Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Data Acquisition System
Transféré par
anand007krishnanCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Data Acquisition System
Transféré par
anand007krishnanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
By
Prof.B.Ashok
Data acquisition is simply the gathering of information
about a system or process
Information may be gathered for various reasons
knowledge
research and development
systems or process monitoring
systems or process control
Data acquisition requires one or more transducers
(sensors) to sense the system or process, and a signal
conditioning instrument, Transmitting element, interfacing,
processing, storage and output.
Real Time Data Acquisition relates to data being
acquired and used in the same time frame, such as
when monitoring or controlling a system or process
Data Logging is when acquired data is stored or logged
for later use or analysis. Involves some form of memory.
Data acquisition and data logging is not a complex or
mysterious science as viewed by some one
Data acquisition in its simplest form could be to
measure the length of a piece of string with a ruler
Data logging in its simplest form could be to write that
measured length down on a sheet of paper
A data acquisition or data logging system generally includes the
following components:
sensors or transducers which provide the fundamental
information of the parameters to be measured
a device to convert the primary signal from the sensors
into a form compatible with information processing systems
a computer or other controller which supervises the overall
system, and manages the generated data
There are many different parameters for which sensors or
transducers are commonly available:
temperature
pressure, force, mass, weight
velocity, acceleration, vibration
strain, stress, distortion, fatigue
flow, volume, level
length, width, depth, thickness, displacement
state, pulse, counter
composition, concentration
The purpose of a Data Acquisition system is to measure a
physical phenomenon such as light, temperature, pressure,
sound, etc. The building blocks of a Data Acquisition system
are as follows:
Transducer
Signal
Signal Conditioning eXtensions for Instrumentation (SCXI)
Data Acquisition (DAQ) device
Driver level and application level software
These five building blocks allow you to bring the physical
phenomena you want to measure into your computer for
analysis and presentation.
System
Overview(Conti)
The purpose of a transducer is to convert a physical
phenomena (light, temperature, pressure, sound, etc.) into a
measurable electrical signal, such as voltage or current.
Types
Temperature
Light
Sound
Force
Pressure
Position
Fluid flow
pH levels
Transducer Overview(Conti)
Signal
Physical
Phenomena
A transducer converts a
physical phenomena
into a measurable
signal
Types of Signals
Information in a Signal
State, Rate, Level, Shape, and
Frequency
Signal Overview
With the help of a transducer we have converted a physical
phenomena (light, temperature, pressure, sound, etc.) into a
signal.
Not all signals are measured in the same manner, so we will
need to learn how to categorize our signal as one of two types:
Digital
Analog
Once we have categorized our signal we need to figure out what
type of information we want out of that signal. The possible
types of information we can obtain from a signal are:
State
Rate
Level
Shape
Frequency
Your Signal
Analog Digital
Two possible levels:
High/On (2 - 5 Volts)
Low/Off (0 - 0.8 Volts)
Two types of
information:
State
Rate
Digital
Your Signal
Digital
State
A digital signal only has two possible
states: ON or OFF.
Rate
A digital signal also changes state with
respect to time. how the digital signal
changes states with respect to time.
Your Signal
Analog
Unlike a digital signal, an analog signal
can be at any voltage level with respect
to time.
Since an analog signal can be at any
state at any time, the physical
quantities we want to measure differ
from those of a digital signal.
We can measure the level, shape, or
frequency of an analog signal.
Continuous signal
Can be at any value with respect
to time
Three types of information:
Level
Shape
Frequency (Analysis required)
Your Signal
Analog
Analysis
Required
Topics
Purpose of Signal Conditioning
Types of Signal Conditioning
Signal conditioning circuits improve the quality of signals
generated by transducers before they are converted into
digital signals by the PC's data-acquisition hardware.
Examples of signal conditioning are signal scaling,
amplification, linearization, cold-junction compensation,
filtering, attenuation, excitation, common-mode rejection,
and so on.
Noisy, Low-Level Signal Filtered, Amplified Signal
Signal Conditioning takes a signal that is difficult for your
DAQ device to measure and makes it easier to measure
Signal Conditioning is not always required
Depends on the signal being measured
Low-Level Signal
External
Amplifier
DAQ Device
Lead Wires
Instrumentation
Amplifier
Noise
ADC
+
_
Used on low-level signals (i.e. thermocouples)
Maximizes use of Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) range
and increases accuracy
Increases Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
DAQ Hardware turns your PC into a
measurement and automation
system
Computer
Your Signal
DAQ Device
Terminal Block
Cable
Terminal Block and Cable route your signal
to specific pins on your DAQ device
Terminal Block and Cable can be a
combination of 68 pin or 50 pin
Your Signal
Terminal Block
Cable
50 pin connector
Most DAQ devices have:
Analog Input
Analog Output
Digital I/O
Counters
Specialty devices exist for specific applications
High speed digital I/O
High speed waveform generation
Dynamic Signal Acquisition (vibration, sonar)
Connect to the bus of your computer
Compatible with a variety of bus protocols
PCI, PXI/CompactPCI, ISA/AT, PCMCIA, USB,
1394/Firewire
Computer
DAQ Device
Does not require programming.
Enables developers to design the
custom instrument best suited to their
application.
Examples: TestPoint,SnapMaster,
LabView, DADISP, DASYLAB, etc.
Testing of internal combustion engine with measurement of
various parameters using software.
Speed, load, temperature, and pressure, and vibration, flow
of air, water and fuel by suitable sensors.
Essential components of the data acquisition system are
sensors, signal conditioner, ADC card and computer.
Display forms on the computer monitor can be made by
using software like LabVIEW.
1. Temperature measurement
2. Load measurement
3. Flow measurement
4.Sound and vibration
measurement
5. Data Logging
1. For temperature measurement- RTDs.
2. For load measurement- S-type load cell.
3. For speed measurement- proximity sensor.
4. For water flow measurement- mini turbine flow sensor.
5. For fuel flow measurement- ultrasonic fuel flow sensor.
Field Wiring
Signal Conditioning
Data Acquisition Hardware
PC (operating system)
Data acquisition software
1. Temperature
2. Force
3. Speed
4. Water flow
5. Fuel consumption
6. Air consumption
PARAMETERS TO BE MEASURED
SENSORS
AMPLIFIERS
PARAMETERS TO BE CONTROLLED
RELAYS
SOLENOID VALVES
DC, STEP,SERVO MOTORS
USE A VISUAL PROGRAM
DELPHI
VISUAL BASIC
VISUAL C
MATLAB
PROFESSIONAL PROGRAM
(eg LABVIEW,DASYLAB)
First the engine is started thus air & fuel is consumed.
To measure fuel flow sensor is inserted in between fuel
tank & engine.
To measure cooling water flow, Mini Turbine Flow Sensor
is incorporated.
To measure air flow a fan & proximity sensor arrangement
is used
RTD sensors are used to record the temperatures.
Load on the system is varied by using hydraulic
dynamometer.
Load is measured by strain gauge connected to the
dynamometer.
Proximity sensor is used to calculate speed of engine.
The output of all the sensors is given to the DAQ modules.
According to different parameters obtained performance
characteristics are plotted using LABVIEW interface.
THANK
YOU
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
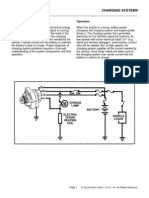
- Alternator CircuitDocument0 pageAlternator CircuithabotugeunimPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Quick Reference CardDocument3 pagesQuick Reference Cardaslam.ambPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- TIME MGMT TRAINING WORKSHOPDocument22 pagesTIME MGMT TRAINING WORKSHOPanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual: Installation, Operation & MaintenanceDocument86 pagesManual: Installation, Operation & MaintenanceNhân NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- GearboxesDocument70 pagesGearboxesanand007krishnan0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Covey Time Management MatrixDocument2 pagesCovey Time Management Matrixanand007krishnan100% (2)
- Characterizing Engine Performance With BSFC Maps: OrientationDocument2 pagesCharacterizing Engine Performance With BSFC Maps: Orientationanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Electrical Systems GuideDocument14 pagesAutomobile Electrical Systems GuideDeepankumar Athiyannan100% (1)
- Formation Damage ExamplesDocument89 pagesFormation Damage ExamplesLaurensius Raymond SanjayaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluent-Intro 16.0 L02 IntroCFD PDFDocument45 pagesFluent-Intro 16.0 L02 IntroCFD PDFAnonymous 8209ZTPas encore d'évaluation
- OBGYN Form 3 Answers KeyDocument2 pagesOBGYN Form 3 Answers KeyGrace0% (1)
- ASFP Launch Fire Risk PDFDocument44 pagesASFP Launch Fire Risk PDFamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Scada On Hydro Power Plant Cascade - Case StudyDocument49 pagesScada On Hydro Power Plant Cascade - Case StudyRaju KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Application Format - AYUSH CoE Reserach Fellow - 24.052019Document3 pagesApplication Format - AYUSH CoE Reserach Fellow - 24.052019anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Knock Sensor Overview - Piezoelectric Effect and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesKnock Sensor Overview - Piezoelectric Effect and Applicationsanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ayurved PG Brochure DPU 2018Document32 pagesAyurved PG Brochure DPU 2018anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparitive Study of Port Injected and Carburated EngienDocument8 pagesComparitive Study of Port Injected and Carburated Engienanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- FALLSEM2013 14 CP0566 26 Jul 2013 RM01 Lecture 3 Calibration SensorsactuatorsDocument67 pagesFALLSEM2013 14 CP0566 26 Jul 2013 RM01 Lecture 3 Calibration Sensorsactuatorsanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronic Throttle Body Datasheet 51 en 10726070795Document5 pagesElectronic Throttle Body Datasheet 51 en 10726070795anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Is 14599Document26 pagesIs 14599anand007krishnan100% (1)
- 5-Day Automotive Engineering Programme at ARAI PuneDocument10 pages5-Day Automotive Engineering Programme at ARAI Puneanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive DrawingDocument114 pagesAutomotive Drawinganand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Permutations (Unit Practise Problems)Document5 pagesPermutations (Unit Practise Problems)anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Indian Standard-114Document3 pagesAutomotive Indian Standard-114anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biodiesel Optimization Project PlanDocument1 pageBiodiesel Optimization Project Plananand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensotronic Brake ControlDocument15 pagesSensotronic Brake Controlanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 1E44C007C6B744D9B3DC0221D6002F22Document2 pages1E44C007C6B744D9B3DC0221D6002F22anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5-Day Automotive Engineering Programme at ARAI PuneDocument10 pages5-Day Automotive Engineering Programme at ARAI Puneanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Automotive Engnieering 2014Document2 pagesAutomotive Engnieering 2014rudey18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Static and Dynamic Analysis of Space FrameDocument6 pagesStatic and Dynamic Analysis of Space Frameanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- FALLSEM2013-14 CP1956 07-Aug-2013 RM01 MediumcarbonsteelsHeattreatmentHardenabilityDocument20 pagesFALLSEM2013-14 CP1956 07-Aug-2013 RM01 MediumcarbonsteelsHeattreatmentHardenabilityanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- SMSB 2: 3667 18138 05-NOV-2013 12:37PM 369800265Document12 pagesSMSB 2: 3667 18138 05-NOV-2013 12:37PM 369800265anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Interview Questions Asked For Mechanical EngineerDocument5 pagesList of Interview Questions Asked For Mechanical Engineeranand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Knock Sensor Operation Using Piezoelectric EffectDocument15 pagesKnock Sensor Operation Using Piezoelectric Effectanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- These Are My 5 Year Goals - Here Come The Rewards!!: Goal 1 Goal 2Document13 pagesThese Are My 5 Year Goals - Here Come The Rewards!!: Goal 1 Goal 2anand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- WINSEM2013 14 CP0776 TB05 Road Vehicle Safety in Windy EnvironmentsDocument18 pagesWINSEM2013 14 CP0776 TB05 Road Vehicle Safety in Windy Environmentsanand007krishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rajan 2013Document12 pagesRajan 2013TheNourEldenPas encore d'évaluation
- Comprehensive Land Use Plan in Municipality of TigbauanDocument4 pagesComprehensive Land Use Plan in Municipality of TigbauanmaygracedigolPas encore d'évaluation
- Moral vs Non-Moral Standards ExplainedDocument2 pagesMoral vs Non-Moral Standards ExplainedLee PascuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Stentorian December 2009Document8 pagesStentorian December 2009amplourde3106Pas encore d'évaluation
- Deniform 13 Tds PDFDocument1 pageDeniform 13 Tds PDFNicolae MariusPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer PackagesDocument72 pagesComputer PackagesBildad JoashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ttrack 514889Document24 pagesTtrack 514889Fernando Shadow100% (1)
- trs5 Key Cho Cac BanDocument35 pagestrs5 Key Cho Cac BanNguyệt NgôPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Jurnal Karajata2020Document3 pagesTemplate Jurnal Karajata2020Andi Ryan YuliyanaPas encore d'évaluation
- BX 560GDocument20 pagesBX 560Gmacanipharoldf6220Pas encore d'évaluation
- DMAE Powder Safety Data SheetDocument3 pagesDMAE Powder Safety Data SheetAInhoaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lumino - HTLSDocument11 pagesLumino - HTLSvishnu ojhaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Study On Financial Analysis of Tri Van Drum AirportDocument81 pagesA Study On Financial Analysis of Tri Van Drum AirportN.MUTHUKUMARAN100% (1)
- Li HongDocument4 pagesLi HongJiwen SalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Gastrointestinal System Nuclear Medicine Part 2Document45 pagesGastrointestinal System Nuclear Medicine Part 2api-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- SSCM Roads and Bridges - Annex III Technical Specifications 105 C1 PDFDocument254 pagesSSCM Roads and Bridges - Annex III Technical Specifications 105 C1 PDFSite Engineer.2p2100% (1)
- Ficha Técnica Electroválvula JJ08Document1 pageFicha Técnica Electroválvula JJ08Jorge JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- People Vs VelardeDocument4 pagesPeople Vs VelardeFred SperryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument40 pagesCardiovascular SystemDouglas Jacques100% (1)
- Matrix Analysis of Networks: J. R. LucasDocument63 pagesMatrix Analysis of Networks: J. R. LucasNethmini SamarawickramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Balzac GaitDocument7 pagesBalzac Gaithieratic_headPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Declaration Unit # 2 JindalDocument16 pagesEngineering Declaration Unit # 2 JindalVIBHAV100% (1)
- Plinth Beams (1st Joint)Document11 pagesPlinth Beams (1st Joint)Tariq MahmoodPas encore d'évaluation