy Associated With Mitochondrial Disease in ChildrenDocument8 pagesPeripheral Neuropathy Associated With Mitochondrial Disease in ChildrenRenata CardosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of The ThyroidDocument303 pagesDiseases of The ThyroidAtu OanaPas encore d'évaluation