Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Concepts and Issues IN Measurement & Instrumentation: Instructor:Dr Alivelu M Parimi
Transféré par
Saketh DahagamTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Concepts and Issues IN Measurement & Instrumentation: Instructor:Dr Alivelu M Parimi
Transféré par
Saketh DahagamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CONCEPTS AND ISSUES
IN
MEASUREMENT &
INSTRUMENTATION
Lecture 1
Instructor :Dr Alivelu M Parimi
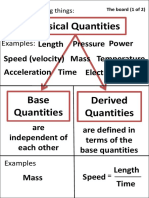
Measurement
A method to obtain information regarding
the physical values of the variable.
Instrumentation
Devices used in measurement system
For the result to be meaningful, the following two requirements
must be met
Standard that is used for comparison must be well
established, highly accurate and reproducible.
The measurement devices and calibration procedure adopted
in the act of measurement must have proven reliability.
2
Definition
In the case of process industries and
industrial manufacturing
To improve the quality of the product
To improve the efficiency of production
To maintain the proper operation.
Measurement is an integral part of
automation, scientific research,
technological inventions and our day to
day life.
3
Why measurement?
BRIEF HISTORY OF
MEASUREMENT
Weights and measures were among the earliest tools invented
by man
Foot , forearm, hand, or finger
"inch," "foot," and "yard
meter , gram, liter
a mass unit for gems, was derived from the
carob seed (1 carat = 200 mg)
THE SYSTEM INTERNATIONAL
meter (m) distance "The meter is the length of the path traveled by light in vacuum
during a time interval of 1/299 792 458 of a second."
kilogram (kg) mass "The kilogram is equal to the mass of the international prototype
of the kilogram."
second (s) time "The second is the duration of 9 192 631 770 periods of the
radiation corresponding to the transition between the two
hyperfine levels of the ground state of the caesium 133 atom."
ampere (A) electric
current
"The ampere is that constant current which, if maintained in two
straight parallel conductors of infinite length, of negligible
circular cross-section, and placed 1 meter apart in vacuum, would
produce between these conductors a force equal to 2 10
-7
newton per meter of length."
kelvin (K) temperatu
re
"The kelvin is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic
temperature of the triple point of water."
mole (mol) amount of
substance
"The mole is the amount of substance of a system which contains
as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 0.012 kilogram
of carbon 12. When the mole is used, the elementary entities must
be specified and may be atoms, molecules, ions, electrons, other
particles, or specified groups of such particles."
candela (cd) intensity
of light
"The candela is the luminous intensity, in a given direction, of a
source that emits monochromatic radiation of frequency 540
10
12
hertz and that has a radiant intensity in that direction of 1/683
watt per steradian."
Supplementary and derived units
Derived Unit Measures Derivation Formal Definition
hertz (Hz) frequency /s s
-1
newton (N) force kg(m/s
2
) kgms
-2
pascal (Pa) pressure N/m
2
kgm
-1
s
-2
joule (J) energy or work Nm kgm
2
s
-2
watt (W) power J/s kgm
2
s
-3
coulomb (C) electric charge As As
volt (V) electric potential W/A kgm
2
s
-3
A
-1
farad (F) electric capacitance C/V kg
-1
m
-2
s
4
A
2
ohm (omega) electric resistance V/A kgm
2
s
-3
A
-2
siemens (S) electric conductance A/V kg
-1
m
-2
s
3
A
2
weber (Wb) magnetic flux Vs kgm
2
s
-2
A
-1
tesla (T) magnetic flux density Wb/m
2
kgs
-2
A
-1
henry (H) inductance Wb/A kgm
2
s
-2
A
-2
degree Celsius (C) temperature K - 273.15 K
radian (rad) plane angle mm
-1
steradian (sr) solid angle m
2
m
-2
lumen (lm) luminous flux cdsr cdsr
lux (lx) illuminance lm/m
2
m
-2
cdsr
-1
becquerel (Bq) activity /s s
-1
gray (Gy) absorbed dose J/kg m
2
s
-2
sievert (Sv) dose equivalent Gy(multiplier) m
2
s
-2
katal (kat) catalytic activity mol/s mols
-1
Second column provides the measure and for the unit, the third column shows how each
unit is derived from the preceding units, and the fourth column gives the formal
equivalence of the unit in terms of the base units.
Classifications of types of
measurement applications
Monitoring
Control
Experimental
Monitoring
Measuring device keeps track of the quantity
Control of processes
Experimental engineering
analysis
Experimental engineering
analysis
Experimental engineering
analysis
To acquire data or information (hence data
acquisition) about parameters, in terms of:
putting the numerical values to the physical quantities
making measurements otherwise inaccessible.
producing data agreeable to analysis (mostly in
electrical form)
Data Acquisition Software (DAS) data is
acquired by the instrumentation system.
13
Why instrumentation?
Conclusion
The history,
definition and
importance of measurement
Find the relationship between applied force F and resulting friction torques
Tf in the simple brake.
Prob: 1.3 b on page 8
Exercise
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Units and Standards of MeasurementsDocument26 pagesUnits and Standards of Measurementsarsenic_94Pas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement and Instrumentation Engineering NotesDocument12 pagesMeasurement and Instrumentation Engineering Notess_natarajan90Pas encore d'évaluation
- İfe 1Document18 pagesİfe 1n295w769vjPas encore d'évaluation
- 20200915-XI-Physics-Unit and Measurement-1 of 4Document13 pages20200915-XI-Physics-Unit and Measurement-1 of 4Omkar DatkhilePas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT I: Introduction To Physics: Lesson 1.1. Measurement in PhysicsDocument36 pagesUNIT I: Introduction To Physics: Lesson 1.1. Measurement in PhysicsFlorelen GarbePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1-Units and MeasurementsDocument22 pagesCh1-Units and MeasurementsALIF SYAKIR SATARPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics FormulaeDocument12 pagesPhysics FormulaeKamlesh Kumar100% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concept of MeasurementsDocument31 pagesChapter 1 - Basic Concept of MeasurementsSarweash RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics & MeasurementsDocument38 pagesPhysics & Measurementsعدنان باحكيمPas encore d'évaluation
- Gimbi Poly Technic College Basic Electrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing NTQF Level - I Learning Guide-28Document38 pagesGimbi Poly Technic College Basic Electrical/Electronic Equipment Servicing NTQF Level - I Learning Guide-28Lemmi GutetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 1 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTDocument20 pagesModule 1 UNITS AND MEASUREMENTMarga BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensor: - The Device Which Change Energy From One Form To AnotherDocument0 pageSensor: - The Device Which Change Energy From One Form To Anotherwww.bhawesh.com.npPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Genphysics 1 UnitsDocument38 pages2 Genphysics 1 Unitspotato macchiatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 - Units, Dimensions and MeasurementsDocument8 pagesTopic 1 - Units, Dimensions and MeasurementsRomel TugadePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Reviewer (First Quarter)Document4 pagesPhysics Reviewer (First Quarter)Jaimarae SumalnapPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Units Measurements OKDocument17 pages1 Units Measurements OKSARANGMUMBAIPas encore d'évaluation
- 01units and DimensionsDocument14 pages01units and DimensionsSumathi SrinivasPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 1: Preparatory Activity Metrology & Instrumentation (3341905)Document6 pagesExperiment No. 1: Preparatory Activity Metrology & Instrumentation (3341905)T.MPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental Physics "Unit and Quantity": Name: Citra Fatima Marsidi NIM: 19101105020 Study Program: PharmacyDocument7 pagesFundamental Physics "Unit and Quantity": Name: Citra Fatima Marsidi NIM: 19101105020 Study Program: PharmacyCitra MarsidiPas encore d'évaluation
- BranchesDocument3 pagesBranchesMelissa A. BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- I Units and Measurements Studver 1Document50 pagesI Units and Measurements Studver 1Margox TerencioPas encore d'évaluation
- EDMDocument15 pagesEDMOds GuysPas encore d'évaluation
- The Basics of Mechanics of SolidsDocument16 pagesThe Basics of Mechanics of SolidsDipankar borahPas encore d'évaluation
- Measurement - 2019 - Lecture - Slides (For Students - Shared Folder)Document117 pagesMeasurement - 2019 - Lecture - Slides (For Students - Shared Folder)Wee Chee LimPas encore d'évaluation
- The Handbook of Groundwater EngineeringDocument11 pagesThe Handbook of Groundwater EngineeringminashahabPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics - 1 Chapter 1Document41 pagesPhysics - 1 Chapter 1Dreamrs TtyPas encore d'évaluation
- NDT Overview M1 Part3Document78 pagesNDT Overview M1 Part3Leon Heart FCPas encore d'évaluation
- International System'S Units: Jebel Ali Power PlantDocument14 pagesInternational System'S Units: Jebel Ali Power PlantAhmed EldosokyPas encore d'évaluation
- U-1 Units and Measurements XiDocument13 pagesU-1 Units and Measurements XiLakshayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem101 Ho1Document12 pagesChem101 Ho1Jordan DingayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide PhysicsDocument14 pagesStudy Guide PhysicsPaula MarsanPas encore d'évaluation
- Week1 MeasurementinphysicsDocument36 pagesWeek1 MeasurementinphysicsJasmin EismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Quantities: Length Mass Speed (Velocity) Pressure Power TemperatureDocument7 pagesPhysical Quantities: Length Mass Speed (Velocity) Pressure Power Temperaturepradipta satriaPas encore d'évaluation
- PhysicsDocument12 pagesPhysicsCristine DiannePas encore d'évaluation
- 1-PSAE Review 2021 Rural Electrification Part 1 - MKSODocument153 pages1-PSAE Review 2021 Rural Electrification Part 1 - MKSOFrances PasanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Measurements & InstrumentationDocument50 pagesElectrical Measurements & InstrumentationBe JohnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics HandbookDocument10 pagesPhysics HandbookNational Physical Laboratory100% (1)
- Easurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: IDocument28 pagesEasurements: Course: Diploma Subject: Applied Science Physics Unit: Ipankaj baviskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsDocument18 pagesChapter 1 Physical Quantities and UnitsJustice WongPas encore d'évaluation
- Ipe JR PhysicsDocument144 pagesIpe JR PhysicsSai Varun KruthiventiPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Introduction of MetrologyDocument5 pagesWeek 1 Introduction of MetrologyWaleed AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Heat PowerDocument82 pagesBasics of Heat Powerharish151984Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class Xi MaterialDocument316 pagesClass Xi MaterialShlok MishraPas encore d'évaluation
- Units Measurements 022524Document12 pagesUnits Measurements 022524r55088299Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pocket PhysicsDocument10 pagesPocket PhysicsFaraz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 9 JARIS Chapter # 1: SECTION 2 Measurements in ExperimentDocument57 pagesGrade 9 JARIS Chapter # 1: SECTION 2 Measurements in ExperimentZnitePas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1Document21 pagesChapter 1Firaa'ol GizaachooPas encore d'évaluation
- ASM Subject Guide - AluminumDocument43 pagesASM Subject Guide - AluminumADIPESHPas encore d'évaluation
- 03nuclear SpectrosDocument10 pages03nuclear SpectrosMohamed AljamaeePas encore d'évaluation
- Physics UnitsDocument5 pagesPhysics UnitsGopan KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- SI Base UnitsDocument20 pagesSI Base UnitsSatish Kumar MauryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hogan 1998 0186Document4 pagesHogan 1998 0186Particle Beam Physics LabPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Thermodynamics (Lecture#01) : Course OutlineDocument16 pagesApplied Thermodynamics (Lecture#01) : Course Outlinevaratharajan g rPas encore d'évaluation
- ECET-56100 Metrology ConceptsDocument14 pagesECET-56100 Metrology Conceptsvivalavaca13Pas encore d'évaluation
- QuantummethnfslfpjgDocument152 pagesQuantummethnfslfpjgMary Grace Magpayo LanwangPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresD'EverandStrength of Materials and Structures: An Introduction to the Mechanics of Solids and StructuresÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Ultrasonic Sensor For Level MeasurementDocument34 pagesUltrasonic Sensor For Level MeasurementAshish RawatPas encore d'évaluation
- SystematixDocument11 pagesSystematixSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Icici Prudential Mutual Fund Statement of Additional InformationDocument386 pagesIcici Prudential Mutual Fund Statement of Additional InformationSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Axis SecuritiesDocument17 pagesAxis SecuritiesSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Eagle Eyes ReportDocument3 pagesEagle Eyes ReportSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- MotialaDocument10 pagesMotialaSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Herbal MedicineDocument220 pagesHerbal MedicineSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- PrabhudasDocument8 pagesPrabhudasSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- ICICI Securities ReportDocument4 pagesICICI Securities ReportSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Quants-BSTREAM-Mental Ability PDFDocument3 pagesQuants-BSTREAM-Mental Ability PDFAshishPas encore d'évaluation
- TS TRANCO Sub Engineer Eelectrical Previous Year Paper-2012 PDFDocument16 pagesTS TRANCO Sub Engineer Eelectrical Previous Year Paper-2012 PDFSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- TSSPDCL AE General Studies Previous Papers MinDocument37 pagesTSSPDCL AE General Studies Previous Papers MinSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Kokate Forensic Pharmacy PDFDocument201 pagesKokate Forensic Pharmacy PDFSouvik Saha100% (2)
- Few RatiosDocument1 pageFew RatiosSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Compund Interest PDFDocument10 pagesCompund Interest PDFSiddhant SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple PDF DocumentDocument1 pageA Simple PDF DocumentSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bapsi Sidhwa 2Document16 pagesBapsi Sidhwa 2Saketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Handout-Post Colonial Literatures 2016Document3 pagesHandout-Post Colonial Literatures 2016Saketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Secret of The UniverseDocument1 pageSecret of The UniverseSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- mvsubtitles.com.txtDocument1 pagemvsubtitles.com.txtSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Bapsi Sidhwa 2Document16 pagesBapsi Sidhwa 2Saketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 14lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 VVDocument23 pagesLecture 14lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 VVSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- CultureDocument16 pagesCultureSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS BY STUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCE,STUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH ANDDocument2 pagesPRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS BY STUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCE,STUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH AND SCIENCESTUDENTS OF TECH ANDSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 13lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 VVVDocument23 pagesLecture 13lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 Lecture 1 VVVSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Resistive TransducersDocument18 pagesGeneralized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Resistive TransducersSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Photoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument32 pagesPhotoelectric Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Resistive Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument28 pagesResistive Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Inductive Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument26 pagesInductive Transducers: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument14 pagesGeneralized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Generalized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiDocument32 pagesGeneralized Performance Characteristics of Instruments: Instructor: DR Alivelu M ParimiSaketh DahagamPas encore d'évaluation
- Olympian Ratings Guide - Generator Sets - CATERPILLARDocument18 pagesOlympian Ratings Guide - Generator Sets - CATERPILLARpevare50% (2)
- Physics Summary Class9Document18 pagesPhysics Summary Class9Ivan dragoPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion Tables of Measuring UnitsDocument14 pagesConversion Tables of Measuring UnitsVic ValdezPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventory ClassificationDocument9 pagesInventory Classificationtamal mukherjeePas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC FormulasDocument7 pagesHVAC Formulasisaiaspaula80Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculations and Tables QRG SlicklineDocument35 pagesCalculations and Tables QRG SlicklineEduardo García SeminarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Based Physics Prelims PDFDocument10 pagesCalculus Based Physics Prelims PDFMark De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- 470 39 Solutions-Instructor-Manual SM Chapter-9 PDFDocument3 pages470 39 Solutions-Instructor-Manual SM Chapter-9 PDFSerajPas encore d'évaluation
- (Crosti - Ru) Mono PDFDocument27 pages(Crosti - Ru) Mono PDFNana biblaiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix & IndexDocument43 pagesAppendix & IndexSeethalakshmi ArunachalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Title Lorem Ipsum: Sit Dolor AmetDocument27 pagesTitle Lorem Ipsum: Sit Dolor AmetJanice BlancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Humble Homemade Hifi - ModulusDocument7 pagesHumble Homemade Hifi - ModulusmerrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Bony IauDocument572 pagesBony IauTommy HectorPas encore d'évaluation
- ES 112 Physics For Engineers Assignment 1Document2 pagesES 112 Physics For Engineers Assignment 1GB SoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Odpowiedzi Do Kart Pracy Ucznia CZ 1 Zakres Podstawowy Dzial 3Document16 pagesOdpowiedzi Do Kart Pracy Ucznia CZ 1 Zakres Podstawowy Dzial 3Marysia KamionkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mage Akka Maashi 4Document32 pagesMage Akka Maashi 4Gayan63% (8)
- Rotel RB-993 - SMDocument4 pagesRotel RB-993 - SML NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Constants and ConversionsDocument32 pagesConstants and ConversionsTan TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Caterpillar Field GuideDocument52 pagesCaterpillar Field Guidesburckhardt86% (7)
- Template - Activitiy 1 Length and Angle-Measuring InstrumentsDocument6 pagesTemplate - Activitiy 1 Length and Angle-Measuring InstrumentsMishreen MarohombsarPas encore d'évaluation
- C12/16 C16/20 C20/25 C25/30 C30/37 C35/45 C40/50 C45/55 C50/60 12 16 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 16 20 25 30 37 45 50 55 60Document1 pageC12/16 C16/20 C20/25 C25/30 C30/37 C35/45 C40/50 C45/55 C50/60 12 16 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 16 20 25 30 37 45 50 55 60vtalexPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 - Drug Calculations (1 Hour)Document42 pages2 - Drug Calculations (1 Hour)LovelyJoy Manalo100% (1)
- Formula RioDocument3 pagesFormula RioCarlo DarwinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 00Document26 pagesChapter 00Fernandus Nico Hutagaol0% (1)
- Chemistry 1 Tutor - Vol 1 - Worksheet 4 - TemperatureDocument12 pagesChemistry 1 Tutor - Vol 1 - Worksheet 4 - TemperatureCarl JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- 02 SCH 008318 06r1 DragonfighterDocument32 pages02 SCH 008318 06r1 DragonfighterHector VillarrealPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus-Based Physics 1 PQ1-PQ2Document19 pagesCalculus-Based Physics 1 PQ1-PQ2Vendaver AlzatePas encore d'évaluation
- Pressureconversion PDFDocument3 pagesPressureconversion PDFShaikhMazharAhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 Gas Conversion ChartsDocument6 pages00 Gas Conversion Chartskarun agrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- TLE Cookery7-8 Week4Document4 pagesTLE Cookery7-8 Week4Karen Arisga DandanPas encore d'évaluation