Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
340 Tutorial 1
Transféré par
AliciaNicoleMeghanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
340 Tutorial 1
Transféré par
AliciaNicoleMeghanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CHEE 340
Tutorial 1
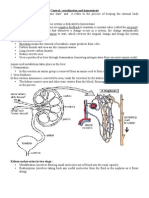
Anatomy
Anatomical Directions
Relative Directions: ______________ and ________________
1
Superior
Posterior/Dorsal
Inferior/Candal
Medial
Lateral
Anterior/Ventral
Proximal
Distal
Anatomy
Anatomical Planes
2
Saggital/Median
Frontal/Coronal Transverse/Horizontal
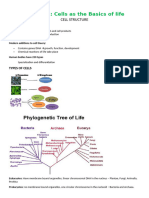
Cell Theory
Cells are mostly composed of __________________________and
__________________________
Cells synthesis molecules that are fundamental for sustaining life namely:
Anatomy
Cell
3
- All organisms are comprised of one or more cells
- The cell is the smallest unit of life
- All cells come from previously existing cells
organic compounds
water
- carbohydrates
- proteins
- lipids
- nucleic acids
Anatomy
Eukaryotic Cell
4
Plasma membrane__ surrounds the cell
Functions of the plasma membrane include:
-Cell movement
-Protection of organelles
-Transport regulation
The plasma membrane is made up of phospholipids which are
amphipathic (polar head and non-polar tail) and combine head-to-
tail to form the phospholipid bilayer .
Anatomy
Plasma Membrane
5
Molecule transport through the cell membrane occurs via:
-diffusion
-active transport vesicles large molecules
-active transport ion channels
The cell membrane allows the cell to maintain both an ion and an
molecule balance between itself and the extracellular fluid.
A typical cell environment has a high concentration of k+ ions
inside the cell and a high concentration of na+ and cl- ions in the
extracellular fluid.
Since ions are charged, they need to be transported across the
membrane using ion channels (This transport mechanism called
active transport).
Anatomy
Cell Transport
6
The four primary types of tissue are:
-epithelial
-connective
-muscle
-nervous
Epithelial tissue
Cell shapes - squamous, cuboidal, columnar, pseudostratified
Simple vs. Stratified
Functions of the epithelial tissue include: absorption,secretion,
transport, protection and sensory receptors.
Anatomy
Tissue
7
Connective tissues are acellular.
Connective tissues are primarily composed of the _________
_________.
Connective tissues encompass
Blood
Bone, cartilage,
Tendon, ligament
The connective tissue that connects muscles to bone is called a
tendon, while the tissue that connects bone to bone is called a
ligament.
Anatomy
Tissue
8
Muscle cells respond to electrical stimuli.
The three types of muscle tissue found in the human body are
skeletal, cardiac and smooth.
Nerves are conduits that serve to transmit signals to other parts of
the body.
Nervous tissue is composed of neurons and glial cells. Neurons
transmit electrical impulses, while Glial cellssupport, protect and
nourish the neurons .
The two major types of nervous tissue are motor and sensory.
Anatomy
Tissue
9
Pulmonary vs. Systemic
Vessels that move blood AWAY from the heart are called
arteries.
Vessels that move blood TO the heart are called veins.
Physiology
Cardiovascular System
10
RIGHT SIDE
Pulmonary circulation
To LUNGS from BODY
Smaller ventricles, shorter path
LEFT SIDE
Systemic circulation
To BODY from LUNGS
Physiology
Cardiovascular System
11
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
_______________
Depolarization of cells due to a self-generating electrical pulse in the
sinoatrial node (SA node) leads to a contraction of the atria
Repolarization restores normal membrane potential
Action potential continues to atrioventricular node (AV node),
which slows the pulse before being propagated to the conduction
conduit (Bundle of His)
Action potential distributed across surface of ventricles (Purkinjie
fibers) - simultaneous contraction of both ventricles, forcing blood
from ventricles to arteries
Wavefront can be measured from start to finish by ECG
12
Physiology
Action Potentials and Heartbeat
P wave: atrial excitation
Q R S wave: atrial systole, atrial diastole, ventricular excitation
T wave:ventricular systole, u is diastole
13
Physiology
ECG Waves
Pressure increased to ~180mm Hg over
brachial artery
Pressure released @ 2 mm Hg/sec
Note pressure at which 1st sound heard
(systolic press.)
Note pressure at which sound disappears
(diastolic press.)
Normal: 120/80
Acceptable: <140/<85
Borderline: 140-160/85-95
High: >160/>95
14
Physiology
Measurement of Blood Pressure
The functions of the skeletal system are protection and support,
help with movement, mineral storage, produces red blood cell
marrow.
An average adult skeletal system consists of 206bones.
Bones are specialized connective tissue (mineralized).
Bones are classified into four categories based on their shape
namely:long, short, flat, irregular shaped.
The two types of bone found in the human body arecompact and
spongy.
15
Physiology
Skeletal System
Cortical/ Compact Bone vs. Spongy/ Cancellous/ Trabeular Bone
16
Physiology
Skeletal System
Cortical
Forms the shaft and hard
outer covering
Has minimum gaps or
spaces
Gives smooth, white, and
solid appearance
Ten times less surface area
than spongy bone
80% of the total bone mass
of an adult skeleton
Spongy
Ends of long bones and the
interior filling
Made of a network of flat
or needle-shaped
trabeculae
Makes the overall bone
lighter and allows room for
blood vessels and marrow
20% of total bone mass of
an adult skeleton
The cells that are involved in bone remodeling are osteoclasts and
osteoblasts.
osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation.
osteoclasts are responsible for bone resorption.
An imbalance in the remodelling cycle leads to osteoporosis.
The two types of bones found in the human body compact, and
spongy.
17
Physiology
Bone Remodeling
The three major joints through which bones are connected are
fibrous, cartiliginous, and synovial.
The six types of synovial joints are:
- ball and socket
- hinge
- gliding
-saddle
-ellipsoid
-pivot
18
Physiology
Joints
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- AP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ PreviewDocument30 pagesAP Biology 2020 Practice Exam 2 FRQ Preview(22) Bahar Baturoglu100% (3)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Practical Answers DCPIPDocument98 pagesPractical Answers DCPIPSanad BashirPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Behaviour Against Newer Methods of Food ProcessingDocument44 pagesMicrobial Behaviour Against Newer Methods of Food ProcessingMonika Mathur100% (1)
- Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast ChromosomeDocument17 pagesCytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Chromosomeardusias100% (1)
- Full Download An Introduction To Human Disease Pathology and Pathophysiology Correlations 8th Edition Crowley Test Bank PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download An Introduction To Human Disease Pathology and Pathophysiology Correlations 8th Edition Crowley Test Bank PDF Full Chapterspentsuffuse9w789100% (12)
- Chapter 4 Nature and Composition of Crops 124136Document79 pagesChapter 4 Nature and Composition of Crops 124136S L A YPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology Lecture 2021 Full ContentDocument119 pagesCell Biology Lecture 2021 Full ContentStreet TunezPas encore d'évaluation
- Use of Herbal Bioenhancers To Increase The Bioavailability of DrugsDocument13 pagesUse of Herbal Bioenhancers To Increase The Bioavailability of DrugsRatan Deep ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For HomeostasisDocument21 pagesNotes For Homeostasisfreednemon83% (6)
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Document54 pagesBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124Pas encore d'évaluation
- Endocrine Physiology Lecture 2Document9 pagesEndocrine Physiology Lecture 2Tofunmi Kunle-KunbiPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochem Practice TestDocument8 pagesBiochem Practice TestEvette SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument7 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsClarence MallariPas encore d'évaluation
- IX-5-The Fundamental Unit of LifeDocument61 pagesIX-5-The Fundamental Unit of LifeAbhay AryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications: Arthur S. Reber, Franti Sek BaluskaDocument8 pagesBiochemical and Biophysical Research Communications: Arthur S. Reber, Franti Sek BaluskaStephanie CorderoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007Document17 pagesMark Scheme Bio 2 Trial Selangor 2007hasimahazitPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz 1 - BIOL 420 U - Advanced Cell and Molecular BiologyDocument6 pagesQuiz 1 - BIOL 420 U - Advanced Cell and Molecular BiologyCumPas encore d'évaluation
- 0610 s14 Ms 33 PDFDocument9 pages0610 s14 Ms 33 PDFCorinSaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDocument16 pagesCell Structure, Function Practice Test With AnswersDJ ISAACSPas encore d'évaluation
- B1.10 Exchanging Materials - Surface Area ACL TeacherDocument19 pagesB1.10 Exchanging Materials - Surface Area ACL TeacherssjundiPas encore d'évaluation
- English For Academics and Professional Purposes: General To SpecificDocument10 pagesEnglish For Academics and Professional Purposes: General To SpecificChristine Joy CagatinPas encore d'évaluation
- Transport MechanismDocument6 pagesTransport MechanismJessie Katrisha Tayag100% (2)
- Chapter 3 The CellDocument68 pagesChapter 3 The CellCarlos FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology Module 2Document11 pagesGeneral Biology Module 2Jee-Anne HerbularioPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1.3 Revision Practice (Ans)Document3 pagesTopic 1.3 Revision Practice (Ans)Mahina WongPas encore d'évaluation
- DDL in Gen Bio With AnnotationsDocument8 pagesDDL in Gen Bio With AnnotationsEarl Caesar Quiba Pagunsan100% (1)
- Biology I: Multiple Choice Questions 20 Items Name: - SchoolDocument3 pagesBiology I: Multiple Choice Questions 20 Items Name: - SchoolEJ RaveloPas encore d'évaluation
- Film Coatings For Taste Masking and Moisture ProtectionDocument12 pagesFilm Coatings For Taste Masking and Moisture ProtectionNg Chai HwaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaDocument10 pagesCell Definition, Types, & Functions BritannicaKolade YousuffPas encore d'évaluation
- GENBIO 2 Lec Topic Guide T3 22-23Document4 pagesGENBIO 2 Lec Topic Guide T3 22-23Mariah Vaness BrionesPas encore d'évaluation